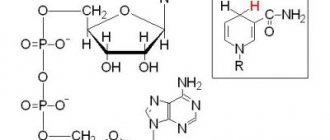
For a pregnant woman at 19 weeks, a kind of milestone comes - almost half of the difficult path to the birth of a new life has already been completed. An enlarged belly at the 19th week of pregnancy is perceived as usual; the need for care over an unborn baby increases every day. The stage of daily mutual communication between future parents and the child begins, since he is already actively making himself known through movements, reacting to intonation, hunger, stroking and other external stimuli. An ultrasound at 19 weeks of pregnancy will help monitor the process of intrauterine development.
Why is the study done and to whom is it recommended?
Ultrasound diagnostics in accordance with the second screening program is prescribed to all pregnant women.
For a certain category of patients, the risk of developing genomic pathologies of the fetus increases:
- Age over 35 years.
- Patients with children or relatives with genetic disorders.
- Age up to 17 years.
- Taking medications contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Poor results of the first screening.
- History of miscarriages, threat of miscarriage during current pregnancy.
Week 19 is considered the most informative period for determining anatomical pathologies accompanying congenital syndromes and diseases.
Important! Patients whose first screening results indicate a high probability of genetic diseases in the child are subject to mandatory examination. Diagnostics will restore calm and confidence to a woman who is worried about the health of her baby.
How is diagnostics carried out?
At nineteen weeks, an ultrasound scan is done with a transabdominal probe: the insides are visible through the anterior abdominal wall. The woman is placed on the couch on her back, with her stomach exposed. The sonologist applies a special gel to the lower abdomen. Afterwards, the sensor is moved into the uterine area. Data from the sensor is transmitted to the screen of the ultrasound machine.
Usually, paid clinics have 2 monitors so that the pregnant woman can also monitor the progress of the procedure. You are allowed to come to the ultrasound with the father of the unborn child.
After the ultrasound diagnosis, you can take a photo of the baby.
To watch a video on the topic:
Mother's condition and fetal development
For the expectant mother, pain in the back and lower back becomes more intense. The joints gradually diverge, ensuring the unhindered passage of the fetus in the upcoming birth.
During this period, the movements of the child in the woman’s womb become intense. The baby begins to react to the mother’s voice, perceives light, and becomes anxious at loud sounds. The immune system is being developed.
Parts of the brain and the central nervous system are intensively developing. The lungs and bronchi pass through a critical stage of formation. The child’s movements acquire a meaningful character as a response to external stimuli.
How does the child develop by the beginning of the second half of the gestational period?
Intrauterine development of the fetus is almost complete by mid-pregnancy. In case of premature delivery, in a prenatal center equipped with the latest technology, the baby has a chance to survive:
- his body is completely proportional and will remain so until childbirth;
- milk and molars are formed;
- subcutaneous fatty tissue accumulates - folds form on the skin and a papillary pattern on the fingers;
- the immune system is actively developing;
- meconium is formed in the intestines - original feces;
- the functional activity of the kidneys begins - they secrete urine;
- hearing and reaction to touch are well developed.
What does ultrasound diagnostics show, what does the doctor look for?
The specialist assesses the possibility of spontaneous abortion and the condition of the cervix. At week 19, the diagnosis establishes Down syndrome, which may not produce symptoms for a long time.
The following indicators are carefully analyzed:
- size, shape of the head;
- body dimensions;
- size and shape of limbs;
- correspondence of the structure of the brain to the age of the fetus;
- gender of the child;
- location, size, construction of internal organs;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
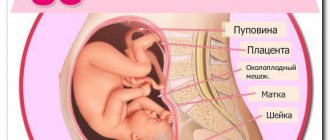
- condition of the placenta;
- structure and location of the umbilical cord, number of vessels;
- uterine tone, ovarian condition.
The absence of external abnormalities of the fetus, internal defects, systems, and complete blood supply to the placenta indicate a successful state of pregnancy.
Deviations from the norm are not a death sentence.
The patient will be asked to undergo an examination after 7 days to monitor the development of the fetus.
Attention! For timely treatment, it is necessary to conduct a timely examination, since after 22 weeks of development, anomalies are difficult to correct.
The specialist carefully examines the baby’s face, identifying markers (signs) of intrauterine pathologies. The examination allows us to identify previously undetected genetic and hereditary diseases.
Method of conducting ultrasound examination
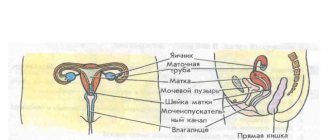
The diagnostic procedure is carried out transabdominally - an ultrasound sensor is placed on the anterior wall of the woman’s abdominal cavity. The patient is not required to carry out complex preparatory measures - the uterine cavity is of impressive size and the amount of amniotic fluid allows high-frequency sound waves to penetrate to the fetus without any problems. The transvaginal ultrasound diagnostic method, with which you can carefully examine the condition of the birth canal, can be used if the patient suspects premature termination of pregnancy.
To conduct an ultrasound examination, the expectant mother is positioned on her back or side (if the fetus is quite large, the position on her back puts pressure on the inferior genital vein)
What does a photo of the fetus allow you to see?
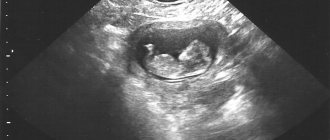
An ultrasound photograph can capture a child while he or she is awake or asleep. Mom will see a face, hands with tiny fingers. If you're lucky, the photo will capture the child's smile or the moment he sucks his thumb.
Parents will be able to examine the baby's appearance in detail. At 18 and 19 weeks, the baby’s body has assumed proportions that will not change until birth. The baby will just grow up and gain weight before birth.
During the study, you can get to know the baby better and enjoy a moment in the life of a future family member. A photo can capture the moment when a child tumbles or sticks out his tongue. An excellent proof of the baby’s well-being will reassure parents and take its rightful place in the family photo archive.
The doctor will help parents look at signs of the baby's gender.
Photo of a boy
The snail-like bulge in the perineal area represents the penis and scrotum.
Photo of a girl
4 parallel folds in the perineum, two of which are located inside, indicate the female sex of the fetus. These are the labia majora and labia minora.
Changes in a woman's body
The nineteenth obstetric week of pregnancy is characterized by the following features in the body of the expectant mother:
- In the second trimester, a normal weight gain of about 250-300 grams per week occurs; by week 19, the total weight gain should be in the range of 4-7 kg.
- This week the belly is already noticeably enlarged and causes some inconvenience: restrictions appear in sleeping positions, and the gait changes. The woman feels the development of the baby thanks to his activity, which at this stage already manifests itself in the form of light tremors. Some women may experience protrusion of the navel - this is an individual phenomenon and will go away after the birth of the child. Abdominal pain at this stage is an alarming symptom, and if it occurs, you should urgently consult an obstetrician-gynecologist.
- The 19th week is characterized by an increase in the size of the uterus to 320-350 g, and this is already 5-7 times its original weight. The upper border of the uterus is located approximately 2 cm below the navel. The growth of the uterus can provoke pain in the pelvic bones - the birth canal gradually begins to prepare for childbirth.
- The breasts continue to increase in volume, the halos darken, and when pressed, discharge from the nipples may appear.
- From time to time, a woman may experience cramps, especially in the calf muscles. Cramps most often occur during sleep. This occurs due to increased load on the lower limbs. Another likely reason for this could be a lack of calcium.
- There is a tendency for hemoglobin levels in the blood to decrease due to an increase in blood volume. This can affect a woman’s well-being in the form of dizziness, weakness, and fatigue. Breathing may be difficult and your heart rate may increase.
- Vaginal discharge may become more intense, but normally should not change color, character and smell, that is, it should be: transparent whitish, uniform in consistency, odorless.
- Dry skin may appear, which will lead to stretch marks. To avoid this, it is important to maintain water balance, eat fortified foods, use moisturizing hygiene products, and wear special bandages.
Every week a woman’s body prepares more and more thoroughly for the process of childbirth. Most changes are manifested by discomfort and inconvenience, but after the birth of a child, all systems will gradually return to their previous state.
Explanation of the examination and normal indicators
The doctor determines the necessary parameters and enters them into the examination protocol. The data is checked against the standard corresponding to the development period.
Fruit size
At the 19th week of embryonic development, the fetal size is approximately 180 mm and the weight reaches 250 g.
Table of embryonic development standards
| Standard parameters at 19 weeks of embryonic development, mm | |||
| Biparental head size | Fronto-occipital distance | Femur, length | Chest circumference |
| 36 – 52 | 48 – 70 | 21 – 35 | 19 – 31 |
| Humerus length | Forearm, length | Calf length | Abdominal circumference |
| 21 – 34 | 20 – 26 | 23 – 31 | 114 – 154 |
| Head circumference | Coccyx-parietal size | Cerebellum size | Size of the lateral ventricles of the brain |
| 142 – 174 | About 140 – 150 | 16 – 20 | 10 – 11 |
The specialist also determines the following:
- location and performance of the child’s organs;
- establishes the heart rate, the performance of the kidneys, stomach, intestines and gall bladder;
- volume of amniotic fluid;
- carries out diagnostics of the child's seat, assesses its thickness, place of attachment, structure;
- accelerated maturation of the placenta (baby place) threatens the fetus with hypoxia.
Reference! In case of deviations from the norm, additional studies are carried out.
Decoding the final diagnostic data
At the 19th obstetric week, the growth of the unborn baby ranges from 19 to 22 cm, body weight is approximately 200 g. All its formed vital systems are actively improving. The contractions of the heart muscle are rhythmic, and in the brain there are already special zones responsible for the basic human senses - hearing, taste, vision, smell and touch. The baby's musculoskeletal system becomes stronger - he can turn his head and bend his limbs. Many expectant mothers have already experienced the pleasant moments of the first tangible movements of the fetus.
In the ultrasound photo, the child looks even thinner, because the subcutaneous fat layer is just beginning to form - it is necessary to ensure thermoregulation of the baby after birth. At this stage of gestation, it is possible to clearly examine the genitourinary organs and reliably determine the sex of the baby. The likelihood of error is minimal - there is still enough space in the uterine cavity and the fetus does not “hide” its genitals, as happens in the third trimester. If a girl is born, the labia majora will be visualized on the monitor; if the fetus has the rudiments of the testicles and penis, a boy will be born.
First of all, the ultrasound doctor studies the heart rate and motor activity of the fetus - this is necessary to assess its viability; presentation (cephalic, pelvic, transverse) - the position of the child in relation to the exit from the uterine cavity. However, the expectant mother should not worry if the baby is “wrongly localized” - before the end of the gestational period, it can change its position several times.
On the screen of the ultrasound machine, the sonologist can see what the baby looks like and his active movements - there is still enough space in the mother’s belly for somersaults and turns over the head.
The ultrasound examination protocol contains a description of the anatomical features of the fetus. The main indicator is fetometry:
3D ultrasound during pregnancy at 20 weeks + video
- BPR (bipariental size) – from 42 to 45 mm;
- LZR (fronto-occipital) – from 54 to 58 mm;
- OG (head circumference) – from 146 to 158 mm;
- Coolant (belly) – from 124 to 134 mm;
- DBC (femur bone length) – from 27 to 34 mm;
- DHA (shins) – from 24 to 27 mm;
- DPK (forearm) – from 20 to 23 mm;
- KDP (shoulder) – from 28 to 31 mm.
The structures and proportions of the brain and internal organs - heart, stomach, lungs, liver, pancreas, kidneys, intestines, gall bladder - are carefully studied. At this time it is possible to determine existing anomalies of their development. The diagnostician shows particular interest in the condition of the placenta, the formation of which has already been completely completed; its main function is to protect and provide the baby with vital nutrients.
The ultrasonic sensor allows you to:
- measure the thickness of the “baby seat” (the norm is approximately 20 mm);
- determine the degree of maturity;
- examine for signs of thickening or growth.
How is it done and how to prepare for the procedure?
An ultrasound at week 19 is done transabdominally, moving the sensor along the skin of the abdomen. A special gel ensures the sensor glides. The procedure does not cause any discomfort and takes about 30 minutes.
The main condition during the examination is the patient’s calm. Anxiety can negatively affect a child's well-being.
No special preparation is needed. You can take a towel or napkin with you to remove the gel.
What will you need for an ultrasound?
Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics does not require special preparation. The procedure itself is also not a complex manipulation. At this stage, there is no need to fill the bladder, since there is already enough amniotic fluid to examine the structure of the areas of interest. Eating food before the procedure does not in any way affect the results of the ultrasound.
Many clinics do not indicate the need to bring anything with you; otherwise, you will be warned about this in advance. Most often, for the procedure, the patient may need a diaper and napkins. The diaper will need to be placed on the couch, since the ultrasound is performed in the supine position. Wipes are used to wipe away excess gel.
Where to do it and how much does it cost?
An ultrasound can be performed free of charge at the antenatal clinic upon referral from a doctor.
Due to the high workload of staff and the influx of visitors, it is more convenient for a pregnant woman to undergo examination in a specialized center.
Certified specialists, using effective equipment, will answer all questions about the child’s health.
The price varies depending on the prestige of the center and the qualifications of the doctor. Paid clinics perform regular (two-dimensional) ultrasound for 1,700 – 2,400 rubles. 3D diagnostics require expenses of 2500 - 3600 rubles. , 4D – 3300 – 4000 rub. The cost of the examination increases in proportion to the length of pregnancy.
Examination price
The cost of ultrasound in the second trimester on average ranges from 600-850 rubles. For the study of uteroplacental-fetal blood flow using Doppler, you need to pay about the same amount. Such a complete examination is advisable, since Doppler allows you to find out the functionality of the cardiovascular system. In case of multiple pregnancy (if twins or more are expected), the price for ultrasound and Doppler examinations will increase by 150-200 rubles. If it is not possible to take a photograph yourself, you can purchase an ultrasound image directly from a sonologist. This service will cost on average 150-300 rubles.
Ultrasound is ideal for prenatal screening. It does not cause discomfort and does not hide any health risks for the expectant mother and her child. In addition to the above, an important advantage is its high effectiveness - with its help, at 19 and other weeks of pregnancy, you can learn in detail the process of formation and stages of development of the child’s body systems, and assess the functionality of the woman’s reproductive organs.
Progress of the study
During diagnosis, the fetal heart rate is assessed; normally it should be 120-160 beats per minute. It also calculates the volume of amniotic fluid (AFV), for this period of development the norm is 83-225 mm. The umbilical cord is also subject to examination; normally it should contain 2 arteries and 1 vein.
The ultrasound diagnostician enters data into the conclusion; no diagnoses are made. Also, the mother can optionally take a photo or video recording of the fetus. The ultrasound conclusion is transferred to the observing gynecologist, and he already interprets it and, if necessary, prescribes additional examinations or treatments.
Gender of the child
During the second screening or already when the 19th week of pregnancy begins, it is 90% possible to correctly determine the sex of the baby, because the reproductive organs are already formed. The accuracy of whether it will be a boy or a girl does not depend on the qualifications of the doctor or the quality of the ultrasound equipment, but on the position of the fetus at the time of the examination.
During pregnancy, some couples deliberately refuse to find out the sex of the child, whether it is a boy or a girl. Since there are not many such cases, it is better to warn the doctor performing the ultrasound diagnosis not to tell you your gender.
If the doctor sees a penis in the perineum, he will assume that it is a boy, but sometimes there may be umbilical cord rings between the legs. To accurately determine whether it is a boy or a girl, you can do a 3-D ultrasound or tissue or amniotic fluid sampling. But the latter procedures are associated with risk and will not be performed without medical indications.
What are the features of pregnancy at 19 weeks?
Pregnancy at 19 weeks is considered to be quite mature and stable. The belly of the expectant mother begins to gradually increase. The baby is already moving. On the ultrasound screen you can even see the baby yawning. Therefore, you need to monitor your health and nutrition.
In order for the baby to develop properly, you need to take vitamins and follow the diet prescribed by the doctor. The products from which food is prepared must contain potassium, phosphorus, and fiber.
The child can already roll over, change position, move his arms and legs. However, the child’s movements do not always indicate that he is developing normally. Sometimes the situation can be completely opposite.