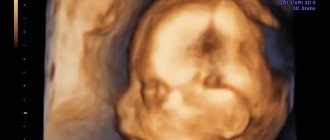
An ultrasound examination can be called the “eyes” of a gynecologist, with the help of which he observes the course of pregnancy throughout its entire duration. New 3D and 4D technologies provide such clear images of the fetus that many of the smallest details of the child’s development can be seen. Ultrasound is performed several times. This is one of the safest methods of examination during pregnancy. We will consider perhaps the most important and informative - the third planned ultrasound.
Purposes of ultrasound examination in the 3rd trimester
In the 3rd trimester, an ultrasound scan is done to detect abnormal development of the baby in the womb. It is impossible to do this at earlier dates. No preparation is required for the examination.
During an ultrasound scan, it is checked whether the gestational age corresponds to the development of the baby in the womb. It is determined whether there is a risk of premature birth and signs of oxygen deficiency. The information obtained helps to track and correct many violations. This helps to bring the pregnant woman to a successful delivery.
During an ultrasound, not only the condition of the child, but also his mother is assessed. All reproductive organs are examined. The examination helps doctors prepare if urgent intervention is required. During an ultrasound, the following is examined:
- motor activity in the fetus;
- respiratory system (especially lungs);
- blood flow condition;
- internal organs of the baby;
- fetometric indicators;
- signs of hypoxia;
- umbilical cord (blood flow, vessels);
- heartbeat and fetal position;
- amniotic fluid level;
- fetal presentation;
- length of the cervical tract.
During an ultrasound, the sex of the baby is determined and an approximate due date is set. Particular attention is paid to assessing the placenta. Its improper attachment (low) is a contraindication for childbirth in the usual way.
Can an ultrasound be done if the baby is post-term?
A pregnancy is considered post-term if its duration exceeds 40 obstetric weeks. Doctors recommend undergoing an ultrasound to determine the maturity of the placenta, the condition of the waters and the fetus itself. The specialist checks the readiness of the cervix. The need for urgent delivery depends on the results obtained.
A period of more than 42 weeks requires medical intervention, which is also preceded by an ultrasound. The doctor evaluates all indicators, after which a decision is made to induce labor or perform a cesarean section.
In the 3rd trimester, an ultrasound scan must be performed at least once, at 32 weeks. Timely measures taken in case of any deviations from the norm will help carry the child to the end of the term, and monitoring the condition of the uterus will avoid a threat to the health of the expectant mother.
Scan timing
The timing of screenings is determined by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated October 1, 2012 No. 572. The document states that a pregnant woman must undergo three examinations. The last, third – at 30-34 weeks.
Diagnostics helps prevent possible complications and developmental defects. If no deviations are noted at 30-34 weeks, then no further ultrasound is performed. If there are complications, scanning is carried out in the third trimester the required number of times. Since the examination is safe, it does not have a negative impact on the health of the mother and fetus.
How many times can you do it during the third trimester?
The regularity of ultrasound depends on the individual characteristics of the woman. In addition to routine ultrasound, it is recommended to check the condition of the fetus in the following cases:
- slow growth of the abdomen or complete cessation of its expansion;
- weight loss in pregnant women;
- if there are scars on the uterus, to monitor their condition;
- to determine the position of the fetus if breech presentation is suspected;
- when a woman receives any type of injury;
- in the absence of movement for a long time.
If there is no movement for more than 12 hours in a row, you should immediately contact a medical facility for an ultrasound examination. This can often help save the life of the fetus.
Additionally, ultrasound is recommended for women whose work involves hazardous work or high physical or mental stress.
Assessment of the condition of the pregnant woman’s organs
During an ultrasound scan, the maternal organs are examined. The risk of premature birth may be indicated by a shortening of the uterine cervix, poor tone, and a strong opening of the pharynx. In such cases, the woman is asked to go to the hospital for safekeeping. It monitors the condition of the pregnant woman and treats her to prevent untimely birth. If there is no improvement, the child's lungs prepare for independent breathing.
If a caesarean section was performed in a previous pregnancy, then the condition of the scar on the uterus that remains after the operation is assessed using ultrasound. Its normal thickness is at least 3.5 mm. If this figure is less, during normal childbirth the uterus may become covered with severe ruptures.
Fetal position during ultrasound
This is one of the most important things; in order to determine the position of the fetus, the first trimester screening and ultrasound are performed before childbirth. If the baby is lying incorrectly (head up or sideways), doctors will recommend a cesarean section. However, a child in the third trimester does not lie still, he moves, turns over and may still turn over and take the correct position. Only after an ultrasound scan at a later date can a final conclusion be made.
The structure of the placenta in the 3rd trimester
Much attention during ultrasound examination in the third 3rd is paid to the placental structure and condition. Normally, at the 32nd week it is from 23.5 to 41.6 mm, at the 34th – 26.8-44 mm. Its position allows us to assess the possibility of natural childbirth. Sometimes the body of the placenta is closed by the uterine os. In this case, surgical delivery is performed.
If the placenta is low and fixed less than 4 cm from the uterine os, then increased monitoring of the pregnancy is necessary. There is a possibility of bleeding both during childbirth and before the start of the process. Other warning signs are hypo- and hyperplasia.
Changes in thickness are alarming “bells”. Thinning is characterized as placental insufficiency. Thickening can be observed with Rhesus conflict. With severe hyperplasia, inflammatory processes or infectious lesions may appear.
Placental maturity
The degree of maturation of the placenta is also of great importance. Changes in it occur gradually. The degree of maturity is divided into 4 categories - from 0 to III (by dividing the tissue into lobules, the basal plate is assessed). This is determined by the structure and condition of the layer closest to the myometrium. At the zero stage there is no lobular structure. It appears with increasing maturity of the placenta.
In the third stage, the placenta is completely divided into lobes. Premature aging is now more common. In this case, the third degree is clearly visible before the 36th week. If the placenta has matured prematurely, it cannot function normally. In this case, fetal nutrition is supported with the help of medications.
Also, ultrasound can reveal other pathologies of the placenta - calcified areas that previously underwent rapid bleeding. The cause is the bad habits of the pregnant woman (drug addiction, smoking, etc.), late gestosis.
Damaged places in the placenta cannot perform their functions, so the load on the healthy part increases greatly. Despite the fact that by nature the body has the ability to compensate for the performance of the affected areas, it is still necessary to control the blood supply to the fetus.
Is ultrasound harmful for pregnant women?
Many pregnant women are worried that ultrasound diagnostics can harm the baby, so they worry about how often an ultrasound can be done. During the entire pregnancy, the mother goes for such diagnostics only three times. Doctors will not force the patient to undergo additional testing unnecessarily. If there is a need to double-check something, for example, changes in presentation, then additional studies may be prescribed in the last trimester.
Mothers should not worry, because medicine has proven that the frequency at which ultrasound machines operate is absolutely safe. This is a routine, everyday procedure, which the doctor can prescribe again in the 3rd trimester if there is a need to monitor the development of organs or perinatal processes.
Condition of amniotic fluid
During an ultrasound, the level of amniotic fluid must be assessed. Its exact volume cannot be determined, so the fluid index (FLI) is used. For this purpose, the uterus is conventionally divided into 4 parts.
In each of them, measurements are taken of the depth of the largest pocket of water. The values are then summed to form the IAF. Normally, at 30-34 weeks the index should be 82-278 mm (average value - 140-145 mm). At the same time, the transparency of the liquid is assessed. If there is a lot of suspended matter in it. This indicates an infection.
Normal placental thickness
| Week of pregnancy | Thickness, mm |
| 28 | 29,9±7,5 |
| 29 | 31±7,4 |
| 30 | 31,5±7,8 |
| 31 | 32,6±8 |
| 32 | 33,6±8,1 |
| 33 | 32,6±8 |
| 34 | 33,2±8,3 |
| 35 | 34,3±8,3 |
| 36 | 37±9 |
| 37 | 36,8±8,9 |
| 38 | 37,3±9 |
| 39 | 36,1±9,1 |
| 40 | 35,7±9,2 |
When the thickness of the placenta exceeds the average, there is a possibility that it is inflamed (placentitis). If there is a suspicion of placentitis, the doctor prescribes a Doppler ultrasound examination.
It is considered normal when the placenta is attached to the posterior wall of the uterus, 6 cm from the internal os. Central presentation, marginal and low attachment of the placenta are extremely dangerous pathologies; they threaten the child and mother. If these diagnoses are present, the woman is transferred to a hospital or, if it is possible to ensure complete rest, to home.
In case of complete placenta previa, a cesarean section is prescribed, since it blocks the exit from the uterus and prevents the baby from being born naturally. If the placenta is low, then natural delivery is possible, but there is a high risk of bleeding during childbirth.
When the thickness of the placenta exceeds 45 mm, this may indicate the following disorders:
- Rhesus conflict;
- dropsy;
- infectious process;
- diabetes.
Blood flow assessment
Assessment of blood flow in the vessels is carried out using Doppler ultrasound. Three degrees of impairment can be diagnosed:
- in the first stage, there are enough drugs that improve blood circulation and periodic medical supervision;
- need constant monitoring and medication support before birth;
- third degree is a direct indication for urgent premature delivery.
If blood flow disturbances and the degree are detected on time, this makes it possible to reduce possible risks and consequences for the fetus or to bring the pregnancy to an end (at least until the moment when it is already possible to give birth).
Carrying out
In the third trimester, ultrasound is performed using the transabdominal method - along the abdomen. The steps of the procedure are as follows:
- The woman lies with her back on the couch, frees the abdominal area from clothes;
- The doctor applies a special ultrasound gel to the surface being examined, which increases the glide of the sensor and the ability of ultrasound waves to penetrate deep into the body;
- Then he places the sensor on the surface of the patient’s body and begins to move it across the entire area of the abdomen, taking readings. All information received is logged.
During the procedure, the doctor may ask the woman to slightly change her body position to obtain a better examination result. Upon completion, the ultrasound gel is removed from the body with napkins or a towel.
Ultrasound in the 3rd trimester: norms and violations
In the third period of pregnancy, a two-dimensional ultrasound is performed. If you need to obtain more accurate data, then use three-dimensional echography. The norms for 32-34 weeks are shown in the table.
| What is being assessed | Acceptable limits of values | |
| Placental thickness | 23.5-41.6 mm | |
| Localization of the placenta | Calculated from the lower border to the opening of the internal pharynx | 70 mm |
| Amniotic fluid | 1750 mm | |
| Cervical length | minimum 30 mm | |
| BPR (biparietal value) | 71-85 mm | |
| OG (head circumference) | 26.5-30.5 cm | |
| LZR (fronto-occipital value) | 89-105 mm | |
| AB (abdominal circumference) | 23.5-29 cm | |
| Length (in mm) | Forearms | from 42 to 50 |
| Shin | from 49 to 57 | |
| Shoulder | ||
| Hips | from 52 to 62 | |
| Height | 41 cm | |
| Weight | from 1420 to 1520 g |
The lungs must be of the 1st degree of maturation. If the ultrasound showed minor deviations from normal values, then this does not indicate pathological changes, since the parameters of the fetus are strictly individual. For example, if both parents are small in height and weight, then the child may be born miniature. When spouses are tall or obese, a large baby will be the norm for them.
Interpretation of ultrasound examination
When decoding the data, the uterus and its cervix, placenta, and the amount of amniotic fluid are assessed. What the changed values may indicate:
- Thickening of the placenta is a sign of Rh conflict or inflammation.
- If the uterine cervix is less than 25 mm long, then there is a risk of premature birth of the baby.
- Too much or deficiency of amniotic fluid may indicate malformations of the baby, the risk of hypoxia, inflammation in the woman, and the risk of untimely (early) birth.
- The placenta is fully formed by the 36th week of gestation. Normally, the degree of maturation is equal to one. If this value appears earlier, rapid aging is observed, which can cause fetal hypoxia.
- If the placenta is lower than it should be, there is a risk of bleeding. When it blocks the pharynx (fully or partially), the woman will not be able to give birth in the usual way.
If the cervix is not shortened, then a slight opening of the throat does not indicate a risk of premature birth.
Fetal health
During the last screening of the 3rd trimester, preliminary parameters of the unborn child are determined: his height, weight, condition of organs. The specialist correlates all this data with previous data obtained from earlier examinations.
What does the doctor pay attention to when conducting ultrasound diagnostics at 32 weeks:
- The size of the fetal head, circumference and length from the forehead to the back of the head (normal - 95-115 mm);
- The baby's abdominal circumference, which should be from 260 to 315 mm;
- Bone sizes: femur (55 - 65 mm), tibia (52-60 mm), humerus (52-62 mm), forearm (45-55 mm);
- Approximate weight. At 32 weeks of pregnancy, the baby should weigh about 1900 g, and by 33 weeks he can add another 100 g of weight. By this time, he is already fully formed, and in the future, he will only gain weight and height.
Fetal measurements at each ultrasound, comparing them with previous data and tables of norms are called fetometry. This method allows you to track the dynamics of fetal growth, and the correlation with the norms from the table - its health.
The doctor evaluates the condition of the organs and the overall development of the baby, namely:
- Brain. If there are developmental delays, infection or genetic anomaly, ultrasound diagnostics will show this and specialists will be able to begin treatment of the baby without waiting for his birth;
- The face, that is, the nasal bone, nasolabial triangle, eye sockets and jaws. This is also done to determine intrauterine malformation;
- The spine and the presence of a spinous process in each vertebra;
- Internal organs, namely the diaphragm and lungs, kidneys, intestines and stomach.
The study will not exclude developmental defects 100%, but will give an approximate idea of the baby’s health and the opportunity to prescribe treatment and vitamins for the mother.
Often, when doing trimester 3 screening, the doctor warns about the umbilical cord wrapped around the baby’s neck. This can be dangerous, especially during childbirth, but there is no need to be afraid in advance: firstly, the baby moves and turns over in the stomach, and the umbilical cord can still unwind. Secondly, only a few studies can provide an accurate picture, preferably 3D and 4D, in order to see the child as clearly as possible. Thirdly, even if the umbilical cord is wrapped around the neck several times, it’s okay - in these cases doctors do Doppler measurements and additional ultrasound before childbirth, and if there is a risk to the child, they prescribe the woman a cesarean section. Single-turn umbilical cord entanglement occurs in a quarter of all pregnant women, and is not a contraindication for spontaneous childbirth.
Ultrasound with Doppler
To assess the blood supply to the umbilical cord and placental bed, an ultrasound with Doppler is performed. The information obtained helps to detect or exclude defects of the central nervous system, cardiac pathologies, and to assess whether oxygen is supplied in sufficient quantities. Ultrasound with Doppler in the 3rd trimester is necessarily done when:
- gestosis;
- disturbances in the amount of amniotic fluid;
- diabetes in a pregnant woman;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- multiple births.
Ultrasound with Doppler is indicated if in the 3rd trimester there is a discrepancy in the size of the fetus according to the term. During the examination, the following indices are determined: resistance (IR), pulsation (PI), as well as systolic and dialistic blood flow velocity (SVR). The standards are indicated in the table.
| Channels | FROM TO | IR | |
| Arteries | uterine | 1,6-2,1 | 0,34-0,6 |
| umbilical cord | 2,2-4,7 | 0,6-0,8 | |
| midbrain | minimum 4.4 | 0,77-0,8 | |
| Fetal aorta | 4,8-6,8 | 0,75 | |
If the norm is exceeded, this indicates a lack of nutrients and oxygen reaching the fetus. Changes in values in the umbilical cord area indicate late gestosis or hypoxia of the baby in the womb. When the values in the aorta exceed the norm, this indicates the presence of a Rh conflict or that the baby is already past term. A possible arrest of fetal development is indicated by changes in the values of the cerebral artery.
Ultrasound examination is necessary at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy. It is during this period that doctors receive the maximum amount of information. This helps to terminate the pregnancy in time or to prepare parents for possible problems if developmental abnormalities are observed and it is decided to keep the fetus. The due date is also determined, and the method of delivery is determined - natural way or cesarean section.
- Standards for screening in the second trimester of pregnancy.
- How often can you do an ultrasound during pregnancy?
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- The test is positive, but the ultrasound does not show pregnancy
- First ultrasound during pregnancy
How to prepare for your third ultrasound
In order for the third ultrasound during pregnancy to go smoothly and without problems, you need to prepare for it in advance.
To prepare the body, experts recommend not eating foods that cause increased gas formation a day or two before the procedure.
It is also necessary to wash the genitals.
It is better to come to the clinic in advance so that the body is not overstimulated. If an ultrasound is performed on a paid basis, then, as a rule, you do not need to bring anything with you. If in a clinic, you may need a diaper, towel and shoe covers.
At the last scheduled ultrasound, the examination is carried out through the abdominal probe. A woman needs to take a comfortable position on the couch and listen to the recommendations of the diagnostician.
What do they look for at the third ultrasound?
When an ultrasound is performed in the third trimester of pregnancy, it is done transabdominally, that is, an examination is performed through the abdominal wall. In the long term, there is no need for special preparation (drinking liquid before the examination), because the amount of amniotic fluid is sufficient for good ultrasound conductivity and ensuring satisfactory visibility of the analyzed structures. At this stage of pregnancy the following are assessed:
- presence of defects;
- physiological parameters;
- fetal anatomy;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- condition of the placenta;
- position of the child;
- blood flow condition;
- physical activity;
- the presence of contraindications for natural childbirth (low attachment of the placenta or entanglement of the baby with the umbilical cord);
- gender and date of birth.
Who will be born - a boy or a girl?
In the last trimester, with a high degree of probability, it is possible to determine the gender of the future person. But at the deadline of 37-38 weeks, it is difficult to determine the identity using ultrasound for a number of reasons:
- the baby either crosses its legs in the womb or turns its back;
- the baby takes the “sitting on his butt” position;
- equipment quality - the higher the nominal resolution of the device, the clearer the image;
- the human factor - the professionalism and experience of an ultrasound specialist may not be enough to answer the question of interest.
Additional examinations
If the doctor has doubts about the health of the pregnant woman or her fetus, he gives a referral for the following procedures:
- cardiotocography (CTG). The baby's heart rate is measured. Helps to hear the heartbeat, analyze frequency and strength.
- Dopplerography. The blood supply in the umbilical cord, uterus and placenta, the filling of the arteries and veins are checked. Allows timely detection of hypoxia (lack of oxygen reaching the child). If the fetus develops within normal limits, then the study may not be prescribed at all.
Difference between 3D and 4D ultrasound
Any 3D diagnostic device can record movement, which is essentially a four-dimensional image. That is, the dimension of time is added to the standard height, length and depth. This turns a static drawing into a video.
Diagnostics shows the child in motion in real time (online). The procedure is recorded on a digital medium, which parents can receive as a souvenir on the same day.
A 4D diagnosis is carried out in the middle of the second trimester, just like a 3D diagnosis.
Degree of maturity of the placenta
| Week of pregnancy | Maturity level |
| Up to 30 | 0 |
| From 30 to 34 | 1 |
| From 35 to 39 | 2 |
| After 40 | 3 |
A change in the structure of the placenta ahead of schedule indicates its premature aging. The cause may be a violation of blood flow caused by gestosis (a complication in which blood pressure increases, protein appears in the urine, swelling) or anemia (decreased hemoglobin). Sometimes this is simply a consequence of the individual characteristics of the expectant mother.
If such a deviation is detected, Doppler and cardiac monitoring studies are prescribed.
During an ultrasound, the amniotic fluid is necessarily assessed - its quantity and quality. It must be transparent and free of any foreign impurities. The presence of mucus, flakes, or cloudy water may suggest an infection.
The amniotic fluid index is used to determine its quantity. A lag from the norm is a sign of oligohydramnios, an excess is a sign of polyhydramnios.