A stool test for dysbacteriosis is usually prescribed as part of the diagnosis of intestinal pathology.
Intestinal dysbiosis (dysbiosis) is a syndrome characterized by changes in the microbial composition of the large intestine. Laboratory diagnosis of dysbacteriosis begins with performing a bacteriological analysis of stool. As a rule, the attending physician, when writing a referral for a test, talks not only about where to get tested, but also about how to properly prepare. Compliance with the rules of preparation and collection technique largely affects the reliability of the results of the study of intestinal microflora.
For the purpose of qualitative and quantitative determination of pathogenic forms of microorganisms in 1 g of feces, tank analysis is used - sowing feces on nutrient media.
What is dysbiosis?
Dysbiosis is an imbalance of all existing types of microflora of the human body, and dysbiosis is an imbalance of only the bacterial composition of the microflora. The causes of dysbiosis are constant stress, irregular nutrition, and uncontrolled use of antimicrobial drugs in the treatment of all kinds of infections. Signs of dysbiosis are found in inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract of the vagina, and oral mucosa. They are accompanied by itching, diarrhea, constipation, boils and purulent infections appear.
Rules for taking the analysis
Before taking the test, you need to prepare for the analysis:
- Three days before the test, stop taking any medications that affect intestinal functions and its microflora;
- If antibiotics were taken, stool is donated only after three days;
- A month before the tests, stop taking dietary supplements;
- Three days before the test, do not use rectal suppositories (suppositories inserted directly into the anus);
- Collecting analysis using enemas and laxatives is prohibited;
- Before donating, you need to wash your anus and perineum, or wash in the shower;
- To directly collect the analysis, you must prepare a thoroughly disinfected container. Place the child on a potty rinsed with boiling water;
- Collect fragments of the analysis in an amount of 10-15 g in a sterile container (can be purchased at a pharmacy). Collect feces using a sterile stick. The stool should preferably be in the morning;
- If it is determined that the stool contains blood or mucus, then this indicates a pathology and an urgent need to take the sample to the laboratory.
Indications
Doctors recommend a stool microflora test for the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- discomfort in the intestines;
- long-term stool disorder;
- manifestations of allergies;
- rashes;
- prolonged flatulence;
- blood and mucus in the stool;
- the presence of pieces of undigested food.
Sometimes the disease is not clearly expressed, but if there is frequent discomfort in the intestines of a pregnant woman, it is recommended to submit biomaterial to identify dysbacteriosis.
Methods
There are three ways to test for dysbacteriosis:
- Coprogram;
- Bacteriological;
- Biochemical.
Will the coprogram show dysbiosis?
A coprogram is a microbiological analysis of intestinal microflora, used after long-term use of antibiotics not associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. And it identifies pathology by the appearance of feces and determines the presence of:
- Fragments of undigested food;
- Starch;
- Helminths and their eggs;
- Fat;
- Blood and mucus.
Bacterioscopic examination is the first stage of microbiological analysis. The thick part of stool consists of 30% microorganisms. In this case, the intestinal flora is not microscopically distinguished using colored preparations. Bacterioscopically it is possible to isolate iodophilic flora and tuberculosis bacillus.
Bacteriological research - how much and how it is done
If the coprogram shows an imbalance, then the doctor prescribes a more accurate study. A bacteriological culture of feces is performed in a nutrient medium. In some cases, an analysis is performed for bacteriosis of the oral cavity. A scraping is taken from the oral mucosa, then a tank is performed. sowing. After 5-7 days, when the bacteria multiply, they are recounted. Based on the results of bacteriological examination of feces, the specialist gives an opinion. If organs other than the intestines are involved in the pathological process, a detailed analysis of blood and urine is performed.
Biochemical method
Stool biochemistry - this type of analysis gives results in 1 hour. The advantage of this method:
- Relative speed;
- Increasing the time for delivery of samples to the laboratory to 24 hours;
- You can freeze the sample in the refrigerator;
- Accuracy of the data obtained.
To obtain the correct result from a biochemical analysis, you must:
- Stop taking antibiotics 2 weeks before collection;
- For women, do not take tests until your period ends;
- Take samples from different parts of the stool.
Biochemical research can be carried out in parallel with the coprogram
If these methods cannot confirm the final diagnosis, then a thorough examination is carried out to determine the true cause of the pathology.
General overview of the study
Stool culture is one of the main diagnostic methods. It allows you to determine which group of microorganisms predominates. The biomaterial is first diluted in saline, centrifuged and then seeded. Broth or agar are used as special nutrient media. Stool culture for dysbacteriosis is carried out under sterile conditions. Cups with media are placed in a thermostat, which has all the conditions for the reproduction and growth of microorganisms. The duration of the study is from five to seven days. Next, the medical professional evaluates:
Based on the information received, dysbacteriosis is diagnosed. One of the main tasks is the detection of pathogenic bacteria during stool culture for dysbacteriosis. How many days does the analysis take to prepare? Bacteria take time to grow and multiply. Results are given to the individual after five or seven days. This point is the only drawback of this method of diagnosing dysbiosis.
Decoding stool analysis
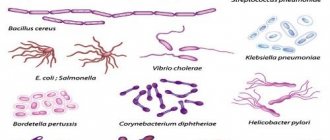
The intestines contain a large number of bacteria and microorganisms. It is necessary to decipher the tests to determine the quantitative and qualitative composition of the intestinal microflora. Among them are:
- Beneficial - 95% - bifidobacteria, up to 5% - lactobacilli;
- Opportunistic pathogens (OPP) – enterococci, staphylococci, clostridia, candida;
- Pathogenic – salmonella, shigella.
The normal microbial landscape, which determines the optimal proportions, is as follows:
- Bifidobacteria – 10 to 8 – 10 to 10 degrees;
- Lactobacilli and Escherichia – 10 in 6 – 10 in 9;
- Streptococci – 10 in 5 – 10 in 7;
- Non-hemolytic staphylococci – 10 in 4 – 10 in 5;
- Clostridia – 10 in 3 – 10 in 5;
- Opportunistic enterobacteria – 10 in 3 – 10 in 4;
- Hemolytic staphylococci – 10 to 3.
In children under one year of age when breastfeeding:
- Bifidobacteria – 10 to 10 – 10 to 11 degrees;
- Lactobacilli norm – 10 to 6 – 10 to 7 degrees;
- Clostridia – 10 to 2 – 10 to 3 degrees.
All these indicators are indicated in CFU/g - colony-forming units in 1 gram of sample.
At birth, the child does not have any microorganisms, and only at the age of two is the content of the intestinal microflora considered formed. He gradually receives all microorganisms along with mother's milk. If the woman in labor does not have antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus, then the child may get dysbacteriosis in the maternity hospital.
If the test results do not correspond to the above parameters, i.e. decreased, it can be assumed that dysbacteriosis has occurred.
Bifidobacteria
These are the main representatives of normal intestinal microflora, the number of which in the intestine should be 95–99%. Bifidobacteria perform the important work of breaking down, digesting and absorbing various food components, such as carbohydrates; they themselves synthesize vitamins and also promote their absorption from food; with the participation of bifidobacteria, iron, calcium and other important microelements are absorbed in the intestines; bifidobacteria stimulate the motility of the intestinal wall and promote normal bowel movements; bifidobacteria neutralize various toxic substances that enter the intestines from the outside or formed as a result of the activity of putrefactive microorganisms. The analysis form indicates the titer of bifidobacteria, which should be no less than 107 - 109. A significant decrease in the number of bifidobacteria is always a sign of severe dysbacteriosis.
Intestinal microflora
Clostridia in analysis
Clostridia
The intestinal microflora consists of many types of microorganisms, one of them is clostridia. They are distributed in the large intestine. They are classified as opportunistic. Under normal conditions, they do not cause harm to the body. If the number of clostridia is increased, they will cause damage to the body, poisoning it. The reason for the increase may be the consumption of large amounts of protein foods (meat, fish, legumes, nuts, etc.). Clostridia also live and reproduce in the soil, so you need to keep your hands and food clean.
Pathology can lead to botulism and tetanus, which can be fatal.
What is enterococcus?
This type of bacteria contributes to:
- Digestion of carbohydrates;
- Vitamin compound;
- Creation of immunity in the intestines.
If the number of enterococci in the stool is greater than the number of E. coli, this can lead to pathologies.
Why does the number of enterococci increase:
- Due to helminths;
- Lack of immunity:
- Allergy to any food product;
- Poor quality food;
- Reducing the number of E. coli.
Bacteroides are reduced - what does this mean?
Bacteroides are actively involved in the digestion of fats. They originate in the intestines of the baby from the eighth month. The number of bacteroids is below normal due to:
- Antibiotic treatment;
- Intestinal infections (dysentery, salmonella, viral infections).
Enterobacteriaceae
They live mainly on the mucous membrane of the small and large intestines and are called anaerobic, that is, they do without oxygen. The pathogenic component is acquired through infection from a person or animal, consumption of low-quality eggs, milk and meat.
Lactobacilli
The number of these bacteria is about 4% of all intestinal bacteria; they are few, but they take part:
- In normalizing the pH level;
- In the synthesis of substances that kill pathogenic microbes;
- In the production of lactose (an enzyme that helps the esophagus digest dairy products).
If the number of lactobacilli is reduced it means:
- Antibiotics, laxatives, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were used;
- The diet was incorrect, fasting or artificial feeding (for infants) was used;
- There were intestinal infections;
- There were chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- It was a stressful situation.
Bifidobacteria for the intestines
Bifidobacteria live mainly in the large intestine. There are 24 strains of these bacteria, that is, pure, homogeneous offspring. Bifidobacteria:
- Produce organic acids (lactic, acetic, etc.);
- Maintain normal pH;
- Protect against pathogenic flora;
- Accelerate protein hydrolysis and fiber dissolution;
- Strengthens intestinal peristalsis;
- Helps absorb B vitamins, vitamin K and D;
- They accelerate the functioning of the lymphatic system and the production of immunoglobulins, thereby strengthening the immune system.
When the number of bifidobacteria decreases, diarrhea, constipation, allergic reactions, and deterioration of immunity occur.
Escherichia coli
Bacteria of the E. Coli species are found in the intestines of humans and animals. They are non-pathogenic and help the digestion process and the production of vitamins. Their main role is to block the passage of pathogenic bacteria. If there is no pathology, then the normal amount of this E. coli is 10 6 CFU/g.
Lactic acid bacteria
The backbone of normal intestinal microflora includes lactic acid bacteria. They are considered anaerobic, that is, oxygen is contraindicated for them. All lactic acid bacteria process carbohydrates into lactic and acetic acids and protect the liver from toxic substances. They also improve intestinal motility and produce vitamins and microelements.
Video: Examination of stool for dysbacteriosis
Degrees of microbiological disorders
When assessing the results of a study, correct counting of opportunistic microorganisms is important. The following degrees of microbiological disorders are distinguished after stool culture for dysbacteriosis:
What to do if symptoms of dysbiosis appear?
To save time, there is a service on the Internet - ask a doctor online, you can even make an appointment with a specialist. Your doctor may recommend various medications and herbal remedies.
Herbal mixture for dysbiosis
The therapeutic effect of herbs is due to the fact that they contain the necessary nutritional enzymes for the intestinal microflora. The collection is prepared from:
- Mint leaves – 1 part;
- Valerian root – 2 parts;
- Chamomile flowers – 2 parts;
- Raspberries – 2 parts.
Add a tablespoon of the mixture to a glass of boiling water, leave for 10 hours and consume. This amount is enough for up to 3 times. Children take one teaspoon at a time. Course 1 month.
References: https://www.gmsclinic.ru/gms/press/articles/art-enough-dysbacteriosis https://www.invitro.ru/library/labdiagnostika/16123/ https://www.gemotest.ru/ catalog/po-laboratornym-napravleniyam/biokhimicheskie-issledovaniya/biokhimicheskie-issledovaniya-kala/biokhimicheskiy-ekspress-analiz-kala-na-disbakterioz/ https://kdl.ru/analizy-i-tseny/disbakterioz-s-opredeleniem- chuvstvitelnosti-k-antibiotikam-i-bakteriofagam https://www.zdorovo365.ru/biohimicheskij-e-kspress-analiz-kala-na-disbakterioz.html https://newlab-med.ru/uslugi-i-czenyi/ laboratornyie-issledovaniya/issledovanie-kala/analiz-kala-na-disbakterioz-kishechnika.html https://vetlab.ru/catalog/issledovanie_kala/issledovanie_kala_na_disbakterioz_kolichestvennoe_s_podtitrovkoy_k_antibiotikam_i_fagam/ prezident-med.ru/poliklin ika/sdat-analizy/analiz-kala-na -disbakterioz/ www.treskunov.ru/kishki/tact-disbakterioz.html This material is exclusively subjective in nature and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 04/11/2020