Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder in children is considered a routine, harmless and informative type of instrumental methods for studying the urinary system. Ultrasound diagnostics is completely painless and is carried out without violating the integrity of the skin, so it can be performed even on newborn children.
Due to the increase in congenital anomalies of the urinary tract and kidneys, the latest clinical guidelines have introduced mandatory screening ultrasound examination of children at the age of 18 months.
Indications
The need to prescribe an ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys in children is determined by the following factors and symptoms:
- Manifestations of dysuria: pain and burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, urgency, nocturia (prevalence of nocturnal diuresis).
- Acute retention or vice versa – a sudden increase in the amount of daily urine.
- Macroscopic pathological impurities in the urine: the appearance of scarlet blood or clots, pus, white thick sediment.
- Arterial hypertension syndrome.
- A neoplasm palpable through the anterior abdominal wall (nephroblastoma or Wilms tumor may occur in young children).
- Pain of various types in the lumbar region or lateral abdomen.
- The appearance of pastosity and edema.
- Fever of unknown origin.
- Closed injury to the anterior abdominal wall or lower back (to avoid rupture of parenchymal organs and the formation of hematomas in them).
Also, an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is prescribed to a child if the stigma of dysembryogenesis is determined, resuscitation measures are carried out at his birth, the presence of diseases of this system in close relatives (poly- or multicystic kidneys, their doubling, nephroptosis, chronic pyelonephritis, etc.) , increased levels of total bilirubin in peripheral blood, detection of salts in urine samples.
On an empty stomach or not?
If you are doing an ultrasound examination of the kidneys as part of an examination of all internal organs, then the doctor will tell you not to eat anything and come on an empty stomach. But if the referral is only for an ultrasound of the urinary system, then the requirement to come on an empty stomach is not at all mandatory and you can eat before the procedure.
However, please note that in this case, food must be taken no later than 8 hours before the examination and must not contain foods that cause gas.
Preparation
Careful preparation for performing an ultrasound of the kidneys in children is mandatory and important for obtaining a reliable picture of the condition of the organs of the urinary system.
- Firstly, 1-2 days before the study, foods and dishes that cause increased gas formation should be removed from the child’s diet, namely: legumes, fruits, smoked sausages and cheeses, fermented milk products and rye bread. If a child, regardless of nutrition, often experiences bloating, then a couple of hours before the test you can take drugs from the group of antifoam agents in an age-specific dosage (Espumizan, Bobotik). On the eve of the ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys, it is advisable to refrain from eating at least three hours before the procedure.
- At the second stage, preparing the child for a kidney ultrasound involves adequately filling the bladder 60-90 minutes before the examination. This is necessary to determine the volume of residual urine, exclude vesicoureteral reflux and assess the condition of the organ walls. In addition, the liquid is a good conductor for ultrasonic waves. The volume of drinking directly depends on the age of the child and the size of his bladder:
- From 1 to 2 years – 100 ml.
- From 2 to 7 years – about 250 ml.
- From 7 to 11 years – on average 400 ml.
- Over 11 years old – 500-800 ml of liquid.
If the child has a strong desire to urinate before the examination, then only partial emptying of the bladder is possible, since overstretching its walls can contribute to distortion of the data on the ultrasound. However, then replenishment of lost fluid is necessary.
Carrying out an ultrasound
Several positions can be used for an ultrasound examination of the kidneys: lying on your side, lying on your back, standing or sitting. To improve the contact of the sensor with the patient’s body and improve the quality of the signal, a special gel is applied to the skin.
First, longitudinal sections of the lumbar region are examined, after which the kidneys are scanned in transverse and oblique directions. The patient, in turn, changes position from the right side to the left. Compliance with these methods allows you to determine the size of the organ, its shape, and assess the condition of the pyelocaliceal system.
During the procedure, the diagnostician must ask the patient to hold his breath for a while. This allows you to get a better picture and determine the mobility of both kidneys. The whole procedure lasts about 15 minutes .
During ultrasonography of the bladder, the patient lies on his side. The bladder is filled with a volume of 200-250 ml. Insufficient filling of the bladder can cause a diagnostic error. During the examination, a series of transverse and longitudinal images are obtained through the abdominal wall by moving the sensor in the suprapubic region.
To determine the height of the organ, a sagittal section . If the bladder behind the sections is oval and has the same echogenicity, then it is filled correctly. There are 2 types of sensors that are used for ultrasound of the bladder: abdominal and abdominal.
An excellent way to visualize the bladder in women is a transvaginal examination. You can even see the transmural portion of the ureter. The greatest information content is achieved by a combination of both methods.
How it goes
An ultrasound of a child’s kidneys is performed in three positions: on the back, on the side and on the stomach (see the article on how to do an ultrasound of the kidneys). In some cases, in particular, to exclude kidney prolapse, it is possible to conduct a study in a standing position under breathing control.
To obtain an ultrasound picture, the doctor places the sensor on the desired area of the body and moves it over the patient’s skin, as a result of which an image of the organ is displayed on the screen. In order to reduce the resistance of organs and tissues, a special transparent gel is used, which is odorless and does not cause irritation. At the end of the examination, the doctor concludes with the size of the organs, the state of their echostructure, and the presence or absence of pathological changes. Thus, ultrasound of the kidneys in children is performed completely painlessly and safely.
How long does a bladder ultrasound take?
Usually the appointment does not take more than 15-25 minutes. Be sure to tell your child how everything will go so that he does not worry or be afraid. At the appointment, the little patient will need to lie quietly while the doctor conducts the examination.
Using the device, a specialist will determine the shape and size of the bladder (which is very important for diagnosing various diseases), the presence or absence of an inflammatory process, pathologies, tumors, stones or polyps. Upon completion of the examination, you will receive a detailed statement.
What is revealed
Ultrasound does not show all inflammatory and structural changes in organ tissue. For example, the initial stages of acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis or acute cystitis will not be visualized during the examination. Therefore, sometimes just doing an ultrasound is not enough; in some cases, laboratory and invasive methods will be more informative.
Children's ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder reveals:
- Presence of echo-positive stones in case of urolithiasis.
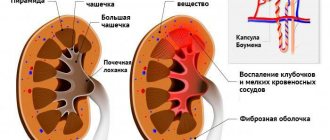
- Chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidney parenchyma involving the pyelocaliceal system), in which pyelectasis and moderate sclerosis are detected.
- Chronic glomerulonephritis is an autoimmune disease in which necrosis and sclerosis of the kidney tubules develop.
- Neoplasms, both benign and malignant.
- Cystic formations (single cysts that do not cause discomfort, multi- or polycystic kidney disease).
- Nephroptosis, or kidney prolapse.
- Developmental anomalies in the form of hypo- and aplasia (underdevelopment or absence of a kidney), duplication of the kidney, horseshoe, S and L-shaped kidneys.
- Hydronephrosis is a pathological transformation of the kidney due to impaired urine passage.
- Narrowing or developmental abnormalities of the renal vessels using Doppler ultrasound.
- Sand, stones and tumors in the bladder.
- Chronic cystitis (the wall of the bladder will be unevenly thickened and tortuous).
If pathological changes are detected on an ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys, the doctor who conducted the study must notify the parents about this, after which the conclusion must be contacted by the attending physician to clarify the full diagnosis and treatment tactics.
What problems can ultrasound of the genitourinary system help detect?
Ultrasound diagnostics helps to identify many diseases of the genitourinary organs. Among them:
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- urolithiasis (kidney stones are visualized very well on ultrasound, as are stones in the ureter; ultrasound in general is one of the preferred methods for diagnosing urolithiasis);
- inflammation of the bladder (cystitis);
- inflammatory process in the urinary tract (urethritis, etc.);
- prostate diseases (prostatitis, prostate adenoma, prostate stones);
- vascular pathologies;
- cysts, nodes and other neoplasms, etc.
Decoding
Interpretation of kidney ultrasound is carried out by a diagnostician or nephrologist/urologist, but the data below allows parents to independently judge the size of the organs of their child’s urinary system:
- For children in the neonatal period (up to 28 days inclusive), the dimensions of the left kidney are in the range of 48-51.1 by 20.5-21.3 (length and width, respectively), the right one - 47.5-50.0 by 20.3 -24.6 mm.
- In children aged 1-6 months, the normal size of the left kidney is 53.8-58.3 by 22.9-23.8; right - 52.7-56.9 by 26.1-28.2 mm.
- From 7 to 11 months, the size of the left kidney is 61.8 by 24.6; right - 60.6 by 29.7 mm.
- For children from 1 to 4 years old, the following indicators of the left kidney are characteristic: 69.6-76.0 by 27.6-30.2; for the right - 68.3-75.4 by 31.2-32.7 mm.
- From 5 to 9 years, left kidney – 82.5-86.8 to 31.9-34.6; right kidney – 80.5-85.4 by 34.5-36.3 mm.
- In children 10-14 years old, the left kidney is 95.5-114.79 by 37.8-45.5; right - 94.5-113.1 by 37.9-41.0 mm.
- In children over 15 years of age, the indicators of the left kidney are 116.7 to 46.8; right - 115.2 by 42.1 mm.
Also important indicators for ultrasound of a child’s kidneys are the thickness of the parenchyma (normally 15-21 mm) and the width of the pelvis (up to 10 mm), an increase in which indicates the active stage of inflammation. With a normal ultrasound picture of the organs of the urinary system, the kidneys have age-appropriate sizes and correct localization, the echostructure of the parenchyma is homogeneous, without inclusions, the pelvis and initial parts of the ureters are not dilated.
Kidney test results
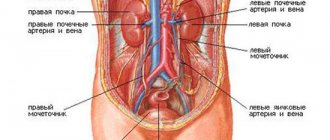
When performing an ultrasound, each kidney is detected as an oval-shaped organ. The lateral edge is convex, and the medial edge is concave. The central echo complex is considered the most echogenic part of the organ. It includes the pelvis, calyxes, vessels, adipose tissue, and nerves located in the renal sinus (in the kidney cavity).
Less echogenicity in adults and children is characteristic of the parenchyma. Its thickness is about 1.2-1.8 cm. The parenchyma includes the medullary and cortical sections. The first of them consists of 10-18 peculiar pyramids. Their tops are directed towards the renal sinus, and their bases are facing the surface of the organ. Along the bases of the pyramids, a conditional line can be drawn dividing the sections of the parenchyma.
Kidney agenesis
During the scan, abnormalities in the number of kidneys and their position may be detected. Anomalies of quantity include agenesis. This term refers to the development of the urinary system in which one of the kidneys does not form. Both organs may be absent, but this pathology is extremely rare. Children born without kidneys die in the first hours of life.
Abnormalities in the position of the kidneys (dystopia) are disturbances in the movement of the organs of the urinary system during embryonic development. These pathologies can be of the following types:
- Pelvic. An ultrasound shows that the kidneys are located in the pelvis. In women they are located behind the uterus, and in men they are behind the bladder. The shape of the organs of the urinary system is often correct.
- Iliacs. With such dystopias, the kidneys are located at the level of the wings of the ilium. The organs have an abnormal appearance.
- Lumbar. The kidneys are located in the lumbar region. They are located slightly lower than usual. The organs have an unusual flattened and elongated shape.
- Thoracic. The kidneys are located in the pleural cavity or above the diaphragm. Such an anomaly in the position of the organs of the urinary system is extremely rare.
Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the size of the kidneys. Normally in adults and children they should be as follows:
- in adults – length from 10 to 12 cm, thickness from 4 to 5 cm, width from 5 to 6 cm;
- at 10 years – length from 8.5 to 10 cm;
- at 5 years – length from 7.5 to 8.5 cm;
- at 1 year – length from 5.5 to 6.2 cm;
- in a newborn – length from 4 to 4.5 cm.
A change in the size of organs (their volume) indicates the development of serious diseases. A symmetrical increase may indicate acute renal failure, glomerulonephritis, occurring in an acute form. Asymmetrical increase is a sign of acute pyelonephritis, renal vein thrombosis. A symmetrical decrease in the kidneys is observed in old age. In young people, this can occur with hypertensive nephropathy and chronic glomerulonephritis. Asymmetrical organ reduction occurs in chronic pyelonephritis, renal infarction, and chronic ischemia.
What is ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract
Ultrasound of the urinary system and kidneys is a non-invasive ultrasound examination that examines the physiological state of organs and identifies their features. It can accurately and quickly detect developmental abnormalities and the presence of injuries.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for ultrasound:
- chronic kidney disease;
- the presence of protein and leukocytes in the urine;
- blood pressure is higher than normal;
- painful urination;
- modification of urine;
- high body temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- lumbar pain;
- mechanical trauma of the abdominal cavity;
- increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- swelling of the limbs and face.
Only a doctor can accurately determine the indications for an ultrasound of the genitourinary system and kidneys based on the examination and complaints of the patient.
Contraindications:
- Increased gas formation. Recommendations: find out the reason why this happened and go on a special diet. It is better to postpone the next appointment for 6-9 days.
- Full stomach. You must go to the procedure hungry so that leftover food does not interfere with visualization of the organ.
- Presence of burns or scars. The sensor can cause pain in the patient. Also, any irregularities reduce the contact of the device with the skin.
- Obesity. The layer of fat interferes, like food, and prevents accurate visualization of the organ. Ultrasound sensors have a certain penetration depth: the organ will be examined partially.
- The presence of barium in the intestines after the appropriate procedure.
Which doctor conducts
Diagnosis of the urinary tract and kidneys is carried out by highly specialized specialists:
- urologist - deals with surgical treatment of the kidneys;
- nephrologist - prescribes medications.
A local physician can also prescribe an ultrasound examination to perform a preventive examination.
How long does the examination take?
The procedure lasts from 3 to 7 minutes. The duration of the study may increase if the doctor needs to diagnose other organs.
How often can the procedure be done?
For an adult, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and urinary tract is performed as often as the doctor recommends. The study is harmless and does not cause disturbances in the functioning of the body.
How is an ultrasound scan performed?
The transabdominal method of performing the procedure involves placing the patient on a couch. The position is determined by a specialist. It depends on the need to use a particular projection. The skin of the subject is treated with a special air-tight gel. It is necessary to improve the echo signal. The sonologist then places the sensor, including the equipment, on the person’s body. After that, he studies the image that appears on the monitor.
Transvaginal ultrasound is most often performed on women when diagnosing diseases of the reproductive organs. The patient lies down on the couch or takes a seat on the gynecological chair. A condom is put on the sensor, treated with gel and inserted into the vagina to a depth of about 6 cm. Sometimes there is a need to change position for a better view.
The transrectal method is carried out in a similar way. Most often, a person needs to lie on the couch on his side, with his back to the doctor, with his legs slightly bent at the knee joints.
Possible pathologies and their interpretation on ultrasound
Complications and pathologies of the kidneys:
- Glomerulonephritis with renal failure. Increased echogenicity, enlarged kidneys, too clear boundaries of the organ, “knocked out pyramids”;
- Chronic pyelonephritis . Reduction in kidney size;
- Nephrosclerosis. Increased echogenicity of the organ, the presence of dense connective fibrous tissue;
- Fibrolipomatosis . Systemic inclusions of adipose tissue in the structure of the parenchyma;
- Kidney swelling. Decreased echogenicity of the organ against the background of anechoic pyramids, enlargement of the capsule and too sharp structure of its contours.
Diagnosis of bladder pathologies:
- Organ inflammation. The presence of small multiple echogenic particles, thickening of the walls of the bladder (they also become uneven);
- Neoplasms in the pelvic organs with metastasis to the urinary tract. Large round echogenic formations in large numbers;
- Stones . Small, medium and large hyperechoic formations with an acoustic track. Have mobility when changing the patient’s position during ultrasound;
- Tumors . With a malignant nature - a combination of echo-negative zones of necrosis and hyperechoic areas and uneven and blurred edges. With a benign nature, the structure of the neoplasms is slightly echogenic, homogeneous with smooth edges;
- Anomalies of organ development . Backflow of urine into the ureters, atypical sizes while maintaining standards for other parameters;
- Neurogenicity. Thickening of the walls of the bladder, mostly uniform (from 0.5 centimeters or more).
What does the doctor look for during an ultrasound examination of the abdomen?
The doctor examines the health of the kidneys, their location relative to the spine and each other, size, condition of the parenchyma, contours, presence of sand or stones. In addition, it looks at the condition of the adrenal glands, which belong to the endocrinological system. The fact is that in normal condition they are small in size, no more than 4 cm and are poorly visualized, but if the doctor sees them as voluminous and distinct, then the glands require additional examination for tumor, stagnation or inflammatory process.
Proper preparation for an ultrasound of the urinary system will allow the doctor to make a correct and correct diagnosis of the kidneys, prepare an opinion on the condition of the internal organs and the urinary system and prescribe a treatment regimen.