Home » Laparoscopy » How much does laparoscopy cost: features of the operation
April 9, 2020 Laparoscopy
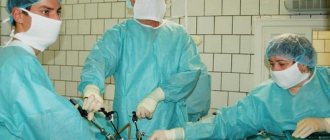
Laparoscopy is a procedure for surgical examination and treatment of internal organs without the need for an incision. In order to be able to perform therapeutic manipulations in the internal organs, 3-4 punctures are performed in the abdominal area. Through these punctures, the surgeon inserts a special device and instruments into the pelvic and abdominal cavity. This type of operation is not only gentle, but also safe, due to the absence of the need to make an incision on the body.
Why is laparoscopy performed?
Diagnostics
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a highly accurate diagnosis that helps the doctor assess the condition and functioning of internal organs, take tissue from a suspicious area for further laboratory testing, and most importantly, make an accurate diagnosis. It is used quite rarely for purely diagnostic purposes. Most often, diagnostic laparoscopy turns into therapeutic laparoscopy during one surgical procedure.
Treatment
Laparoscopy is a modern method of performing low-traumatic surgical interventions that help to carefully get rid of a number of diseases of internal organs and restore the patient’s strength much faster after surgery.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
This is the main method of treating chronic cholecystitis and gallbladder polyps. Laparoscopic surgery allows you to remove the gallbladder through several small punctures, minimizing blood loss and the risk of possible complications.
Types of laparoscopy
The laparoscopy technique itself allows for various manipulations, namely:
- diagnose diseases of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs;
- perform surgery;
Diagnostic laparoscopy allows you to most accurately assess the complexity of the disease and helps to create an effective plan for further treatment. With the help of operative laparoscopy, it is possible to provide high-quality surgical intervention while minimizing damage to external tissues.
In what cases is diagnostic laparoscopy prescribed?
Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic laparoscopy if you have:
- Acute or chronic abdominal pain
Diagnostic laparoscopy allows you to accurately determine the underlying cause of pain, which can be caused by appendicitis, adhesions, pelvic infections, endometriosis, bleeding, cancer and many other diseases. - Suspicion of a tumor in the abdominal cavity
Diagnostic laparoscopy will help the doctor examine the suspicious formation in detail and take pieces of its tissue for further laboratory testing. - Suspicion of gynecological diseases
Diagnostic laparoscopy is widely used in gynecology, as it is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing various diseases and pathologies of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Abdominal diseases, if left untreated, can one day lead to serious complications that could cost you your life.
If you feel that something hurts inside you, do not try to heal yourself - you will only make the disease worse. Meanwhile, getting rid of many pathologies of the abdominal organs in the early stages can be easily and effectively if they are identified in time.
Don't waste your precious time. Make an appointment with our specialists right now.
What is laparoscopy
This low-impact method is used if difficulties or doubts arise when making a diagnosis. Often, tests and other diagnostic measures do not provide a complete picture of what is happening inside the body, then to identify the cause of the disease, an optical examination of the internal organs is carried out using special devices.
Fallopian tube laparoscopy is widely used to determine the causes of infertility in women and other pathological processes occurring inside the reproductive organs. Indications for laparoscopy are as follows:
- resection of ovarian cysts and tumors;
- sterilization;
- removal of benign formations in the uterine cavity;
- dissection of the adhesive process;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- endometriosis of the genital organs and abdominal cavity;
- diagnosis of various pathologies leading to infertility;
- preparation for artificial insemination.
Diagnosis of fallopian tube patency
This method is used to identify the widest range of pathologies of the reproductive system and peritoneum. Diagnostic laparoscopy of fallopian tube obstruction is carried out using endoscopic instruments, which makes this manipulation practically bloodless and painless. However, preparation for the procedure completely duplicates the preliminary stage of any operation.
The attending physician usually prescribes a complete preliminary examination of the patient for possible cardiovascular and other pathologies. Laparoscopy for infertility is a mandatory element in diagnosing possible causes of a woman’s lack of fertilization ability. There are the following contraindications for conducting a fallopian tube examination:
- severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- hemophilia;
- acute infectious diseases;
- kidney or liver pathologies;
- second trimester of pregnancy;
- purulent peritonitis;
- adhesions;
- coma;
- state of shock.
Operation laparoscopy
- How is a pelvic ultrasound done in women?
- Therapeutic exercise for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
- D-panthenol cream
Minimally invasive surgical intervention is usually preceded by diagnostic measures, during which the main cause of the disease is identified. Often, during an optical examination of internal organs, a decision is made to further eliminate the pathological phenomenon. For these purposes, laparoscopic surgery is prescribed. Through this type of surgery, the doctor eliminates abnormal changes in the woman’s reproductive organs. Laparoscopy of tubes is prescribed for the following reasons:
- internal bleeding;
- infertility;
- genital endometriosis;
- pain in the lower abdomen of unknown nature;
- torsion of the cyst stalk or its rupture;
- pathologies of development of reproductive organs;
- tumors of the uterus, ovaries;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- suspicion of pelvic inflammatory disease;
- acute non-purulent peritonitis;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology
Laparoscopy in gynecology is an indispensable method for diagnosing a whole range of diseases and pathologies, including:
- Chronic pelvic pain of unknown origin
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Ovarian cyst rupture
- Torsion of ovarian cyst and impaired blood flow
- Inflammation of the appendages and accumulation of inflammatory fluid in the abdomen
- Damage to the uterine wall
- Uterine fibroids
- Endometriosis
- Infertility
- Anomalies in the development of internal genital organs
Advantages of laparoscopy at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
- Doctors. Experienced, highly qualified surgeons with extensive experience in diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy.
- Modern equipment. The clinical hospital on the Yauza is equipped with equipment from the world's leading companies, “Covidien”, “Erbe”, etc.
- Safety. Minimal risks of bleeding and complications.
- Innovative design of operating rooms. Infection-resistant seamless monolithic blocks, 5 levels of sterility, thanks to a complex ventilation system.
- Low morbidity. Absence of significant postoperative scars and pain.
- Fast recovery. The length of stay in the hospital is no more than a day. The recovery period is 2 times shorter compared to abdominal surgery.
- Only positive patient reviews about laparoscopy. Patients who underwent laparoscopy in our hospital are satisfied with the results.
- Good cosmetic result. After the laparoscopy procedure, there are no scars left on the skin.
Laparoscopy in urology
Laparoscopy in urology helps to diagnose and treat diseases such as:
- Kidney neoplasms (benign and malignant up to stage 2)
- Kidney cysts
- Hydronephrosis stage I-II
- Secondary wrinkled bud
- Tumors of the ureter
- Kidney stones
- Ureteral stones
- Kidney prolapse
- Localized prostate cancer
- Localized bladder cancer
- Varicocele
- Prolapse of the uterus, bladder, rectum
- Stress urinary incontinence in women
Endoscopic surgery: advantages
Endoscopic surgery
is an excellent alternative to open surgery for a number of diseases. Why?
It’s all very simple: in traditional surgery, large incisions, which extensively traumatize the tissue, are usually indispensable. This is why you experience pain after surgery, and the rehabilitation and healing period takes quite a long time.
During endoscopic surgery, the surgeon makes only a few minor punctures, resulting in:
- After surgery you feel virtually no pain – often you don’t even need to take painkillers
- You spend an order of magnitude fewer days in the hospital
- You recover much faster and easier
- Instead of post-operative scars, you have only barely noticeable spots
Possible complications
After administration of anesthesia, some patients complain of the following symptoms:
- pain in the shoulders (muscles) and peritoneal area;
- bloating;
- painful sensations in the upper and lower extremities.
These symptoms disappear after a few days and have underlying pathological manifestations.
Immediately after surgical procedures, complications may occur:
- injury to blood vessels and internal organs during surgery with a surgical instrument;
- divergence of surgical sutures;
- blood clot formation;
- suppuration of the suture;
- pneumonia;
- internal bleeding;
- associated infections;
- pre-stroke or pre-infarction condition;
- stroke, heart attack.
All of these complications are exceptions to the rule and occur in rare cases.
Diagnostic laparoscopy: price and what does it depend on?
The price of laparoscopy is influenced by a number of factors that may vary in each specific case. Here are the main aspects that one way or another determine the cost of this procedure:
- The disease itself and the degree of its development
- Your general physical condition
- Purpose and level of complexity of the operation
- Equipment class
- Consumables
- Need for postoperative follow-up
And a number of other factors. The price of laparoscopy in your case will be determined by your attending physician after a preliminary diagnosis, which will help you understand the objectives of the future operation.
Advantages of laparoscopic over abdominal surgery
The main advantage of this intervention is the preservation of the fallopian tubes and the restoration of the possibility of conception. The obvious advantages of laparoscopy include:
- accelerated recovery after surgery, requiring about 3-5 days of inpatient observation - with abdominal surgery, healing and removal of sutures occurs in two weeks;
- after laparoscopy, three small marks remain, about 1.5 cm in diameter;
- high level of information content - video monitoring of the progress of manipulations allows you to increase the surgical field by 10 times;
- gentle treatment of adjacent tissues - due to multiple magnification, accidental damage does not occur.
Due to the obvious advantages of this intervention, the technique is almost always used. Separately, we can emphasize the need for the patient to be deeply immersed in anesthesia in both types of surgical interventions.
Contraindications to laparoscopy
The value of laparoscopy as a method outweighs the risk of possible complications. However, it is not always possible to carry out this intervention without harm to the patient's health. Eliminating contraindications that are incompatible with laparoscopy is a key task of preliminary diagnosis. Here are the main reasons why a doctor may refuse to conduct an examination and choose alternative diagnostic methods:
- Any serious illness associated with severe circulatory and respiratory problems
- Bleeding disorders
- Acute renal-liver failure
- Infectious skin lesions
- Severe obesity
Whether to perform laparoscopy or not is a question that the doctor decides strictly individually in each specific case. This depends on the results of preliminary diagnostics, your general condition - both physical and psychological, as well as on the individual characteristics of your body.
Planning pregnancy after surgery
It is carried out together with the attending physician, who will recommend the best periods for conception and warn against spontaneous abortions. Unsuccessful pregnancies almost always end in the soldering of the fallopian tubes, after which repeated surgical intervention will be required.
Planning for the timing of conception is carried out depending on the underlying reasons for which laparoscopy was prescribed:
- when removing adhesions in the fallopian tubes - according to the recommendations of specialists, conception should occur no earlier than 4-5 months after the operation;
- when excision of adhesions in the pelvic organs - a month after the first menstruation (when the cycle is restored);
- when a detected cyst or fibroid is removed, the ban on pregnancy is valid for up to 8 months;
- removal of overgrown endometriotic tissue predicts an additional course of treatment, without pregnancy.
If all the requirements of the attending gynecologist are met, the prognosis for further pregnancy during tubal laparoscopy is favorable (excluding sterilization).
The effectiveness of surgery to treat tubal obstruction lasts for several years, after which a relapse of the disease is possible. To exclude the recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to contact specialists for preventive measures.
Regular visits to your local gynecologist, tests and indicated treatment for diseases of the genital area will help avoid the repeated need for laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes.
What hormonal medications did you take to stimulate ovulation?
- Gonal 33%, 3977 votes
3977 votes 33%3977 votes - 33% of all votes
- Clostilbegit 25%, 2989 votes
2989 votes 25%
2989 votes - 25% of all votes
- Menopur 16%, 1937 votes
1937 votes 16%
1937 votes - 16% of all votes
- Puregon 14%, 1699 votes
1699 votes 14%
1699 votes - 14% of all votes
- Decayed 8%, 984 votes
984 votes 8%
984 votes - 8% of all votes
- Menogon 3%, 365 votes
365 votes 3%
365 votes - 3% of all votes
Total votes: 11951
Voted: 8788
January 17, 2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Preparation for laparoscopy
Preparation for laparoscopy is the most important stage, on which the accuracy and safety of the upcoming examination directly depends. Your attending physician will help you prepare for the examination, who will explain the purpose of the examination, describe each stage in detail and tell you what measures you need to take on your own.
- Eliminate various painkillers and other medications that your doctor has told you to avoid.
- A week before surgery, strictly follow the necessary diet: exclude from your diet fruits, vegetables, especially legumes, brown bread and other foods that your doctor considers undesirable; eat low-fat broths, fish and meat, cottage cheese, porridge, kefir
- During the day of surgery, eat only liquid foods.
- 8 hours before laparoscopy, refrain from eating at all.
- Before the operation, a complete cleansing of the intestines is also recommended: the method of cleansing that is suitable for you will be determined by the attending physician
- Before the procedure, take a shower and shave the hair on your stomach and pubic area.
- To relieve anxiety, take the sedatives recommended by your doctor a few days before laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy of fallopian tubes postoperative period
The duration of the recovery period depends on the volume of anesthesia administered, the type and duration of the operation, general health, existing concomitant pathologies and the presence of chronic forms of diseases.
It takes place exclusively under inpatient observation conditions for 3-5 days. Monitoring is carried out around the clock due to the anesthesia used during surgery, in order to avoid the development of a deterioration in the general condition.
Rehabilitation in the postoperative period is carried out depending on the type of intervention:
- anti-inflammatory therapy - to prevent possible failure of the second fallopian tube;
- physiotherapy with electrophoresis;
- prescribing absorbent drugs;
- hormone therapy.
As general recommendations, the patient is advised to:
- moderate physical activity - short walks;
- full compliance with personal hygiene conditions;
- prohibition on lifting weights and heavy physical activity (carrying a child, shopping, etc.).
If during the manipulations both fallopian tubes were treated, then rehabilitation measures include:
- drugs that restore endometrial layers;
- hormonal medications to normalize the general level of hormones and stabilize the general condition.
With the complete restoration of the endometrial level and hormonal balance, the first menstruation will occur, indicating the normalization of the body’s condition and the possibility of conception.
Patients are discharged from inpatient observation starting from the fourth day, sick leave is issued for a week, sutures are removed after 7 days.
The first menstruation that comes often comes with heavy bleeding and pain - this is a normal phenomenon after this operation. The menstrual cycle should be restored within a few visits and proceed in its standard mode - with discharge, passage time and duration of cyclic phases that are normative for each organism.
Prohibitions in the postoperative period
Medical professionals do not recommend:
- sexual contacts earlier than 21 days after surgery - to exclude infection with pathogenic microflora and reduce the risk of injury;
- heavy physical labor is prohibited for a quarter;
- take baths, visit swimming pools, saunas and open ponds;
- become pregnant without the approval of the attending gynecologist.
To speed up the recovery process, patients need to undergo a course of sanatorium-resort treatment in gynecological health resorts, physiotherapeutic measures, change their diet to one approved by a doctor, and undergo a course of treatment for possible bad habits.
How is laparoscopy performed?
Depending on the goals set by the attending physician, laparoscopy can be performed under either epidural anesthesia or general anesthesia. The methodology - again, depending on the goals - may partially differ, but the key actions of the doctor do not change:
- The doctor makes several small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall (about 4) with a diameter of no more than 5 mm
- The abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide to improve the visibility of internal organs and possible pathologies
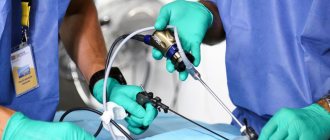
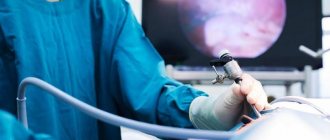
- Through one of the holes, the doctor inserts a laparoscope probe into the abdominal cavity, which transmits an image to the monitor screen from a video camera
- Through another hole, the doctor inserts a special manipulator, with the help of which he moves the internal organs in the desired direction and monitors the image of the studied areas on the monitor screen
- After the task of laparoscopic surgery is completed, the doctor removes the laparoscope probe, other instruments and sutures the punctures
The procedure can last from 15 minutes to 3 hours. This depends on the purpose of the procedure, individual anatomical features and possible complications during the operation.
Features of the recovery period
Elements of accelerated rehabilitation have been introduced into the work of the gynecological oncology department of UKB 4. One of the aspects of “fact track” surgery is the early activation of the patient, which in such an operation is carried out 5-6 hours after completion of the operation. The patient is allowed to sit down, stand up (the first time under the supervision of medical personnel) and walk if she feels well.
In order to reduce the intensity and relieve pain, intramuscular injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which also contribute to accelerated rehabilitation. Since laparoscopic operations, in comparison with surgical interventions performed by transection, are accompanied by less severe pain, in most cases, the use of narcotic analgesics is not required.
These measures can reduce the risk of postoperative thromboembolic and inflammatory complications, as well as the risk of adhesions.
In addition, all patients are prescribed elastic compression (wearing compression stockings or elastic bandages) to prevent thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities. Depending on the degree of risk of thromboembolic complications in the postoperative period, low molecular weight heparins or antiplatelet agents may be prescribed, which reduce blood clotting.
As part of rehabilitation therapy, antibacterial drugs are used, as well as agents that normalize intestinal motility and eliminate nausea (if it occurs).
An important point is to follow the correct diet: on the day of the operation, you are not allowed to eat (you can drink still water); for the next 2-3 days, a gentle diet is prescribed until intestinal function is restored.
The following products are not allowed during this period:
- -raw vegetables and fruits;
- -sweets;
- -bakery products;
- -juices, sweet drinks, coffee, carbonated drinks;
- -sweet sour milk products.
If surgical treatment is not associated with an ectopic pregnancy and is not accompanied by intervention on the ovaries (for example, removal of a cyst), menstruation occurs on time (according to the calendar).
However, 1-2 days after chromosalpingoscopy there may be a slight discharge associated with the release of the contrast agent.
The patient spends several days in the hospital (4-6 days), after which she is discharged home (if there are no complications).
It is recommended to limit strenuous physical activity for 21 days after laparoscopy. The duration of sexual rest is determined by the attending physician and depends on the type and extent of the surgical intervention.
In addition, sitz baths, steam baths, saunas, swimming pools, and swimming in the sea are not recommended for about 2 weeks, but the period may vary depending on the extent of the operation and the healing of the sutures.
Sutures are removed 5-7 days after laparoscopy (the day of surgery is not taken into account in the calculation). After this, you can shower completely, including soaking post-operative scars.
At first, the scars are pink in color, then gradually fade and become almost invisible.
Compliance with all doctor’s instructions during the recovery period after laparoscopy helps reduce the likelihood of complications and successful rehabilitation.
Possible complications after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
– one of the safest and most gentle methods of surgical intervention. As with any other operation, complications can occur, but this happens extremely rarely:
- Bleeding due to damage to a large vessel of the anterior abdominal wall
- Gas occlusion of blood vessels
- Damage to the outer lining of the intestine or perforation of its wall
- Accumulation of air in the pleural area
- Common subcutaneous emphysema
- Adhesions that can occur in the abdominal cavity due to the characteristics of the body itself, the traumatic nature of the intervention performed, or the presence of pathologies in the abdominal cavity
- Slow bleeding into the abdominal cavity from damage to small vessels or rupture of the liver capsule
- Hematomas
- A small amount of gas in the subcutaneous tissues
- Purulent inflammation at the puncture site
- Postoperative hernia
Complications some time after surgery:
Remember:
If the procedure is performed by experienced specialists, the risk of complications is significantly less. But if any of them do occur, tell your doctor immediately.
Bottom line
Some women have to undergo a tubal laparoscopy procedure. The operation is quite common and has many indications; sometimes laparoscopy is prescribed for diagnostic purposes. This type of surgical intervention, unlike laparotomy, has many advantages. Among them, it is worth noting: low trauma due to minimal punctures in the abdominal cavity, an easier postoperative period, the possibility of applying cosmetic stitches.
It is important to take full responsibility in preparing for an operation that consists of several stages. The most important of them is a complete examination of the body, including tests, ECG and other checks. Their results will help to avoid risks during laparoscopic tubal surgery.
Laparoscopy in the Stolitsa network of clinics: why should you contact us?
High tech
To carry out highly accurate laparoscopic diagnostics and effective low-traumatic operations, we use modern premium PENTAX video endoscopes. Thanks to a powerful optical system, they allow the doctor to assess in detail the condition of the abdominal organs, study pathological foci in detail, take tissue particles from them for further analysis, and most importantly, select the necessary low-traumatic operation and carry it out safely for your health.
Professionally
The experience and professionalism of a doctor is the main condition for accurate diagnosis and safe treatment. Only an experienced doctor can correctly interpret the examination results and perform the operation without harm to your health.
Over the years of successful practice, our specialists have performed a huge number of laparoscopic examinations, low-traumatic operations and have restored health to hundreds of people.
That’s why, when you contact us, you can be sure that our specialists will help you: they will thoroughly understand the situation, carry out the diagnosis correctly, make an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, perform the necessary low-traumatic surgery safely for your health.
In our cozy rooms for single and double occupancy you will feel comfortable, because they have everything you need: a button to call a nurse at any time of the day, a separate bathroom, air conditioning, a refrigerator, a TV, a microwave and Wi-Fi.
Good nutrition and rehabilitation procedures - physiotherapy, massage, manual procedures - will help you quickly regain strength after surgery and return to a full life.
Make a choice in favor of professional medicine!
How is the operation performed?
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and requires careful preparation:
- taking tests, urine and blood;
- performing an ultrasound.
As a rule, it is carried out on days 8-10 of the menstrual cycle, until ovulation occurs.
The essence of the procedure is:
- supply of carbon dioxide to increase the size of the abdominal cavity;
- lifting the abdominal walls to gain maximum access to the internal organs;
- carrying out manipulations by a doctor in the form of several punctures with a diameter of up to 5 mm.
All manipulations are controlled and displayed on the monitor. This allows doctors to quickly identify the affected area with the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tube. A contrasting colored solution is injected and the doctor remains to dissect, remove adhesions, and restore the lumen in the fallopian tubes as far as possible.
Preparation
It is important to identify contraindications to surgery. The doctor carefully examines the patient’s medical history and performs a visual assessment to determine the possibility of emergency intervention.
Preparation is prescribed several months before the procedure, unless, of course, there is an emergency intervention.
In about 2 weeks, patients will have to take:
- blood test for coagulability, group and Rh factor;
- test for HIV, hepatitis;
- urine analysis to exclude or refute the inflammatory process in the body;
- flora smear;
- Ultrasound;
- Fluorography;
- ECG.
Only after receiving ready-made tests in hand, the doctor will decide to carry out surgical measures. In particular, certain contraindications are taken into account.
Laparoscopy is not performed if the body contains:
- acute infection;
- malignant neoplasm affecting the genital area;
- highly active endometriosis;
- poor blood clotting;
- cardiovascular pathology;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- excessively short fallopian tubes (less than 4 cm) due to a previous operation;
- diseases of the kidneys, adrenal glands;
- operated hernia;
- state of shock.
On the eve of the operation, it is important for women to carry out a fasting diet for several days, excluding gas, drinks, vegetables, and fruits. Do not eat after 6 o'clock and give an enema at night.
REFERENCE! Analyzes are prepared for at least 10 days. The doctor must identify the possible chronic course of diseases in the body, when laparoscopy can be canceled and other therapeutic measures taken.
The day of the operation to remove the fallopian tubes is of no small importance. The procedure is not performed during the menstrual period. As a rule, it is recommended in the first half of the menstrual cycle to avoid and exclude the possibility of pregnancy.
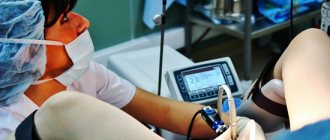
Anesthesia
Anastasia is appointed as an anesthesiologist, since laparoscopy involves performing the operation under general anesthesia, when nerve impulses in the spinal cord and brain will still be involved. This can lead to partial loss of consciousness, increased pain as a reaction to external stimuli.
Before the operation, the patient’s blood pressure and the degree of oxygen saturation of the blood must be checked.
It is intended to administer (intravenous) solutions (sodium thiopental) to provide short-term anesthesia lasting up to 25 minutes. It is possible to use a mask or endotracheal method of anesthesia, in particular the administration of inhalation anesthetics together with gas (Halothane, Sevoflurane).
REFERENCE! Anesthesia is fraught with side effects (swelling of the larynx, respiratory failure, myocardial infarction, gagging). Only an experienced anesthesiologist will be able to determine the degree of administration of the necessary narcotic drugs and dosage, and control their intake into the body.
Operation stages
The operation is performed by a surgeon and gynecologist under sterile conditions. A woman needs to perform hygiene the day before, shave her pubic hair, and empty her bladder.
Anesthesia is administered immediately before the procedure, and the surgical area is treated with antiseptics.
Stages of implementation:
- placing the patient on the operating table;
- introduction of general endotracheal anesthesia;
- putting a woman to sleep;
- sanitizing the operated area with alcohol and antiseptics;
- making the first puncture of the navel with a Veress needle without injuring neighboring organs;
- supply of carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide into the cavity to artificially expand the space and free visualization for the doctor;
- insertion of a video camera through another puncture with a diameter of 10 mm;
- insertion of laparoscopic instruments through 3 punctures to examine the organ cavity and assess the situation;
- designation of the site of the adhesive process;
- carrying out manipulations to release tissue from adhesions, dissecting them;
- embryo removal during ectopic pregnancy;
- retrieving used tools;
- suturing;
- release of gases from the abdominal cavity.
The operation takes no more than 0.5 hours. The average duration is 40 minutes.