What does the indicator mean?
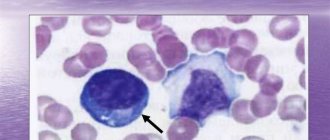
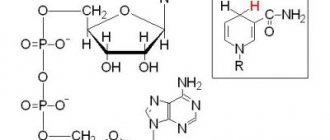
Blood contains a large number of different substances that circulate in the human body constantly. One of the parts of total hemoglobin contained in the blood, and also closely related to glucose, is HbA1c. Its unit of measurement is percentage. Deviation of the indicator from the established target value indicates the presence of health problems.
The analysis is carried out in two cases:
- by doctor's direction (if indicated);
- if the patient wishes to independently monitor the indicator, even if there are no obvious signs of the disease.
The HbA1c indicator reflects the average glycemic level over 3 months. The test result can usually be obtained the next day or in the next 3 days, since the production speed depends on the chosen laboratory.
Why is it going down?
Doctors identify several reasons that contribute to the development of an anemic condition. Anemia is a pathology in which the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood is significantly reduced. These pathological conditions can be very different. Iron deficiency anemia is the most common in pregnant women.
Below is a table of anemic conditions by severity:
Doctors note that most cases of anemia develop after 26–27 weeks of pregnancy. The presence of anemia is indicated when the obtained values are below the lower limit of the established norm.
To establish a specific clinical variant of the anemic condition in the expectant mother, doctors may prescribe auxiliary tests. They usually include determination of serum iron, ferritin and other laboratory parameters.
Doctors use several classifications to assess the degree of anemia. When the hemoglobin concentration in the blood is from 90 to 110 g/liter, the anemic state is mild. The average degree of violation is characterized by a decrease in this indicator below 89, but it still exceeds 70 g/liter. A lower concentration indicates the development of a severe anemic condition.
A variety of reasons can lead to the development of such pathologies. The most common of them is a decrease in dietary iron intake. In this case, the macronutrient does not enter in sufficient quantities with food. Quite often, this condition manifests itself in expectant mothers who are on a vegetarian diet.
In the first half of pregnancy, toxicosis leads to the development of an anemic state. The most dangerous clinical variants are those accompanied by severe repeated vomiting. This condition leads to a decrease in the volume of circulating fluid, which contributes to the development of an anemic state.
Taking certain types of medications is also a trigger that leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood. Such situations arise especially often with long-term use of medications during pregnancy.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines can also lead to the development of an anemic condition in the expectant mother. Ulcerative defects and erosive colitis, occurring with the development of clinical symptoms, can lead to a pronounced decrease in iron in the blood. These conditions are extremely unfavorable, especially during pregnancy. They should still be treated before pregnancy.
Optimal bowel function is very important. It ensures the absorption of all nutrients and also helps maintain the consistency of microflora and vitamins in the body. Dysbacteriosis or irritable bowel syndrome are common pathologies in which anemic conditions occur. As a rule, the severity of functional impairment is mild.
Multiple pregnancy is a common situation in which an anemic condition develops. Babies growing in the womb consume large amounts of nutrients. This inevitably leads to the development of anemia in a pregnant woman. To compensate for this condition, doctors strongly recommend that expectant mothers carrying twins or triplets regularly take multivitamin preparations.
Another very interesting reason leading to the development of an anemic condition in the expectant mother is previous recent childbirth. Obstetricians-gynecologists note that if a woman has a second pregnancy a year after the birth of her first baby, then the risk of her developing an anemic condition increases several times. Typically, this pathology is completely normalized immediately after childbirth.
The advisability of taking the test for pregnant women
The optimal method for determining glucose concentration in pregnant women is considered to be the study of glycated hemoglobin.
This analysis makes it possible to identify deviations of glycemia from normal values and take appropriate measures to stabilize the indicator. Otherwise, high sugar levels during gestation can negatively affect not only the condition of the expectant mother, but also the development of the child.
Consequences of elevated HbA1c:
- the risk of having a large baby increases;
- labor may be difficult;
- blood vessels are destroyed;
- disturbances in kidney function occur;
- visual acuity decreases.
Benefits of the study:
- The analysis is characterized by more accurate results compared to conventional determination of sugar levels or the method of detecting glucose tolerance.
- Makes it possible to find out about the presence of diabetes at an early stage of its development.
- The method of collecting blood for research is to maintain preanalytical stability, so the resulting material is in a test tube until the analysis itself.
- Blood can be donated at any time of the day. The time of last food consumption does not affect the result.
- Various patient conditions, including being under stress, having a cold or taking medications, do not distort the result.
- The study is considered universal, therefore it is applicable to all age categories of patients.
Disadvantages of the analysis:
- high cost of research;
- the analysis is not performed in all laboratories, and in some regions it is completely impossible to determine HbA1c;
- the result is often unreliable if the pregnant woman has anemia or hemoglobinopathy.
It is important to understand that it is not always possible to prevent undesirable consequences that develop under the influence of high concentrations of HbA1c.
This is explained by the fact that an increase in glucose values occurs in women closer to the end of the period of bearing a child. This usually happens at 8 or 9 months, when it is almost impossible to change the situation. It is mandatory to conduct a test for glycated hemoglobin in pregnant women who already had diabetes mellitus before conceiving a child. The results obtained will allow you to keep glucose levels under control and, if necessary, adjust the treatment regimen. The frequency of testing is usually once every 1.5 months.
Video from Dr. Malysheva - review of hemotests:
Glycated hemoglobin during pregnancy - what is the essence of the study, what does it show
The gestation period lasts 9 months. This period presupposes regular completion of various tests and hardware tests. Many doctors pay special attention to glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) standards in women during pregnancy. Often the results obtained are not at all normal, requiring repeated tests and special therapy.
Glycated hemoglobin during pregnancy
Significance of the Study
During the period of bearing a baby, hormonal changes occur in the female body, and along with it, changes in the concentration of sugar in the bloodstream.
Because of this, it is very important to monitor sugar concentrations and understand what its levels indicate during pregnancy. Any violation of the norms can have a bad effect on the condition of the woman and the fetus.
In pregnant women, glycated hemoglobin may change, but should not deviate greatly from the norm.
Research and identification of glycosylated hemoglobin norm in pregnant women helps to see changes in sugar levels over the past 2 - 3 months.
Thanks to this analysis, the doctor can predict the development of pathology in time and carry out therapy. Every woman undergoes examination during pregnancy if a sugar test shows that the level is exceeded.
If measures are not taken, there is a high likelihood of developing gestational diabetes (GDM) and its complications. This disease appears only during pregnancy. It is provoked by hormonal changes.
The placenta produces hormones in a certain amount that reduce the amount of insulin produced. This provokes metabolic failures in the mother and unborn child.
Indications for testing
An endocrinologist prescribes pregnancy tests for appropriate indications:
- diagnosis of diabetes, if standard methods do not make it possible to accurately diagnose the disorder and additional confirmation is needed;
- monitoring glucose levels during pregnancy in women with diabetes, when it was diagnosed before conception;
- assessment of glucose concentration in gestational diabetes;
- establishing the degree of diabetes compensation;
- identifying problems with glucose tolerance – the condition of prediabetes.
According to WHO recommendations, the test is recognized as the most informative for assessing blood glucose levels in diabetes. The analysis helps to establish the degree of glycemia, identify the risks of complications and make predictions.
During pregnancy, the test plays an important role. While waiting for a baby, a woman experiences a physiological impairment of glucose tolerance, and the body reduces sensitivity to insulin.
This happens under the influence of progesterone, corticosteroids, and estrogen. The mechanism is very similar to the development and progression of diabetes. Thus, doctors perceive pregnancy as a risk factor for the disease.
Women may experience gestational diabetes, which goes away after childbirth.
During the normal course of the period, the analysis is implemented twice:
- at first appearance;
- at 30 weeks.
One-time unsatisfactory results are not a reason to panic. When a general analysis shows an increase in glucose, a glucose tolerance test and blood donation for glycated hemoglobin are prescribed. Such comprehensive diagnostics helps to identify violations.
If a woman has already been diagnosed with diabetes before becoming pregnant, then the analysis is carried out at least once every 1.5 - 2 months. The doctor who is caring for the pregnancy draws up a table where he records the indicators.
Normal during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the glycated type should not exceed 6.5% of total hemoglobin. In patients diagnosed with diabetes, it is important to monitor carbohydrate metabolism in order to diagnose sudden changes in time. There is no normal level.
Normal indicators in pregnant women
When deciphering the result, the doctor must take into account the woman’s general health, the presence of anemia, fainting, loss of strength, and frequent bouts of vomiting.
Anemia leads to a lower level in the test results, and therefore they turn out to be unreliable.
glucose will not be normal, but it is not affected by diabetes, but, most likely, by these pathological problems.
Features of the study
During pregnancy, it is necessary to constantly monitor glycemia. Diabetes that develops in pregnant women is usually characterized by normal fasting glycemia, and food increases the levels.
Levels may remain elevated for only a few hours after a main meal or even a light snack. But this time is quite enough to harm the development of the fetus.
In this regard, it is recommended to check the indicators immediately after eating; there is no need to refer only to the results of the HbA1c study.
If it differs when analyzing sugar at different times, then an HbA1c test is required, since it shows the concentration of the substance over the last 3 months. It is carried out in the following cases:
- with hyperlipidemia;
- for problems with the metabolism of the unborn baby;
- at risk of transmitting diabetes from mother to child;
- with gestational diabetes;
- with diabetes diagnosed before conception;
- with high blood pressure.
Disadvantages and advantages of the research method
The HbA1c result is much less likely to be distorted by environmental factors. Its advantages also include:
- speed of obtaining results and its high accuracy;
- identifying the problem at the very initial stages of development, when other methods do not indicate pathology;
- versatility, possibility of carrying out for patients of any age group;
- colds, taking medications and physical activity do not affect the results of the analysis.
But there are also some disadvantages:
- high cost of implementation;
- lack of equipment in a medical facility;
- unreliable results when diagnosing hemoglobinopathy or anemia;
- the result can be distorted by thyroid hormones if the endocrine system malfunctions.
How to take it
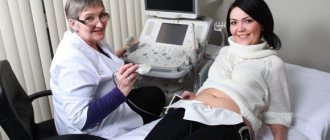
Blood sampling is done from a finger or a vein; no special preparation is needed, but you must donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning, before this, do not eat for at least 8 hours, only drink plain water.
Within a few minutes, the nurse takes the required volume of blood from a vein - approximately 4 - 5 ml. Recently, sampling is more often done from a finger.
Mild discomfort immediately after donating blood
After the procedure, a woman may complain of slight malaise and dizziness. This is normal, symptoms disappear within 1 – 1.5 hours.
Interpretation of results
The HbA1c norm is the same for each person, equal to 4 – 6%. The level is not affected by gender or age. The doctor must adhere to the criteria that are the same for Russian and foreign clinics - the norm for women during pregnancy, the table was compiled by WHO:
- less than 6% is normal, the risks of diabetes are low;
- 6 – 6.5% – increased risk of developing diabetes;
- above 6.5% are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.
With normal indicators, a woman can lead a normal lifestyle, taking into account her situation. Therefore, it is recommended to limit fatty, fried, very salty and spicy foods, and eat in small portions.
In case of increased risk of diabetes, the following rules must be observed:
- monitor a sufficient amount of available physical activity;
- avoid physical inactivity;
- change your diet;
- do a glucose tolerance test;
- monitor your weight;
- Before giving birth, regularly visit an endocrinologist.
If diabetes is detected, the settings for a woman are as follows:
- additional testing for glucose tolerance;
- follow low-carbohydrate diet standards;
- take medications prescribed by the doctor.
Proper nutrition is mandatory if HbA1c levels are abnormal
Antihyperglycemic drugs are not prescribed for pregnant women. Insulin can be used; the dose and frequency of use are selected by the doctor individually.
During pregnancy, a slight increase in HbA1c is a natural process. This is a physiological reaction of the body to changes in hormonal levels and restructuring of the system. But when the levels increase too much, you need to pay attention to nutrition and, on the advice of a doctor, undergo special treatment to reduce HbA1c levels without risks to the child.
Source: https://BezDiabet.ru/diagnostika/obsledovaniya/677-glikirovannogo-gemoglobina-pri-beremennosti.html
Reasons for carrying out
The HbA1c indicator reflects the content of hemoglobin bound to glucose. It makes it possible to reliably determine the average glycemic value for the 3 months preceding the day of the study. The norms of glycated hemoglobin are the same for all people, including pregnant women and children.
The result of this study plays an important role in diagnosing diabetes and assessing the effectiveness of treatment provided to the patient.
Purpose of analysis:
- identify metabolic disorders in a person as early as possible;
- confirm or deny the presence of type 1 or 2 diabetes, as well as the gestational form of the disease;
- control the course of hypertension;
- assess glycemic levels in gestational diabetes;
- prevent the progression of the disease and the early occurrence of complications by identifying pathology at the first stage of development.
The following symptoms may be the reason for conducting an HbA1c test in pregnant women:
- dry mouth, increased thirst;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- fast fatiguability;
- frequent diseases (infectious);
- decreased visual acuity;
- long-term wound healing.
Monitoring blood glucose is considered a mandatory test for pregnant women. A deviation of one unit from the normal value is practically not felt by a person, but at the same time the body undergoes unfavorable changes. It often happens that changes in HbA1c, even with constant monitoring, become noticeable closer to the 8th month of pregnancy, when it is impossible to prevent a negative effect on the fetus.
Reasons for the increase
An increase in hemoglobin in the blood does not always occur with pathologies. It is interesting that expectant mothers who live in high altitude conditions have a physiologically high concentration of hemoglobin in their blood. This feature is due to the presence of a huge amount of oxygen dissolved in the air.
Expectant mothers who live in environmentally friendly places may also have slightly increased levels of hemoglobin in the blood. If no other changes in the blood are detected, then they should not worry about this. After the baby is born, these indicators return to normal.
A significant increase in hemoglobin in the blood of a pregnant woman is, as a rule, a manifestation of pathology. In most cases, deficiency conditions in vitamins B9 and B12 lead to the development of this situation. These substances are necessary for many hematopoietic reactions that develop both in the body of the expectant mother and her baby.
An increase in hemoglobin may be a manifestation of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in a pregnant woman. Quite often it happens that before pregnancy, the expectant mother does not even know that she has such pathologies. Many diseases do not manifest themselves clearly enough and have “erased” symptoms.
Diseases of the urinary tract and kidneys can cause an increase in hemoglobin in the blood of the expectant mother. In this case, an additional set of diagnostics is required. A general urine test, and in some situations, bacterial culture, will help doctors establish the correct diagnosis. To clarify the pathology, an ultrasound examination may also be necessary.
In some situations, increased hemoglobin is a family trait. In this case, it is necessary to clarify whether close family members have had such manifestations. Some genetic diseases are also accompanied by increased hemoglobin levels in the blood. However, it should be noted that an increased level of hemoglobin in this case is recorded in a woman even before pregnancy.
High hemoglobin levels are very dangerous, especially over a long period of time. They can lead to increased blood clot formation.
Preparing for the HbA1c test
Many blood tests are recommended to be performed only on an empty stomach.
Glycosylated hemoglobin does not require this condition, since this indicator can be analyzed even after eating. This is because it displays the average glycemic value over 3 months, and not at the time of measurement. The HbA1c result is not affected by:
- snacks;
- taking antibacterial drugs;
- cold;
- mental state of the patient.
Factors contributing to distortion of the result:
- disorders of the thyroid gland that require the use of special hormonal drugs;
- presence of anemia;
- taking vitamins E or C.
The HbA1c level is most often determined by intravenous blood sampling, but in some cases the material for the study is a sample taken from a finger. Each laboratory chooses its own analysis method.
How to take it
Blood sampling is done from a finger or a vein; no special preparation is needed, but you must donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning, before this, do not eat for at least 8 hours, only drink plain water.
Within a few minutes, the nurse takes the required volume of blood from a vein - approximately 4 - 5 ml. Recently, sampling is more often done from a finger.
After the procedure, a woman may complain of slight malaise and dizziness. This is normal, symptoms disappear within 1 – 1.5 hours.
Norm and deviations of indicators
Based on the obtained result of glycated hemoglobin, we can conclude about the likelihood of developing diabetes during pregnancy.
HbA1c Results Interpretation Table
| Glycated hemoglobin | Decoding the result | Recommendations |
| Less than 5.7% | Glycemic levels are within normal limits, the risk of diabetes is minimal | No lifestyle adjustments required |
| From 5.7% to 6.0% | There are no signs of diabetes. The disease can develop due to poor diet and lifestyle. | You should limit the amount of carbohydrates in your daily diet |
| From 6.1% to 6.4% | There is a high risk of diabetes | Mandatory diet required |
| More than 6.5% | The indicator values indicate suspicion of diabetes of any type or gestational form of the disease. To confirm the diagnosis it is necessary to undergo additional examinations | Consultation with a specialist is necessary to choose treatment tactics for the disease. |
No new indicator standards have been developed for pregnant women. The target values are the same for all people.
Prevention of hemoglobin level disorders
To avoid iron deficiency in the body, a pregnant woman should eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, and spend more time in the fresh air.
You need to include foods in your diet to increase hemoglobin levels:
- Animal products, meat (especially beef, lamb), liver, tongue, milk. Of these foods, iron is absorbed best.
- Eggs (yolk).
- Bananas, pomegranate, raspberries, persimmons, quinces, apples, apricots, peaches, plums.
- Beet.
- Rose hip decoction.
- Grated carrots seasoned with sour cream.
- Legumes.
- Spinach, parsley.
- Buckwheat.
- Walnuts, almonds.
- Potatoes, baked or boiled with skins.
- Sea fish, caviar.
For better absorption of iron, you need walks in the fresh air. You can also take folic acid and vitamin C.
To prevent elevated hemoglobin levels, it is worth excluding seafood, sweets, and baked goods from your diet. Eat fresh fruits, legumes, whole grain bread, nuts. Drink more fluids.
Hemoglobin is the most important protein in the body. An increase and decrease in its level is dangerous for the pregnant woman and the fetus. Mild forms of deviations are corrected by the correct diet and exercise. In severe forms, drug treatment under medical supervision is indicated.
Reliability of the test during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is important to constantly monitor glycemic levels. Most often, diabetes that occurs during pregnancy is characterized by normal fasting blood glucose levels and elevated levels after meals.
Although the level may remain high for only a few hours after any snack and then stabilize again, this time is enough to harm the body of the child and mother. This is why it is important for pregnant women to check their blood glucose after meals, and not rely solely on the result of an HbA1c test.
The results of glycosylated hemoglobin may not be informative, since the glycemic value increases noticeably only in the last months of pregnancy.
A low HbA1c level is often detected in the first trimester, and before childbirth it can sharply exceed the norm and negatively affect the development of the fetus. This situation can be prevented by performing glucose tolerance testing or self-measuring glycemia using a glucometer.
Symptoms
With a pronounced decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, the expectant mother develops specific symptoms. At first, their severity is insignificant. As the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood decreases, negative symptoms begin to progress.
At first, the expectant mother feels only a slight general weakness. She gets sleepy more often. Pathological drowsiness is more disturbing in the first half of the day. As anemia progresses, a pregnant woman experiences a feeling of shortness of breath. In some cases, sleep is disrupted. This symptom usually manifests itself as severe insomnia.
Exercise tolerance also decreases significantly. Mothers suffering from anemia in the third trimester of pregnancy find it much more difficult to perform even the usual household activities. Climbing several flights of stairs can also cause shortness of breath. This symptom progresses noticeably with each subsequent week of pregnancy.
Women suffering from anemia often complain of headaches. It is usually of moderate intensity. With a significant decrease in hemoglobin, the intensity of the headache increases significantly. Pregnant women may also complain of severe dizziness.
Abnormal bowel movements are another characteristic symptom encountered in an anemic state. A pregnant woman experiences constipation. Abdominal pain is also a common symptom that occurs with this condition.
With a pronounced decrease in hemoglobin, the appearance changes greatly. The skin becomes very pale. The mucous membranes of the lips and the area of the nasolabial triangle turn blue and acquire a cyanotic color. In some cases, the skin becomes gray and earthy in appearance.
Hair begins to fall out a lot. At the same time, the nails become very brittle and peel off greatly. The expectant mother develops “strange” eating habits. Pregnant women want to eat chalk or are drawn to incompatible combinations of foods.
Significance of the Study
Identification of pathological metabolic failures and diabetes in the early stages of development allows timely selection of the most effective therapy. Such timely therapy helps to avoid dangerous complications that seriously worsen the condition of patients. When conception occurs in patients prone to diabetes, the study of glycated hemoglobin is the most optimal method for determining blood sugar.
In pregnant girls, glucose levels are characterized by uneven growth, so routine tests for blood sugar may give inaccurate results. Typically, the maximum increase in pregnant women is observed at 8-9 months. But in healthy girls, a slight jump in sugar in the bloodstream usually does not carry any threats or negative consequences. If the patient has previously been diagnosed with diabetes, then with the help of such an examination it is possible to ensure constant monitoring of sugar and make the necessary correction in a timely manner. The norm for glycated hemoglobin during pregnancy is generally similar to that for ordinary patients.