Purpose of the survey
Between 10 and 12 weeks the fetus is just beginning to develop, and ultrasound can help identify and prevent possible future health problems. It is necessary to examine the amniotic sac and umbilical cord. An ultrasound at 12 weeks is the first of three scheduled examinations of this type; the Ministry of Health recommends undergoing ultrasound diagnostics every trimester of pregnancy.
This screening allows you to:
- find out whether fetal development is proceeding correctly;
- understand whether the embryo has genetic pathologies;
- find out the gender of the child;
- detect ectopic pregnancy in time.
Indicators studied
When undergoing an ultrasound at 12 weeks, the doctor evaluates the following indicators of fetal development and the course of pregnancy:
- Fetal dimensions : body length, fetal head size, length of some bones.
- Symmetry of the cerebral hemispheres. This indicator allows you to objectively assess the correct formation of the central nervous system and exclude the occurrence of pathologies. Normally, when performing an ultrasound at 12 weeks, the image of the brain should look like a “butterfly”. Asymmetry of the cerebral hemispheres is one of the signs of such a chromosomal disorder as triploidy (a complete additional set of chromosomes).
- Location of the stomach, heart and other organs.
- Determining possible heart defects.
- Assessing brain structure . Disruption of the formation of brain structures can be diagnosed in the presence of Patau syndrome and some other diseases. For example, with triploidy, the process of dividing the brain into sections is disrupted.
- Identification of signs of possible genetic diseases (Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc.).
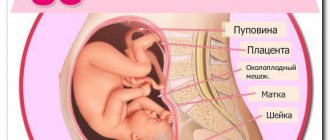
- Place of attachment of the fetus to the placenta . Normally, the “baby place” should be attached to the front or back wall of the uterus at the bottom of the uterus. With central placenta previa (it covers the internal os), a cesarean section may be recommended as the baby’s due date approaches, if the situation does not normalize in the future.
- Inspection of the umbilical cord . The norm is the presence of two arteries and one vein in it. Detection of only one artery indicates the possible development of Edwards syndrome in the fetus.
- Determination of the condition of the walls and cervix . The length of the cervix should not be less than 30 mm, otherwise the expectant mother may be prescribed bed rest and hospital treatment.
- Clarification of gestational age.
important The sex of the fetus can also be determined, but not in all cases, since external differences in gender during this period are still barely distinguishable.
At week 12, ultrasound can be performed either transvaginally (using a probe inserted into the vagina) or abdominally (using a transabdominal probe) through the skin of the abdomen. To prepare for an abdominal examination during this period, a woman needs to drink 0.5 liters of still water half an hour before the examination.
Methods of carrying out
There are two ways to perform an ultrasound at twelve weeks of pregnancy:
- Abdominal. When examining with this method, the doctor runs a sensor along the outer surface of the peritoneum.
- Transvaginal. This examination is performed when the sensor is inserted into the vagina.
The choice of method for conducting an ultrasound examination depends on the following factors:
- exact date of pregnancy;
- mother's weight;
- general condition of the pregnant woman.
An ultrasound scan takes place at a local clinic or at a private doctor. The doctor may allow the woman to choose the method of carrying out the procedure if there is no indication for examining the vagina from the inside.
Abdominal method
The abdominal method is rarely used at such a short stage of pregnancy, because due to the small size of the embryo, the resulting image is of very low quality.
Transvaginal method
The transvaginal technique allows you to most accurately examine the condition of the embryo. Also, using this method, you can reliably estimate the size of the collar area of the unborn child, deviations from the norm which may indicate the possible presence of Down syndrome.
Preparing for the study
Transabdominal ultrasound does not require special preparation. It can be performed immediately after visiting the obstetrician-gynecologist's office. All that is necessary is to drink about half a liter of liquid before the examination. This is necessary to improve the passage of ultrasonic waves.
A transvaginal ultrasound will require slightly more preparation. The day before the test, you will need to follow a diet that excludes all gas-forming foods. These include fermented milk products, fresh vegetables and fruits (especially legumes, cabbage, banana, etc.), fresh baked goods.
Before the study, if you still cannot get rid of the gases, then you need to take a carminative, for example, espumizan. Also, some sonologists recommend emptying the bladder.
How to prepare for the examination
Preparing for an ultrasound at 12 weeks of pregnancy includes several simple steps:
- Before the examination, hygiene procedures are required.
- If an ultrasound is to be performed using the abdominal method, you must drink at least half a liter of liquid before the examination. Thanks to this, the internal organs will expand slightly and the fetus will be better visible during diagnosis.
- You do not need to drink water before a transvaginal ultrasound. Before visiting a doctor, you should drink activated charcoal to reduce gas formation in the intestines.
For an ultrasound, a woman must bring a towel and napkins with her, and for a transvaginal examination a condom is required.
You should also take with you to your appointment with a diagnostician:
- medical card;
- medical insurance;
- passport.
How is an ultrasound performed?
The method of ultrasound examination of pregnant women at the end of the first trimester is chosen by the doctor depending on the structure of the woman’s organs, body type, and the presence of obesity. In early diagnosis, some details of pregnancy may not be visible due to the above factors.
Most often, gynecologists use transvaginal ultrasound in the first trimester. Later, in the second trimester, when the fetus begins to move beyond the pelvic area, the doctor conducts a transabdominal examination. A pleasant bonus when examining through the anterior abdominal wall is that during pregnancy no preliminary preparation is needed, you do not need to drink a liter and a half of water in advance. The uterus with amniotic fluid will act as a screen conducting high-frequency waves.
Some gynecologists combine both methods in the first trimester: through the surface of the abdomen and transvaginal. Before starting an ultrasound, ask your doctor what preparation is required.
Transvaginal ultrasound is performed with the woman lying horizontally with her back down on the couch. Some medical centers use a special ultrasound chair. For the study, the gynecologist uses a narrow sensor, no more than 3 cm in diameter, protected by a special disposable condom without lubricant. The converter operates at a frequency of 5–7.5 MHz and allows you to examine even the smallest nuances in the development of the fetus.
For the fetus, a short-term examination, no longer than 15 minutes, is safe with ultrasound. During the entire gestation period, the number of ultrasound scans is limited to three to four.
What does an ultrasound show?
During an ultrasound, pregnancy development is analyzed using the following indicators:
- Formation of the umbilical cord. For the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth, there must be two arteries in it.
- Condition of the cervix and uterine walls.
- Fruit size. The size of the body, head, and the length of some bones are specified.
- The point where the baby attaches to the placenta. The optimal location should be on the side or at the bottom of the uterine wall. A different situation may give reason to recommend a cesarean section during childbirth.
- Formation of the baby's nervous system. They look at the condition and development of the brain hemispheres. This makes it possible to identify genetic diseases at an early stage.
- The position of the child's vital organs. Screening will show how the baby’s heart, kidneys, liver, and lungs are located at the initial stage.
- Formation of the brain.
- Exact gestational age.
- Amount of children. An ultrasound allows you to find out whether a woman will have twins or twins.
- Work of the heart.
In the video provided by the Sparrow Family / Life of a Large Family channel, you can see what a baby’s fetus looks like at the 12th week of pregnancy.
With an ultrasound at 12 weeks, the baby’s movements can already be tracked. Its activity starting from 7–8 weeks of pregnancy is an important indicator of development.
Fetal development at 12 weeks of gestation
It is at the first planned ultrasound that a woman is able to find out what her unborn child looks like, and the doctor is able to study in detail the internal and external development of the embryo. At week 12, it has the size of a small plum or an exotic passion fruit - its weight is approximately 19 grams and the length of the body reaches 9 cm. But at the same time, despite such small sizes, the child’s brain has already managed to fully form and become a smaller copy of the adult’s brain.
Now the face is more clearly visible, but in comparison with the forehead it is small, the eyes are recognized, and the inner part of the ear is being formed. Also during this period, the pituitary gland continues its development - the main endocrine gland, on whose activity human growth, metabolic processes and reproductive function depend.
The peripheral nervous system is already so formed that the fetus has quite high sensitivity in the face and limbs
By this time, he can bend and straighten the formed fingers and toes, on which tiny nails are already growing. Moreover, the baby can suck his thumb, which some mothers were sometimes even lucky enough to see during the study, and he already has grasping reflexes. Someone could see on an ultrasound how the child opens and closes his mouth, since his oral muscles are already developed.
He not only moves his mouth, but also swallows amniotic fluid and also urinates in it. The entry of such water into the fetus’s body is not considered dangerous for two reasons - first, because the child’s urine is not similar in composition to the urine of an adult. And the second is the complete renewal of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) within an hour. The woman and her companions for the procedure can see how the baby floats in the liquid surrounding him, and although his movements are erratic, they perfectly train his small muscles.
Some parents can sometimes get lucky at the first ultrasound screening and be able to find out whether they are having a boy or a girl in the near future. It’s not often, but it still happens that a good specialist manages to accurately determine the gender of the fetus. Although it happens that the baby is positioned in such a way that his sexual characteristics are covered by an arm or leg or the umbilical cord and then it is simply impossible to see them.
An error may occur due to the inexperience of the doctor, who will mistake the umbilical cord section for the boy’s genital organ, and the parents will remain until the next ultrasound, waiting for the birth of their son. So it’s better not to rely too much on a 100% determination of the baby’s gender at 12 weeks, but to wait until 20-22 weeks when the information obtained using high-precision ultrasound machines in 3D format will be as reliable as possible.
Ultrasound procedure
With transvaginal and abdominal methods, the ultrasound examination procedure is carried out in various ways.
Transvaginal ultrasound examination proceeds as follows:
- The woman should expose her lower body for ease of insertion of the sensor.
- A condom is placed on the transvaginal sensor and lubricated with gel.
- An ultrasound probe is passed through the woman’s reproductive organ.
- The sensor transmits data to the monitor using an ultrasonic wave.
- The information received is analyzed by a doctor.
This method allows you to get close to the baby and professionally determine the parameters and characteristics of the fetus. At the same time, the ability to correctly determine the sex of the child increases.
The abdominal method involves the following stages:
- The woman exposes the abdomen.
- The sensor is treated with gel and moved over the pregnant woman’s abdomen.
- The monitor displays a picture of the study, where you can see the outlines of the unborn child.
- The specialist takes indicators of the fetus’s condition and enters them into the ultrasound protocol.
- The result is checked by a diagnostician and reported to future parents. The doctor also gives them pictures of the baby.
What will an ultrasound show at 12 weeks?
The examination allows you to safely assess the condition and development of the fetus. If the gestation period is successful, it is the first examination of the pregnant woman. With the help of ultrasound examination at this time you can:
- clarify the duration of pregnancy and determine the expected date of birth;
- determine the number of fetuses in the uterus;
- determine fetal viability;
- look at the child’s development, assess his vital functions;
- search for markers of chromosomal pathology of the fetus indicating the possible presence of Edwards, Down, Patau, Turner syndrome, Cornelia de Lange disease;
- detect pathology of the mother’s reproductive organs;
- diagnose threatened miscarriage, detachment of the ovum and other possible pathologies$
- measure the size of organs and compare them with the norms at the prescribed time - fetal fetometry.
Fetometry of the fetus
At this stage, the fetus already looks like a person, its arms and legs are already formed, even its fingers are visible. The baby is very active, moves his arms and legs, and may play with the umbilical cord or suck his thumb.
The internal organs have formed and many are already functioning. The weight of the fetus is 14-15 grams, height 45-80 mm.
Important! Not all of the above features can be seen on an ultrasound at 12 weeks; not all antenatal clinics and clinics have a modern ultrasound machine with high resolution and detail. But any scanner will show the movement of the fetus and the mother can hear the heartbeat of her child.
Decoding the results
Diagnosticians and geneticists are engaged in a detailed interpretation of the research results. Only they can give professional answers and recommendations at the end of the procedure.
There are several basic normative values that are used as a guide when performing an ultrasound:
| Parameter | Normal at 12 weeks of pregnancy |
| Height | 8–10 cm |
| Weight | up to 19 grams |
| Thigh length | 7–9 mm |
There are also certain norms specific to the 12th week of pregnancy:
- KTR;
- BPR;
- TVP;
- nose length;
- Heart rate;
- embryonic structures.
KTR norms
The coccygeal-parietal size, or abbreviated CTR, is the maximum distance that can be measured from the head to the tailbone at 10-14 weeks. CTE is the most accurate parameter for determining the duration of pregnancy. Normally it should be from 51–59 mm.
Norms of BPD of a child's head
Bi-parental size (or BPR) allows you to determine the size of the head, and therefore the level of development of the child’s brain. BPR is the width of the head, measured along the minor axis, from temple to temple. Normally it should be 21 mm.
Neck fold size, or TVP
The thickness of the collar space (or neck fold) in a child should be from 1.6 to 2.5 mm.
Norms for the length of the nose and nasal bone
A twelve-week-old fetus has a nose (nasal bone) 3 mm long.
Heart rate norms
The heartbeat is the main indicator of the vitality of the unborn child, which reflects its condition and changes if any unfavorable situation arises. The heart rate should be 150–174 beats per minute.
Standards for the study of embryonic structures
Extraembryonic structures are:
- Yolk sac. A provisional organ that performs various functions in the body of the embryo until the corresponding organs are formed (for example, the liver and spleen). By the 12th week, the yolk sac should not be visible; by the 10th week it may look like a white ring up to 7 mm in size.
- Chorion. The outer shell of the embryo is formed in the first days after conception and ensures the exchange of substances between the body of the mother and the baby throughout the pregnancy. The chorion has the appearance of a white ring with villi. Its thickness in millimeters in digital value is approximately equal to the woman's gestational age in weeks.
- Amnion. The aqueous membrane that fits tightly to the chorion. The amniotic material must form correctly. Its developmental pathology may be associated with an infection in the mother's body.
The correct formation of these structures affects the entire course of pregnancy, as well as childbirth and the health of the baby.
Data obtained during the study
During a 12-week pregnancy, ultrasound allows you to study many parameters that are important not only for determining the current state of the woman’s and child’s organs, but also for predicting the course of pregnancy and even childbirth. In general, week 12 heralds the end of the first trimester, which means a third of the pregnancy is already over.
At this stage, the number of fetuses is clearly visible and you can even clarify whether they will be twins or twins. That is, starting from the first trimester, future parents can know how many children are waiting for them.
Another important indicator is presentation. This indicator characterizes the position of the fetus relative to the birth canal. At 12 weeks, it can be very varied and often changes until the third ultrasound, which will be performed at 32 weeks. This means that there is no need to take measures regarding presentation after the first ultrasound. The situation may indeed be completely askew.
But as for the parameters that are digital, everything is much more complicated. Of course, there are standards, but it will not always be correct to rely on them. This is because any clinical case must be assessed individually.
The doctor looks at the constitutional characteristics of the father and mother, their race and other indicators, because we are all different, which means there will be different children. That is, during an ultrasound scan of a 12-week pregnancy, the parameters should be deciphered by an obstetrician-gynecologist who has the maximum amount of information about the woman and her closest relatives, both on her side and on the father’s side. But as for the general rules, they are as follows:
- height - about 82 mm;
- weight - within 17-19 grams;
- biparietal size (BPR) - a size equal to the segment drawn between the parietal bones - about 12 mm;
- thigh length (DlB) - 7-9mm;
- The coccygeal-parietal size (CTR) is a size that is equal to a segment drawn from the highest point of the parietal bone to the farthest point on the coccyx. It is on average 4.3-7.3 cm.
Separately, it is worth highlighting such an indicator as the size of the collar space. It is important in the diagnosis of gross chromosomal diseases. A striking example is Down syndrome. Normally, this parameter should not exceed 2.7 mm. On average, the parameter is within 1.6 mm.
The parameters described above are not the entire list of those necessary for diagnosis and a complete picture. The following are assessed: the volume of the abdominal cavity, the growth of individual limbs, some internal organs and many others. Thanks to this, the fetal body is studied comprehensively, and not separately by organ. That is, if there is no growth of limbs or any organs, then this is a very serious problem, which may well lead to the need for artificial termination of pregnancy.
However, do not panic if any parameters are not within the normal range. Usually, if a serious pathology is suspected, a repeat examination is prescribed, which is necessary to clarify the diagnosis of intrauterine growth retardation. Sometimes the reason for suspicion may be a simple error in calculating the week of pregnancy.
In addition to the characteristics of the fetus itself, amniotic fluid is also assessed. The very first thing people pay attention to is volume. A large or small number of them, polyhydramnios (polyhydramnios) or oligohydramnios (oligohydramnios), respectively, indicates problems in the functioning of the central nervous system or the mother’s kidneys. Also, this parameter, together with the fact that the waters are cloudy, indicates an intrauterine infection.
We must not forget about the authorities that provide “temporary residence” for the child. First, you should discuss possible problems with the placenta. The doctor conducting the diagnosis must first pay attention to the place of its attachment. The best place is the posterior wall of the uterus, followed by the anterior and fundus. Sometimes the placenta can block the internal os of the uterus - this is called central placenta previa.
In this case, delivery must be carried out by caesarean section. Such early detection positively contributes to the earliest possible preparation of doctors and the woman herself for the upcoming operation.
A similar situation is called low placenta. It differs in that in this case the placenta is extremely close to the os of the uterus. The danger lies in the high probability of bleeding if childbirth takes place naturally. If this is detected, then the woman needs to limit her activity. In this case, the placenta often “rises” at 32 weeks and there is no need for a caesarean section.
The next indicator is “placenta maturity.” Normally, its degree at this time is zero. If the structure becomes lobulated, then it already indicates the second degree and now you need to see a doctor to solve this problem, which, unfortunately, is not uncommon.
Among the pathological inclusions, it is worth highlighting calcifications. Formations that appear as a result of spasm and then death of blood vessels, which leads to calcium deposition and, as a result, hardening. Most often occurs in pregnant women who smoke, since smoking promotes vasospasm. If a small number of vessels are damaged, this is not dangerous and is compensated by other vessels. A placenta with calcifications has the first degree of maturity.
Detection of areas of infarction in the placenta requires urgent consultation with a doctor. A heart attack is the death of a section of the placenta. If it is detected, you need to urgently find out the reasons, and later perform a repeat ultrasound. As it progresses, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus decreases, which leads to hypoxia. The developing fetus is extremely susceptible to the effects of the already mentioned hypoxia and its effects can lead to irreparable consequences in the central nervous system.
Ultrasound photo at 12 weeks of pregnancy
Possible pathologies
Ultrasound examination for pregnant women is a way to find out about possible pathologies in time and take medical measures if necessary.
Deviations from the norm
Deviations from the norm during this period are considered:
- Greatly increased TVP. In addition to the thickness of the collar zone, the length of the nose is checked; its shortening (hypoplasia) indicates the development of pathology.
- For doctors, a dangerous sign is the underdevelopment of the yolk sac (if it is less than 7 mm) and the size of the chorion and amnion at 6 weeks is less than 10–12 mm.
- The heartbeat in pathologies can be either greatly reduced (85–100 U/m) or very high – up to 200 beats per minute.
Symptoms of genetic abnormalities
Genetic abnormalities occur during the process of conceiving a child, when two single-chromosomal sperm fertilize the mother's egg.
An ultrasound can show the following diseases:
- Down syndrome;
- triploidy (the presence of 69 chromosomes in each pair instead of 42);
- Edwards syndrome;
- Patau syndrome;
- Turner syndrome.
More detailed descriptions of genetic diseases and their consequences:
| Genetic disease | Manifestations in appearance | Intelligence and mental state | Forecast |
| Down syndrome. The chromosomes of the 21st pair are represented by 3, not 2. |
|
| Socialization is possible in case of constant attention and care. Life expectancy is up to 60 years. |
| Patau syndrome. Trisomy on chromosome 13. |
| Thought and speech are not present | Life expectancy is from 3 to 5 years. However, more than 95% of patients survive only up to a year. |
| Edwards syndrome. Trisomy on chromosome 18. |
| There are different degrees of mental retardation:
| 90% of patients survive only up to a year |
| Turner syndrome. Mutation of the X chromosome. |
|
| Treatment is possible. A course of hormonal medications is prescribed. But most patients cannot have children. |
Cervix and myometrium
The data obtained during the study is extremely important. Deviations in these indicators may indicate a very possible spontaneous termination of pregnancy. The length of the neck should not be shorter than 3 cm. If the indicator is small, then urgent hospitalization and careful observation are necessary. In this situation, the problem can only be solved surgically.
Another important indicator is the condition of the external and internal os of the cervix. They should both be closed. As for the condition of the myometrium, that is, the muscular layer of the uterus, everything is no less serious. The presence of uterine hypertonicity can lead to termination of pregnancy.
In addition to confirming such a diagnosis on an ultrasound, a woman may feel that her stomach seems to “turn to stone.” In this case, hospitalization is also necessary. But if hypertonicity is not severe and there are no complaints, then treatment can be carried out at home.
What signs are used to determine the gender of a child?
At 12 weeks of pregnancy, the sex of the child is not determined with one hundred percent probability using ultrasound - the baby’s physiology is not yet sufficiently developed, and it is difficult for the doctor to give an unambiguous answer. The baby himself can help the doctor with this if he is in a position comfortable for the ultrasound examination. Then the specialist will be able to see the developing genital organs of the fetus.
Definition of boy
To confirm pregnancy with a boy, the doctor must see the rudiments of the genital organs of the male fetus.
If it's a boy, the ultrasound shows:
- A tubercle (labioscrotal eminence) between the baby’s legs. There is an angle of thirty degrees between this hill and the child’s back.
- The jaw is shaped like a square.
- In a pregnant woman, the placenta is on the right side of the uterus.
Definition of a girl
If a woman is having a girl, an ultrasound will show:
- the placenta is on the left side of the uterus;
- the skull and jaw are visually similar to a circle;
- the genital organ has transformed into the clitoris from the genital fold, and the labia are already noticeable;
- The angle between the genital tubercle and the back is less than 30 degrees.
How are twins determined?
It is possible for a woman to become pregnant with twins. There are monozygotic and dizygotic pregnancies. In the first case, the children are very similar to each other and are always of the same sex. Dzygotic twins are often born opposite sexes.
A doctor can determine a multiple pregnancy based on the following parameters:
- two heads of children are displayed on the display;
- a woman’s uterus enlarges at very early stages;
- a depression appears in the structure of the uterus.
To hear the heartbeat of the twins, phonocardiography is prescribed. This study can be done at the twentieth and earlier weeks of pregnancy.
Photo gallery
Photo of a girl, about 12 weeks
Photo of twins
Ultrasound photo, girl
Ultrasound photo, boy
Photo of a boy, 12 weeks
The difference in ultrasound images of a boy and a girl
What is screening and how does it differ from regular ultrasound?
Screening is a set of mandatory procedures performed to monitor the progress of pregnancy. The main examination is carried out using ultrasound to determine the physical characteristics of the fetus and the reproductive system of the mother. As part of the first screening, blood is also taken from a vein, followed by a biochemical analysis of the biological material taken.
On the one hand, a genetic ultrasound scan at 12 weeks is part of a regulated routine screening, on the other hand, it can be performed separately if there are appropriate indications, including when the patient is classified as a risk group for one or a group of indicators.
Video
This good quality video, presented by the Doctor Nikolaev Medical Center channel, will help you learn more about how an ultrasound is performed and the gender of the child is determined.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 1 vote(s), average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Why is ultrasound diagnostics needed in the first trimester of pregnancy?
An ultrasound examination, along with a biochemical blood test, is included in the first screening, which is usually carried out between the 11th and 14th gestational weeks. It is mandatory for all pregnant women. The patient has the right to refuse to undergo it, but must be aware of all the risks to which she exposes herself and the baby.
Screening at 12 weeks of pregnancy is an important step towards having a healthy baby. During this procedure, the doctor may:
- analyze the growth and maturation of the fetus;
- detect pathologies in the formation of internal organs;
- compare the results obtained with established standards;
- carry out diagnostics to determine if there is a threat of miscarriage.
Is it necessary to do an ultrasound before 12 weeks?
An ultrasound scan before 12 weeks of pregnancy is not necessary if the woman does not belong to the so-called risk group. This includes:
- primiparous women whose early pregnancies ended in miscarriages;
- the presence of genetic diseases of one or both parents, including in previous generations;
- patients who have previously given birth and whose children were diagnosed with Down syndrome;
- if a pregnant woman took prohibited medications for medicinal purposes in the early stages;
- women over 35 years of age.
In these cases, the observing gynecologist may refer the expectant mother for an unscheduled ultrasound.
When to do the next ultrasound
The first examination procedure using ultrasound is an important and crucial moment in the life of every expectant mother. Even if this is the second pregnancy, and the woman knows what it is like to meet a baby in her tummy, the sensations are indescribable every time. Especially at the moment when the mother is allowed to listen to the brisk and loud heartbeat of the little man. I want this moment to last as long as possible.
So, what week are the next ultrasound scans performed? If the pregnancy proceeds calmly and without complaints, then the next ultrasound screening will not be earlier than in two months.
At 20-24 weeks, the mother will have a second screening with a mandatory visit to an ultrasound diagnostic doctor. He monitors the anatomical structure of the fetus, and also assesses the condition of the placenta, umbilical cord, and cervix.
After this, the woman will have to undergo a third screening test in the period from 32 to 34 weeks. On it, the determining indicators are the position of the child (head down or up) in order to develop a strategy for the upcoming birth. The baby’s motor activity and the degree of maturity of the placenta are also recorded. With the help of ultrasound, gynecologists want to make sure that the baby is comfortable and calm in the mother’s belly, and nothing threatens his health.
Normal values for the thickness of the collar space
The norm of TVP developed for each stage of pregnancy is presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
| Gestational age | Normal value of TVP, mm |
| 10 weeks 0 days – 10 weeks 6 days | 0,8 – 2,2 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 11 weeks 6 days | 0,8 – 2,4 |
| 12 weeks 0 days – 12 weeks 6 days | 0,7 – 2,5 |
| 13 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 0,7 – 2,7 |
If during an ultrasound your unborn child’s TVP is revealed to be higher than normal, you should not immediately panic, since we have already described above that there may be many reasons for this, including his completely healthy condition.
But still, fetuses with TVP of more than 3.0 mm at 11-14 weeks have a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
TVP is also measured to predict possible risks of pregnancy. In fetuses with a normal karyotype and an increase in TVP, the risk of preterm birth, heart defects and other fetal abnormalities increases.
TVP values at 14 weeks of pregnancy and later
Normally, after the 14th week of pregnancy, the collar area begins to gradually decrease.
If an increase in TVP continues to be recorded during examination at week 14 and later, or the accumulation of fluid turns into swelling of the neck or generalized edema of the fetus, then this indicates a high probability of infectious infection of the baby or the presence of a genetic pathology. In this case, the blood of a pregnant woman should be examined primarily for the presence of toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus and parvovirus B 19. Also in this situation, regular repeat ultrasounds every four weeks are indicated to identify the dynamics of edema.
Thus, ultrasound, and in particular the measurement of TVP at 11,12,13,14 weeks of pregnancy, helps to identify and, in some cases, prevent the birth of children with chromosomal pathologies. Therefore, women are strongly advised not to avoid undergoing the 1st screening.
Why they do it and what can be seen on the first ultrasound
Summarizing the above, we can conclude that ultrasound in the 1st trimester of pregnancy is done to ensure that conception has taken place, the correct course of the gestation process, as well as the health of the mother and child. Each week of the first three months of bearing a child has its own characteristics in improving the anatomical structures of the embryo. The picture that the diagnostician and mother will see at the first screening depends on this.
- From 5 to 9 weeks, the outlines of the fertilized egg are visible. From the 5th week, the baby’s heartbeat can be traced in the form of a pulsation; from the 7th week, the embryo begins to acquire human characteristics. On the monitor you can see a disproportionately large head, as well as a small tail. With modern equipment, from the 9th week you can hear the baby’s heart beating. At an early stage, when the tissues of the internal organs of the fetus are not yet formed, its size is an indicator of development.
- At 10 and 11 weeks, specialists have the opportunity to measure not only the size of the fetus, but also some parts of the body. Many internal organs are clearly visible, including the heart, kidneys, liver, bladder and stomach. The specialist can identify the risk of possible abnormalities in the child and markers of chromosomal abnormalities (including Down syndrome).
- If we talk about planned ultrasound screening of the 1st trimester, it is carried out for all pregnant women at approximately the same time - at 12-13 weeks. This period was not determined by chance: it is during this period that there is a chance to find out reliable information about the baby’s health condition. The doctor will already see the outlines of the face, chest and tummy. The limbs are clearly visible in the photo, and with modern equipment the fingers are clearly visible.
A mandatory step is to examine the heart with the sound of its beating. The doctor measures not only the size and weight of the child, but also CTR (size from the coccyx to the crown), BPR (bipariental head size), the length of the nasal bones and TVP (thickness of the collar space). This is necessary to identify genetic abnormalities.
During the ultrasound screening, a video is recorded and photographs are taken in 3D format, which are kept as souvenirs for the parents. In addition, you can find out the gender of the child. It is possible to determine who is in the womb - a boy or a girl - if the study is carried out using high-precision equipment and there is a convenient angle. However, when determining the sex of a child, there is a possibility of error.
Ultrasound results of 12 weeks pregnancy
The ultrasound examination procedure at 12 weeks of pregnancy is carried out using a transvaginal sensor. The procedure is carried out in a supine position, with the legs pulled up to the stomach. An ultrasound device, covered with a condom, is inserted into the vagina; the woman does not feel any sensations in the form of pain.
A transabdominal examination consists of the following: a sensor is passed along the abdomen, selecting the best position for displaying the results of the fetal condition on the screen. The ultrasound photo will clearly display the size of the body, which has disproportionate shapes: the head of the embryo is much larger than the body.
Prenatal screening is prescribed to assess fetal development. The procedure is possible after undergoing an ultrasound. Its use is recommended for the study of women aged 35 years and older who have previously had stillbirths. Screening is done in special medical centers for women who are 12 weeks pregnant.
The ultrasound image and its results are issued by a geneticist. Particular attention is paid to the collar zone and the levels of free β-hCG and PAPP-A after blood donation. Ultrasound during pregnancy does not have any negative effects on both the mother and the child.
The price of an ultrasound scan during pregnancy ranges from 1,000 to 3,000 rubles.
What can you see on an ultrasound?
- Child sizes.
- Cerebral hemispheres and their symmetry.
- Location of the internal organs of the embryo.
- Brain structure.
- Heart pathologies.
- Symptoms of genetic disorders.
- The place where the embryo is attached to the placenta.
- Condition of the umbilical cord (normally, 2 arteries and one vein should be visible).
- Indicators of the walls of the uterus and its cervix.
- Exact gestational age.
The average fetal ultrasound findings are as follows:
- baby weight - 9-13 g;
- fruit length - 6-9 cm;
- KTR - 51-63 mm;
- biparietal head size - 21 mm;
- chest volume - 24 mm;
- thigh length - 9 mm;
- thickness of the collar space - 1.6-2.5 mm;
- nasal bone size - at least 3 mm;
- heart rate - 150-175 beats/min.
Woman's condition
At 12 weeks, a woman will finally be able to say goodbye to toxicosis, which was caused by the work of the corpus luteum (temporary gland). At the end of the first trimester, its function (the production of progesterone, which is responsible for maintaining pregnancy) passes to the placenta. Against the background of the disappearance of nausea and vomiting in the morning, the general health of the pregnant woman improves.
If the expectant mother’s toxicosis was mild or completely absent, then by 12 weeks she will gain 2–3 kg of additional weight. If vomiting was frequent, then body weight may not change or even decrease (normal). If a woman is lucky enough to be carrying twins, then the symptoms of toxicosis may accompany her longer (up to 14–16 weeks).
The size of the fetus at the 12th week of pregnancy reaches 6–7 cm in length, and its weight does not exceed 13 grams
By the 12th week, the size of the uterus already reaches 10 cm. As a rule, this reproductive organ at the end of the first trimester no longer fits in the pelvis, so it gradually rises into the peritoneum. This has its advantage - now the uterus puts less pressure on the bladder and the frequent urge to urinate no longer bothers the woman so much. But a new problem appears - the uterus can put pressure on the intestines, which causes constipation and flatulence.
In addition, an increased amount of female sex hormones in the blood is reflected on the skin. The face and other parts of the body may become covered with dark pigment spots, which usually disappear after delivery. Some pregnant women experience improvement in the condition of their hair, nails and skin during pregnancy. Others, on the contrary, develop acne and seborrhea.
What is a screening test and why is it needed?
The 12th week of carrying a baby is special in that planned prenatal screening is prescribed for the first time at this time. This is a comprehensive examination, during which all data about the condition of the child and his mother is collected. What is included in the first screening during pregnancy?
The main screening procedure is a two-dimensional ultrasound scan of the fetus. Screening also includes an ultrasound of the mother’s pelvic organs, a biochemical blood test, and a three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound of the baby.
A regular ultrasound scan at 12 weeks is absolutely safe and does not pose any danger to the baby and his mother, contrary to countless rumors. During examination, ultrasound waves are scattered in all directions, and the child does not receive the slightest radiation. Moreover, ultrasound is practically the only method for diagnosing the condition of a little man, which has no contraindications. Ultrasound scanning can be used at any time and as many times as desired.