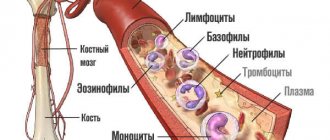
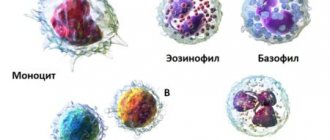
Formed blood cells are represented by a wide group of cytological structures. According to the generally accepted classification, white blood cells are divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes.
Granulocytes are represented by three types of cells:
- Basophils. They are fat structures. The largest of all the others.
- Eosinophils. Significantly less. Capable of phagocytosis. They mainly fight parasitic infestations.
- Neutrophils. These are the most numerous cells. They make up up to 70% of the total mass of immune structures, and are divided into band and segmented.
If granulocytes enter the battle first and are responsible for the initial response of the defense system, agranulocytes start later. They are represented by monocytes and lymphocytes.
If neutrophils are low, this is a clear sign of inflammatory processes, disorders of the bone marrow, allergic reactions and other diseases. Which ones exactly need to be clarified separately.
The condition is called neutropenia and has its own ICD-10 code - D72. Accompanied by a group of symptoms, mainly caused by the primary pathological process.
What do you need to know about this violation?
Norms and functions of immune cells
The immune system is represented by cells grouped into certain groups according to types and characteristics. Each group performs a specific task aimed at protecting the body from the effects of harmful microorganisms.
All components of the human body are interconnected, and this also happens at the intercellular level. Immune cells decipher foreign “agents,” collect information about them, and respond to elements harmful to the body by destroying them.
The immune system cell consists of particles:
- leukocytes;
- phagocytes;
- neutrophils;
- monocytes;
- dendritic cells.
Based on a blood test, an immunogram evaluates cells and the antibodies they produce and provides information about the person’s condition. The interpretation of this analysis consists of a large number of indicators that comply with current standards.
In research laboratories belonging to different medical institutions, standards may differ. This is due to the use of various diagnostic methods, tools and reagents.
The norm of neutrophils in the blood in adults
The percentage of neutrophils is as important as the absolute number
For a more complete picture of the patient’s condition, both the absolute and relative content of immune cells in the blood are assessed. The absolute value is the total number of detected neutrophils in a unit of blood, the relative value is the percentage of neutrophil cells to all leukocytes.
Standard indicators for adults.
| Types of neutrophils | Absolute (*10^9/l) | Relative (%) |
| Segmented | 2, 0 — 6,5 | 42 — 75 |
| Rod | 0,04 — 0,4 | 1 — 5 |
Functions of leukocytes
The basis of the human body's immune system are leukocytes, which come in several types. These blood cells prevent infection from infecting healthy cells.
Leukocytes are divided into several types with different functions:
- T-lymphocytes guarantee cell immunity and eliminate foreign microorganisms and defects. In addition, they provide resistance to infections, promote blood formation, and also control the functions of B lymphocytes.
- B lymphocytes protect the body from bacterial and viral infections by producing antibodies. Cells of this type give the immune system the ability to remember. Once, faced with a harmful microorganism, information about it is postponed, and along with it, methods for its destruction. Subsequently, the cells transmit information by inheritance.
- Monocytes are the orderlies of the immune system, absorbing parasitic remains of the products of active cell activity. They not only cleanse the body of pests, but also transmit information about them to new cells.
When leukocytes work together and properly, the human body is maintained in a healthy state.
Leukocytes, according to their morphological properties, are divided into 2 units:
- granulocytes are granular particles of blood, the main of which are neutrophils;
- agranulocytes.
The number of lymphocytes in the blood is an important indicator of a healthy body. Reduced levels indicate immunodeficiency, while high values indicate autoimmune abnormalities or excessive immune function. The reasons for deviations are found only with additional research.
Why are there low neutrophils?
A low level of protective bodies may indicate many disorders, some of which do not pose a particular danger to humans. In order to simplify the understanding of the causes of neutropenia, the causes of its occurrence are conventionally divided into 2 types: pathological (indicating the presence of diseases of various natures) and physiological (caused by any changes in the body, caused, for example, by exhaustion or taking medications). Now a little more about each variety.
Pathological causes
A small number of neutrophils is often associated with the development of a disease of viral origin. These include:
- Amerrilosis (yellow fever, attacking primarily the liver and kidneys, and then the rest of the internal organs, the choroid plexuses).
- Chicken pox.
- Flu.
- HIV (immunodeficiency virus).
- Rubella.
- Laryngitis.
- Pig.
- Hemorrhagic fever (a deviation that primarily affects blood vessels).
- Sore throat.
- Lichen.
- Measles.
- Hepatitis (all types).
- Encephalitis (inflammatory process in the brain).
- Polio.
- Typhoid or typhus.
- Papillomatosis.
- Syphilis.
- ARVI.
- Herpes.
And also a large group of diseases in which there are fewer neutrophils than normal are formed by bacterial forms of abnormalities, among them:
- Tularemia (a disease localized on the mucous membranes and lymph nodes).
- Salmonellosis.
- Pneumonia.
- Tuberculosis.
- Meningitis.
- Typhus.
- Sepsis (blood poisoning).
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity).
- Dysentery.
- Cholera.
- Otitis.
- Tonsillitis.
- Diphtheria.
- Brucellosis.
- Appendicitis.
Diseases that attack the hematopoietic and circulatory system also have the ability to reduce neutrophils. We are mainly talking about leukemia, thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the veins), acidosis (increased acidity of the blood), hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) and lymphoma.
Of particular note are malignant tumors - myeloid leukemia, erythremia (pathological proliferation of red blood cells), leukemia, osteosarcoma, fibrous histiocytoma (cancer that affects ligaments, muscles and tendons) and Ewing's sarcoma, which modifies bone cells. Parasitic diseases, such as trichomoniasis and toxoplasmosis, can significantly reduce the level of neutrophils in the blood.
Diabetes mellitus also causes neutropenia
The following diseases are also among the deviations characterized by a low granulocyte content:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Splenomegaly (pathological enlargement of the spleen).
- Cachexia (severe form of exhaustion).
- Gout.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Osteomyelitis (necrosis of bone structures).
- Acute form of cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder).
By the way, anaphylaxis (anaphylactic shock) is one of the “triggers” of neutropenia.
We must not lose sight of the fact that a person may have Kostman's syndrome. It is a congenital immunodeficiency that is caused by the body's inability to independently synthesize neutrophils, which are an integral part of the immune system.
Physiological reasons
Now about the causes of non-pathological neutropenia. The most common are the use of medications: cytostatics, analgesics (painkillers), a number of antibiotics (for example, chloramphenicol) and antibacterial agents (streptocide, zidovirine), extremely severe burns, the post-morbid period, living in an area characterized by unfavorable environmental factors, chemical or radiation treatment. therapy.
Very often, a low content of neutrophils makes itself felt due to an unbalanced diet, in which, as a rule, there is a clear deficiency of folic acid (B9), as well as cyanocobalamin (B12). This is usually due to the almost complete absence of seafood, meat, cheese, fish, dairy products, chicken eggs, nuts, herbs, porcini mushrooms, etc. in the diet.
In order to increase the level of neutrophil granulocytes in the blood, you need to balance your diet by adding the missing components and limiting junk food as much as possible. If a patient has had slight fluctuations in neutrophils throughout his life, not accompanied by unpleasant physiological symptoms, then, most likely, there is no point in talking about pathology. This condition in individual cases is considered a type of normal.
Types and functions of neutrophils
Neutrophils are low in an adult and can signal a source of inflammation in the body. Bacteria contained in cell granules, as well as receptors located in their membrane partitions - this composition is capable of combining certain antibodies.
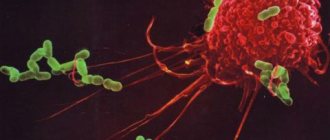
Neutrophils enter the area of inflammation and counteract harmful substances. Just one particle of a neutrophil cell absorbs about 30 “enemy” bacteria.
To understand the activity of neutrophils, you need to pay attention to two important points:
- First, this cell can sacrifice itself. If a harmful microorganism appears on its way, neutrophils destroy it by absorption, and then the process of phagocytosis and digestion occurs. After this, the foreign intracellular element is split and dies along with the pest.
- Secondly, white cells have 6 stages of development. At the initial 4 steps, the cells are located in the bone marrow. At the remaining stages, they move together with the bloodstream and perform their actions.
Neutrophils in the initial period of maturation, as well as their reduced number in an adult, determined in the laboratory, become a sign of damage to the body by the virus.
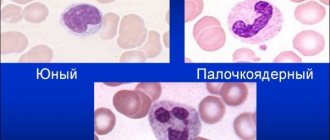
Neutrophils are divided into the following types:
- myeloblasts - primary cells;
- promyelocytes - the appearance of granules in cells;
- myelocytes;
- metamyelocytes;
- band granulocytes;
- segmented granulocytes.
Mature segmented cells are taken for the initial destruction of the infection. If the disease is not advanced, then their action is sufficient to suppress it. With a complex course of the infectious disease, granulocytes of the band type enter. Behind them are young myelocytes and metamyelocytes that mature in a healthy state of the body.
A decrease in neutrophils is observed in severe cases of the disease, since the segmented elements die first. The body must produce young cells, otherwise there will not be enough mature elements. As a result, an excess of new immature neutrophils will be observed, which indicates a shift in the parameters of leukocytes in the blood in adult men and women.
The functions of neutrophils can be described in a simple diagram:
- Harmful bacteria are identified.
- The phagocyte attaches to the pest and immerses itself in it.
- The neutrophil engulfs the object.
- Under the influence of enzymes, breakdown occurs.
- The “agent” is digested, and the cell removes its remains.
A single neutrophil cell destroys up to three dozen harmful microorganisms. The functions of such cells are not limited only to phagocytosis, but their activity is aimed at eliminating pathogenic bacteria. After complete victory over the “enemy,” the neutrophil begins to produce antibodies, which give the body information about foreign elements, and immunity increases.
Is it possible to increase the level of leukocytes and neutrophils?
Chemotherapy drugs are toxic substances. There are indications and contraindications for their use, because they can both help the patient and cause great harm if used thoughtlessly. The only appropriate and reasonable method to increase the level of white blood cells and neutrophils is to wait.
Yes this is true.
Firstly, because each organism has its own characteristics and is not always able to recover by the time specified by the recommendations.
The intervals between cycles are optimal, but a deviation from the timing by 1-2 weeks (sometimes more, if necessary) is acceptable if there are contraindications to chemotherapy.
Secondly, any drugs that stimulate an increase in the level of leukocytes and neutrophils are dangerous because after several such stimulations, the bone marrow reserve can be depleted, and after this, recovery will take much longer and will be associated with possible complications.
If leuko- and neutropenia is constant, and the body does not recover properly even with increasing intervals between cycles, then specialized drugs are prescribed, which should be used only under the supervision of a doctor in strictly indicated situations.
Any so-called immunomodulators, immune stimulants will not bring any benefit, there will be no effect from them, because leukocytes will still decrease during chemotherapy, as it should be, but at the same time such drugs can provoke the development of undesirable reactions.
What happens in the body when the level of neutrophils decreases?
Neutrophils are low in adults - this is the main symptom of “neutropenia.” When viruses penetrate, cells independently create a focus around the area of inflammation, preventing the spread of microbes. The wound produces pus and inflammatory syndrome. If a person is already sick with neutropenia, then the disease occurs without symptoms. The infection spreads quickly and can cause sepsis.
For the first time, the disease manifests itself as side diseases:
- purulent-necrotic sore throat;
- stomatitis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- osteomyelitis.
In diseases of the bone marrow in adults and children, the level of neutrophils decreases
Microbes are safe for a healthy body, but lead to serious problems in sick people with insufficient neutrophil counts.
Neutropenia is diagnosed as a disease:
- acquired;
- congenital;
- unclear.
In the case of a reduced level of neutrophils in the blood, patients experience disruptions in the digestive system and the intestinal microflora is disrupted. Patients experience symptoms of similar diseases. Only a specialist is able to detect low levels of various forms of neutrophils, and a doctor, based on the data, can indicate changes in health status and prescribe treatment.
The dangers of low neutrophil levels in the blood
The danger of neutropenia is the possibility of infection
When the immune system works optimally, the body copes with many pathogenic particles. If the number of protective cells decreases, pathogenic organisms easily penetrate, destroying the tissues of various organs. Already on the third day of neutropenia, the risk of infectious lesions increases.
The oral cavity is one of the first areas to suffer from low neutrophil levels, as it is where many bacteria naturally circulate. Neutropenia is manifested by diseases of the gums, throat, skin, and the presence of ulcers. Gradually, other organs are connected, and the infection attaches to the tissues.
A characteristic feature of complications from neutropenia is the vagueness of symptoms. This occurs due to the fact that a small number of neutrophils are not able to destroy harmful objects, and therefore there is no inflammatory process. A person may not feel the severity of pathological phenomena. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically monitor the condition of your blood, completely cure all diseases only under the supervision of a doctor, excluding any self-medication.
Reasons for decreased neutrophils
Neutrophils are also reduced in adults during the treatment of viral diseases due to the use of medications. However, this condition returns to normal after treatment is completed.
If after 3 days the immune cells do not increase, the possibility of developing an infection increases. The body may require additional examination, as a result of which the true cause of the pathology will be established. This phenomenon occurs after or during a serious illness and subsequent exhaustion of the body.
The most common reasons for this are:
- ARVI;
- rubella, measles;
- hepatitis A;
- chicken pox, typhus;
- HIV infections;
- tonsillitis;
- acute otitis and appendicitis;
- chronic anemia;
- side effects of radiation therapy;
- environmental pollution.
Raising leukocytes during chemotherapy (the experience of an experienced cancer patient)
Leukocytes - These are one of the cells in our blood. They are also called white blood cells. Leukocytes have a very important role in the body.
their scope of action is protection. Leukocytes protect the body from microbes, viruses, and protozoan pathogens.
In a word, white blood cells provide immunity. Normally, the number of leukocytes in adults ranges from 4 to 9 * 109 cells/l.
During chemotherapy, most drugs cause inhibition of such an important function of the bone marrow as hematopoiesis. As a result, the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets decreases.
A decrease in the level of white blood cells is called leukopenia.
It is very important to maintain leukocytes at the proper level during aggressive treatment of cancer.
This will help avoid the severe consequences of chemotherapy, which manifest themselves in the body’s increased susceptibility to infectious diseases.
To begin with, if after the next course of chemotherapy the decrease in leukocytes is not critical, you can try to increase them using publicly available methods and methods.
1. Oncologists recommend that if you have a low white blood cell count, eat fruits, vegetables, and red berries
(red peppers, beets, red and black currants, cranberries, red apples, pomegranate).
Baked apples and pumpkin are very good for raising white blood cells. Cut the apples and pumpkin into arbitrary pieces, add a little dried apricots and bake in the oven until the pumpkin and apples become soft.
2. It is useful to drink beet juice.
But not pure, but mixed with apple or carrot. The proportion is 3 parts beet juice and 1 part carrot or apple juice. It is important to keep beet juice in the refrigerator for a couple of hours before drinking. You can add a teaspoon of honey to the juice mixture.
Traditional medicine considers beet juice an effective remedy for treating cancer.
. This was confirmed in his experiments by the Hungarian doctor Alexander Ferenczi. In his works, he described examples indicating the positive effect of beet juice on the condition of cancer patients and the prognosis of the disease.
There are contraindications to drinking beet juice:
Exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers and gastritis with increased acidity of gastric juice, acute inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
Kidney stone disease with the formation of oxalate stones, chronic renal failure.
3. Buckwheat with kefir helps well with low leukocytes.
Prepare this mixture the night before. Add 6-8 tablespoons of kefir to a couple of tablespoons of buckwheat and leave until morning. Eat it for breakfast in the morning.
4. Don't forget about decoctions of oat and barley grains.
A glass of barley or oat grains, washed thoroughly and chopped a little. Then I filled it with one liter of water. Quickly bring the mixture to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer for about an hour, until the amount of liquid is reduced by one third. It’s easy to remember: glass-liter-hour.
Drink before meals, three times a day. You can alternate. Drink a decoction of barley grains for a week, and oat grains for another week.
5. It is also useful to include bran from sprouted wheat grains in your diet.
.
6. Another way to increase white blood cells is beer with sour cream.
Ingredients:
sour cream – 200 grams;
beer – 0.33 liters
Preparation:
Pour sour cream into a beer mug. Add 100-150 ml of dark, unfiltered beer, stir until smooth. Add the rest of the beer and stir again.
7. Royal jelly and pollen help a lot
.
8. Try eating a small piece of salted lard every day.
9. If funds allow, red caviar in small portions and seafood.
Of course, it is important that the nutrition is complete. This was discussed in the previous article.
If all these measures do not give the desired result and your white blood cells fall below the acceptable level, your oncologist will prescribe you special drugs to increase white blood cells. For example leukostim, filgrastim, pegfilgrastim or neoplastim.
These drugs stimulate the production of white blood cells in the bone marrow, rather than redistributing their content, increasing the number in the blood, as happens with the use of prednisolone or dexamethasone.
They are not cheap, but, in principle, they should be provided free of charge and used only as prescribed by a doctor. No self-medication.
What does this mean if neutrophils are low and lymphocytes are high in an adult?
Neutrophils are low in an adult and lymphocytes are high - this information picture indicates infection. To establish the correct diagnosis, you will need some analytical indicators in conjunction with other methods of examining the patient. The results are deciphered by a specialist; you cannot try to establish a diagnosis yourself, much less prescribe treatment.
Such indicators pose a danger in the event of extensive infection, accompanied by the penetration of microorganisms into the systemic bloodstream. The bone marrow does not have time to produce new neutrophils, which die after contact with a harmful “agent.”
The condition is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- weakness and clouding of consciousness;
- tachycardia and increased breathing;
- lowering blood pressure.
The patient must be hospitalized to prevent septic shock, which is fatal in every second patient.
How to increase neutrophils in the blood during chemotherapy
Experienced specialists even treat cancer using chemotherapy. The treatment itself involves the use of drugs that suppress or slow down too active cell division.
These drugs can affect both rapidly dividing cancer cells and stem cells that affect the course of hematopoiesis. The drugs suppress hematopoietic functions, reduce the number of particles in the blood, and reduce white blood cells. In patients who have undergone chemotherapy, leukopenia immediately develops.
Therefore, such people urgently need to raise their white blood cells after chemotherapy. Experienced specialists categorically prohibit leaving the body without the necessary protection.
After the course, patients have the main question - how to increase white blood cells after chemotherapy? Health workers recommend special diets, the use of additional medications, healthy foods, and traditional medicine recipes. Let's look at a few basic techniques.
Types of neutropenia
This disease occurs due to adverse effects on the body from the outside, as well as intracellular pathology.
There are several types of disease:
- autoimmune - the immune system itself destroys neutrophils;
- medicinal - drugs have a detrimental effect on cells;
- cyclic - a rare congenital type;
- isoimmune - maternal antibodies “attack” fetal neutrophils through the placenta;
- myelocathexis - neutrophils do not move from the bone marrow into the blood;
- Kostman's syndrome is a genetic disease of insufficient cell production.
Causes of neutropenia
Drugs can affect neutrophil levels
The state of neutropenia is caused by taking various medications, a number of diseases, lack of microelements (B vitamins), chemotherapy, and intoxication (including alcohol).
Medications that cause a decrease in neutrophils:
- antiviral (Viferon, Interferon, Alfaferon);
- immunosuppressants (Cyclosporine, Auranofin, Batriden);
- cytostatic drugs (Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Fluorouracil);
- antimicrobial agents (Chloramphenicol, Fluorocytosine, Trimethoprim);
- sulfonamides (Sulfafurazole, Sulfadiazine, Sulfamethoxazole);
- drugs of the penicillin group (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Ticarcillin);
- antibiotics of the cephalosporin class (Cefaperazone, Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime);
- antiretroviral drug Zidovudine.
Rheumatoid arthritis may be accompanied by neutropenia
Diseases that serve as a source of decrease in neutrophils:
- viral (hepatitis, polio, Epstein-Barr virus, HIV),
- bacterial (tuberculosis),
- autoimmune (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis),
- parasitic infections (malaria),
- fungal (candidiasis, mycosis),
- diabetes,
- pathologies of the circulatory system,
- cancer diseases.
Severity
The more severe the degree of damage, the more serious the complications. The extreme stage is characterized by both acute inflammation and its disappearance, which signals the complete depletion of granulocytes.
There are 3 stages of the disease:
| degree of expression | number of NPs in 1 μl of blood | risk of infection |
| light | 1000-1400 | minimum |
| moderate | 500-1000 | average |
| heavy | below 500 | high |
The first, mildest degree of the disease does not have pronounced symptoms and does not require special treatment. Moderate neutropenia is treated on an outpatient basis, but with regular visits to the doctor. And in severe cases of the disease, hospitalization of the patient is required.
Stages of violation
The disease or, more precisely, the pathological condition is accompanied by a decrease in the content of neutrophils. How pronounced a change occurs depends on the primary cause.
As for the stages or severity of the disorder, there are three of them.
Lightweight
Or the very first one. The concentration of granulocytes drops to the level of 1-1.5*109 /l. There are no symptoms yet. The patient does not even suspect that there are any health problems. Minor disorders and changes in well-being are possible.
Neutrophil norms by age in both sexes are described in detail here.
Moderate
The cell concentration drops to 0.5-1*109 /l. Much more noticeable in terms of symptoms. The patient suffers from frequent colds. It is necessary to strengthen the immune system and treat the primary pathological process.
Heavy
It is accompanied by either a complete absence of neutrophils or a significantly reduced number of formed cells. Urgent treatment in a hospital is required. Measures are being taken to strengthen the immune system.
Typically, the disorder develops as a result of immunodeficiency. Viral or otherwise. Possibly with severe radiation sickness.
Attention:
The condition poses a real threat to the health and life of the patient.
Stages are a laboratory indicator. It is examined as part of a general blood test. In case of disorders or disorders that were detected earlier, additional examinations are prescribed.
Preparing for the study
The process of preparing for analysis consists of meeting certain conditions:
- Refrain from any food 12 hours before your appointment, this does not apply to liquids.
- Stop physical activity and avoid stress.
- For 2 days before the test, do not eat fatty or fried foods, drink alcohol, or smoke.
- Stop using any medications for 3-4 days. If taking medications is vital, you must notify your doctor.
If the patient is undergoing a comprehensive examination, then blood is first taken for a general analysis. Other diagnostic procedures are carried out later.
What are neutrophils?
There are six sequential stages of neutrophil maturation - myeloblast, promyelocyte, myelocyte, metamyelocyte (juvenile), band and segmented cells. Mature cells are segmented neutrophils. All other forms of these cells are considered immature (young). In human blood there are much more segmented neutrophils than young forms. If a person becomes ill with some kind of infectious disease, the bone marrow releases immature cells into the blood. By their number, doctors determine the presence of a bacterial infection, as well as the degree of its activity.
Decoding the analysis results
When deciphering blood indicators, it is necessary to remember that the standards for such cells in adults are the same, regardless of gender, but different depending on age. There is no column for “neutrophils” in the form, so the norm is considered according to some of their subtypes.
| Age | Neutrophil norm | |
| stab | segmented | |
| adults | from 1 to 4% | from 40 to 60% |
Enlarged neutrophils are a specific function of the body’s defense, accompanied by an increased number of leukocytes. A slight increase in neutrophil levels occurs during heavy physical activity, psychosis, and anxiety. Pregnant women also experience elevated rates.
A large increase in the number of such cells means the occurrence of a disease. If the initial forms of neutrophils are detected, this is manifested by infectious phenomena in the form of purulent discharge.
Low levels of such cells indicate dysfunction in the bone marrow. Toxic factors destroy cells, this becomes the source of the disease.
Norm value and deviation
To detect a low level of neutrophils, you should do a complete blood count with a detailed formula for the percentage of leukocytes. Neutrophil cells are a type of white blood cell. The ratio of different types of leukocytes is determined as a percentage. Types of white blood cells differ in appearance and function. Neutrophils are the most numerous type of leukocyte cells; their purpose is to protect a person from infections by destroying pathogenic microorganisms and the slightest foreign particles.
These types of blood cells are of 2 types: young (immature forms are called rod) and mature - segmented. Over time, the former change their structure and become segmented. In the analysis, these cells are referred to as NEUT.
Normally, the percentage of band neutrophils in adults is 1-6%, and segmented neutrophils vary from 42 to 72% of the total number of leukocyte cells. Values below these numbers in the analysis indicate that neutrophils are below normal. Normal indicators do not depend on gender, but change with age - in young children the percentage of segmented mature cells is lower than in adolescents and adults.
A decrease in the level of neutrophils is accompanied by an increase in other blood components, most often lymphocytes, monocytes or eosinophils, because in this case, the total content of leukocyte varieties should total 100%.
In test results, the number of neutrophils can be indicated relative to other types of leukocytes (NEUT%) or in absolute value (abs). Absolute neutrophils are reduced if their number is less than 1500 cells per 1 ml of blood fluid.
Treatment with drugs
Any disease begins for some reason, and the correct therapy depends on it. The cause of neutropenia is an infection, and it is this that needs to be fought. The attending physician may advise the patient to undergo treatment in a hospital or at home, depending on the severity of the disease.
The main direction of treatment is to ensure stable immunity and further support it with preventive measures.
Treatment therapy includes the following:
- glucocorticoids;
- antibiotics;
- vitamins B12, folic acid;
- immunoglobulin;
- medications for symptomatic therapy.
The doctor selects antifungal drugs, among which the most popular are Ketoconazole and Fluconazole.
In case of advanced disease, the patient can be placed in a separate room, where sterility is ensured , as well as regular ultraviolet radiation. An important part of treating neutropenia is preventive measures.
For frequent recurrent bacterial infections, doctors recommend a course of sulfamethaxazole or trimethoprim. In clinical studies, the effectiveness of these drugs is high, but strictly individual. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out a course of preventive medication under the supervision of a doctor.
To reduce the risk of complications during treatment, it is important to follow some recommendations:
- avoid crowded places;
- get vaccinated against influenza and other viral diseases in a timely manner;
- be sure to follow the rules of hygiene;
- Do not eat raw eggs and seafood.
Antiviral therapy, in addition to its benefits, can cause unpleasant side effects. Therefore, treatment is a complex process and must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of neutropenia
A specialist weighs all the pros and cons of treatment
Before treating low neutrophil levels, it is necessary to find the cause and eliminate it.
- If medications are a factor in reducing neutrophils, they must be excluded.
- For autoimmune pathologies, corticosteroids are used.
- Viral diseases require the use of antiviral drugs. In case of severe diseases, specific therapy is carried out.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to patients with infections caused by bacteria.
- If the factor in the decrease in neutrophil cells is a vitamin deficiency, the doctor will recommend a special diet and prescribe a course of vitamins.
- In severe cases of neutropenia, the patient is placed in a sterile room where the air is periodically disinfected.
Traditional medicine recipes
You can increase your immunity with the help of various folk remedies, using medicinal balms, herbal preparations and infusions. This is especially true in autumn and winter, when the risk of disease is greatest.
To make such balms, plant components are used:
- aloe;
- nuts, honey, lemon;
- cranberries and apples.
To make aloe balm, you need to find a plant that is at least 3 years old. Before cutting the leaves, it is not watered for 2 weeks.
The method of preparing the medicine consists of the following steps:
- Dry 0.5 kg of aloe plant leaves and place in the refrigerator for 5 days.
- The leaves are ground in a meat grinder to obtain ½ cup of a porridge-like mixture.
- Add ½ cup of honey, 300 g of Cahors.
- Mix everything thoroughly.
- Use 3 times a day before meals.
An effective remedy for treating wounds in the oral cavity is sage, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
It’s easy to prepare this infusion:
- 2 tsp. sage pour 400 ml of boiling water.
- Wrap the infusion with a warm blanket and leave for 2-3 hours.
- Strain the mixture and rinse your mouth.
Vitamin drinks strengthen the immune system and are a preventive measure against viral infections. Herbal infusions have an ideal effect on the human body.
To prepare medicinal decoctions, you will need:
- valerian root;
- hop cones;
- Linden;
- motherwort;
- Melissa and others.
Warm baths with the addition of various herbs are recommended. Usually dry branches and leaves of bushes are used: currants, rose hips, raspberries. A decoction of rowan and lingonberry leaves added to the bath has beneficial properties.
Correction of leukocyte levels
All subgroups of blood particles mature in the bone marrow before they enter the blood. Any damage to this organ can lead to a severe drop in the number of white blood cells. The formation of white blood cells can quickly decline. The causes may be sports injuries or various factors of internal origin. Therefore, correction of leukocyte levels should be carried out not only after chemotherapy, but also at values that do not correspond to the average. It is worth noting that minor fluctuations in the level of blood particles are accepted by most experts as a normal phenomenon.
Products
Experienced experts advise consuming foods that increase the level of white particles in the blood.
- It is necessary to consume fresh berries, vegetables and fruits. You should choose products that have a red tint. For patients with leukopenia, it is best to consume red currants, beets, juicy carrots, bell peppers, and pomegranate seeds.
- Freshly squeezed fruit or vegetable juices are also very beneficial. For leukopenia, it is recommended to consume pomegranate, beet or carrot juice. The drinks should not be too concentrated. Otherwise, the juice can be diluted with mineral or distilled water in a ratio of 1:2.
- The body must be provided with food containing easily digestible proteins. Such products include broth, boiled chicken or veal. This category also includes fresh seafood: seaweed, crabs, shrimp, white or sea fish. The consumption of red caviar is also recommended.
- You need to take nuts daily. You can consume peanuts, cashews, macadamia nuts, almonds, nutmeg, pecans, pine nuts, pistachios, hazelnuts, chestnuts. But the most valuable and useful is the walnut.
- Buckwheat is welcome in a proper diet. You can use either boiled or soaked in hot water. Buckwheat is especially easily digestible with kefir or milk.
- Consumption of fresh fermented milk products is necessary.
- Natural honey is very useful.
- Natural red wine affects the level of blood particles. Alcoholic drinks should be taken in small quantities.
- The most important component is drinking water. The amount of fluid you drink should be at least two liters per day. Natural green tea, fruit juice, compote, and fresh juice are also suitable to quench your thirst.
Diet
No. 1. For breakfast, it is recommended to consume buckwheat porridge, boiled in lightly salted water or steamed. You need to drink a glass of freshly squeezed vegetable juice. For lunch you can cook sea fish with a side dish of potatoes. A red apple is a good snack. For dinner - boiled chicken, eggplants and a butter sandwich with red caviar.
No. 2. After waking up, you need to drink a glass of mineral water. For breakfast, boil chicken eggs. For lunch, it is recommended to cook boiled vegetables with veal or beef. A glass of kefir or yogurt is suitable for a snack. For dinner - boiled crayfish, a sandwich with honey and hot green tea.
No. 3. Fermented milk products are suitable for breakfast. For lunch, you can make chicken broth soup. Walnuts are used as a snack. For dinner you can cook vegetable stew.
No. 4. After waking up, you need to drink a glass of mineral water. For breakfast, a light salad of crab sticks is suitable. For lunch, veal cutlets with a side dish of buckwheat are suitable. It’s better to make beet juice for a snack. For dinner you can have a glass of red wine.
No. 5. Milk porridge is suitable for breakfast. For lunch, it is better to cook squid with boiled chicken eggs. For a snack, it is better to consume fresh pomegranate seeds. For dinner, boiled rice with chicken is perfect.
Medications
Foods alone may not always increase white blood cells after chemotherapy. If leukopenia is severe, the doctor will prescribe medications.
Gentle products include Polyoxidonium and Imunofal.
If they turn out to be ineffective, stronger drugs may be prescribed, such as Leukogen, Neupogen, Batilol, Methyluracil, Pyridoxine, Cefaransin, Sodium Nucleinate and others.
An increase in white blood cells in the blood after chemotherapy is possible with the help of extracorporeal pharmacotherapy, in which drugs are sent directly into the bloodstream along with donor red blood cells.
ethnoscience
The best effect is observed in preparations made on the basis of medicinal plants. But before use, it is recommended to contact a specialist and agree with him on the use of traditional methods. Otherwise, self-medication can negatively affect a person’s health.
Walnut infusion
Peel the nuts from the shell, put them in a container and fill them with vodka. Leave in the light for 14 days. Take one tablespoon three times a day. Store the tincture in a dark place. Treatment is expected to be long-term.
You can prepare a decoction of nut partitions. They are removed from the shells, as in the first recipe, filled with vodka, allowed to brew in a dark place for ten days, then drunk one teaspoon at a time before meals.
To increase white blood cells after chemotherapy, it is useful to drink fresh pomegranate juice
Oat decoction
Wash the oats thoroughly under running water (2 tablespoons) and add water (0.5 l). Bring to a boil and simmer for another 15 minutes. Drink 100 ml of decoction before meals three times a day. Treatment lasts a month, then a month's break is needed, after which another course is carried out.
Rose hip decoction
The decoction should be prepared in the evening. Chop fresh or dried fruits and add water (take 5 tablespoons of raw materials per liter of water). Place on the fire, bring to a boil, then turn the heat to low and simmer for about 10 minutes. Wrap the container with the broth in a towel and leave to infuse overnight. In the morning, strain and drink as tea throughout the day.
Sweet clover tincture
To prepare the medicine, take two tablespoons of the herb and pour 300 grams of cold water. You need to leave for about two hours, then filter and drink ¼ cup twice a day.
Barley decoction
If leukocytes have dropped, traditional healers recommend treatment with a decoction of barley. Pour water over the grains (take 2 liters of water for 1.5 cups), put on fire, bring to a boil and cook until the water is half as much. It is recommended to drink the decoction with honey.
Herbal collection
Grind 10 grams of kupena root and currant leaves, 40 grams of dandelion root and mix. Pour one teaspoon of the mixture with boiling water (a glass) and boil for 10 minutes. Then remove from heat and let sit for about 20 minutes. After straining, add boiling water to a full glass and drink three times a day before meals.
other methods
Under conditions of sports stress, the body will be able to return to normal faster. The work of the muscles “displaces” the snow-white cells into the bloodstream. This promotes rapid hormone production.
The level of blood particles can be raised with the help of chemicals, diet, and traditional methods. Treatment must be comprehensive. It is necessary to spend more time outdoors and consume fresh foods. Also an important active action is restful sleep and daytime rest.
Forecast
The prognosis is influenced by the degree of damage and timeliness of treatment. If the disease is mildly benign, then a cure is guaranteed. If the disease is caused by a malignant tumor, nothing can be predicted. According to statistics, for 20% of such patients the prognosis is unfavorable.
Today, many medical centers use modern techniques, with which results can be obtained very quickly. Sometimes doctors resort to surgery, bone marrow transplantation. A successful operation guarantees a good prognosis for the treatment of the disease. Neutropenia of this type has a very small percentage of the likelihood of the body contracting an infection.
Neutrophils in the blood of an adult suffering from a congenital disease are significantly reduced. To bring them back to normal, the patient needs long-term preventive treatment. Regularly after antiviral therapy, the patient must be examined, namely, a blood test for the absolute number of neutrophils and leukocytes.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Symptoms of decline
If neutrophils are low due to the development of a viral or bacterial infection, protozoal disease or metabolic pathology, tumor formation, symptoms of the disease that caused the change in tests will appear.
Neutropenia, which occurs due to vitamin deficiency or physical fatigue, does not manifest itself by any external clinical signs. Also, as in the case of congenital neutropenia, only test results indicate a deviation from the norm.
Important information: How much ESR for oncology in an adult (table)
If the decrease in the level of neutrophil cells has not reached a critical value, it means that the body has enough resources to protect itself. Other leukocytes are able to perform the protective functions of neutrophils, but the fight against infection in such conditions takes longer.
A lack of these types of white blood cells can lead to unpleasant health consequences. With such a violation, there is a possibility of the disease becoming chronic, because There are not enough neutrophil cells in the body to neutralize the source of inflammation. Decreased immunity, characteristic of the state of neutropenia, increases the risk of contracting an infection in crowded places and leads to the accelerated spread of bacteria and viruses in the body.
In severe neutropenia, when neutrophil cells are practically absent in the blood, the body does not respond to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, there is a rapid increase in the specific symptoms of the disease.
Band neutrophils: what does a decrease in indicators mean?
The action of mature leukocytes is controlled by different compounds: enzymatic, platelet, arachidonic acid metabolites. Their increased activity is observed in young people. Band neutrophils are quickly released into the bloodstream and mature under various physiological factors:
- Stress;
- Hormone surges;
- Physical activity;
- Eating;
- Pregnancy.
Their normal level should not exceed 1-6% of the number of all leukocyte cells. But the largest number of segmented elements is found - 45-70%.
A drop in young white blood cell counts indicates a decrease in the functionality of the immune system. Neutropenia with a sharp decrease in NEU is called agranulocytosis. It appears due to immune or myelotoxic disorders.
The cause of low young neutrophil cells can be:
- Infectious lesions (fungal or intracellular microbes);
- Viruses of severe diseases (hepatitis, rubella);
- Bacteria (tuberculosis, endocarditis, etc.);
- Anaphylactic shock (allergic reaction);
- Leukemia;
- Bone marrow diseases (metastasis, damage, aplasia);
- Collagenosis.
Hereditary diseases, the toxic effects of heavy metals, and radiation exposure can also reduce neutrophils in the blood. Temporary neutropenia is observed during exacerbation of chronic ailments.
The main reasons for the increase in the concentration of neutrophils in the general blood test
According to medical specialists, neutrophilia (increased levels of neutrophils in the blood) can be observed in the following situations:
- Necrotic processes (extensive burns, stroke, gangrene, myocardial infarction).
- Acute bacterial infections that are accompanied by purulent-inflammatory processes (ENT infections, tonsillitis, abscesses, tuberculosis, acute pyelonephritis, appendicitis, salpingitis, pneumonia, peritonitis, sepsis, scarlet fever, cholera, etc.).
- Intoxication (poisoning) with bacterial toxins without infection itself.
- Intoxication affecting the bone marrow (lead, alcohol).
- Malignant tumors.
- Recent vaccination.
- A recent infectious disease.
A variant of the norm of neutrophilia is:
- Pregnancy.
- Physical stress endured.
- Transferred mental stress.
- A hearty lunch.
Degrees of neutrophilia:
- Moderate neutrophilia – up to 10*109/l.
- Severe neutrophilia – from 10 to 20*109/l.
- Severe neutrophilia – from 20 to 60*109/l.
The degree of neutrophilia makes it possible to determine the intensity of the suspected disease: the higher the neutrophil count, the more severe the disease.
Content:
- The concept of neutrophils and their types
- Functions of segmented neutrophils
- Indications for donating blood for neutrophils
- The norm of neutrophils and the reasons for their decrease
← Reasons for an increase or decrease in neutrophils in a blood test in children?
What does a high level of neutrophils mean and is it dangerous? →
To determine the state of the human body, a blood test will help, which shows whether there is a disease. When segmented neutrophils are low, the specialist determines that an infection is present.
Natural causes of increase
An increase in the concentration of neutrophils (a shift in the leukocyte formula to the right) is not always of an abnormal origin. Although this is true for most possible clinical situations.
If we talk about natural factors, they will be like this:
- Pregnancy. Gestation creates a large load on the mother’s body, and all immune processes intensify. Which ultimately causes an increase in levels in a laboratory study. This is not dangerous, because the answer is false. However, just in case, you need to check other indicators. Sluggish manifestation of pathology is possible.
- Delivery.
- The menstrual cycle and the period right before it. The body considers the natural monthly processes of egg maturation and release as intense stress. The result is a false immune reaction. This does not pose any danger; you need to wait until the end of the period and everything will return to normal on its own.
- Exercise stress. The more intense it is, the more significant the deviations in neutrophil levels will be. Levels return to adequate levels without medical assistance or external influence in general.
- Consuming large amounts of food. In general, food causes a temporary increase in the concentration of formed cells. The relationship is directly proportional. Everything returns to normal after a few hours.
Stress affects performance in the same way. This also applies to any emotional manifestations.