Hidden blood in the stool is an alarming signal when a person needs to undergo a comprehensive examination. Positive results mean the development of numerous dangerous diseases that require timely treatment.
A person develops characteristic clinical signs, which are also taken into account by the proctologist when making a diagnosis. Without a timely and correctly designed treatment regimen, progressive pathological processes will lead to serious complications.
Reasons for hidden blood impurities in stool
In children, women and men, there are various reasons that provoke the appearance of hidden bleeding. Pathological processes cause disturbances in the body that cannot be ignored; it is important to immediately go to the hospital.
There are the following causes of blood impurities in stool:
| Age, gender | Causes |
| In infants and other children |
|
| Among women |
|
| In men |
|
In each case, regardless of age and gender, a person develops accompanying clinical signs, which also help to establish an accurate diagnosis. Treatment is prescribed by a proctologist, guided by the results after a comprehensive examination.
Immunoassay
Involves the determination of hemoglobin in feces using the immunochromatographic method. This is the only way to diagnose blood particles that the microscope cannot “see”. Moreover, they do not affect the color of stool (they can only slightly change its consistency). But their concentration is quite significant: more than 3 mg. for 1 year of stool.
Since the most common benzidine and guaiac tests, although informative, are true only if a strict algorithm is followed, doctors are increasingly turning to immunochemical tests.
The latter are especially sensitive to human hemoglobin and do not require special preparation (this includes diet). The only significant disadvantage is their “limitation”: they are aimed at identifying colon cancer.
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
Pathologies of the upper gastrointestinal tract, unfortunately, are not always amenable to diagnosis in this way. But they identify cancerous tumors of “their” department with 98% accuracy.
In what cases is an occult blood test prescribed, and which doctor?
Diagnosis and treatment is carried out by a proctologist. It is important to consult a specialist at the first signs or disturbances. He will conduct an examination and prescribe additional diagnostic methods to make an accurate diagnosis.
There are certain situations when a patient is prescribed a stool occult blood test:
- a person is worried about painful sensations in the abdominal area of unknown origin;
- I am concerned about prolonged nausea in the absence of diseases of the digestive system;
- periodic vomiting;
- bowel dysfunction;
- peptic ulcer of the digestive system;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- infection of the body by parasites;
- a sharp decrease in body weight for no reason;
- development of polyps;
- mechanical injury to the digestive system.
An occult blood test is also prescribed to patients who suspect the development of malignant processes, especially if there are relatives in the family with this disease.
Stool research methods
Hidden blood in the stool (positive means that a person is developing a serious pathology that requires medical attention) is detected by certain diagnostic methods, which have their own advantages and disadvantages:
| Name | Description |
| Gregersen reaction or benzidine test | Preparing for the test requires the mandatory exclusion of meat products. The chemical reagents used make it possible to identify human and animal red cells. The Gregersen reaction is the most informative diagnostic method, which allows you to detect bleeding in any part of the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Weber's reaction or guaiac test | The results will show a positive answer if the blood loss is at least 30 ml. The Weber reaction has low sensitivity and requires the patient to follow a strict diet during preparation. Guaiac resin helps detect hidden blood in stool. |
| Immunochemical analysis | A modern diagnostic method with which human hemoglobin is determined. It is not necessary to adhere to a diet, but this test is informative if the doctor suspects damage to the lower part of the digestive tract. |
| Fluorescence test | The accuracy of the analysis is 80%, but the patient is advised to follow a strict diet, since the chemicals used by specialists during tests react with human and animal hemoglobin. |
Taking into account the results of diagnostic tests, the proctologist determines the main cause of hidden bleeding and selects the most effective treatment. It is important to adhere to medical prescriptions to prevent possible complications.
Immunochemical method and its advantages
Examination of feces for occult blood using the immunochemical method has a number of advantages over the Gregersen reaction:
- sensitivity is much higher;
- specific only to human hemoglobin, does not react to meat myoglobin, vitamins and medications;
- does not require special dietary preparation;
- is more suitable for diagnosing bleeding from the lower intestines, because the technique uses a reaction to the protein part of hemoglobin, and it is actively digested in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
The test is included in the algorithm for examining patients with suspected colorectal cancer (localized in the colon and rectum). The test result does not contain information about the specific area of the bleeding digestive system and the causes of bleeding.
It should not be treated as a ready-made diagnosis. If the result is positive, the test indicates that an additional colonoscopy is recommended to determine the cause of the bleeding. The essence of the method: the use of antibodies to human hemoglobin makes it possible to detect the presence of antigens in the material under study and provide a quantitative characteristic.
When is an immunochemical study indicated?
The main indications for studying the pathology of the lower intestine are suspicion:
- on a tumor;
- polyps;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease.
The use of the technique in the early diagnosis of colorectal cancer (the most common cause of cancer mortality in the population) helps to conduct timely follow-up examinations and improve the prognosis of the disease.
The population screening algorithm provides for the priority carrying out of an immunochemical study with stool testing by all persons over 50 years of age, and in case of hereditary disadvantage from 40 years of age - three times. If a positive result is detected, a colonoscopy is prescribed.
Experts believe that following this program can reduce the death rate from colorectal cancer by 25%.
Technique for conducting immunochemical research
The technique uses the principle of immunochromatography:
- a drop of the test material is placed in a well of a plate into which a reagent with specific antibodies and a dye has previously been applied;
- in the presence of antigen from the hemoglobin of red blood cells, a reaction occurs between them;
- a colored complex is formed;
- with the liquid the complex passes into the test zone, along the way it additionally combines with antibodies;
- In the testing area, a certain threshold level of hemoglobin concentration is set; its excess in the sample is indicated by pink-violet markings.
A laboratory technician can perform several tests at once
Preparation for analysis, diet
The preparatory stage before taking tests requires special attention, since the treatment regimen depends on the results obtained.
To obtain the most accurate data, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- It is necessary to stop taking medications that may affect the condition of stool a week before submitting the material. The same goes for intestinal motility.
- 3 days before the tests you must adhere to a certain diet. Avoid eating meat and fish products. Exclude tomatoes, broccoli, red and hot peppers. The same goes for offal, beets, beans, green onions, and apples.
- During preparation, you should also avoid vegetables and fruits; they affect intestinal motility.
- You should not take laxatives or perform mechanical bowel cleansing before tests.
- It is not recommended to brush your teeth before taking tests in the morning.
To obtain reliable results when collecting material, it is better to wait for the natural process of bowel movement.
How to properly collect and donate feces?
It is recommended to collect the test material in the morning after a hygienic shower. For collection, you must use a special stick and a sterile container. The total volume of the test material should not be less than 20 g. The maximum shelf life of stool is 12 hours.
It is better to deliver the material to the laboratory within 3 hours after its collection.
Stool collection
The collection of material for analysis is carried out at home in a sterile dry container, which can be purchased at a pharmacy. As already mentioned, bowel movements should be spontaneous without the help of any means. It is advisable to collect feces during morning bowel movements after carrying out hygiene measures for the genitourinary organs and anus.
The stool must be delivered to the laboratory within 3 hours. If this is not possible, then stool can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 12 hours.
Decoding research: what does a positive result mean?
Positive occult blood in the stool means that a serious pathology is developing in the human body.
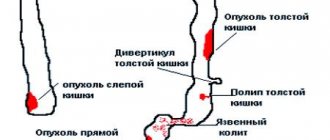
Among these conditions the following diseases can be distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Crohn's disease | The pathological condition is characterized by a chronic inflammatory process. Nodules form in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. The patient is worried about severe pain, skin rashes, and fever. Blood or pus is released along with diarrhea. In some situations, joints hurt. |
| Haemorrhoids | The disease is accompanied by swelling and prolapse of veins in the anal area. Constipation with hemorrhoids provokes bleeding. Progressive pathological processes provoke swelling of the soft tissues in the anal area. A person is worried about discomfort and irritation. The pain syndrome intensifies. |
| Intestinal diverticulosis | The pathology affects the gastrointestinal tract. The inflammatory process provokes the formation of sac-shaped protrusions (diverticula) in the organs of the digestive system. Residues of food and feces accumulate in the resulting depressions. The process of fermentation and putrefaction begins, which leads to inflammation. |
| Peptic ulcer | Chronic pathology, which is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. The mucous membrane on the walls of the stomach becomes covered with ulcers. A person is worried about acute pain, nausea and vomiting. |
| Varicose veins of the esophagus | A pathological condition that is characterized by venous dilatation of the veins in the lower part of the esophagus. The main cause in most cases is impaired blood circulation. Massive and unexpected bleeding occurs, which is sometimes the only symptom of the disease. |
| Parasitic infestation | The human body is affected by parasitic worms. The stool is disrupted due to blockage of the bile and intestinal ducts. Infection with parasites primarily manifests itself as an allergic reaction. |
| Nonspecific ulcerative colitis | The intestinal mucosa becomes covered with bleeding ulcers. The stool becomes disrupted, and as the pathological processes progress, the stool contains pus or blood. The disease is accompanied by intoxication of the body, pain and fever. |
| Tumor neoplasms | Cancerous processes can appear in the intestines or stomach. The tumor grows and in the process of enlargement destroys the walls of the affected organ. Severe bleeding occurs and the patient requires surgical intervention. |
| Cirrhosis of the liver | A serious disease in which liver cells are gradually replaced by connective tissue. The pathology cannot be cured, but modern medicine can slow down degenerative processes. |
| Amoebiasis | An infectious disease characterized by ulcerative lesions of the large intestine. Abscesses appear in various organs. A person’s stool is disrupted, and the stool contains blood impurities. Symptoms of anemia also appear, body weight decreases sharply, and the patient is bothered by severe pain in the abdominal area. |
| Proctitis | The pathology provokes an inflammatory process that affects the mucous membrane of the rectum. Accompanying symptoms are frequent urge to defecate, burning, itching and a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the anal area. |
| Intestinal ischemia | The pathological condition is characterized by impaired blood circulation in the intestinal area. Problems with blood vessels disrupt the nutrition of the digestive system. A person is bothered by severe pain. Necrotic foci form in the intestines. |
| Intestinal tuberculosis | An infectious disease caused by mycobacteria. Inflammatory foci in the form of multiple granulomas form on the intestinal walls. |
| Polyposis | A precancerous condition that requires surgical treatment. In different parts of the digestive system, benign neoplasms are formed that can degenerate. The pathological condition is accompanied by mucous and bloody discharge, intestinal obstruction and severe pain. |
Diseases in which occult blood in stool is positive
Hidden blood in stool is positive means that there are ruptures in the organs of the digestive system, the main cause of which is hemorrhagic syndrome.
The same applies to food allergic reactions, endomithreosis in women, and intestinal infectious diseases. Taking certain medications that affect blood clotting may also affect a comprehensive examination.
Decoding the result
The analysis is based on the reaction that occurs when specific antibodies come into contact with human hemoglobin. The essence of the procedure: the laboratory assistant applies the brought sample to a special test strip with reagents. If there are blood impurities in the feces, the component bodies bind to the antibodies, causing a purple stripe to appear in the control zone, indicating a positive result.
Normally, an immunological stool test should show the absence of blood in the biomaterial being tested. A false positive result may be due to the following reasons:
- ignoring the diet (if the analysis is carried out using a benzidine test);
- collection of feces during menstruation;
- recent nosebleeds;
- excessive bleeding gums.
In the rarest cases, testing may show a false negative result. A similar disorder usually occurs if unchanged red blood cells are present in the stool. For example, they may appear due to fissures in the anus or due to hemorrhoids.
If the patient followed all the preparation rules and the analysis showed a positive result, this is not always a cause for concern. Doctors claim that a small amount of blood in feces is a natural phenomenon characteristic of the body’s functioning.
The permissible rate of blood discharge is not higher than 2 mg per 1 kg of sample. If the value exceeds this indicative value, it is necessary to conduct additional diagnostics that will help identify what was the primary source of the violation. If testing gives a positive reaction, this may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal tuberculosis;
- formation of polyps;
- exacerbation of ulcers;
- the formation of tumors of a benign or malignant nature in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract);
- helminthic diseases;
- haemorrhoids.
Only a qualified specialist should decipher subsequent tests and make a diagnosis. In Moscow and other large cities, the cost of this varies from 350 to 700 rubles (depending on the type of clinic). Decoding the result usually takes from 3 to 7 days.
Reasons for false indicators
The results of studies of stool from a healthy body will be negative. But there are situations when the information received is not completely reliable.
Causes of false-positive and false-negative results of stool occult blood tests:
- the rules of preparation before taking tests were violated;
- gums bleed;
- there are nosebleeds;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines;
- the patient did not follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding dietary nutrition.
To obtain the most accurate results, it is important not only to adhere to your doctor’s recommendations, but also to take three tests in a row.
Treatment of pathology in adults and children
Occult blood in the stool is often treated on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization of patients is required in case of a dangerous pathological condition, when it is necessary to monitor the patient’s health. The person is prescribed medications and a special diet is selected, taking into account the main reason for the positive results of occult blood in the feces.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Vascular drugs | Aescusan, Detralex | Medicines increase the tone of blood vessels. The recommended dosage for adults is 12-15 drops 3 times a day. The medicine is taken before meals; it can be diluted with a small amount of water. The course of therapy lasts 2-12 weeks. |
| Antibacterial drugs | Azithromycin, Amoxiclav | Drugs are necessary if the source of occult blood in the stool is a bacterial infection. The medicine is taken before or after a meal. The recommended dosage is 250-500 mg once a day for 3 days. |
| Antiviral agents | Arbidol, Viferon | Medicines are prescribed to combat pathology of viral origin. Capsules are taken orally before meals. The dosage is selected depending on the patient’s age and is 50-200 mg per day. The course of treatment lasts 10-14 days. |
| Antiparasitic drugs | Metronidazole, Pyrantel | The drugs are prescribed for parasitic infection of the body. Adults are recommended to take 1.5-2 g orally 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts a week. |
| Probiotics | Bifidumbacterin, Linex | Medicines help restore beneficial intestinal microflora. The dosage of the drug depends on the age of the patient. The doctor prescribes 1-3 sachets 2-4 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 3-5 days. |
For hemorrhoids, patients are prescribed special rectal suppositories. To combat peptic ulcers of the digestive system, cytostatics are used.
Norm
Laboratory testing for the presence of hidden blood in the masses is prescribed not only for those who suffer from chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but also for those who outwardly look absolutely healthy and have no complaints, but previous tests confused their gastroenterologist.
In order to “decipher” the ready-made results of the analysis, you should be at least a little familiar with generally accepted norms . This is useful both for those for whom high indicators immediately cause panic, and for at least a little informed people who know what to expect at a doctor’s appointment.
The results of the examination depend on the reaction of the blood pigment to particles of latent hemoglobin, the intensity of which is measured in “+”:
- “+” - weakly positive reaction;
- “++”, “+++” - positive reaction;
- “++++” - the reaction is strongly positive.
If you look at the numbers, then normally there is 1 mg per 1 g of feces. hemoglobin (or 1 ml. blood). Permissible deviations should not exceed 2-3 mg. hemoglobin. Otherwise, the examination will need to be carried out at least once more.
It should not be overlooked that bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract is not always diagnosed the first time; the most sensitive tests are needed to determine it.
Folk remedies
Positive occult blood in the stool means that a person needs to undergo a full examination to determine its cause and begin treatment. In complex therapy, you can use recipes from witch doctors and healers, but strictly after making an accurate diagnosis.
It is necessary to consult with a proctologist to select effective methods, taking into account the state of health and the individual characteristics of the body.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Baths | Brew 2 tbsp boiling water. pharmaceutical chamomile. Infuse the resulting mixture and strain. | Baths are recommended for hemorrhoids. Water procedures take 20-30 minutes. |
| Nettle | Dry leaves of the plant are poured with boiling water, infused and filtered | It is recommended to take the finished product 3 times a day. Nettle stops bleeding well. |
| St. John's wort | The herb (15 g) must be brewed in a thermos with hot water (250 ml). The resulting mixture should be infused overnight. In the morning, strain the medicine and dilute with warm boiled water to obtain 200 ml. | It is recommended to take the finished product orally before meals, 3 times a day, 25 ml. The course of treatment lasts 14 days. |
| Herbal collection | Mix 2 tsp. yarrow and calendula 5 tbsp. Add 3 tbsp. chamomile and clover, also 7 tbsp. cudweed and birch leaves. Pour boiling water (0.5 tbsp) into 1 tbsp. herbal collection. Infuse, cool and strain. | It is recommended to take the finished decoction an hour after meals 3 times a day. |
| Slippery elm bark | Pour 0.5 tsp. powder with hot water (1 tbsp.). Add 1 tsp. simple or granular bark. Place the resulting mass on medium heat and heat for an additional 20 minutes. Cool and strain well. | It is recommended to take the finished medicine orally, 1-3 tbsp. every day. |
| Healing infusion | Mix chopped dill and rose hips in equal proportions. Add stinging nettle, chamomile flowers and motherwort. Pour 1 tbsp. the resulting mass with boiling water (200 ml). It is better to infuse all components in a thermos for 1.5 hours. Strain the broth and take it orally. | It is recommended to use the finished product in the morning and evening, 0.5 tbsp. The course of therapy lasts a month. |
For internal bleeding, it is also recommended to use a decoction of orange peels. Onion infusion has a bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect against parasitic infections.
Early diagnosis of occult blood in human feces will make it possible to identify pathological processes in the first stages of development. Also conduct additional examination and begin treatment, which will help prevent possible complications.
In most cases, positive stool test results are accompanied by characteristic symptoms. This means that the patient must begin treatment. Otherwise, he will face serious consequences.