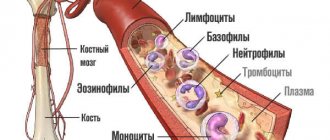
Increased levels of neutrophils (neutrophilia)
Phagocyte engulfs bacteria
The main function of neutrophils is to protect the body from all kinds of pathogenic particles. They instantly react to the penetration of a foreign microorganism, absorb it and digest it. The neutrophils themselves then die, releasing a large amount of specific substances that destroy the remaining bacteria.
Neutrophils are the most numerous group of leukocytes; their levels are usually determined during a standard clinical blood test. If the values exceed the norm, an inflammatory process occurs in the body. This condition is called neutrophilia. Depending on the degree of increase, you can determine how extensive the inflammation is.
The study of the number of neutrophil cells involves measuring their total number in a unit of blood, as well as their percentage of the total number of white blood cells.
Values above normal for adults:
- in absolute quantity - > 6.5 * 109/l;
- as a percentage - > 75%.
Causes of neutrophilia in adults
Neutrophilia is a faithful companion of bacterial infection
The growth of immune cells indicates the body's response to pathogens. Detection of an increased value of neutrophils indicates the following reasons:
- diseases caused by bacteria: pneumonia, tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis, dysentery, tuberculosis, diphtheria, lymphoreticulosis, osteomyelitis, tetanus, syphilis, gonorrhea and others;
- tissue necrosis resulting from gangrene, extensive burns, cardiovascular diseases;
- fungal diseases: mycosis, candidiasis, lichen;
- oncological diseases of various organs;
- diabetes;
- inflammatory lesions of the skin;
- anemia;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- intoxication, including alcoholic beverages.
Causes of increased blood levels
The reasons for the increase in segmented neutrophils in the blood are very different. Numerous studies have shown that their high activity is observed during bacterial infection. The function of these cells is to identify, subsequently engulf and digest the infectious agent through phagocytosis.
An increase in segmented neutrophils is observed in the following situations:
- otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis and other bacterial infections;
- allergic diseases, diabetes mellitus, various metabolic disorders;
- autoimmune group of pathologies: rheumatism, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis;
- purulent-septic conditions;
- psoriasis, dermatitis and other skin problems;
- open extensive damage to the skin - burns, trophic ulcers;
- diseases of the circulatory system, bone marrow.
There are other causes of neutrophilia - this is the term used in the medical literature when an increased number of neutrophils is present in the tests. Segmented representatives are mature forms that perform the entire range of intended functions. They are also called granulocytes due to the content of specific inclusions with biologically active components in their structure.
What does a reduced level of segmented neutrophils in a child indicate? Reasons for the increase in band neutrophils in the blood of an adult.
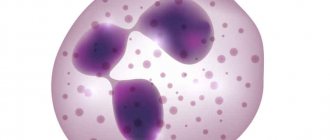
Segmented neutrophil under a microscope
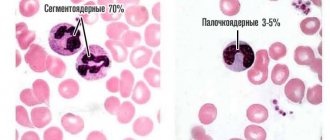
Segmented neutrophils are increased in adults
Neutrophil development
Neutrophils originate in the bone marrow and go through developmental stages from myeloblast to band cell and then segmented cell. Mature cells contain a nucleus, which consists of segments interconnected by nucleoprotein threads. In the bloodstream of an adult, they make up about 70% of all leukocytes.
Segmented neutrophils live for about 14 days, after which they are destroyed in the liver and spleen. If cells encounter pathogenic particles, they die earlier in the fight against them. Accelerated cell death provokes the active generation of new neutrophils. This process continues until the tissues damaged by microbes are completely restored. Therefore, an increased amount indicates an inflammatory process in the body or its presence in the recent past.
Having detected increased values of segmented neutrophils, the doctor will prescribe additional examinations to determine the cause. Factors that cause the growth of mature cells can be inflammatory phenomena, infectious processes, malignant tumors, diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
The indicator is higher than the norm for adults - > 72%.
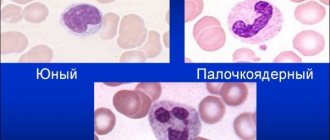
Band neutrophils are elevated in adults
Band neutrophils in a blood smear
An immature neutrophil has a nucleus that resembles a rod in appearance, hence its name. Band cells undergo maturation in the bone marrow, so their number in the bloodstream of an adult is small. On average, they make up 3 to 5% of all types of immune cells.
Unlike segmented cells, immature cells do not have all the tools to fight harmful microorganisms. Their main task is to develop to the next, mature level. An increase in their number per unit of blood means that new neutrophils are being actively produced.
An increase in units of immature cells is called a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. This is a characteristic indicator that in most cases means a deterioration in the patient’s condition. For example, if an increase in band neutrophils is detected against the background of influenza, we are talking about the addition of a bacterial infection.
Therefore, diagnosis of band cells is mandatory during therapy, the postoperative period, and termination of a course of medications. An elevated reading will indicate a complication.
The value is higher than the norm for adults - > 6%.
Description of band neutrophils and signs of their increase
Band neutrophils are neutrophils whose main function is to absorb small foreign particles, bacteria and microbes
Neutrophils make up the majority of all leukocytes. Their main task is to protect the body from foreign cells by absorbing and digesting them. This process is called phagocytosis. After engulfing and breaking down a foreign cell, neutrophils destroy themselves.
Neutrophils are able to penetrate through the walls of blood vessels and tissues to the affected area. They have several stages of development. The youngest and immature neutrophils are called band neutrophils. This is due to the fact that their core has not yet split; it looks like an elongated stick. These cells are not yet able to penetrate tissue or absorb foreign cells because they do not have enough enzymes. Their main function is to mature in order to become a full-fledged cell capable of phagocytosis.
The bone marrow, spleen, and liver are responsible for the production of neutrophils.
Bands are increased when an inflammatory process begins in the body. The body begins to actively produce young neutrophils to fight infection. Neutrophils are localized at the site of inflammation, actively engulf pathogenic cells, and then die off themselves. The breakdown products of neutrophils soften tissues, causing them to suppurate. Therefore, the main sign of increased and active work of neutrophils is a purulent process. It can manifest itself in the form of sinusitis, otitis, purulent wounds, purulent plaque on the tonsils, etc.
An increased content of neutrophils is called neutrophilosis. Because band neutrophils are produced early in the disease and take time to mature, neutrophilia may begin asymptomatically.
When neutrophils mature and begin to act, typical signs of the inflammatory process appear: swelling and redness of the skin or mucous membranes, increased body temperature, purulent discharge, soreness of the affected areas, fatigue and poor health, headache.
How to detect neutrophilia?
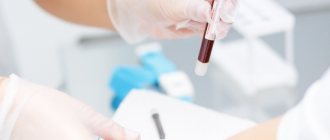
The basis for diagnosing neutrophilia is a clinical blood test
The level of neutrophils is diagnosed based on a detailed clinical blood test. Before analyzing the level of neutrophils, it is necessary to refuse food 8 hours before blood collection, exclude physical overexertion, alcoholic beverages and medications.
Values above normal indicate the presence of neutrophilia. This pathology is divided into 3 stages, depending on the level of excess of the norm.
- The absolute number of neutrophils is up to 10 * 109/l - inflammation of a moderate nature, localized in one focus;
- The number of cells is diagnosed from 10 to 20 * 109/l - pronounced neutrophilia with a more severe inflammatory process that has spread beyond one focus;
- The level of neutrophils in a unit of blood is determined from 20 to 60 * 109/l - a severe stage, indicating extensive damage to the body as a whole.
If the form with the analysis results indicates only a percentage, you can calculate the absolute indicator using the formula:
Relative indicator * number of leukocytes / 100.
If the percentage is 68, and there are only 7 * 109/l leukocytes, then 68 * 7 / 100 = 4.76.
Normal blood cell count in children
In children and adolescents, the normal number of segmented cells differs from adults and changes as they grow older. A blood test is very important for children, especially very young ones, since they often cannot detect a disease in themselves and correctly describe the symptoms.
Doctors compare the results obtained with the following normal indicators:
- children 12-15 years old – 40-65%;
- children from 7 to 12 years old – 35-60%;
- children from 1 to 6 years old – 25-26%
- children from 6 to 12 months – 16-45%;
- babies from 1 to 6 months – 16-45%;
- babies up to 1 month – 45-80%.
In children, the number of segmented neutrophils regularly changes depending on age.
When segmented neutrophils are increased in a child, this indicates the presence of a disease or a congenital pathology, so additional examination is necessary.
If segmented neutrophils are reduced, the following phenomena may be observed:
- heavy sweating;
- pneumonia;
- strong temperature changes;
- chills;
- increased heart rate;
- frequent colds.
With a strong decrease in these blood fragments, the child may develop severe neutropenia, which primarily manifests itself as severe nervous tension and weight loss.
The reason for the decrease in leukocytes can be congenital pathologies, poor environmental situation, long-term illnesses, weakening of the body due to improper nutrition and daily routine, long-term use of medications, etc.
What could affect the results of the study?
Eating the day before the test can trigger neutrophilia
Moderate neutrophilia indicates not only pathogenic processes, but also reflects some physiological conditions. Small cell growth can be caused by:
- pregnancy,
- increased physical activity,
- stress,
- large meals.
A number of drugs also cause an increase in the number of neutrophils. If taking medications cannot be stopped before taking the test, you must inform your doctor about this.
Medicines that increase neutrophil levels:
- Acetylcholine chloride,
- Chlorpropamide,
- Heparin,
- Histamine,
- Norepinephrine,
- all corticosteroid medications,
How to treat deviation
To begin treatment, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. The cause of the deviation may be temporary and go away on its own (allergies to medications and food, surgery, vaccinations). A temporary increase is most often an effect on the treatment of another disease.
If the cause of elevated indicators is any disease, then to stabilize the level of the protective element it is necessary to cure the underlying disease.
It is not recommended to engage in self-treatment using medications, homeopathy or various folk remedies. The restoration of cell number will be positively affected by:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- seasonal intake of vitamins;
- good nutrition;
- distribution of physical activity;
- reduction of stressful situations.
Important information: Norm of leukocytes in the blood of children (table by age)
How to lower neutrophil levels in adults?
The cause of neutrophilia must be determined by a specialist
If the number of neutrophils has increased, then the immune system needs this number of cells to suppress pathological processes in the body. Therefore, there is no need to specifically reduce the level of neutrophils. It is necessary to find the reason for their increase, eliminate it, then the number of immune cells will return to normal.
The most common factor in the growth of neutrophils is bacterial infection. Depending on the disease, the patient will be prescribed a course of narrow or broad spectrum antibiotics. To treat fungal infections, various antifungal agents are used, and if they recur, antibiotics are used.
The danger of increased levels of neutrophils in the blood
Neutrophilia without attention is fraught with complications
An increase in the number of neutrophils is not always accompanied by severe symptoms. A person can consider himself absolutely healthy, but detect a deviation from the norm only on a form with test results. This may mean that there is a hidden infection in the body. If no action is taken, the inflammatory process will spread to larger areas.
Malignant and benign tumors are manifested by increased levels of neutrophils. If over a long period the number of cells significantly exceeds the norm, the doctor may suspect the oncological nature of the pathology in the patient.
During pregnancy, a small increase in neutrophils is considered normal. But too high values can lead to miscarriage, since neutrophils perceive the fetus as a foreign organism in the woman’s body.
Causes in healthy people
It happens that neutrophilia is observed in healthy people. Such results may turn out to be false. Violation of preparation rules can greatly inflate real indicators. Most often, elevated neutrophils in the blood occur in the following cases:
- If the patient has eaten the day before, the blood test must be taken strictly on an empty stomach; it is allowed to drink a little clean water.
- Before collecting biological fluid, you drank alcohol or smoked a cigarette.
- Before visiting the laboratory, the person drank strong coffee, tea, or energy drinks.
- For 2-3 days before the test, the patient was engaged in heavy physical work or intense training.
- The day before, the person had suffered severe stress; during the test, the person was excited or very excited.
- In women during premenstrual syndrome, segmented neutrophilia is observed with a simultaneous decrease in the number of lymphocytes.
- An increase in the number of neutrophils is considered a physiological reaction of the body during pregnancy and does not require correction.
To clarify the reliability of test results, the doctor often prescribes a repeat examination. This allows us to exclude false neutrophilia and correctly assess the patient’s condition.
Prevention
Prevention of neutrophilia is the key to good health
In order for neutrophils not to have to intensively fight pathogenic bacteria, it is necessary to help the body avoid the penetration of pathogenic microbes.
- Berries, fruits and vegetables should only be consumed clean. Meat, fish, milk must be thermally processed correctly.
- It is necessary to maintain personal hygiene: thoroughly wash your hands, brush your teeth, and keep household items clean.
- The living space must be ventilated daily and wet cleaning must be carried out regularly.
- It is necessary to avoid contact with sick people.
- Wounds and abrasions should be disinfected and protected from the external environment with a bandage or plaster.