Benefits of CT angiography
- Minimum radiation dose (compared to x-rays), which eliminates the possibility of any complications associated with exposure to x-rays.
- High efficiency of the study, allowing you to visualize the tissues surrounding the vessel and make the correct diagnosis.
- Availability of special vascular programs and modes for CT angiography, which improve the quality of the study.
- This technique gives an idea of the topography of arteries and veins (this information is indispensable during surgical interventions).
If you are wondering where you can undergo CT angiography of the neck vessels, call our center. We cooperate with the best diagnostic centers and clinics in the capital, which are equipped with expert-class equipment.
Features of the method
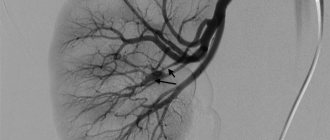
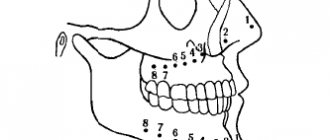
The vessels of the neck are anatomical structures that connect the left side of the heart with the vasculature of the brain. The adequacy of brain tissue perfusion depends on their functional state. Angiographic examination of the neck allows precise examination of the brachiocephalic arteries, carotid and vertebral arteries that carry blood to the head.
Modern medicine has two methods of performing this procedure, which differ in the technology of execution:
- CT scan of neck vessels (angiography with computed tomography);
- MRI of the neck (angiography with magnetic resonance imaging).
The essence of the first technique is to visualize vascular formations using X-ray radiation. For a more detailed study of the anatomical structures, the patient receives a contrast agent intravenously. This substance is represented by isotopes of radioactive iodine, which accumulates on the endothelial lining of blood vessels. The procedure allows the specialist to examine all the details and identify the slightest circulatory disorders.
Angiographic examination with magnetic resonance is a more gentle procedure. This is due to the fact that visualization of blood vessels and blood flow in them is performed under the influence of magnetic fields. This type of examination does not require the administration of a contrast agent.
Indications for examination
- Congenital anomalies of the development of the vascular bed (in particular, the carotid arteries - kinking syndrome).
- Complaints of headaches of unknown origin.
- therosclerotic lesion of the carotid arteries.
- Autoimmune vascular pathologies (vasculitis): Takayasu disease.
- Suspicion of thrombosis of veins and/or arteries.
- Traumatic injury to the blood vessels of the neck.
- Insufficient blood supply to the organs and tissues of the neck due to narrowing of the arteries (compression by a tumor, a hypertrophied thyroid gland, the presence of scars).
- Suspicion of dysfunction of the vascular wall (aneurysm).
- A set of symptoms that suggest cervical vascular disease (tinnitus, dizziness, loss of consciousness, sleep disturbance).
When is an MRI of the cervical spine required?
Neck pain has various origins. Often, unpleasant sensations occur due to irradiation (spread) of pain from neighboring organs. MRI of the cervical spine allows the doctor to understand the true cause of the disease, since all anatomical structures of the cervical spine, without exception, become clearly visible on the tomograms.
The main indications for MRI of the cervical spine are:
- headaches, migraine;
- dizziness, fainting;
- osteochondrosis, herniation, spinal stenosis;
- pain in the neck, radiating to the shoulders and arms;
- limited mobility in the cervical spine, stiffness;
- changes in blood pressure;
- numbness of the shoulder girdle or head;
- multiple sclerosis;
- tumors of various etiologies of the spinal cord, nerve endings, meninges, vertebrae;
- atherosclerosis, stenosis, vascular thrombosis;
- infectious foci localized in the cervical spine and spinal cord;
- circulatory disorders at the cervical level.
Important! MRI of the cervical spine can be performed either in combination with simultaneous MRI of the neck vessels, or as a separate procedure, depending on the prescription of the treating doctor.
Contraindications to CT angiography of neck vessels
Considering the teratogenic effects of X-rays, the examination is contraindicated during pregnancy (at any stage). Remember: contrast is excreted from the body in milk, so angiography is not recommended for nursing women. If the procedure is necessary for health reasons, the baby can be put to the breast 48 hours after the procedure.
There is a restriction on body weight: vascular scanning is performed only on patients whose weight is less than 200 kg.
Most clinics and diagnostic centers for angiography use contrast agents that contain iodine. Therefore, patients with allergies to this substance are not tested.
In case of renal failure, the contrast is slowly excreted from the body, which can lead to intoxication and/or allergization of the patient. Administration of the drug to patients in serious condition (shock, coma) may aggravate the course of the pathology. Therefore, the decision about angiography of the neck vessels should be made carefully.
Contraindications and risks
Despite its high accuracy and information content, computed tomography of the head and neck has a number of contraindications. This technique is strictly contraindicated for persons with a history of allergy to iodine. This is due to the fact that the contrast agent is represented by radioactive isotopes of iodine. Therefore, all patients without exception need to do an allergy test before the study. If there is an individual intolerance to contrast, the research method will be MR diagnostics.
Contraindications to computed tomography include: the period of gestation, hemostasis disorders, infectious diseases in the acute period, thyroid diseases, acute cardiac, renal, pulmonary, and abdominal pathologies. The fourth stage of obesity is considered a relative contraindication.
Alternative Research
If it is not possible to use CT angiography to diagnose pathologies of the neck vessels or there are contraindications, the following methods are used:
- MR angiography with contrast.
- Ultrasound with duplex scanning: replaces CT for vascular spasms, injuries, developmental anomalies, and determination of neoplasms.
- Triplex scanning: it is used to obtain a color image illustrating blood movements, which allows you to accurately calculate blood flow parameters and assess the condition of the vascular wall.
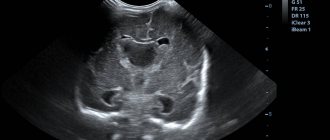
Color duplex scanning of blood vessels
Color duplex scanning is the most modern and informative method for studying blood vessels - arteries and veins. It allows you to directly see the vessels themselves and the tissues surrounding them, as with conventional ultrasound, and also study blood flow using spectral analysis and color flow mapping based on the Doppler effect.
Color duplex scanning of extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries
The study is carried out for headaches, dizziness, hypertension, and various signs of cerebral blood supply disorders.
The method allows:
- examine the condition of the vessels supplying blood to the brain,
- determine the presence of atherosclerosis,
- the presence and nature of atherosclerotic plaques,
- degree of stenosis (narrowing) of the lumen of blood vessels,
- condition of the cervical segments of the vertebral arteries, their course,
- the presence or absence of vertebrogenic effects on the vertebral arteries,
- as well as the condition of the carotid and subclavian arteries.
No additional preparation for the study is required. During the examination, the patient lies on his back, with his head slightly turned in the direction opposite to the one being examined.
Study duration 20-40 minutes
Transcranial color duplex scanning
The study allows you to assess the state of blood flow in the vessels at the base of the brain. As a rule, it is carried out after color duplex (triplex) scanning of the extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries.
The duration of the study is 20-40 minutes. There are no absolute contraindications to conducting research.
Color duplex scanning of the arteries of the extremities
The study allows you to assess the condition of the arterial walls, the presence of atherosclerotic changes, the degree of stenosis of the lumen, and the nature of the blood flow. The method is indispensable for diagnosing obliterating atherosclerosis, Raynaud's syndrome, and surgical interventions on the arteries.
Measuring the ankle-brachial index in addition to the main study serves as an additional diagnostic criterion in assessing the signs of chronic ischemia of the lower extremities - a marker of atherosclerosis.
The study is recommended for adult patients with an increased risk of acquiring or developing peripheral artery disease as an angiological screening, as well as for apparently healthy individuals.
No additional preparation for the study is required. During the examination, the patient is in a horizontal position. The duration of the study is 20-40 minutes. There are no absolute contraindications to conducting research.
Color duplex scanning of limb veins
It is the most informative method for varicose veins; it is used for early diagnosis of thrombophlebitis, determining the need for surgical treatment, as well as monitoring the condition of the veins after surgery.
The method is indispensable for diagnosing the condition of the deep venous system of the extremities and identifying thrombosis. Examination of the veins of the lower extremities is mandatory in preparation for abdominal surgery.
No additional preparation for the study is required. The study is carried out in a horizontal (the patient lies on the couch) and in a vertical (the patient stands on a special pedestal designed for studying the venous system) position of the subject.
The duration of the study is 20-40 minutes. There are no absolute contraindications to conducting research.
All studies are highly informative and absolutely safe for the patient.
Pre-registration by phone:
- department of functional diagnostics: 8 (499) 262-46-12,
- registry
Polyclinic of the Central Clinical Hospital “RZD-Medicine”
Moscow, st. Novaya Basmannaya, 5
No additional preparation for the study is required. During the examination, the patient is in a horizontal position. The duration of the study is 20-40 minutes. There are no absolute contraindications to conducting research.
Features of the triplex scanning method
The diagnostic technique is divided into three main parts:
- Greyscale scanning. The main method of ultrasound examination with obtaining a two-color image-visualization of internal organs and body cavity. Allows you to see changes in the geometry and anatomy of the patient’s vessels, as well as confirm the presence or absence of plaques, blood clots, and damage.
- Spectral analysis (ultrasound Dopplerography). The study is carried out on the spectrum of blood flow with its graphical display. Pathologies are displayed here not only visually, but also as incorrect indicator values.
- Doppler mapping. For specialists, this technique has a number of branches and varieties, but the main task remains the same: photographing vessels in action. Here, the presence of blood clots, the speed and direction of blood flow, as well as the presence of resistance and areas with altered blood flow are determined.
Triplex scanning of veins and arteries for the patient is practically no different from ultrasound. At the same time, high demands are placed on both the ultrasound scanner and the specialist conducting the examination.
- Triplex scanning of neck vessels (or extracranial examination) with additional tests when turning;
- Triplex scanning of veins and arteries of the upper extremities;
- Triplex scanning of the lower extremities with functional tests;
- Examination of large vessels of the abdominal cavity;
- Scanning the kidneys and checking the quality of their blood supply;
- Triplex scanning of the vessels of the head and eyes;
- Diagnosis of circulatory disorders in the vessels of the pelvis and genital organs.
Algorithm for CT angiography
During the examination, the patient lies in a lying position on a mobile topographer table. Before starting the procedure, the doctor selects a scanning mode and adjusts the tomograph parameters. At this time, the patient is given intravenous contrast. At the end of the preparatory stage, the staff leaves the room, but you will be provided with a transmitter with which you can communicate with the technologist.
During the examination, the table moves inside the tunnel, and the ring part of the tomograph rotates around the table, generating slight noise. Scanning of neck vessels is not accompanied by unpleasant or painful sensations.
How is it carried out?
The examination procedure is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The patient should take a horizontal position.
- The doctor administers an antiallergenic drug.
- The specialist treats the needle insertion site with an antiseptic and applies Lidocaine for local anesthesia.
- A tubular probe is inserted into the lumen of the vessel.
- The catheter is passed into a vein or artery.
- A contrast agent is injected.
- An examination is being carried out.
- The catheter with the probe is removed.
- The needle insertion site is treated with an antiseptic and sealed with a band-aid.
Taking into account the method of carrying out the procedure, it can last from 15 minutes to 1.5 hours. Each type of angiography has its own characteristics:
- CT angiography. First, the body is scanned without contrast injection, then it is injected into a vein in the elbow, and at the final stage, venous blood flow is assessed. Several layers of the brain are removed, the information is processed and converted into three-dimensional images.
- If the patient suffers from an allergic reaction to the contrast agent or is contraindicated for X-ray radiation, then MR angiography is performed. To reduce the noise level from the operating device, the patient is given earplugs. If unforeseen situations arise, you can inform a medical professional via a microphone. The lights are on in the chamber and the air conditioning is on so that the patient feels as comfortable as possible.
- If necessary, multislice computed tomography is prescribed to examine the vessels of the retina. The special tube of the device rotates around the patient in a spiral, and the table moves at the same time. The result is the clearest 3D images possible.
After the examination is completed, the patient is not immediately sent home. A puncture of a vein can provoke bleeding, the body of the subject may react unexpectedly to the administration of contrast, so observation is required for some time.
After the examination, the patient receives the diagnostic results, with which he goes to the doctor.