MRI of the pelvis is one of the most informative and at the same time safe research methods, which is based on the use of magnetic wave radiation. The type of diagnosis in demand in our time allows us to examine in detail the structure of the internal organs of both women and men. A comprehensive examination of the structures of the pelvic region can be divided into three main categories, each of which contains its own list of elements recognized by electromagnetic waves.
Introduction
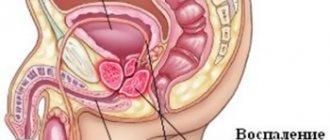
Hip bone
- This is a reliable support for the entire human skeleton, as well as a strong structure for protecting the organs that are located in the lower abdomen. Each pelvic bone is divided into the following three:
- The ilium is an opening bone that forms the upper pelvic lobe of the bone. You can feel (touch) it by simply placing your hands on your hips.
- The ischium is the part of the hip bone that is located at the back below, resembling an arch in appearance.
- Pubic - the anterior lobe of the base of the pelvic bones.
MRI of the pelvic bones can be carried out individually, for a detailed study of the structures, or can be part of a comprehensive diagnosis of the whole body. The cost of the procedure is quite high, so it is prescribed in the presence of serious symptoms and injuries.
| The structure of the pelvic bones | MRI of pelvic bones and soft tissues |
Classification of tomographs
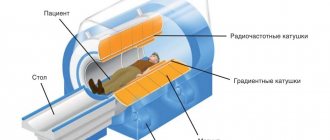
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed in special equipment called a tomograph
.
By type, tomographs are divided into open and closed
.
| Open MR tomograph | Closed-type MR tomograph |
The advantages of an open type tomograph are:
- It is suitable for patients suffering from claustrophobia and for children who may be scared in the confined space of a closed CT scanner;
- It has an air gap in which the patient is placed, usually larger than that of closed-type tomographs. This makes it possible to conduct examinations for overweight patients.
The advantages of a closed-type tomograph are:
- The examination time is shorter than that of the open one. The timing of the examination is important for those patients who, for one reason or another, cannot remain motionless for a long time.
- The quality of images from a closed tomograph is higher, because the quality of images depends on the magnitude of the created magnetic field strength, measured in Tesla units. Due to their design features, open-type tomographs cannot create tension comparable to closed-type tomographs.
According to the strength of the created magnetic field, tomographs are divided into
:
- Low-floor - up to 0.5 Tesla.
- Mid-field - from 0.5 to 0.9 Tesla.
- High-field - from 1.0 to 1.5 Tesla.
- Super high-field - 3 Tesla.
As a rule, a voltage of 1.5 Tesla is enough to obtain images of acceptable quality.
| Image quality depending on equipment power |
Indications for tomography
Magnetic resonance imaging is mandatory for people who have a history of:
Which pelvic ultrasound is best to do?
- suspicion of oncology;
- abnormal structure of the abdominal organs;
- congenital pathologies;
- long-term infertility;
- damage to bones and pelvic organs;
- suspicion of cyst rupture;
- unexplained vaginal bleeding not related to the menstrual cycle;
- endometriosis;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- alarming chronic pain.
Indications
There are a number of indications for MRI of the pelvic bones:
- Structural anomalies due to intrauterine developmental defects or birth trauma.
- Age-related changes in the structure of the pelvic bones.
- Old and new injuries to the pelvic area, even in the absence of external signs.
- Tuberculosis, syphilis or other bacterial, viral, infectious disease affecting bone structures.
- Pain in the pelvic area.
- Swelling, numbness, impaired mobility of bones and joints.
- Difficult childbirth.
- Sedentary work.
- Preparing for surgery.
- Postoperative control.
- Monitoring the dynamics of pelvic bone pathology.
- Checking the effectiveness of treatment.
- Preventive diagnostics in the remission stage.
- Suspicion of the formation of neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature, the presence of penetrating metastases from other affected systems.
What does a pelvic MRI reveal?
Most often, MRI of the pelvis is prescribed to identify malignant neoplasms and functional disorders of the structures of this area. In general, the indications for MRI of the pelvic organs will be as follows:
- suspicions of benign, malignant, hormone-dependent neoplasms;
- injuries, including those accompanied by internal bleeding;
- anomalies in the structure and development of organs;
- pain of unknown nature in the pelvic area, sacrum;
- acute surgical pathologies;
- urinary disorders;
- stones in the urinary ducts;
- genital dysfunction;
- infertility.
What is checked in a particular case is usually indicated in the direction. It is this organ that will be given the closest attention, but all other structures of the pelvis will also be examined during the procedure.
What can be seen on an MRI of the pelvis
Since magnetic resonance imaging is most effective in studying soft tissues, the images best visualize parenchymal organs, vessels, ligaments, joints, and tumors. Less clearly, but sufficiently to make a correct diagnosis, the inner surface of the bladder, cysts, pelvic bones, and other dense and hollow structures are visible.
When examining this area of the body, a tomography of the lymph nodes is also performed - if they are enlarged, we can talk about the presence of serious inflammation or an oncological process.
An MRI of the pelvic bones checks their integrity; you can see cracks and damage to soft tissues after injury, the pathology of their development and pinched nerve endings.
What does MRI of the pelvic organs show, in addition to the listed structures?
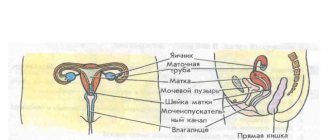
- Digestive system . This is mainly the large intestine, in which pathological neoplasms are clearly visible. Anomalies of its structure and other pathologies are determined.
- Bladder and ureters . The main task of such an examination is to identify stones, their size and location.
- The uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries - everything that is part of a woman’s reproductive system. Tomography allows you to see defects in these organs. The extent of the inflammatory process will depend on whether ovarian adhesions are visible and the state of the lymphatic system.
- Prostate gland in men . Diagnostics using a magnetic field allows you to see its size, which reveals the presence of prostate adenoma. The examination determines the degree of the inflammatory process and the required amount of treatment.
The answer to the question of what an MRI of the pelvic organs shows often depends on the scanning mode - whether contrast is introduced, since without it small tumors are difficult to see in the images.
What does MRI of the pelvis provide?
First of all, this is making the correct diagnosis and prescribing the correct therapy when malignant tumors are detected. MRI is especially effective for cervical cancer, and MRI diagnostics of prostate cancer reveals more than 50% of cases of this disease . Ovarian cancer is clearly visible on MRI images, including the extent of its spread to neighboring organs and tissues. The same applies to prostate cancer. The study allows you to accurately determine the location of the tumor, its exact size, the presence of metastases, and the degree of damage to the organ. For example, timely MRI of bladder cancer in the vast majority of cases makes it possible to preserve the organ and prevent the spread of metastases to the kidneys, spine, and reproductive organs.
Excellent results are shown by MRI of the pelvic lymph nodes, especially those that are deep. Other research methods, including ultrasound, are not always able to visualize them and record the presence of changes.
In addition, based on MRI images, diagnoses such as:
- inflammatory processes (endometriosis, abscesses, paraproctitis, etc.);
- benign tumors and hormone-dependent formations (hemangioma, adenoma, polyps, fibroids, ovarian dermoid cyst, etc.);
- vascular pathologies (thrombosis, aneurysms, narrowing);
- abnormalities of organ development (cryptochorism, aplasia, “baby uterus”, etc.);
- traumatic injuries;
- stones in the urinary system.
Patients often ask the question, are adhesions visible on MRI images, what does the image show? This issue is especially of concern to women who have problems conceiving. Magnetic resonance imaging reliably reveals adhesive processes and allows you to view them in several projections. This allows you to determine the need for surgical intervention and minimize its consequences.
Despite all the advantages of MRI, in some cases other diagnostic methods will be more effective. For example, the description of MRI of the pelvic bones is performed in general terms, since the scan does not clearly visualize the structure of the bone tissue. In such situations, X-ray methods will be more informative.
Contraindications
Contraindications to MRI of the pelvic bones are divided into absolute, when it is impossible to do an MRI, and relative, when it is possible to do it under certain conditions.
Absolute contraindications
:
- Installed pacemaker. Magnetic fields can interfere with the operation of electronic equipment, causing it to malfunction.
- The presence in the body of metal implants or other metal objects (for example, fragments) that react to the influence of a magnetic field. If the patient has implants in the body that do not respond to the magnetic field, then documents confirming this should be provided.
Relative contraindications
:
- Claustrophobia. This contraindication is relevant for closed-type tomographs and can be avoided by conducting examinations on open-type tomographs.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- The patient cannot remain still during the entire examination. The images will be blurry and therefore not suitable for diagnosis if the patient moves during the examination. The solution may be a sedative or anesthesia.
- The patient's weight exceeds the permissible weight for which the tomograph table is designed. In this case, you need to look for tomographs with a large permissible weight. As a rule, open-type tomographs have an advantage in this regard over closed-type tomographs.
- The diameter of the circumference of the widest part of the body exceeds the length of the air gap of the tomograph. In this situation, you also need to look for a tomograph with the necessary parameters. As a rule, open-type tomographs have a larger air gap than closed-type tomographs.
- The patient has decompensated heart failure.
- The patient is in serious condition.
- Inappropriate behavior, including alcohol intoxication.
Contraindications to CT scan of the pelvic bones
Contraindications to computed tomography of the pelvic bones:
- any stage of pregnancy;
- childhood;
- recent x-ray diagnostics;
- renal failure;
- serious condition of the patient;
- diabetes;
- claustrophobia;
- psychical deviations;
- motor excitement;
- heavy weight of the patient.
When using a contrast agent, the list of contraindications additionally includes an allergy to an iodine-containing substance. Lactation becomes a relative contraindication. During lactation, when scanning the pelvic bones, a young mother needs to stop breastfeeding, because the contrast penetrates into all biofluids of the human body. During this period, the milk is expressed and not used.
How does the procedure work?
Carrying out an MRI of the pelvic bones consists of three stages: preparatory, the procedure itself, and issuance of results.
Preparatory stage.
The patient needs to arrive some time before the appointment in order to:
- Complete the documents. If the procedure is paid, then a contract for the provision of paid medical services must be drawn up. If the procedure is for compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance, then the necessary package of documents is checked.
- Find out contraindications. Contraindications are described in the section of the same name in the article.
- If an MRI with contrast is required, contraindications for administering contrast are clarified. The doctor also needs to select the type and dose of contrast agent, which will take a certain amount of time.
- Next, before the examination, you should change into loose clothing without metal elements and remove all metal objects.
Procedure
:
- The patient is escorted to the tomograph.
- Placed on the table.
- The body is secured with soft straps to avoid micro-movement. Movements during MRI lead to blurring of the image and the examination needs to be redone.
- If necessary, fix the area being examined with a special coil.
- The examination is accompanied by specific noises produced by the tomograph mechanisms. To reduce the negative effect of noise, the patient is given headphones in which music is played, and the instructions of the doctor conducting the examination can be transmitted to the headphones.
- If the procedure is performed on a closed type tomograph, the patient is in a confined space.
Delivery of results
:
- Immediately after the examination, the patient is given an image on film and/or disk.
- For some time after the examination, the patient is given an examination report from a radiologist. Usually this time is about 30 minutes, but it can be longer depending on the doctor’s workload. It may be that the conclusion will be issued the next day. Some MRI centers send the report by email.
In some MRI centers, you can ask the radiologist any questions you have after the procedure.
Preparation for CT scan of the pelvic bones
The session does not involve complex preparatory measures.
When using a contrast agent, a kidney function test should be performed. On the eve of the pelvic bone scanning session, it is important to refrain from eating dinner and breakfast. It is recommended to stop drinking water 4 hours before the start of the session. Liquids are used less often to prepare the patient, as they put stress on the kidneys. Smoking is prohibited for several hours before the scan. You must stop drinking alcohol 1-2 weeks before the expected procedure.
At the appointed time, the patient comes to the diagnostic room, having in hand all the necessary medical information in documents. You need to take with you the card and the results of preliminary additional research. You may need radiography, ultrasound, and clinical diagnostic tests.
Before entering the office, jewelry and belts are removed from clothing. During the examination, there should be no metal elements on the body to avoid possible changes in the area of examination in the diagnostic results.
As for the results, a CT scan of the pelvic bones - what exactly it will show - can be found out after the procedure.
Duration of the procedure
MRI of the pelvic bones in a closed high-field tomograph with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla takes up to 20 minutes.
A similar examination using open-type equipment takes up to 40 minutes. If tomography using a contrast agent is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis, the duration of the procedure increases approximately 2 times. An initial scan is performed without contrast, then the solution is injected, and the manipulations are repeated.
Computed tomography technique
Before starting the diagnosis, the patient talks with a radiologist. The specialist is interested in such aspects as a preliminary diagnosis, whether there have been surgical operations in the past, the results of previous examinations, whether there are any metal structures in the body, etc. Then the patient takes off things that could distort the image and lies down on the mobile table of the device. The doctor adjusts the settings, places the patient in the ring-shaped chamber of the CT scanner, and monitors the scan on a computer monitor in an adjacent room. The procedure lasts from 5 to 15 minutes. During this time, the subject must lie still.
Native diagnosis is usually not accompanied by discomfort. Mild malaise, dizziness, and nausea sometimes appear after the administration of contrast, but these phenomena pass rather quickly. Computed tomography, as a rule, does not cause complications, and after the procedure you can return to your usual activities.
Fibrous dysplasia of the pelvic bones on CT
Fibrous dysplasia is a tumor-like disease characterized by impaired skeletal development with partial replacement of bone structures by connective fibers. Because the new tissue is not strong enough, fractures occur repeatedly in the affected area. Most often, one or both iliac bones are involved in the pathological process, very rarely – the ischium and pubis.
The disease is caused by disorders of intrauterine development and mainly occurs in children and adolescents. The peculiarity of fibrous dysplasia of the pelvic bones is the absence of symptoms at the initial stage. In the early stages, it is accidentally discovered during an examination for another reason.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and the results of an X-ray, CT or MSCT of the hip joint: the images show an increase in the volume of the pelvic bones without disturbing their contours and foci of darkening resembling ground glass.
What does it show
If the examination did not reveal degenerative changes in the pelvic bones, the specialist enters the following data into the examination protocol:
- No congenital anomalies were found.
- There are no signs of trauma or mechanical damage to muscles, bones, ligaments, or blood vessels.
- Age-related changes are within normal limits.
- No deformities of joints and bones were detected.
- Blood circulation meets standards.
- Signs of inflammatory diseases, neoplasms and metastases were not found.
MRI is a highly informative examination method and allows you to detect the following disorders and pathologies with up to 95% accuracy:
- Abnormal bone structure.
- Signs of an old birth injury.
- Cracks and fractures of the bone structure.
- Hematomas and soft tissue compactions.
- Wear and tear of connective tissues and cartilage due to age.
- Rupture of the vessel membrane.
- Compression and pinching of nerve endings.
- Bone deformation due to improper load distribution (occupational violations).
- Signs of infectious, bacterial, viral damage, necrotic damage.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Cystic formations.
- The presence of benign and malignant tumors.
- A neoplastic process caused by the penetration of metastases from affected organs.
- Vector of spread of metastases from the pelvic area.
What's the difference with and without contrast?
The contrast consists of saline solution and a special substance, is injected into the body intravenously, and transported through the circulatory system to the object of study.
Thanks to the reaction of the components to the influence of the magnetic field, the area of localization of the pathology is “highlighted”, the size and shape of the defect is clearly indicated. Secondly, due to its properties, contrast affects pathological areas in such a way that they are shown on images more clearly (in contrast) relative to areas without pathologies.
This is what the doctor will see in the image taken with and without a contrast solution:
| On the left is an MRI performed with contrast; on the right without contrast solution | ||
There are contraindications for the use of contrast agents
:
- Hypersensitivity to components
- Allergic reactions
- Kidney failure
- Pregnancy
- Lactation.
How long does it last?
On average, the duration does not exceed 5 minutes if the procedure is performed without enhancement, and about half an hour when a contrast agent is administered. The characteristics of the tomograph can influence the duration - the more modern the equipment, the faster the scanning takes place.
Important! Equipment parameters affect not only the time of CT diagnostics, but also the accuracy of the results. You should consult your doctor about the optimal power of the tomograph.
CT or MRI, which is better?
It is not entirely correct to compare these methods with each other, since they are based on different principles of image acquisition. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. The doctor decides whether to send the patient for a CT or MRI based on the purpose of the examination.
If we consider the difference between CT and MRI, then for comparison it is necessary to take the following factors:
Device capabilities
. MRI scans best soft tissue, ideal for assessing the condition of the muscles, ligaments, and tendons around the shoulder joint. CT most accurately demonstrates bone tissue. If a fracture, arthritis or bone tumor is suspected, it is better to entrust the diagnosis to a computed tomography scan. The device is capable of constructing a 3D projection of the joint based on the data obtained during scanning.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you may need to use both methods.
Duration of the procedure
. For a computed tomography scan, it only takes 1-2 minutes. Scanning using magnetic waves will require the patient to remain motionless for 15 to 30 minutes.
Harmfulness
. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner has no restrictions on the number of examinations, since it emits impulses that are less harmful to the body than X-rays. A CT scan, on the other hand, is based on X-rays and cannot be performed on a single patient more than twice a year.
A visual demonstration of the capabilities of CT and MRI devices:
| CT | MRI of the pelvic bones |
CT allows you to build 3D models:
| 3D model |
Alternative Methods
Examination of the condition of the pelvic bones is carried out not only using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. In some cases, additional diagnostics may be required:
- Computed tomography (CT). The most accurate examination to study the condition of bone tissue. Contraindicated in pregnant and nursing mothers due to radiation exposure.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Allows you to obtain information about the condition of bones and internal organs after injury.
- X-ray. Prescribed for fractures, dislocations or to identify congenital pathologies. Not recommended for pregnant women and infants.
- PET-CT. It is a comprehensive examination of internal organs, joints and bones.
PET CT is the most expensive; in Moscow it is performed for 40,000-55,000 rubles. Ultrasound or x-rays are performed in some clinics for free, the average cost is from 1000 rubles.
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
X-ray and MRI are fundamentally different examination technologies. If we compare them with each other, then according to the following criteria:
Image quality
. A tomograph scans the human body and builds an image in layers. The image has high resolution, detail, data on soft and bone tissues. An X-ray machine can highlight only one layer and demonstrate the condition of the tissues; the quality of the image will be worse.
| X-ray | MRI of the pelvic bones |
Harmfulness
. X-ray radiation in large quantities is dangerous to health, while MRI can be done at least every day.
Availability of procedures
. An X-ray machine can be found in every ordinary clinic. Equipment for MRI requires large financial costs and the availability of specialists who know how to operate it, so large city and regional medical centers and commercial hospitals can afford a tomograph. You can get an X-ray quickly, but the appointment for an MRI is distributed over weeks in advance.
Price
. An X-ray examination can be done free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy in a regular clinic. Only patients from surgery and inpatient departments can get an MRI free of charge.
General questions about MRI of the pelvic area, is it painful to do a pelvic tomography?
The non-contrast scanning time ranges from 30 to 45 minutes; with the introduction of contrast, the duration increases by approximately 15 minutes.
Many people are interested in whether it hurts to do an MRI. Unpleasant sensations can only occur when a contrast agent is administered, since this is done by intravenous injection. Otherwise, the procedure is absolutely painless. The only thing that can cause discomfort is that you will have to remain completely still during the entire examination. For patient comfort and to prevent involuntary movements, MRI machines are equipped with a system of rollers and belts.
To kid
There are no age restrictions for MRI of the pelvic bones.
To perform an MRI, a prerequisite is immobility throughout the entire examination. Children may find it difficult to lie still, so anesthesia may be considered.
Children may be afraid to be in the confined space of a closed-type CT scanner. In this case, an examination can be performed using an open-type tomograph. The parent will be able to stay next to the child and hold his hand.
How is a CT scan of the pelvis performed and how long does it take?
Clinical diagnostic CT is performed natively in the office of a medical institution. The patient is placed on a retractable hardware table. Typically, scanning the pelvic bones occurs in a lying position. The diagnostician is in the next room, behind a partition. The radiology doctor monitors the patient and gives him short commands using an intercom. It is acceptable to have a pacemaker when scanning bone CT cases if the device has low sensitivity.
The chest and limbs of the person being examined may be covered with a lead apron. This measure will significantly reduce the X-ray dose. Non-contrast bone tomography does not cause discomfort. When contrast is introduced, hot flashes may occur. The duration of the tomographic examination does not take more than 20 minutes. Using a staining agent increases the diagnostic time slightly.
After completing the scan of the pelvic bones, the diagnostician studies all the data obtained using the device. A medical diagnostic report is drawn up. Certified with a wet seal, it is handed over to the patient. Subsequently, he gives the medical report form to his attending doctor, who referred the patient for examination.
Along with the conclusion, the patient is given printed photographs and records on digital media. The research results are confirmed by panoramic images, the CD displays all important diagnostic information. It is important to understand that the diagnostician does not make an accurate diagnosis. He simply describes in the medical report all the changes that he visualized. The diagnosis is clarified by the specialized medical specialist to whom the patient first contacted.
Photo
| Metastases in the pelvic bones. |
| Coxarthrosis of the hip joint, passing into the bone. |
| Metastases of the ilium. |
| Fracture of the pelvic bone. |
| Pelvic bone fracture. |
Price
On our website, many clinics list prices for MRI, including MRI of the pelvic bones.
To see prices, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
On the page for the list of city clinics, in the form for selecting a clinic based on parameters, in the “Research area” field, select “MRI of the pelvic bones.”
The list will be filtered and the clinics will be sorted by ascending price, which will allow you to find out where to get an MRI of the pelvic bones cheaper.
| List of clinics filtered by MRI of the brain using the example of the city of Moscow |
If prices are not indicated on the website, then you need to call all the clinics and find the best price for you yourself.
When talking with the operator, be sure to ask if there are any promotions or discounts. For example, some 24-hour clinics offer discounts on MRIs at night.
You can get an MRI with compulsory medical insurance or VHI insurance. To do this, you need to find out which clinic does MRI under insurance, using the information on the website or calling the clinics yourself if there is no information on the website. In the form for selecting a clinic by parameters, there is a field “MRI under insurance”. Next, you need to find out the list of documents that the clinic operator will tell you, collect them and you will be able to undergo an MRI with insurance, which will allow you to save a lot.
Preparation and cost
The price for the procedure in Moscow ranges from 4,500 and above. It can vary not only on the location of the clinic and its prestige, but also on the time of day: in some medical institutions the procedure is performed at a discount at night.
This is a painless, progressive and most informative diagnosis that requires a short preparatory period. Preparation consists not only of refusing to eat a few hours before the test, but also of changing your diet 3-4 days before it.
Products that contribute to increased gas formation are excluded from the daily menu:
- dairy and fermented milk;
- legumes and some vegetables;
- carbonated water, alcohol and tonic drinks;
- bread and pastries.
Such regulation is due to the specifics of the area where the research will be conducted: gases accumulated in the intestines can simply distort the information obtained, lead to a false positive result, or make it impossible to see a truly existing process.
The examination procedure using an MRI scanner, unlike a CT machine that uses X-ray radiation, is so safe that it can be performed daily.
Only some serious illnesses and severe mental disorders can be considered absolute contraindications.
Reviews
On our website, people leave reviews for clinics about their MRI experience.
To read patient reviews, you need to go to the list of clinics in your city. To do this, select your city on the “Addresses” page.
The list in the block of each clinic will show a button to go to the list of reviews, if there are reviews, or a button to go to write a review, if there are no reviews yet.
| This is what review buttons look like, using the example of the city of Moscow |
You can also leave a review about your MRI experience so that other people can choose the most suitable clinic.
To leave a review, you need to click the “Your review” button and you will be taken to the review writing form. Or if there are already reviews, then you need to go to the end of the list of reviews and there will be a form for writing a review.
To open the review writing form, click the “Leave a review” button.
Fill out the form and send it for moderation.