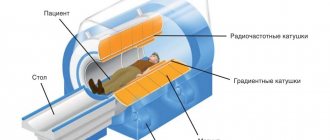
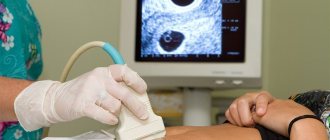
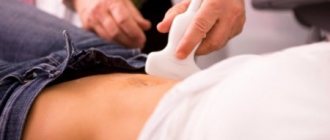
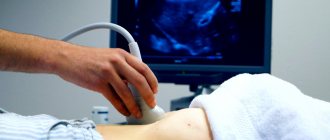
Ultrasound of the penis is a diagnostic procedure that allows you to obtain information about the condition of the male genitalia and the presence of pathologies or diseases.
The study is publicly available and absolutely safe, often has no alternative, and can be administered many times without harm to health.
Such ultrasound diagnostics is almost never prescribed as an independent procedure; in most cases, ultrasound is complemented by Doppler ultrasound.
Indications for examination
An ultrasound of blood flow through the penile artery and vein is performed if a man has erectile dysfunction. The reasons for this are various obstacles to blood circulation:
- penis injury;
- Peyronie's disease, accompanied by organ deformation;
- neoplasms;
- urethral foreign bodies.
Doppler ultrasound of the penis is recommended if a man experiences pain during intercourse. Ultrasound is used for examination before surgery.
Watch a video about ultrasound examination of the vessels of the penis:
What happens during an ultrasound session?
A man lying on his back is examined. In this case, a high-frequency linear sensor is used. He is given pharmacological drugs that cause an erection. To do this, prostaglandin E1 or papaverine is injected into the patient's penis using a syringe. After 10 minutes, they begin the diagnosis itself. The cavernous arteries are visualized and the fluid flow rate through them is assessed. If necessary, it is additionally recommended to do an ultrasound of the testicles. How are indicators deciphered according to the norm? The flow of blood in the arteries is judged by the following parameters:
- an indicator of high systolic fluid flow velocity in the arteries (30 cm per second is the norm);
- the rate of increase in systolic arterial fluid flow.
Venous outflow of blood from the penis is characterized by the following indicators:
- final arterial velocity of the corpora cavernosa (5 cm/sec. 0 – normal);
- two indices: resistance (less than 0.85 - there is dysfunction) and pulsation (over 4 - normal).
How to do an ultrasound of the vessels of the penis
Ultrasound examination is performed on an outpatient basis. The patient is asked to sit on the couch and relax. Ultrasound of the vessels of the male penis is carried out in two stages.
- First, blood circulation is assessed at rest. The sensor is passed along the entire length of the penis to determine the number of vessels and the area of the cavernous bodies.
- Then a pharmaceutical test is performed - artificially inducing an erection with a drug. The drug “Caverject” is injected using a syringe into the cavernous body. After a few minutes, the arteries fill with blood, the doctor evaluates the speed of their filling, the duration of the erection, and the nature of the blood flow.
The administration of the drug is accompanied by a short-term rise in pressure, redness of the skin, and pain. These symptoms disappear after 30-40 minutes.
In some situations, an ultrasound scan is required - a combination of ultrasound and Dopplerography. The Doppler method provides complete information about the state of the vascular wall of the arteries and veins of the penis, the nature of the blood flow through them.
Dopplerography of the vessels of the male penis has the function of color mapping. This is the coloring of vessels with different blood flows in different colors on a computer screen. Ultrasound of the penis, performed with a central dorsal cavity, accurately identifies problem areas.
Watch the video to see how an ultrasound of the penis is done:
Preparation rules and procedure
A few days before the ultrasound examination, the patient should stop drinking alcohol.
When prescribing an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the penis and scrotum, the doctor explains to the patient the essence and necessity of the study. After this, the specialist introduces him to simple rules for preparing for the scanning procedure:
- 1-2 days before the test, stop drinking alcohol.
- The day before the procedure, thoroughly wash the area being examined.
- Do not urinate 1-2 hours (in extreme cases, half an hour) before the ultrasound scan.
During the first conversation with the patient, the doctor must be able to establish a trusting relationship with the patient, since the procedure for ultrasound examination of the penis is performed with exposure and erection of the genital organ and involves the endocavernosal administration of drugs that ensure the onset of an erection necessary for a more accurate diagnosis.
The patient should also be aware of the fact that after the scan is completed, he will need to achieve ejaculation through self-stimulation in order to eliminate the drug-induced erection.
On the day of the examination, the patient comes to the ultrasound diagnostic room; to create the most comfortable conditions for performing the procedure, about 1 hour is allocated. Diagnosis is carried out on a couch in a supine position.
Before the scan begins, the doctor injects endocavernosally (i.e. into the penis) one of the drugs that quickly causes an erection. Solutions can be used for this:
- Papaverina;
- Prostaglandin E1;
- its analogues (Alprostadil, Caverject).
This measure is taken to obtain more informative ultrasound data, since measurements taken in a relaxed state of the penis can only be speculative or distorted.
Unfortunately, this method of artificially inducing the erection necessary for scanning can lead to a number of undesirable side reactions:
- pain at the injection site;
- excessively strong erection with painful sensations;
- formation of a hematoma at the site of injection of the medicinal solution.
To prevent these negative consequences, another safer method can be used to ensure sufficient blood flow to the corpora cavernosa of the penis - taking a pill:
- Levitra;
- Viagra;
- Sildenafil.
If it is necessary to perform such a test, the doctor prescribing an ultrasound scan will definitely instruct the patient about the rules for using the prescribed drug and indicate the time of its administration. Typically, a Viagra tablet should be taken 40-60 minutes before the procedure, and to induce an erection in the ultrasound room, visual and self-manual erotic stimulation is performed to promote blood flow to the tissues of the penis.
Approximately 20-25 minutes after the injection of the drug or the onset of action of the tablet, the corpora cavernosa are filled with blood and the doctor begins scanning using a special ultrasound sensor. He places it on the penis and scrotum in a certain sequence every 5 minutes (i.e., depending on the erection phase) for 25 minutes.
After completion of the ultrasound examination, the erection may persist for some time. To get rid of it, the patient is asked to perform self-stimulation in a separate room. If the erection of the penis does not go away within 4 hours, then the patient can be helped by a urologist who urgently prescribes the necessary measures.
The results of ultrasound examination of the vessels of the penis can be obtained in person 30-40 minutes after completion of the procedure or sent to the doctor. Some clinics provide research data to the doctor and/or patient’s email address. The general state of health does not change in any way after the scan.
Obtained results
Evaluation of ultrasound results is carried out according to the protocol:
- echogenicity, or tissue density;
- structure of the cavernous bodies;
- thickness of the tunica albuginea;
- tone of arteries and veins;
- vessel diameter;
- blood flow speed.
Changes in any of these indicators indicate the presence of a pathological process.
- An increase in density indicates the proliferation of connective tissue, or fibrosis of the penis. A decrease in density is a sign of inflammation.
- The heterogeneous structure of the cavernous bodies is also a sign of fibrosis.
- Thickening of the tunica albuginea over 2 mm at rest is a symptom of Peyronie's disease.
- Thickening of artery walls is a sign of atherosclerosis.
- An increase in the diameter of the arteries by more than 1.4 mm indicates anomalies in their development. Reduced diameter - atherosclerosis or diabetes.
- The speed of blood flow at rest is up to 25 mm/s, during erection—up to 35 mm/s. If less - arterial insufficiency.
The diagnosis is made by the attending physician based on the results of ultrasound and other examination methods.
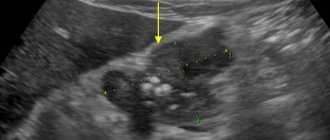
Images (templates) of ultrasound protocols for pathologies of the uterus and appendages
Polycystic kidney disease
Sonographic signs of calcification in the myometrium of the anterior wall of the uterine body
Sonographic signs of intramural uterine fibroids, uterine endometriosis (fluid cavities in the ovaries, possibly endometrioid cysts)
Sonographic signs of intramural-subserous fibroids of the anterior wall of the uterus with signs of secondary changes (anechoic inclusions in the node) with a demonstration of the scanogram
Sonographic signs of uterine fibroids. Avoid pelvic organ prolapse
Sonographic signs of intramural uterine fibroids
Uterus dimensions 75 x 72 x 47 mm, anteflexio, pear-shaped, smooth contours, myometrium of increased echogenicity, homogeneous, in the projection of the cavity an oval-shaped liquid formation measuring 10 x 8 mm is located, having homogeneous contents without internal acoustic reflections, the structure resembling a fertilized egg
Sonographic signs of intramural-subserous fibroid node near the fundus of the uterus on the left
Sonographic signs of small cystic transformation of both ovaries
Sonographic signs of multifollicular transformation of the ovaries
Sonographic signs of a follicular cyst of the right ovary (to differentiate from an endometrioid cyst) with a scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of an intramural-subserous node of fibroids of the posterior wall of the uterus on the right and an intramural node of the anterior wall (fibroids or nodular form of endometriosis) with a demonstration of the scanogram
Sonographic signs of intramural nodular formation of the anterior wall of the uterine body (to differentiate intramural fibroids from the nodular form of uterine endometriosis)
Sonographic signs of a neoplasm of the left lobe of the liver, chronic calculous cholecystitis with a scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of right-sided scrotal hernia, right-sided chronic epididymitis, left kidney parenchyma cyst, moderate bilateral hydrocele with scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of prostatic hyperplasia, simple cyst of the left lobe of the liver
Sonographic signs of chronic hepatitis, chronic prostatitis
Sonographic signs of bladder diverticulum, mild hypertrophy of the bladder wall, mild prostatic hypertrophy, chronic prostatitis with scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of a wrinkled right kidney, a calculus (possibly a calcified scar) in the projection of the mouth of the right ureter, local thickening of the mucous membrane of the left lateral wall of the bladder
Sonographic signs of chronic pancreatitis, fatty hepatosis, chronic predominantly left-sided pyelonephritis. No echostructural changes in the gallbladder were detected
Sonographic signs of a wrinkled right kidney, vicarious hypertrophy of the left kidney, prostate adenoma, trabecular structure of the bladder wall
Sonographic signs of microlith of the right kidney, chronic prostatitis, mild prostatic hyperplasia. No echostructural changes in the bladder were detected
Sonographic signs of right kidney stone, prostatic hyperplasia, chronic prostatitis with scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of a heterogeneous formation in the lumen of the gallbladder neck (differentiate a tumor of the bladder neck with a hard clot of bile), a disconnected bladder, dilatation of the common bile duct, right-sided nephroptosis with a scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of chronic calculous cholecystitis with wrinkling of the gallbladder. Condition after amputation of the uterine body. Echostructural changes in the thyroid gland, kidneys, liver, pancreas and spleen within the age norm with a scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of bilateral nephrolithiasis, right-sided nephroptosis, salt crystals in the bladder
Sonographic signs of fibroadenomas of both mammary glands (a formation in the left mammary gland at 16 o’clock is differentiated with a cyst filled with echogenic content; a formation in the right mammary gland is differentiated with a fatty lobule)
Echographic signs of a hypoechoic formation in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast, with a structure resembling a fat lobule (differentiate with fibroadenoma)
Sonographic signs of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, more pronounced in the left mammary gland (differentiate with additional formations of the mammary glands) with a scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of multiple cystic cavities of both mammary glands
Sonographic signs of a cyst of the left breast with a scanogram demonstration
Sonographic signs of hyperplasia of the lymph nodes of the neck (mainly on the right), fluid formation in the upper part of the neck on the right with a demonstration of the scanogram
Cost of the procedure
The procedure is currently available to a small number of public hospitals. It is usually done in private clinics. The cost depends on the region of residence and the type of examination.
Table. Prices for ultrasound of the penis.
| City | Price |
| Moscow | From 500 rubles |
| Ekaterinburg | From 400 rubles |
| Novosibirsk | From 500 rubles |
An ultrasound of the penis helps to determine the cause of erectile dysfunction. The procedure is carried out in two versions - conventional ultrasound and with Doppler ultrasound. It can be done in some government agencies and private clinics.
Leave comments with your opinion, share information with friends on social networks. All the best.