You are here: Blood test -
Hemoglobin -
Low hemoglobin during pregnancy
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention and prognosis
Low hemoglobin during pregnancy is a condition that, if left untreated, can lead to dangerous complications for the expectant mother and child. The anomaly is detected only through laboratory blood testing.
There are a lot of sources of pathology, ranging from exacerbation of chronic diseases, for example, the digestive organs or hematopoietic system, ending with multiple pregnancies and the influence of stressful situations.
Low hemoglobin during pregnancy has several characteristic clinical signs, but the symptoms may remain unnoticeable because they are masked as toxicosis or symptoms of the underlying disease.
The problem can only be identified thanks to data obtained during a general clinical blood test. To find out the provoking factor, a blood test is not enough - there is a need for a comprehensive examination of the body.
Low hemoglobin can be raised during pregnancy using conservative methods, including enriching the diet with foods rich in iron, folk remedies and taking medications (all drugs are prescribed by the attending physician and are used under his strict supervision.
Why do pregnant women need to monitor hemoglobin?
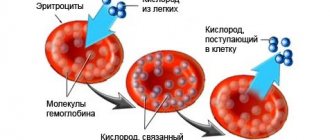
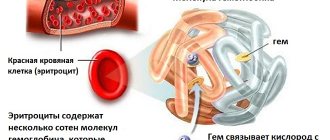
Why does the human body need hemoglobin? With its help, oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. That is, hemoglobin is the most important microelement for the proper functioning of the respiratory function.
A child, while in the womb, also needs oxygen, but he cannot breathe on his own - gas exchange occurs through the placenta along with the blood. What happens if there is a deficiency of hemoglobin? In simple terms, the unborn child will experience oxygen deficiency .
In critical cases, oxygen deficiency in the baby in the womb can lead to asphyxia and subsequent fetal death. This is why it is so important to monitor hemoglobin levels - the normal course of pregnancy directly depends on this.
It is also worth mentioning that hemoglobin deficiency may also indicate a lack of B vitamins and folic acid. And this is fraught with an imbalance of sex hormones in the body of the expectant mother, which can cause self-abortion of the fetus (premature birth, when the body provokes it on its own, even though the child has not yet fully formed).
Why is low hemoglobin dangerous?
The development of anemia due to low protein levels in the blood is a dangerous condition for pregnant women that requires immediate treatment. Oxygen starvation threatens to harm the unborn child.
At the beginning of pregnancy, pathology can lead to the death of the fetus in the womb. In the second trimester, the disease can negatively affect the development of the child’s brain and cardiovascular system. Therefore, when a disease is detected, preventive measures should be taken immediately and comprehensive treatment of the problem should begin.
Normal blood content
The average hemoglobin level in a non-pregnant adult woman is 139 grams per liter of blood. During pregnancy, this figure decreases slightly. The following readings are not a deviation:
- first trimester – 132 grams per liter;
- second trimester – 120 grams per liter;
- third trimester – 112 grams per liter.
After childbirth, the hemoglobin level returns to normal, but this will take from 1 to 6 months (the recovery period for each woman may vary, but after the birth of the first child it is longer than after the second and all subsequent children).
In the first trimester, in particular, for 2–3 months, hemoglobin may increase slightly, which is due to the cessation of menstruation. This is also a normal phenomenon and is not a deviation from the norm - this is the physiology of the female body.
Hemoglobin norms
The normal hemoglobin level for women is considered to be 110-150 g/l. During the planning process, a woman is especially recommended to monitor this indicator. Of course, you can get pregnant even with low hemoglobin levels, and in order to eliminate possible problems and complications during pregnancy, it is necessary to normalize the hemoglobin level even before conception. With the onset of pregnancy, hemoglobin levels change in accordance with the gestation period. The normal hemoglobin level for the first months is 112-160 g/l.
Attention! If a woman has a tendency towards a pathological decrease in hemoglobin concentration, then it is recommended to take the necessary therapeutic measures to normalize its content, then during pregnancy it will be possible to reduce the risk of developing anemia to a minimum. Taking folic acid and eating foods fortified with iron will greatly help in this matter.
In the first months after conception, patients are usually prescribed folic acid and vitamin E. If hemoglobin levels are at the lower level of normal, they may be prescribed multivitamin complexes and iron supplements.
In the second trimester
When the gestation period reaches the second trimester, the hemoglobin concentration decreases slightly. The normal level is considered to be 108-144 g/l. If hemoglobin has dropped to much lower values, then urgent restoration of its normal level is necessary. Self-medication is excluded here; taking any drug must first be agreed with a gynecologist.
Folic acid, which is recommended to be taken in the first trimester, can be stopped with the onset of the second, because the formation of the neural tube has already completed. The appointment is prescribed when there is a need for vitamin B9.
In third
The normal hemoglobin content in the third trimester is about 100-140 g/l. In general, during pregnancy, a decrease in hemoglobin level within the indicated limits is considered a variant of the norm, because it is natural. There is no need to treat such changes as a disease. Such metamorphoses are associated with changes in water-salt balance and an increase in the volume of blood circulating in the pregnant woman’s body.
The body changes daily, and the load increases; the body needs time to adapt to these metamorphoses. Therefore, it thins the blood and relaxes vascular tissues. As a result, by the third trimester, the volume of liquid components of the blood increases, and the number of red blood cells decreases, which is a factor in the decrease in hemoglobin levels.
Signs of a low level
Hemoglobin deficiency in a pregnant or nursing mother can manifest itself in a very wide list of symptoms, and for each woman their combination can vary dramatically.
The most common signs are:
- general weakness and chronic fatigue;
- the appearance of problems with skin, nails, hair;
- pale skin;
- accelerated heartbeat (occurs with a significant deficiency of hemoglobin when the body experiences oxygen starvation);
- the emergence of an addiction to certain odors (most often the smell of paint, gasoline, acetone, various types of solvents, synthetic adhesives, motor oil, exhaust gases, and so on);
- tendency to toxicosis (especially noticeable in the early stages of pregnancy);
- signs of immunodeficiency (susceptibility to infectious diseases, manifestations of thrush, skin diseases, and so on);
- decreased taste sensitivity (also often develops against the background of toxicosis).
But it is worth considering that often hemoglobin deficiency is not accompanied by any symptoms at all. However, doctors still prescribe a blood test (almost every month) to monitor the level of hemoglobin in the blood of a pregnant woman.
Diet for iron deficiency anemia
Iron is a trace element that our body needs and is vital. Its assimilation, transfer, storage and excretion are distinguished by a fine organization. Iron is involved in oxygen metabolism, being part of hemoglobin, is used for the synthesis of thyroid hormones and the full functioning of the immune system, takes part in redox reactions and a number of metabolic processes.
During pregnancy, iron is consumed more actively, some of it is excreted in feces, urine, and sweat. Therefore, it is important that its reserves in the body are replenished on time and in sufficient quantities. And the normal functioning of all organs and systems involved in iron metabolism guarantees its adequate consumption. During pathological processes in the body, the mechanism of absorption and distribution of iron may be disrupted, and then anemia develops.
For the treatment and prevention of iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women, first of all, a special diet is prescribed. In addition to diet correction, the complex of therapeutic measures includes taking iron supplements. When creating a menu, it should be taken into account that the body absorbs approximately 50% of the iron supplied from food.
From products of plant origin - vegetables, fruits - we get non-heme iron (in trivalent - Fe3, and divalent form - Fe2). The valency of non-heme iron determines the solubility of salts formed by its atoms and organic acids of food products. Iron in divalent form is absorbed better than Fe3.
In order for non-heme (not part of protein) iron to be absorbed in the intestines, it must be transformed. Vitamin C acts as an activator of the reaction of transformation of iron from one form to another (from trivalent to divalent). This means that in plant foods, iron is biologically available only if it also contains ascorbic acid (or other organic acids).
Most vegetables and fruits contain vitamin C in varying amounts. But it is destroyed during their preparation - during heat treatment. Therefore, it is better to consume the gifts of gardens and vegetable gardens raw, then the iron from them will be absorbed by about 5–10%. The least iron is absorbed from spinach - only 1% of the amount contained in the plant.
Products of animal origin - meat and offal, fish and seafood, eggs - contain heme iron (part of protein and associated with four nitrogen atoms). From meat, it is freed from protein chains in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) and is easily absorbed by the cells of the inner lining of the intestine. 25% of heme iron is absorbed from meat products; we get 10–15% from fish and eggs.
75% of iron coming from food is heme, of animal origin. But do not forget that nutrition during pregnancy should be balanced and rational.
Iron can be heme and non-heme: heme is found in products of animal origin, non-heme - in plant foods.
Iron penetrates the intestinal wall with a nonspecific transporter protein, which simultaneously transports some other minerals - manganese, copper, zinc. The high content of these elements in foods can interfere with the full absorption of iron. Calcium also prevents heme and non-heme iron from entering the body. Therefore, it is better to eat foods with a high concentration of calcium at intervals of 4 hours after consuming iron-containing foods.
Iron absorption is impaired by:
- grains and bran;
- green leafy vegetables;
- corn and beans;
- any types of tea;
- dairy products (except lactic acid).
Some medications and dietary supplements also interfere with the absorption of iron in the body.
The diet for anemia with iron deficiency is rich in:
- complete proteins (at least 130 g per day, and this amount includes 80–95 g of animal proteins) - they contribute to the synthesis of hemoglobin and red blood cells;
- vitamins - especially C and group B (B9 and B12) - with their participation, iron is absorbed and blood elements are produced;
- minerals - copper, nickel, cobalt, manganese, etc.
Fat consumption should be somewhat limited - no more than 70–80 g per day. And carbohydrates in meals must meet the norm - 400–500 g per day, while simple carbohydrates (lactose and fructose) are not prohibited. Products containing any organic acids are very welcome - citric, malic, acetic, as well as lactic acid (lactic acid products).
The menu of an expectant mother with iron deficiency anemia should include:
- offal - pork, veal, beef liver, heart, brains, tongue, liver and poultry heart;
- lean meat - beef, veal, turkey and rabbit, chicken breast;
- low-fat sea and river fish - mullet, hake, cod, flounder, blue whiting, carp, carp, pike perch, pike;
- eggs - chicken and quail;
- fermented milk products - yogurt, kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt, sour cream, cottage cheese, cheese;
- dairy products - butter (30–40 g), milk, cream;
- vegetable oil - 25–30 g per day;
- dishes prepared with the addition of brewer's and baker's yeast;
- bread - both coarsely ground black rye and white (200 g each);
- bran - oat, wheat, rice;
- sugar (50 g), honey;
- cereals - oatmeal, buckwheat, millet, rice, etc.;
- legumes - beans, beans, lentils;
- vegetables - cabbage (fresh and pickled), carrots, green peas, zucchini, eggplant, corn, tomatoes, beets, bell peppers;
- fruits - apples, pears, lemons, grapefruits, oranges, bananas;
- berries - cherries, grapes, apricots, pomegranates, plums, viburnum, cranberries, gooseberries, currants, blackberries, raspberries, rose hips and sea buckthorn;
- dried fruits - dried apricots, quince, raisins, prunes, dates, figs, etc.;
- seeds and nuts - pumpkin and sunflower seeds, walnuts, cashews, almonds, hazelnuts.
If the expectant mother has a weakened appetite, which is often observed with anemia due to a decrease in the secretory function of the stomach, it is better for her to prefer soups - fish and meat with vegetables, diversify the diet by adding spices, herbs, and various sauces. As for contraindications, in case of anemia there are no special restrictions on food consumption. You just need to maintain an interval between meals rich in iron and foods containing many substances that can interfere with its absorption (copper, zinc, calcium, manganese).
Meat and fish should be cooked and brought to full readiness. Iron is not destroyed during heat treatment. But vegetables and fruits containing vitamin C, which promotes the absorption of iron, are best eaten fresh.
Photo gallery: iron-rich foods
100 g of spinach contains 13.51 mg of iron
100 g of beef liver contains 6.9 mg of iron
100 g of pork kidneys contain 7.5 mg of iron
100 g of pork liver contains 20.2 mg of iron
100 g of chicken liver contains 17.5 mg of iron
100 g of beef tongue contains 4.1 mg of iron
100 g of oatmeal contains 3.9 mg of iron
100 g of liver sausage contains 6.4 mg of iron
100 g of beef heart contains 4.8 mg of iron
100 g of peas contain 6.8 mg of iron
General nutrition rules
To normalize hemoglobin levels in the blood as quickly as possible during pregnancy, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Provide sufficient iron for the body in the food you eat. In an adult, the daily norm is only 8–15 mg per day; in pregnant women it increases to 22–25 mg.
- Ensure that the body receives a sufficient amount of B vitamins, omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids, ascorbic acid, sodium, potassium, silicon, zinc - all these microelements increase the bioavailability of iron, that is, they help the body absorb it normally (if there is a deficiency of the same folate acids, the body practically does not absorb iron).
- Include foods and dishes with complex proteins in your diet - when digested, they break down into amino acids, which enter into a biochemical reaction with iron and vitamins, after which the hemoglobin molecule is created in the cell.
Doctors also recommend avoiding neuroses and stressful situations - they can make adjustments to the hormonal levels, which regulate the pregnancy process itself, as well as hematopoietic function.
Not all foods and drinks rich in iron and other essential microelements can be consumed during pregnancy. For example, turmeric and parsley are good for increasing hemoglobin. But they can also act as antispasmodics on smooth muscle , which also causes uterine contractions. Therefore, they should absolutely not be used during pregnancy.
Prevention of hemoglobin disorders
Preventive measures during pregnancy regarding hemoglobin levels include following the diet recommended by the doctor with the obligatory consumption of lean meat, seafood and vegetables. Every day the menu should include dried fruits and nuts, fresh fruits and juices from them. Iron is better absorbed from animal foods (≈6%), and its absorption from plant foods is slightly lower (only 0.5%).
Low hemoglobin levels are detected quite often in pregnant women, especially in the third trimester. This condition is quite dangerous, and therefore requires mandatory treatment, which a woman should not ignore.
What should you limit?
It is recommended to avoid the following foods during pregnancy, as they most contribute to a decrease in hemoglobin:
- Pasta. In fact, this includes everything that is prepared on the basis of wheat flour (without bran).
- Dairy products. Almost all of them contain calcium in fairly large quantities, which impairs the absorption of iron. This directly affects hemoglobin levels. This includes almost all types of cheeses, butter, sour cream, kefir, yoghurts and other dairy desserts, condensed milk, fermented baked milk.
- Chicken egg whites. They also impair the absorption of iron by interfering with biochemical reactions with it involving amino acids. Interestingly, consuming chicken proteins has virtually no effect on the concentration of iron and folic acid (unlike dairy products and any others that contain calcium).
You should also avoid eating greens during pregnancy. More precisely, you can include it in your diet, but in limited quantities. Parsley, dill, turmeric, basil - all these products are rich in vitamins and even iron, but they cause spasms of smooth muscles, which is extremely dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy.
During this period, it is better to receive vitamins in the form of multivitamin complexes - this will be much safer for the expectant mother and child.
How to quickly increase hemoglobin during pregnancy
Of course, the fastest way to raise hemoglobin levels is to administer drugs (intravenously or intramuscularly) containing iron. But, since during pregnancy you need to be careful when taking any medications, this method is used only with a very low level of hemoglobin - with the most severe level of anemia. Of course, the prescription and use of such drugs must be agreed upon with specialists.
The drugs that are used in this case include the following:
Venofer
A medicine based on iron hydroxide. This drug is prescribed to patients suffering from anemia. It is administered intravenously. It is strictly prohibited for use in the first trimester; the attending physician can prescribe it only from the second trimester of pregnancy.
Ferrum lek
A medicine that has three types: injection solution, syrup and chewable tablets. It is prescribed in case of anemia, improper absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract, as well as for the prevention of iron deficiency during pregnancy and lactation. There are also contraindications for use in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Fenyuls
A medicine that maintains normal hemoglobin levels even with high iron consumption in the body. As you can understand from the above, this is an excellent way to quickly increase hemoglobin during pregnancy, or more precisely, to keep it at a normal level. The drug is based on ferrous sulfate, ascorbic acid (helps better absorption of iron) and B vitamins. Do not forget that during pregnancy you are responsible for two lives - yours and your child's, so you can take any medications only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Sorbifer Durules
A medicine prescribed for the treatment and prevention of anemia from iron deficiency. The base is ferrous sulfate and ascorbic acid. A distinctive feature of this drug is that it is not dangerous during the entire period of pregnancy and lactation. However, you still need to be extremely careful - if at least one of the side effects occurs - nausea, diarrhea, allergic reaction, and so on - you should immediately consult a doctor.
Maltofer and maltofer foul
Two drugs that are essentially the same thing. It is based on iron polymaltosate. But Maltofer Fol also contains folic acid, which is why this particular drug is prescribed during pregnancy and lactation. Moreover, this drug is taken not only until hemoglobin returns to normal - it is usually taken until childbirth. This medicine has no side effects, which is very much appreciated by expectant mothers, whose body has a special reaction even to the “wrong” one.
Do not forget that these drugs contain a very high iron content , therefore, if you are already taking any vitamins that contain iron, then you need (with the help of a doctor and logic) to make a choice in favor of one of the drugs in order avoid oversaturation of the body with iron. Beware of an overdose of components, it is no less dangerous than a deficiency!
Other Important Recommendations
You can also increase hemoglobin using the following tips and recommendations:
- Include the following dessert in your diet: a mixture of dried apricots, raisins, and walnuts. To prepare a hemoglobin mixture, you will need to take 50–60 grams of the above components, grind them using a meat grinder, coffee grinder or blender and add honey (the same amount as the ground mixture). Store in the refrigerator, take 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. The course is at least 2 weeks, further – if necessary.
- Take a course of the following vitamin complexes (to choose from): Complivit iron, Perfectil, Sorbifer, Fenyuls. You should first consult with your doctor.
- It is also important to maintain a daily routine (activity/rest). The process of hematopoiesis itself mainly occurs at night during sleep. Accordingly, chronic insomnia can provoke hemoglobin deficiency, even if the pregnant woman follows a healthy diet.
Hemoglobin deficiency does not always indicate a lack of iron or certain vitamins. This condition can be caused by certain diseases. This even includes blood cancer. Therefore, if you suspect a hemoglobin deficiency, you should not delay going to the doctor. It must be remembered that for the unborn child this is many times more dangerous than for the expectant mother.
How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy without drugs
When a new life develops in your body, as a rule, you are very afraid of taking various chemical compounds, including pills. In fact, this is a fairly justified fear, because many iron-containing drugs have either not been tested at all for their effects on pregnant women, or have been tested, but still, it is virtually impossible to predict all reactions. So what should you do if you have low hemoglobin levels? The answer is simple: turn to the wisdom of our grandmothers.
Of course, it is worth remembering that a rapid decrease in hemoglobin at home is also possible during pregnancy, but you must remember that the level of anemia should be practically zero. In any case, any manipulations must be agreed upon with the supervising physician.
Folk remedies for lowering hemoglobin during pregnancy
Let's start with the fact that, as a rule, any folk remedies for anemia consist of obtaining the iron missing in the body naturally: through foods, decoctions, juices, infusions, and so on. For example:
- You can brew blackberry leaves or dry rose hips and drink 3-4 times a day. This not only enriches the body with essential iron, but also has a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
- A healthy and tasty mixture of dried apricots, dates, raisins, lemon, walnuts and honey . All these ingredients are taken in equal proportions, thoroughly ground in a blender or meat grinder until smooth and taken every day, a tablespoon half an hour before meals.
- A fruit drink made from fresh cranberries with the addition of apple and beet juice in a ratio of 2/2/1 helps to raise hemoglobin very well . This drink is taken before meals 3-4 times a day.
- And, finally, the simplest thing - every morning we eat a teaspoon of honey on an empty stomach , 10-20 minutes before breakfast.
Hemoglobin can also be increased with the help of foods
It has been said more than once above that there are a fairly large number of products that themselves contain iron. And if sometimes you don’t want to prepare yourself a cranberry decoction, then you can quickly increase your hemoglobin by eating the following foods .
- The first product that is a kind of champion in iron content is pistachios . 100 grams of pistachios contain 60 milligrams of iron.
- Second place is shared by dried mushrooms, halva, pork, black caviar and quail eggs .
- The third (and all other places) is beef, any seafood and cereals .
Among other things, there is a lot of iron in vegetables. Onions, pumpkin, cabbage, radishes, garlic, asparagus, beets, broccoli - all these products, which can probably be bought at any market, and some lucky women even have them growing in their gardens, are incredibly healthy and tasty in their own way.
Seasonal berries and fruits, which are tasty both in their pure form and in the form of decoctions, juices and fruit drinks, bring special benefits. In general, fruits and vegetables during pregnancy are an irreplaceable source of vitamins and essential elements. This, by the way, is another reason why it is better for a pregnant girl to be in the village - besides the fact that there is fresh air and better ecology, it is thanks to this ecology that the healthiest fruits and vegetables grow there.
The most iron is found in:
- grenade
- strawberries
- plum
- raspberries
- black currant
- strawberries
- blueberries
In addition, do not forget that it is not enough to get the missing iron into the body - you also need to do everything so that it is well absorbed and “stays” with us. To do this, you need to remember that foods that interfere with the absorption of iron (and not only it) are coffee, cheese and milk. It would be ideal, of course, if you completely exclude them from your diet while getting rid of anemia, but you can simply not combine them with foods that contain iron.
And, of course, expectant mothers should not forget about walks in the fresh air, which replace some physical activity and are simply beneficial for the muscles and the body as a whole. Just don't overexert yourself, and under no circumstances do anything that your doctor hasn't recommended you do.
Methods for eliminating anemia
Today, the most effective method of increasing hemoglobin during pregnancy is considered to be an appropriately formulated diet.
However, many experts believe that it is impossible to cope with this problem without the use of certain medications.
It should be noted that simultaneously with the treatment of a pregnant woman, monitoring of the condition of the fetus is carried out. For this purpose, blood flow in the placenta and weight gain are assessed.
Procedures of this kind can only be performed in hospital settings. It is taken into account that too high a hemoglobin level can lead to blood clots.
Medications
Hemoglobin-increasing tablets are prescribed when a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with a significant deviation in hemoglobin levels from the norm.
Drug treatment for anemia is resorted to after the appropriate diet has not brought the desired results.
Among the effective drugs that have proven themselves to be effective is Sorbifer-Durules. The tablets contain ascorbic acid and ferrous sulfate.
Take one tablet twice a day. The tablet must not be crushed or divided into pieces. The drug is prescribed during pregnancy both for treatment and for preventive purposes.
You can quickly and without any special consequences increase hemoglobin during pregnancy, as is done in other cases, by taking multivitamin complexes in combination with tablets containing iron.
A vitamin complex including high con is prescribed for a sharp drop in hemoglobin. The drug is available in pharmacies without a prescription.
You should take 1 capsule per day with plenty of water. In this context, it should be emphasized that during pregnancy, all medications, including vitamins and iron, are taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies
Many years of experience show that in order to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy, an integrated approach is used.
Before prescribing vitamins to a pregnant woman, you need to adjust your daily diet.
Everyone knows that during the period of gestation the expectant mother should eat well. However, not every woman knows which foods increase hemoglobin during pregnancy.
To increase hemoglobin during pregnancy, you must include lean meat in your daily menu and prepare liver dishes.
Buckwheat contains a high concentration of iron, which is why buckwheat porridge should be present on the table as often as possible. When creating a diet, it is necessary to maintain an optimal balance of foods.
Any deviation from the norm during pregnancy can cause serious complications. Apples, beets in any form, nuts and fresh honey are good for anemia. At the same time, you need to monitor the condition of the digestive system.
When preparing for pregnancy, a woman has to take into account a large number of factors.
Among others, daily routine and daily diet are important.
If hemoglobin fluctuations occur within the established norm, then no additional actions should be taken.
When there is a need to increase hemoglobin, all procedures should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
It is important to remember that low hemoglobin is not considered a terrible phenomenon. The main thing is to notice the characteristic symptoms in a timely manner and increase the concentration of red blood cells
Anemia: what is this disease?
The blood disease is characterized by a reduced number of red cells - red blood cells. In normal health, the norm is 120 g/l.
However, during pregnancy 110 g/l is considered normal, since the female body spends additional resources on the full development of the fetus.
If the readings are below normal, then we are talking about a blood disease - anemia or anemia. In medicine, there are three degrees of the disease:
- Light form (109-90 g/l).
- Medium form (89-70 g/l).
- Severe form (from 69 g/l and below).
Blood testing during pregnancy is a mandatory procedure. Hemoglobin indicators are considered based on the duration and presence of concomitant pathological disorders.
What affects the decrease in hemoglobin
The production of hemoglobin is closely related to the presence of a number of essential substances
Particularly important for its production is the presence of adequate amounts of iron, folic acid or vitamin B9 and vitamin B12
Iron is extremely important for the construction of hemoglobin. Iron deficiency causes what is called iron deficiency anemia, which is the most commonly diagnosed form of anemia
Iron deficiency causes what is called iron deficiency anemia, which is the most commonly diagnosed form of anemia.
Folic acid improves the absorption of iron in the body.
If there is not enough folic acid, megaloblastic anemia may develop. It is much less common than iron deficiency.
Its distinctive feature is a disruption in the formation of red blood cells themselves, which become too large and cannot carry out their functions of transporting oxygen. In pregnant women, megaloblastic anemia is diagnosed more often, especially if there is a B9 deficiency.
Vitamin B12 is also involved in the production of red blood cells.
Its deficiency increases the risk of developing anemia.