MRI of the brain for epilepsy
In modern medicine, the most progressive method for diagnosing epilepsy is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Thanks to this method, doctors have the opportunity to detect the disease even at the earliest stages with high accuracy - up to 98%. Since epilepsy is often asymptomatic, only timely research will make it possible to create an appropriate treatment program and alleviate the patient’s condition.
MRI helps to identify the causes that provoked the appearance of a neurological disorder, predict the rate of development of the disease, and select the most appropriate therapy. An examination will also be required in cases where epileptic seizures have not yet occurred, but alarming signs of a developing disease are already making themselves felt.
MRI allows timely detection of:
- foci of gliosis, their size and number;
- neurological pathologies;
- inflammatory processes;
- a brain tumor;
- disturbance of blood supply.
In case of a brain injury or other suspected pathological condition, an MRI according to the epilepsy program is performed on a high-frequency 3 Tesla tomograph . In this case, the result obtained is considered the most informative.
Is it possible to detect epilepsy using MRI?
Unlike other diagnostic methods, only MRI can accurately determine the presence or absence of epilepsy. Moreover, the accuracy of the result will not depend on whether the disease is at an initial stage or whether it has already acquired a chronic form.
Most often, epilepsy develops as a result of changes in brain tissue. A radiologist is able to notice such pathologies in images taken by a tomograph and determine how much of a threat they pose.
In addition, MRI allows not only to determine the presence of epileptic foci, but also to detect the causes of their appearance.
What does an EEG look like for epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a common neurological disease that manifests itself in the form of seizures. Seizures are expressed in disturbances of consciousness, motor and sensory functions, behavior and emotions. Epilepsy is treatable. But before starting therapy, an accurate diagnosis should be established. A single case of a seizure is not enough to establish the fact of the disease; there must be two or more of them. Electroencephalography is considered one of the most effective examination methods.
At the Yusupov Hospital, this diagnostic method is used to determine epilepsy as one of the main ones.
Causes of epilepsy
Epilepsy has more than 50 forms of manifestation of the disease, so it is extremely important to establish an accurate diagnosis and cause of the disease. This will contribute to the correct choice of treatment method
With the help of electroencephalography, it becomes possible to determine the indicators characteristic of each form, since the pathology is expressed by the discharge of brain neurons.
The main causes of epilepsy include:
- oxygen starvation during difficult childbirth;
- infections suffered by a woman during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus, rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis and others;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- alcoholism or drug addiction;
- brain tumors;
- strokes;
- hereditary factor.
Based on the causes of epilepsy, the disease is divided into three groups:
- idiopathic – the presence of a genetic predisposition;
- symptomatic – there are structural defects in the brain;
- cryptogenic – the causes of the disease cannot be determined.
At the Yusupov Hospital, genetic studies are carried out to determine the hereditary factor. This helps determine the possibility of a hereditary factor in the development of the disease. Also during the examination, other tests are prescribed to determine the concentration of substances in the drugs in the body. These actions are carried out to adjust the dose of medications.
EEG for epilepsy
To obtain accurate EEG readings for epilepsy, it is necessary to prepare the patient for the procedure. You need to wash your hair thoroughly to keep your hair clean. Installation fixing agents are not allowed. This will allow you to get closer contact with the scalp. It is not recommended to eat two hours before the procedure, but also not to feel hungry. You should also remove all jewelry before the procedure.
Two days before encephalography, you should not consume foods that affect the nervous system (drinks containing caffeine, alcohol, chocolate, cigarettes).
The essence of the study is to compare the EEG data obtained in epilepsy and accepted standards for a healthy person. In this regard, analysis of indications is a key factor in diagnosis.
Signs of epilepsy with EEG
EEG in epilepsy helps to identify foci of neuronal activity. EEG indicators determine the form of pathology. They can also be used to track dynamics and determine the dosage of medications. The greatest value of this method is that painful changes can be identified in the intervals between attacks.
In the presence of pathology, the device registers waves and peaks, elements specific to certain forms of epilepsy. The appearance of bursts of activity in the encephalogram in the form of peaks and waves of large amplitude signals a painful condition. But to confirm the diagnosis, indicators alone are not enough, since they may also indicate oncology, stroke, sleep disorders, etc. Therefore, at the Yusupov Hospital, examination using an encephalogram is an integral part of a comprehensive diagnosis.
The following types of EEG are distinguished:
- routine electroencephalography. Diagnostics, in which the recording and recording of brain biopotentials is carried out to determine epilepsy;
- using additional electrodes;
- during night sleep. EEG indicators are recorded during night sleep;
- long-term EEG in epilepsy. Recording indicators during the day;
- EEG with standard activation procedures. Hyperventilation, photostimulation and the use of other types of stimulation such as reading, watching movies, music;
- video monitoring;
- sleep deprivation procedure.
Quite often, changes in the EEG occur when eye movements, changes in breathing rhythm, pulsation of blood vessels or motor reflexes
Therefore, it is very important to correctly interpret the signs of epilepsy in the EEG. This requires high professionalism of a specialist.
Such specialists work in the neurology clinic. You can make an appointment with an epileptologist by calling the Yusupov Hospital at any convenient time.
Causes of epilepsy
Epilepsy is one of the types of dangerous neurological disorders. The reasons for its development include:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- malignant and benign neoplasms;
- stroke;
- unsuccessful operations;
- chronic alcoholism;
- addiction;
- meningitis;
- intracranial hemorrhage.
There is also epilepsy, which appears at birth and is associated with impaired brain development during pregnancy.
Epilepsy can be acquired or hereditary. In the latter case, the disease develops against the background of neuronal dysfunction and is passed on from generation to generation.
How does epilepsy differ from episyndrome?
Epilepsy in various forms is diagnosed in 10% of the population, including children. The main symptom of the pathology is seizures. There is another neurological disease similar to epilepsy - episyndrome. How do pathologies differ from each other, and what danger do they pose to humans?
Epilepsy is a chronic disorder characterized by sudden attacks. The problem is characterized by increased excitation of neurons to the highest degree. Episyndrome manifests itself as a result of any brain disease and does not have a chronic course. The attacks are sporadic. In most patients, after an exacerbation of the episyndrome, a phase of long-term remission is observed.
Symptomatic epilepsy develops due to:
- tumors and head injuries;
- purulent processes in the membranes of the brain;
- degenerative processes in brain vessels associated with age-related characteristics.
Which is better - CT or MRI
When diagnosing epilepsy, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used.
Computer diagnostics is a fairly effective method for determining epilepsy. However, it has a significant drawback - exposure to x-rays, which makes it difficult to display soft tissue deformation. For this reason, CT for epilepsy is prescribed only if the patient has a contraindication to MRI.
The accuracy of the computed tomography results is about 50%. This method has proven itself in determining anomalies of the vascular system and the presence of neoplasms and hematomas.
Only a doctor can help determine which of the two examinations is required to diagnose epilepsy, and he will order an MRI or CT scan. Based on the results of a computed tomography scan, an MRI scan is performed, which can provide more accurate data on the pathology.
Medical examination for epilepsy
A complete medical examination for a disease such as epilepsy consists of collecting information about the nature of the patient’s life, the stage-by-stage development of the disease and, most importantly, collecting a very detailed description of the attacks and the conditions preceding them. Sources of information are the patients themselves and eyewitnesses of attacks.
If epileptic seizures occur in a child, the doctor is always interested in the course of pregnancy in the mother, as well as childbirth
Sources of information are the patients themselves and eyewitnesses of attacks. If epileptic seizures occur in a child, the doctor is always interested in the course of pregnancy in the mother, as well as childbirth.
In case of epilepsy, a general medical and neurological examination, as well as electroencephalography, are required. The special neurological research tools used include nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography.
The main task of any examination is to identify current concomitant diseases of the patient’s body or diseases of the brain, as they can cause epileptic seizures.
Electroencephalography (often called by its corresponding abbreviation - EEG) is a method of recording the electrical activity of certain cells in the patient's brain.
EEG is the most important test in diagnosing epilepsy. It is carried out immediately after the appearance of the first epileptic seizures. The EEG shows specific changes in epilepsy (so-called epileptic activity). These changes are expressed in the form of island-wave discharges and peaks of higher amplitude than ordinary waves.
During generalized epileptic seizures, the EEG always shows groups of generalized peak-wave complexes in all areas of the brain.
With focal epilepsy, such changes appear only in certain areas of the brain.
Based on the EEG data obtained, a specialist epileptologist will be able to determine the nature of the changes that have occurred in the brain, find out the type of epileptic seizures, and then determine what type of drugs will be preferable for adequate treatment.
EEG also helps to monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment (which is especially important for absence seizures).
Computed tomography (common name - CT) is a method of studying the brain using radioactive (i.e. X-ray) radiation. A CT scan takes a series of pictures of the brain in multiple planes, allowing the doctor to view the brain in all three dimensions, which is different from conventional x-rays.
CT scan reveals structural changes in the brain (namely, hydrocephalus, tumors, atrophy, calcifications, cysts). But at the same time, computed tomography data may not be informatively significant for certain types of epileptic seizures, in particular:
- for any epileptic seizures that occur over a fairly long period of time, which is typical mainly for children;
- for generalized epileptic seizures, when there are no focal changes in the EEG and there is no indication of brain damage during a parallel neurological examination.
MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) is another method of medical examination of a patient’s body with epilepsy. This is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing possible structural changes in the patient’s brain.
How is the examination carried out?
The MRI procedure is simple and does not require any special preparation from the patient. Since the device is based on a strong magnet, all metal objects must be removed from the body before the examination. Otherwise, the brain pattern may be blurry.
MRI is performed as follows:
- The doctor questions the patient about possible contraindications to the procedure and identifies the characteristics of the body.
- After completing the survey, the patient goes into a special room and lies down on the tomograph table, the doctor secures him with special belts. Complete body stillness is necessary to obtain accurate images.
- The doctor leaves the room into a separate office, from which he controls the device. He moves the table with the patient inside the tomograph, where the brain scan takes place. The duration of this procedure is about 30 minutes.
- At the end of the examination, the patient is released from the belts and helped to leave the office.
MRI images can be printed or recorded on electronic media. This is necessary so that the patient can consult with several doctors if desired.
MRI with contrast for epilepsy
To obtain a higher quality image, specialists may recommend a procedure using contrast. It consists of introducing a special chemical into the patient’s blood, which improves the quality of the images.
The contrast is harmless and is eliminated from the body after some time. However, when using it, the doctor must ensure that the patient does not have an allergic reaction to the drug.
In the first minutes, a person may feel a metallic taste in the mouth and chills in the extremities. In the future, the procedure proceeds in exactly the same way as without the use of contrast.
Indications
A brain examination will be required if the following symptoms occur:
- involuntary head nodding and muscle spasms;
- temporary loss of consciousness and spatial orientation;
- visual and hearing impairment.
It is believed that the main symptom of epilepsy is seizures. But this disease can manifest itself in different ways. In some cases, it occurs without visible symptoms; in mild forms, a person’s head may only tremble slightly and a nervous tic may appear. At the same time, the time of the attack can be very short - no more than 5-10 seconds, which makes it invisible to outsiders.
MRI is also prescribed for people who complain of severe headaches, prolonged problems with night sleep, and speech disorders. All these signs indicate a neurological disorder and may serve as prerequisites for the onset of epilepsy.
Contraindications
Despite its high efficiency and almost complete safety, in some cases MRI of the brain is prohibited.
Contraindications to this procedure are:
- visual and hearing impairment;
- metal implants in the patient's body;
- heart disease;
- installed pacemaker or other ferromagnetic electrical device;
- tattoos created using dyes with metal particles;
- claustrophobia;
- pregnancy.
If one of the contraindications is present, MRI is unacceptable. The only exceptions are patients suffering from panic attacks and claustrophobia. In this case, examination under anesthesia is allowed.
Detection methods in adults
How to diagnose epilepsy? Doctors have the right to consider such a diagnosis after two seizures. And most often teenagers or elderly people (60+) are susceptible to the disease.
To accurately diagnose epilepsy, a neurological examination alone is not enough. The patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination, which includes several types of mandatory procedures: MRI, EEG, testing and analysis.
Epileptic activity on EEG
How to detect epilepsy on EEG?
This is one of the most informative examination methods for this disease.
Its essence lies in the fact that special electrodes are attached to the patient’s head, which record the activity of brain neurons.
There are two types of EEG: regular and video monitoring. During the usual procedure, the patient is laid horizontally, in a dimly lit room, with his eyes closed.
Its duration is no more than 20 minutes. But a single encephalogram may not be effective.
The duration of video monitoring can be from 3 to 10 days, and it is carried out only in a hospital. It can give the most accurate results no later than a day after the next attack.
Video monitoring is carried out by:
- with a single attack of illness;
- in case of repeated night or morning seizures;
- when planning pregnancy;
- before surgery;
- in case of hereditary predisposition.
To identify pathological changes, the patient is asked to quickly open and close his eyes, speed up or slow down his breathing, and turn the lights on and off sharply. All these factors provoke electrical activity in the brain, making it possible to notice possible disturbances.
Is epileptiform activity epilepsy or not?
Epileptic activity on the electroencephalogram can be recorded both at the time of a seizure and in a calm state.
It is expressed in the form of single flashes, sharp peaks or waves on the graph. High-amplitude fluctuations in brain activity (150 mKV and above) are signs of epilepsy.
EEG for epilepsy:
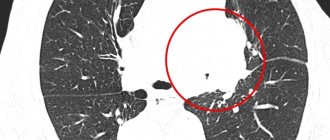
What will an MRI of the brain show?
Does MRI show epilepsy? What is 3 Tesla MRI for epilepsy?
This procedure appeared later than EEG, but has already gained popularity in the diagnosis of epileptic pathology. It is carried out on devices of different power: 1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla.
The first of them is considered less powerful and is recommended for examining children and adolescents, but does not always give accurate results.
The second is the most powerful tomograph, which allows you to detect not only neurological abnormalities, but also see metastases in oncology.
Also, such a device will allow you to determine the causes of the pathology and see the localization of brain lesions.
The study is very simple and has virtually no contraindications. Before the procedure, the patient must remove all metal jewelry and change into special clothing.
The doctor talks with the patient and then escorts him to a separate room where the device is located. The patient is placed on a pull-out couch and secured with straps.
The doctor goes into the adjacent room, and the couch moves inside the device. The brain scan lasts about 40 minutes, after which the resulting images are printed and analyzed.
To obtain a higher-quality image, contrast (a special preparation) can be used.
It is absolutely safe for the body, but can cause a metallic taste in the mouth and cold extremities.
Only a more powerful device reveals the most complex pathologies that a 1.5 Tesla tomograph cannot “see.”
Analyzes
In addition to hardware diagnostic methods, laboratory tests are also used. To get a more complete picture, a person must pass biochemical and general blood tests, and a glucose test.
This will allow you to determine the presence of genetic abnormalities in the body, exclude infectious diseases, poisoning, diabetes or anemia. Any of them can manifest itself in the form of an attack resembling an epileptic one.
Tests
To complete the picture, the doctor often conducts neuropsychological testing, including assessment of attention, perception, speech, memory, reaction, and emotional state.
The specialist’s opinion is formed based on a survey of the patient, observation of his motor skills, and praxis.
Testing consists of many exercises offered to the patient: for memorization, recognition, sorting objects, etc.
Find out more about epilepsy:
- what are the forms and stages of the disease;
- what are the consequences and complications of the disease;
- whether changes and personality disorders are possible in the patient;
- whether the sick person is assigned a disability;
- is it possible to prevent the disease;
- what lifestyle should epileptics adhere to;
- What is epileptic syndrome?
How else can you determine
How to recognize epilepsy in other ways? Additionally, the neurologist has the right to prescribe several more research methods.
These include:
- CT (computed tomography);
- neurological visual examination (checking reflexes);
- PET (positron emission scan);
- taking anamnesis;
- rheoencephalography (reaction of brain vessels to electric current);
- ECHO-encephalogram;
- angiography.
All these studies are used as additional (optional) measures. The specialist will receive basic information from MRI, EEG-video and testing.
MRI for epilepsy in children
In children, MRI is done to confirm dangerous pathological changes that require urgent surgical intervention. These include cortical dysplasia, neoplasms, congenital defects in brain development, consequences of injury, and manifestations of genetic abnormalities.
To diagnose all possible pathologies in brain tissue, the examination must be carried out on a high-field apparatus (at least 1.5 Tesla) using special scanning protocols, with the help of which a specialist can notice the slightest changes indicating the development of a dangerous disease, among which primary manifestations of hippocampal disease are especially common. sclerosis and minor forms of cortical dysplasia.
Since MRI requires complete immobility of the patient, the child is given a sedative before the examination. The presence of a mother or close relative is also allowed.
4. Features of the study for epilepsy
Diagnosis of chronic forms of epilepsy is difficult. The cause of pathology in childhood is severe infectious diseases and defects of the organ cortex. Microstructural abnormalities are detected only with the help of contrast agents and special scanning modes, which are not used for survey MRI. For targeted research, thinner sections are needed - 2-3 mm and a device with a power of at least 3 Tesla.
To increase the effectiveness of the study, the patient undergoes electroencephalography before MRI. The procedure identifies the area of the brain in which the pathological focus is located.
Deciphering MRI for epilepsy
The images obtained during the examination need to be decrypted. The photographs show epileptic foci, which can only be identified by an experienced specialist. After carefully studying them, the doctor determines possible deviations from the norm, the degree of development of the pathology and draws up a conclusion.
If desired, the patient can show the images to other specialists and even get a transcript of the images online on one of the specialized medical websites. However, the accuracy of such results must be confirmed by a medical practitioner with extensive experience in this field. Only in this case can an accurate diagnosis be made and the most effective therapy selected.