A doctor can prescribe effective treatment for suspected pathologies of arteries and veins only after establishing an accurate diagnosis, so modern methods of examining patients are of great importance. CT scan of cerebral vessels (CB) is indispensable in cases of suspected pathology of arterial and venous vascular trunks, as well as the plexuses formed by them.
An effective diagnostic method
The undoubted advantages of this method include the wide availability of the study and its relatively low cost, as well as the speed of obtaining results. There are practically no contraindications or restrictions for the study, and the patient can be prepared for diagnosis in a few minutes.
What does a CT scan of the vessels of the head and neck show?
Thanks to the CT scan of the brain and neck vessels, you can:
- study the features of the structure and relative position of veins and arteries;
- set the diameter of the vessels;
- identify atherosclerosis of artery walls;
- diagnose vasoconstriction and make an assumption about the possible cause of this pathology;
- identify the presence of collaterals (bypass routes of blood flow).
The pictures will show:
- developmental defects (malformations, aneurysms, etc.);
- stenosis, thrombosis, embolism;
- vascular networks of neoplasms;
- vasculitis;
- angiopathy of various etiologies;
- atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of the arteries;
- traumatic vascular injuries.
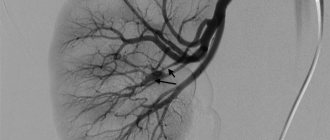
CT scan of the cervical arteries. On the left is a two-dimensional image, on the right is a three-dimensional image. Arrows indicate stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery
CT scan of head and neck vessels with contrast
Since the vessels practically do not stand out against the background of other tissues, CT angiography of the head and neck is necessarily performed with contrast. To improve the clarity of images, iodine-containing preparations are used for injection into the blood. By staining arteries, veins and capillaries, contrast agents visualize the smallest vessels, as a result of which diagnostic possibilities are significantly increased.
Computed angiography is especially informative when:
- inflammation of blood vessels;
- the need to study the blood supply to tumors;
- suspected compression of blood vessels by neoplasms or spread of metastases to the walls of veins and arteries.
Often, the introduction of contrast causes the appearance of specific sensations. A person may feel heat, a rush of blood to the face, and a metallic taste in the mouth. Occasionally, complications occur in the form of nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, redness and swelling at the injection site. You must inform your doctor about any changes in your condition without waiting for the end of the diagnostic procedure.
The contrast agent is eliminated from the body approximately one day after the injection. To speed up this process, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids.
CT scanner and contrast bolus injection system (pictured left)
If you have already had an X-ray or contrast test two to four weeks before your angiography, tell your doctor about it. It is possible that the specialist will recommend rescheduling the date of the procedure.
How does the procedure work?
Hagiographic research can only be carried out in special medical centers by highly qualified specialists. A certified medical institution must have a room equipped with the necessary equipment. Including preliminary preparation of the patient and the examination itself, the procedure can take about 60 minutes. In this case, the effect of the x-ray lasts 15–20 minutes. Depending on the doctor's actions, the angiography may take longer. For the procedure, anesthesia of only the lower part of the body, or general anesthesia, can be used.
Angiography of the vessels of the lower extremities consists of the following stages:
- The area where the catheter is inserted with a contrast agent must be disinfected.
- The vessel being examined is punctured using a catheter, which has a special mandrel (necessary for greater hardness and easy insertion).
- After the puncture, the rod is removed from the catheter.
- Then an iodine-containing substance is injected to obtain contrast in the image.
- Using a CT scan, the doctor captures images of the vascular pattern of the lower extremities.
- After obtaining the necessary images, the doctor removes the catheter and treats the puncture site. Sometimes a couple of stitches are applied to close the wound.
Next, the person is transported to the ward for rest and recovery after the invasive procedure. After some time, the doctor should make a follow-up visit to assess the general condition.
How to do a CT scan of the vessels of the head and neck
It is better to come to the diagnostics in loose clothes made of natural fabric. It is important to make sure that there are no fittings, decorative elements or metal threads on it. Before the examination, remove jewelry, glasses, watches, and warn the staff about the presence of dentures or implants.
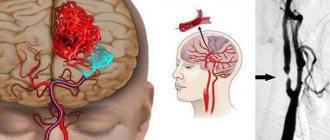
CT angiography of the brain - photo (3D reconstruction)
CT angiography of the vessels of the brain and neck proceeds as follows:
- the patient lies down on the tomograph couch;
- the radiographer administers a radiopaque solution through a dropper;
- the table moves towards the scanning system so that the head is in the radiation zone;
- the x-ray tube and sensors rotate inside the tomograph ring, the device takes pictures and transmits them to the computer;
- At the end of the study, the device turns off.
Analysis of cerebral vessels is a painless procedure. The only thing that can cause minor discomfort is the noise and crackling of a working tomograph. To combat this problem, many clinics provide hearing protection or earplugs.
The scan lasts 20-30 minutes. During this time, you should lie still and not move, so as not to spoil the quality of the pictures.
Instruction before the computed tomography procedure
The information obtained during angiography is processed in a special program. The results are saved to disk or, at the patient’s request, printed on film.
Preparation for angiography
Computed tomography of the head and neck does not require complex preparation. To reduce side effects from contrast contrast, a light snack (sandwich, yogurt or fruit) is advisable before leaving home. Breastfeeding mothers need to express and store milk, since after angiography you cannot immediately put the baby to the breast.
CT of the head and neck vessels requires blood test results for creatinine. In some diagnostic clinics, a rapid test is performed right on the spot. You can find out about the availability of such a service when making an appointment for an examination. The patient must inform the doctor about the medications he is taking: a number of medications cannot be combined with iodine-containing drugs. In agreement with the specialist, they are canceled or replaced at least 12 hours before the procedure.
Drawing blood for creatinine testing
Indications for CT scan of head and neck vessels
CT scan of the head and neck vessels is prescribed for suspected:
- congenital anomalies;
- atherosclerosis of vessel walls;
- embolism, arterial stenosis;
- vascular tumors or a network supplying blood to neoplasms of a different nature;
- vasculitis.
Atherosclerosis, critical stenosis of the internal carotid artery on CT angiogram (3D reconstruction)
Computed tomography is indicated for:
- regular headaches of unknown etiology;
- periodic loss of consciousness;
- dizziness;
- persistent increase in intracranial pressure;
- pain and swelling in the neck;
- recurring attacks of nausea with vomiting;
- the appearance of tinnitus;
- pain in the eyes, blurred vision;
- numbness of arms, legs;
- convulsions;
- difficulties with coordination of movements;
- repeated loss of balance.
CT angiography of vessels is necessary for people who have suffered a stroke, heart attack, head injury, suffering from cerebral circulation disorders, vegetative-vascular dystonia, patients with a history of diagnoses such as brain contusion, encephalopathy, pituitary adenoma, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, hydrocephalus.
CT angiogram of the vessels of the brain and neck - photo
This study is performed before brain surgery (it helps clarify the location of the main branches, which are important not to damage during the intervention) and to monitor the recovery process after surgical treatment.
A CT scan is prescribed if a magnetic resonance examination is not possible.
In what cases is the technique used?
Before the procedure, tests are required and additional studies are carried out. They are summarized in the following table.
| Name | Ongoing research |
| Blood analysis | General analysis. Determination of blood group. Detection of Rhesus status. Detection of the causative agent of syphilis or determination of its absence. Testing for hepatitis. Determining the presence of HIV infection. |
| Ultrasound | Duplex scanning in progress |
MSCT of the brachiocephalic arteries is performed in the following cases:
- Detection of asymptomatic stenoses during ultrasound examination (USD). MSCT is prescribed if ultrasound, for some reason, is uninformative.
- A transient disruption of the blood supply to the brain is a transient attack. It is often called a microstroke.
This study helps detect the effects of stroke
- Discirculatory encephalopathy, accompanied by signs of poor blood supply to the brain.
- Recently suffered a stroke. Angiography can identify the causes of ischemic manifestations, even if the results of ultrasound examination are normal.
- Abnormal anatomical structure of the BCA.
- Conducting control studies after reconstructive intervention on the BCA.
- Detection of any neoplasms on the neck, accompanied by pushing or compression of blood vessels, as well as germination into them.
The initial study prescribed to patients is usually an ultrasound scan.
What are the advantages of CT angiography
The value of tomography-angiography of the BCA is that the procedure allows you to clarify the indications of the initial examination. For example, quite often ultrasound shows a higher percentage of stenosis. A clarifying procedure can reduce this figure by even 15%. However, this value is not an error. When performing an ultrasound, the condition of the vessel wall is assessed. At the same time, angiography determines how full the vessel is. In this study, the information content is higher. The procedure occupies this position not only due to the fact that when it is performed, vessels are visualized over a larger area. Another advantage of CT angiography of the BCA with contrast is that the result does not depend on the operator (which is the case with ultrasound).
In this video you will see what a CT image of blood vessels looks like:
Contraindications to CT angiography of the head and neck
Contraindications to computed tomography
Due to the use of iodine-based contrast agents, CT of the head and neck vessels has a number of limitations. The examination is contraindicated in the following situations:
- allergy to iodine and seafood, intolerance to the components of the amplifier: contrast can cause redness of the skin, rash, itching, difficulty breathing, bronchospasm, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock;
- exceeding the permissible value of creatinine in the blood: there is a high probability of kidney disease, in which the drug for improving the quality of CT photos of the brain and neck will not be removed from the body in time;
- treatment of diabetes with metformin: the drug reduces the rate of renal filtration and, together with iodine-containing drugs, can provoke a dangerous accumulation of lactic acid (lactic acidosis);
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland: the introduction of contrast will increase the symptoms of the disease or provoke other complications (arrhythmia, etc.).
Due to the harmful effects of X-rays on the fetus, CT diagnostics of the vessels of the head and neck is not performed on pregnant women. According to strict indications, patients in the position can undergo a magnetic resonance examination. Unlike CT, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, therefore it is safer and is indicated even for children. But this diagnostic method is not suitable for those who have fixed metal dentures, braces, ear implants, etc.
The design features of the devices do not allow the procedure to be carried out if the person’s body weight is more than 150 kg or the chest (abdomen) circumference exceeds 150 cm. In this case, preference should be given to another research method, for example, magnetic resonance imaging using an open-type scanning device.
3D CT angiography of cerebral vessels
Contraindications
- Pregnancy is one of the main contraindications; exceptions are cases where the lack of immediate diagnosis entails a danger to the patient’s life.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Mental disorders.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
Also, diagnostics are not performed using a multislice tomograph if the patient is diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, according to tests, the creatinine level is above 130 µM/l, there is a history of severe bronchial asthma and an allergy to iodine-containing drugs. It may be difficult to undergo the examination in patients whose weight is 170-180 kg or more.