Rehabilitation after laparoscopy is many times faster and easier than after strip surgery. The modern minimally invasive method of endoscopic surgery can significantly reduce the time required for regeneration of tissues and organs. Thus, discomfort after laparoscopy is minimized. However, recovery after laparoscopy is still necessary. Its duration depends on the type and complexity of the operation, and the individual characteristics of the patient. Some people feel good after a few hours, while for others the process lasts for a couple of weeks.
What to do in the first days after the procedure
The first 3–4 days after laparoscopy are the most critical. Most patients spend these days in hospital. After the operation, sutures and an aseptic bandage are applied to the insertion sites of the laparoscopes. The wounds are treated every day with a solution of brilliant green or iodine. The sutures are removed on days 5–7. To restore the tone of the abdominal muscles, stretched due to the introduction of carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity, a bandage is needed. Sometimes a drainage tube is installed to drain the ichor. After a couple of days, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is performed to track the dynamics of healing. A postoperative bandage is applied for 2 to 4 days. It cannot be removed. It is recommended to rest on your back. If the patient feels well, is not bothered by stitches and does not have a drainage tube installed, he can sleep on his side. Lying on your stomach is strictly prohibited. The first hours are the most difficult. The patient recovers from the effects of anesthesia and is half asleep. Possible chills and feeling of cold.
Also often occur:
- moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- frequent urge to urinate.
These are normal postoperative symptoms that go away on their own. If the pain is severe, anesthetics are indicated.
Additional Information! A normal symptom also includes discomfort in the throat - it appears as a result of the insertion of an anesthesia tube. In addition, on the 2nd day after laparoscopy, pain often occurs in the shoulder and cervical region - the sensations are explained by gas pressure on the diaphragm.
After laparoscopy, recovery is quick and easy. Usually the patient’s health is satisfactory, and complications rarely occur. They are mainly provoked by the patient’s non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations.
The need for a dietary diet in the postoperative period of laparoscopy
First of all, proper nutrition requires an optimal balance of nutrients (fats, carbohydrates, proteins). This, in turn, ensures the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The patient does not experience dyspepsia (difficult and painful digestion) or flatulence. There are no problems with bowel movements (diarrhea, constipation).
The postoperative diet consists of so-called healthy foods. The use of which helps strengthen the immune forces of a weakened body. The sutures, even small ones, are tightened faster, and the risk of adverse postoperative complications is extremely limited. In addition, such products accelerate the elimination of toxic substances accumulated under the influence of anesthesia, facilitating the functioning of the liver.
The diet promotes the regeneration of the body's hormonal and reproductive systems. Especially in cases where laparoscopic surgery in the field of gynecology was performed. If you have difficulty creating a menu on your own, you should seek help from a nutritionist.
How long to stay in hospital and temporary disability
The rehabilitation period for everyone after laparoscopy is different. Some may go home immediately after the anesthesia wears off. For others, recovery takes 2–3 days. However, doctors strongly recommend spending the first day in a hospital. This is the most critical period during which complications can develop. How long after you can get up is determined individually. Usually after 3–4 hours the patient can walk a little. Movements should be as careful and smooth as possible. It is necessary to walk - this normalizes blood flow and the release of carbon dioxide, preventing thrombophlebitis and the formation of adhesions. But the main regime should be bed. Most of the time you need to lie down or sit. After a couple of days, when you can get up without fear, walks along the hospital corridors or in the clinic’s courtyard are recommended. Patients are usually discharged after 5 days if there are no complications or complaints. But complete rehabilitation requires 3–4 weeks. Not only should the scars heal, but also the internal organs should heal. Sick leave is issued for 10–14 days. If complications are noted, the certificate of incapacity for work is extended on an individual basis.
Consequences of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a surgical operation for resection of the affected organ or part thereof, performed through small incisions using trocars and a laparoscope.
In addition, the laparoscopic method is used to diagnose diseases as it is extremely accurate. One of the prerogative aspects is the shortened postoperative period of laparoscopy. Rehabilitation is accelerated, since tissues and skin are not injured, as during abdominal surgery. For the same reason, the possibility of infection of incisions and the formation of adhesions is minimized.
About the technique and types of laparoscopy
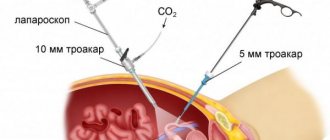
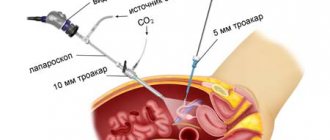
Laparoscopy is performed under anesthesia. Several incisions are made in the area of the operated organs, through which surgical instruments and a laparoscope - a device equipped with a lighting component and a video camera - are inserted. The image, enlarged several times, is projected onto the monitor.
For better visualization of the internal space and access to organs, carbon dioxide is supplied to the operated area. Under its influence, the folds of the abdominal cavity are straightened, which allows the surgeon to work fully.
At the end of the process, the instruments are removed and surgical sutures are applied to the incision sites.
Most often, laparoscopic surgery is performed on the organs of the digestive and genitourinary systems, less often on the chest (thoracic surgery).
The most popular operations include:
- appendectomy (appendicitis);
- colectomy (removal of a section of the colon);
- cholecystectomy (excision of the gallbladder during a tumor process and cholelithiasis);
- hernioplasty (removal of umbilical hernia);
- cystectomy (resection of ovarian, kidney, liver cysts)
- distal pancreatectomy;
- gastrectomy (complete removal of the stomach).
In addition, laparoscopic excision of the spermatic vein in men with varicocele (varicose veins of the scrotum and spermatic cord), gynecological operations for endometriosis (proliferation of uterine cells), fibroids (benign tumors) of the uterus, and numerous inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs are widely practiced. Laparoscopy, for emergency indications, can be performed during pregnancy.
Appendicitis or cholecystitis may occur during the perinatal period. Pregnancy is not a contraindication to laparoscopic surgery
Consequences of laparoscopic surgery
The laparoscopic method of resection is more easily tolerated by patients than conventional abdominal surgery.
However, like any external intervention in the body, surgery or diagnosis does not pass without leaving a mark on the patient.
The consequences of laparoscopy usually appear during the patient's hospital stay after surgery, but sometimes they can occur after discharge. The main side effects include:
When can you exercise after laparoscopy?
- Pain syndrome. During the first twelve hours after surgery, intense pain is not considered abnormal. Damage to soft tissue, skin and internal organs causes pain that is localized in the area of the operated organ, and can also radiate (give) to the upper part of the body. To eliminate pain in the hospital, analgesics, non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Less commonly used are narcotic opium alkaloids (opiates).
- Feelings of fullness in the abdominal cavity. This symptom is caused by the introduction of carbon dioxide during surgery. Intense accumulation of gases in the abdominal cavity is not a postoperative pathology. If the symptom does not leave the patient on the first postoperative day, carminative drugs are prescribed.
- Heaviness in the epigastric (epigastric) region, nausea. Occur after laparoscopy surgery, as a result of the administration of anesthesia. Such sensations do not require special treatment and go away on their own.
- Headache. They can be caused by the anesthesia and the anxiety experienced by the patient. As a rule, they are relieved with analgesics along with pain in the area of the operation. If the patient is overly excited, sedatives are prescribed.
- Discomfort in the throat and esophagus. The cause is the use of endotracheal anesthesia (introduction of anesthesia through the airway through a tube). These symptoms are short-lived and do not require treatment.
The intensity of postoperative symptoms depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the quality of the surgery performed.
Small incisions on the body after laparoscopy heal faster than scars after abdominal resection
Complications after laparoscopy are rare, but do occur. The occurrence of complications is due to three main reasons: an unexpected reaction of the patient to anesthesia or the introduction of carbon dioxide, the patient’s failure to comply with medical recommendations during the recovery period, and a poorly performed operation (medical inattention, errors).
Complications of anesthesia
Before laparoscopy, the patient undergoes an examination, which helps the anesthesiologist to choose the best anesthesia (drug and dosage) that is suitable for a particular person, taking into account his individual characteristics.
An inadequate reaction rarely occurs; the most extreme form of manifestation can be an acute allergic reaction - anaphylactic shock. Failure of bronchopulmonary and cardiac activity can occur under the influence of carbon dioxide.
The complication is rare and depends on individual characteristics (chronic heart and bronchial diseases), or non-standard gas administration.
Pathological manifestations due to the fault of the patient
Every doctor must give recommendations after laparoscopy, which the patient must follow during the rehabilitation period.
There are dietary restrictions, as well as prohibitions on serious physical activity after surgery to remove the affected organ or part of it.
If the recommendations are not followed, suppuration and infection of the sutures, bleeding, and inflammatory processes in the gallbladder, uterus, urinary system and other organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis occur.
Complications depending on medical personnel
An improperly performed operation or equipment malfunction can lead to certain negative consequences. Patients with chronic cardiac disorders, atherosclerosis, and varicose veins are given blood thinning medications before surgery.
If the doctor ignores this manipulation, there is a danger of blood clots forming. If the laparoscope malfunctions or the doctor is not qualified, there is a risk of injury to adjacent organs and vessels.
For example, when removing stones from the gallbladder, an inexperienced doctor can damage its walls.
Of particular danger is the primary puncture made by the Veress needle when the laparoscope is not yet functioning. Manipulation blindly may lead to bleeding. The occurrence of adhesions is most typical after resection of appendicitis.
To stop standard bleeding after excision of a part of an organ, the coagulation method (cauterization with electric current) is used. Incorrect use of the method causes severe burns to internal organs.
By cutting off the affected area, the doctor can burn an adjacent organ, which will lead to the development of necrosis (death) of the organ tissue.
Violation of sterility by medical personnel causes infection of the incision, and as a consequence, the occurrence of a purulent-inflammatory process in the suture area.
Incorrect removal of an organ affected by cancer can cause skin cancer when it is removed from the abdominal cavity. The occurrence of postoperative hernias is caused by improper suturing of the troacal openings after the removal of large fragments of organs.
This complication may not manifest itself immediately after laparoscopy, but after several weeks or months.
Errors during gallbladder resection operations lead to disruption of the choleretic process, which can result in serious liver diseases. Pregnancy during surgery requires special attention.
If the doctor acts carelessly, there is a risk of miscarriage (miscarriage) or the development of oxygen deficiency (hypoxia) in the fetus, as a reaction to the introduction of carbon dioxide.
If unexpected situations arise during laparoscopy, the doctor should proceed to open laparotomy to avoid more serious negative consequences.
The listed complications can be prevented if you carefully choose a clinic for the operation. In addition, the patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s advice during the rehabilitation period.
The following symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- severe pain in the operated area after discharge from the hospital;
- stable hyperthermia (high temperature);
- change in color of the epidermis (skin) around the scar to bright red;
- discharge of purulent-bloody substance in the area of incisions;
- constant headache, short-term attacks of loss of consciousness.
By the end of your hospital stay, there should be no acute postoperative pain.
The patient must be hospitalized, undergo ultrasound diagnostics, and take blood tests.
Postoperative recommendations
The postoperative period after laparoscopy in a hospital setting lasts from 3 to 6 days, depending on the complexity of the operation performed. Subsequently, the patient is sent for outpatient treatment.
Rehabilitation after laparoscopic surgery, as a rule, takes place in an accelerated manner.
The sutures, depending on the surgical material used, are removed within 7–10 days, or they dissolve in the body on their own.
After a month, performance is completely restored. It is the patient’s responsibility to follow all recommendations regarding adherence to the regimen and diet.
For a month, the operated person should not resort to heavy physical activity. Do not do strength exercises or lift weights.
Nevertheless, rational physical activity is indicated from the second day after surgery to avoid the development of adhesions.
One of the most important factors is proper nutrition during the postoperative period. In the first days, the diet should consist of weak broths and oatmeal jelly. While on outpatient treatment, the patient should adhere to a light diet. The diet is based on the consumption of the following products:
- pureed soups;
- river and sea fish containing less than 8% fat;
- turkey meat, chicken;
- white omelet and soft-boiled eggs.
- low-fat cottage cheese, unsalted cheese;
- porridge, pasta;
- potato, fruit and berry puree.
It is necessary to eliminate from the diet:
- fat meat;
- mayonnaise-based fatty sauces;
- dishes made from lentils, peas, beans;
- pastries from butter dough;
- spicy and smoked products.
Compliance with doctors’ recommendations is the main condition for preventing complications
The consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited. Rough food can cause difficulty and pain when processed by the digestive tract. Obstipation (constipation) negatively affects the well-being and condition of postoperative sutures. If these symptoms occur, laxatives or an enema are recommended.
In addition to the shortened recovery period, the prerogatives of laparoscopy before abdominal surgery are considered to be: a minuscule likelihood of the formation of adhesions (provided the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations), the aesthetic appearance of the scars (in less than a year, the consequences of the operation are no longer noticeable). In the absence of contraindications, laparoscopic surgery is preferable.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/prochee/posledstviya-laparoskopii
Features of nutrition during the recovery period
The first day after laparoscopy surgery, you are prohibited from eating. When the anesthesia wears off, you can drink clean, still water. You can eat after surgery on the second day. Food should be liquid in consistency and at room temperature. Low-fat broths, yoghurts, jelly, fruit drinks, compotes are allowed.
On the third day include:
- porridge with water;
- fermented milk products – kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, low-fat cheeses;
- easily digestible fruits and berries without peel - apples, bananas, apricots, strawberries, melons and others;
- steamed vegetables - zucchini, peppers, carrots, eggplants, beets, tomatoes;
- seafood;
- boiled eggs;
- whole wheat bread;
- dietary meat and fish in the form of minced meat dishes.
By the end of the week, restrictions are reduced to a minimum. For a month, during the recovery period after laparoscopy, the following are excluded from the diet:
- Fatty, spicy, smoked food. The meat is baked, cooked in a double boiler or slow cooker. Soups are made without frying. Sausages, fatty fish, canned food, marinades, and pork are prohibited. Preference is given to chicken, rabbit, turkey, and veal.
- Products that cause gas formation. Exclude legumes (beans, peas, lentils), raw milk, baked goods (white bread, buns, any homemade pastries), and confectionery.
- Alcohol and carbonated drinks. It is allowed to drink weak tea, fruit drinks, compotes, and still mineral water. It is better to avoid juices, especially store-bought ones, as they contain citric acid and sugar. All alcoholic beverages are completely prohibited for a month. It is also advisable to avoid coffee after laparoscopy - starting from the second week, you can only drink weak coffee without cream.
Important! Doctors do not have a unanimous opinion about cigarettes. Some categorically prohibit smoking for 3–4 weeks, since nicotine and heavy metals slow down regeneration and provoke bleeding. Others believe that abruptly giving up a bad habit and the resulting withdrawal syndrome, on the contrary, can aggravate the patient’s condition.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation, especially in the first few days, meals should be fractional. You need to eat in small portions 6 – 7 times a day. It is necessary to monitor the regularity and consistency of stool. Make up a balanced and nutritious diet. Food products must contain all the necessary vitamins, minerals, and elements. The exact diet is selected by the attending physician, taking into account the specific disease and individual characteristics of the patient.
What should be the basis of the diet?
After the operation, you can eat low-fat yogurt, cottage cheese, and other fermented milk products. But you need to introduce them into your diet gradually. It is better to buy natural products that do not contain dyes or flavor enhancers. Yogurts, in which manufacturers generously put all kinds of additives, should be put aside.
What can you drink after surgery, except fermented milk products? Fruit jelly, homemade jellies, soups, porridges, pureed through a sieve, are useful.
Lovers of fish dishes can prepare cod or pike perch aspic for dinner. The dish does not need to be filled with too fatty broth: vegetable broth with the addition of gelatin is often used to prepare the dish. After surgery, the body needs protein: a lot of this substance is found in seafood: boiled squid, mussels, shrimp.
What can you take and why?
Surgery is only one stage of therapy. Therefore, drug treatment is indicated after laparoscopy. Usually prescribed:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics. Necessary to prevent an infectious-inflammatory process.
- Anti-inflammatory, enzymatic and wound healing medications. They are needed to prevent scars, adhesions and infiltration - a painful compaction that forms at the site of surgery. For this purpose, after laparoscopy, the ointments most often prescribed are Levomekol, Almag-1, Wobenzym, Kontraktubeks, Lidaza.
- Immunomodulatory drugs - “Immunal”, “Imudon”, “Likopid”, “Tactivin”.
- Hormonal drugs. Indicated to normalize hormonal levels if laparoscopy was performed in women due to gynecological diseases - adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages), endometriosis (abnormal proliferation of cells in the inner layer of the uterus), hydrosalpinx (obstruction of the fallopian tubes), . Longidaza, Clostilbegit, Duphaston, Zoladex, Visanne are prescribed in the form of suppositories, injections for injections, and less often - tablets and oral contraceptives. You need to drink OK after laparoscopy for six months.
- Vitamin complexes. Recommended for general support of the body.
- Painkillers. "Ketonal", "Nurofen", "Diclofenac", "Tramadol" and others. Prescribed for severe pain.
- Products based on simethicone. Needed to eliminate gas formation in the intestines and bloating. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Espumisan, Pepfiz, Meteospasmil, Disflatil, Simikol.
Also, after laparoscopy, you can take drugs that reduce blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots - Escusan, Aescin. They are necessary to prevent thrombosis.
What operations and examinations can be performed using laparoscopy?
Laparoscopic operations are performed to remove or restore diseased internal organs. The following types of laparoscopy are currently available:
- Removal of the gallbladder for cholelithiasis and cholecystitis
- Removal of the appendix for appendicitis
- Removal or restoration of kidneys, bladder and ureters
- Removal or ligation of fallopian tubes for sterilization
- Removal of ectopic pregnancy
- Treatment of endometriosis
- Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Hernia treatment
- Stomach operations
- Examination of the liver and pancreas
- Examination and removal of ovarian cysts
- Removal of uterine fibroids
- Removal of adhesions in the fallopian tubes
- Detecting and stopping internal bleeding
Basic rules of behavior during the rehabilitation period
After discharge from the hospital, the patient must strictly follow the following recommendations after laparoscopy:
- treat the seams with antiseptics every day and change the bandages;
- do not try to remove the stitches yourself or violate their integrity in any other way;
- do not remove the bandage until the abdominal muscles are restored - usually it is worn for 4, maximum 5 days;
- scar resorption agents should not be used earlier than 2 weeks after laparoscopy;
- alternate rest with physical activity - walking, household chores;
- a month after the operation, adhere to the diet developed by the doctor;
- take prescribed medications in accordance with the prescribed course - a couple of weeks or several months;
- drink vitamin complexes;
- Wear comfortable clothing that does not constrict, tighten or chafe.
To speed up recovery and prevent the appearance of scars and adhesions, physical therapy is indicated after surgery. Magnetic therapy is most often recommended. If laparoscopy was performed for diagnostic purposes, then physical treatment is not prescribed. You should also not overheat, take a hot bath, or stay in the sun for a long time, as high temperature can lead to internal hemorrhage. When you can go to the sea or go to the bathhouse is determined by your attending physician after passing control tests. If they are normal and the patient’s condition is satisfactory, a trip to a resort or a visit to the sauna is allowed a month after laparoscopy. To recover faster after laparoscopy, all doctor’s instructions must be strictly followed. If you ignore the advice, complications or relapse of the disease may develop.
Possible complications
Complications after laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst can occur both in the first days after surgery and several months later. The early development of negative consequences is often associated with incorrect surgical procedures. Possible complications:
- uterine bleeding;
- injury to neighboring organs and vessels;
- an allergic reaction to anesthesia or gas injected into the abdominal cavity;
- increased body temperature;
- development of infectious diseases.
Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and dizziness are considered normal in the first hours of recovery from anesthesia. This condition does not require urgent medical attention unless the woman’s well-being worsens. Normal body temperature can rise to 37-38 degrees 1-2 days after the intervention.
During late rehabilitation or after complete recovery of the body, the following consequences may be detected:
- periodic uterine bleeding after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, manifested during the intermenstrual period;
- formation of adhesions in the pelvis;
- absence of menstruation is a sign of dysfunction of the appendages;
- pain in the ovary after laparoscopy - often indicates an inflammatory process;
- re-formation of an ovarian cyst;
- lack of conception for 6-12 months;
- hormonal imbalance.
The likelihood of negative consequences increases if a woman has other gynecological or endocrine pathologies.
To reduce the risk of complications, it is necessary to regularly see your doctor. This will allow diseases to be detected in the early stages, which increases the chance of their complete elimination. It is recommended to visit a specialist monthly in the first three months after surgery. In the future, it is enough to carry out an examination 3-4 times a year, and one and a half years after the operation - every 6 months.
Playing sports during the recovery period
Since complete rehabilitation lasts at least a month, it is necessary to limit physical activity. The following are prohibited:
- gymnastics, fitness, callanetics, yoga;
- training in the gym;
- swimming;
- dancing.
Avoid physical activity after laparoscopy for 4–6 weeks. You cannot in any way load the abdominal muscles. Only leisurely walks in the fresh air are allowed. The patient determines how long to walk individually, based on his or her well-being. It is recommended to walk no longer than half an hour at a time. It is important that the patient avoids rough terrain - beams, ravines, etc. The road should be smooth, without ups and downs. A month to a month and a half after laparoscopy, you can introduce physical exercises. It is necessary to start playing sports gradually, increasing the load weekly. You should gradually introduce a simple set of exercises - turns, bends, leg swings. Then more difficult classes are included. It is allowed to work with a load (dumbbells, weights) or on exercise machines no earlier than 1.5 - 2 months after laparoscopy.
Uterine fibroids
What should be the diet after laparoscopy of uterine fibroids? The diet is not strictly limited, however, food should help the body fully recover and get stronger.
Nutrition should help restore intestinal structures, since excessive gas formation and constipation can cause sutures to separate. Therefore, gas-forming products should be excluded. The diet should contain a lot of fiber, which activates peristalsis processes.
To strengthen a weakened body, boil seafood - mussels, shrimp, squid. This protein is well absorbed by the body and does not harm digestion. Seafood can be eaten a month after surgery, having agreed on the diet with the gynecologist after the examination.
What not to do after laparoscopy
Since the body takes a long time to recover after any surgical intervention, it is necessary to refrain from increased stress. Including laparoscopy, a number of restrictions are imposed in the postoperative period. Among them:
- Do not lift weights weighing more than 2 kg;
- it is necessary to minimize housework - cleaning, cooking;
- it is necessary to limit any work activity, including mental activity;
- It is prohibited to take a bath, visit a bathhouse, solarium, or swim in a pool or pond;
- flights, long trips in a car, bus, train are excluded;
- sexual abstinence is imposed for a month, especially if a woman has undergone laparoscopy on the pelvic organs;
- any sports activities - only walking is allowed.
It is also necessary to carefully carry out hygiene procedures. There are no direct contraindications, but it is better to limit yourself to wiping with a damp sponge. It is allowed to take a warm shower if you cover the stitches with a waterproof bandage and do not rub the wounds with a washcloth.
Additional Information! Stitches and scars must not be touched in any way: combing, rubbing, or picking off dried crusts.
The speed of rehabilitation directly depends on how the patient behaves. Negative consequences occur extremely rarely if the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations.
How to prepare for laparoscopy?
Typically, surgeons discuss preparations for surgery with each patient separately.
As a rule, doctors recommend:
- Avoid eating and drinking at least 8 hours before surgery
- Shave the belly (for men)
- Take an enema a few hours before surgery (in some cases)
Before surgery, be sure to tell your surgeon what medications you are taking. Some medications (aspirin, birth control pills) can affect blood clotting and are therefore strictly contraindicated during or before laparoscopy.