Red blood cells normal
Red blood cells make up a large proportion of the total volume of blood elements, their number reaches about 100 trillion. It is important to maintain the normal number of red blood cells, since deviations up or down indicate problems in the body.
Count down 5 seconds. During this time, about 10 million red blood cells were formed in your blood, and the same number died. Isn't it an important part of the body's work?
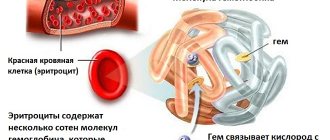
They live for about 110 days, moving around the body along with the blood, and it is these blood cells that deliver oxygen to muscle tissue and “remove” carbon dioxide.
Small size and flexibility allow red blood cells to move through small blood vessels.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which gives them a scarlet tint, that is, makes the blood red. Its small size and flexibility allow it to move through small blood vessels.
The number of these blood cells in the body depends on several factors:
- Floor
- Age
- Health status
Leukocytes
Leukocytes refer to white blood cells that perform a protective function, that is, they represent the immune system. Normally, in a general blood test of a healthy man, the total number of leukocytes should be from 4 to 9 * 109 per liter.
With an increased content of leukocytes, one can judge the body’s immune response, which is observed in infectious diseases (primarily provoked by bacteria), allergic reactions and inflammatory processes. A high level of white blood cells can also be a consequence of recent stress, bleeding, tumor processes and a number of other diseases.
A decrease in white blood cell counts indicates a suppressed state of the immune system. Such results are observed in viral infections (rubella, measles, influenza), sepsis, severe toxicosis, pathologies of the hematopoietic organs, autoimmune disorders and radiation sickness.
It is not only the assessment of the total number of leukocytes that matters. There are five types of leukocytes: monocytes and lymphocytes, basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils. They all have different functions, and therefore it is important to know their proportion in the composition of the blood in the body. The ratio of different types of leukocytes in the total volume is called the leukocyte formula.
What are the norms of red blood cells for different categories of people?
Red cell norms for children
In a growing body, norms change quite quickly, and for different months of life, there are different norms in the blood. (Table 1)
Table 1
Child age:
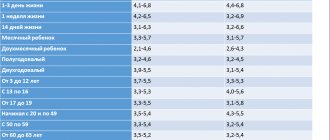
| Up to 2 weeks | Up to 1 month | Up to 4 months | Up to 6 months | Up to 9 months | 1 year | 3 years | 6 years | 9 years | 12 years |
| Normal values, x1012 g/l. | 3.9-6 | 3.3-5.4 | 3,5 – 5,2 | 4-5.5 | 3.9-5.3 | 4-5.3 | 3.7-4.8 | 3.6-4.9 | 3.7-4.9 | 3.9-5.0 |
After 12 years and up to 15, red blood cells gradually equalize to the size of norms in adults.
Norms of red cells for the female body
On average, the norm for women is from 3.8 to 5.1. Indicators also vary depending on age. (Table 2)
Table 2
| Age 15 – 18 years | 18 – 65 years old | 65 and older |
| Normal values, x1012 g/l. | 3,5 – 5,0 | 3,9 – 5,0 | 3,5 – 4,8 |
In adolescence and middle age, red blood cells are in the same position. But at the age of 65, their number drops slightly, but is normal for the body.
Pregnant women have their own norm of such cells. This is easy to explain; during pregnancy, the volume of water in the mother’s body and blood increases, which dilutes the blood due to increased fluid levels. Their number can increase to 5.6 x g/l.
Since most pregnant women do not have enough iron in their bodies, their level may drop to 3.0.
Normal red cell concentration for men
The male body contains more red blood cells than the female body. On average, this figure ranges from 3.9 to 5.6 g/l. Up to 65 years of age, their number should not exceed this figure. And in older age (65+), the upper threshold rises slightly (5.7), and the lower threshold falls (3.5). (Table 3)
Table 3
| Age 15 – 18 years | 18 – 65 years old | 65 and older |
| Normal values, x1012 g/l. | 4,0 – 5,6 | 4,0 – 5,6 | 3,5 – 5,7 |
Results
Erythrocytes are red blood cells that are responsible for the stable delivery of hemoglobin to the body tissues to provide them with oxygen. An increased level of red blood cells accompanies, first of all, diseases of the heart and respiratory system. This is due to thickening of the blood and its inhibited circulation.
The respiratory and cardiovascular systems suffer from oxygen starvation. Not related to pathology, otherwise, physiological reasons for the increased content of red blood cells in the blood are due to oxygen starvation, developing:
- with excessive physical exertion;
- due to residence (temporary stay) in highlands;
- with nicotine addiction;
- due to dehydration (dehydration) of the body.
Male red blood cell values are slightly higher than female values due to gender differences in hormonal levels. The average normal red blood cell count in an adult male ranges from 4.4 to 5.6 (cells ×10^12/l). The permissible deviation from the norm should not exceed 0.5 (×10^12/l).
With chronic erythrocytosis (increased concentration of red cells) and hyperhemoglobinemia (increased hemoglobin levels), a man requires additional examination. Erythrocytosis is not a diagnosis, but a basis for determining the cause that led to a pathological change in blood composition.
Deviations of red blood cells from normal values
The concentration of red cells in the blood can be determined by doing a complete blood count. Now analyzes are processed using modern equipment, so you will receive an error-free result immediately.
You can see the condition and saturation of red blood cells in the general analysis form. With the help of such an analysis, it will be easier for the doctor to assess your body and hurry up with subsequent treatment, if necessary.
Red blood cells sometimes change their size and shape, leading to:
- Microcytosis - the blood contains a large number of red blood cells smaller than average in size (4.9 - 6.4 microns). Such a number of small bodies indicates possible: malignant tumors, thalassemia, hemolytic anemia.
- Macrocytosis – cells are larger than normal. This may occur for the following reasons:
- During pregnancy, the size of red blood cells may increase.Anemia in pregnant women,
- Pathologies of the liver and lungs,
- Decreased thyroid function
- Features of physiology in infants.
- Megacytosis - the size of red blood cells significantly exceeds their standard sizes (more than 12 microns). As they enlarge, they become oval. Such changes may result from:
- Worms,
- Folate deficiency anemia,
- Dyserythropoiesis.
What are antibodies? And how to decipher the results of the analysis?
Why do men and women need regular laboratory screening?
Because sometimes only a test can reveal a health problem. For example, the same infections can cause such different symptoms that it is not easy to suspect one pathogen. In men, pathogenic microorganisms may not manifest themselves at all, but for their wives they become very dangerous (a classic example is the human papillomavirus). Therefore, men and women need regular examinations, with different diagnostic approaches. The same applies to hormonal studies: both men and women are tested for testosterone, but the norms for this hormone differ by more than 10 times. And even classic basic studies: biochemical and general blood tests for men and women have their own nuances... A general blood test is the basis of any serious examination of the body’s condition. Therefore, a general (or clinical) blood test is prescribed for almost all complaints and diseases by doctors of all profiles. It is included in the examination standards for medical examinations, urgent and planned hospitalizations. Unlike the general one, a biochemical blood test makes it possible to assess the functions of specific human organs, as well as the presence and quantitative parameters of basic microelements and vitamins in the body. The general test standards for men and women are not the same; this also needs to be taken into account when interpreting. We provide test standards and a list of blood parameters in the order in which they are usually indicated on the laboratory test form.
Why do red blood cells increase?
An increase in red cells (erythrocytosis) can have completely different causes, associated with both physiological and pathological factors. Changes can occur within a day.
Increases by 0.5x per liter of blood in the following cases:
- Stress
- Hunger
- Excessive sweating in hot weather
- Staying at altitude (mountains, airplanes, etc.)
- Heavy physical activity
Red blood cell maturation
Our red blood cells can often be higher than normal due to diseases, including:
- Vaquez leukosis (chronic),
- Pulmonary hypertension (primary),
- Kidney diseases (polycystic disease, hydronephrosis, renal artery stenosis),
- Oncological diseases: cancer of the kidneys, liver, adrenal glands, adrenal adenoma,
- Dehydration due to diarrhea, vomiting,
- Fluid loss from burns
- Treatment with diuretics,
- Bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis, obstructive pulmonary emphysema.
The work of red blood cells in the body
Red blood cells are, one might say, the most necessary elements of blood in the list of hematological indicators. Thanks to their work, the body breathes much-needed gas - oxygen; cells can receive nutrition and function fully. Red blood cells also remove carbon dioxide from tissues and participate in protecting the body from infections. And what else but blood helps us maintain a constant body temperature.
Without red blood cells, a person could not live. The body of an adult man contains about 5 liters of blood (8% of the total body weight). With this volume of blood, what is the norm of red blood cells in men? Let's take a closer look at these questions.
What are the symptoms of elevated red blood cells?
Symptoms of an increase in red blood cells in the blood mainly depend on the initial disease, as well as on erythrocytosis (the physiological reasons that caused it). With a slight increase in red cells, the skin color does not change, but with an absolute increase, the skin becomes red.
Among the signs indicating their increase are the following:
- Headaches
- Redness on the skin
- Constant fatigue
- High blood pressure,
- Bleeding from the sinuses
- Fainting,
- Itching on the skin after contact with water.
An increased level of red blood cells is possible as a result when a person spends a long time at an altitude of more than several kilometers above sea level, due to the fact that there is less oxygen there. In the presence of such air, the cells suffer due to lack of oxygen and produce more red blood cells than usual.
There is also a less pleasant reason. When swimming in a pool or outdoors, in ponds, dirty water or water with a high content of chlorine may get inside.
Erythropenia and erythrocytosis
There are two types of deviations associated with the quantitative composition of red blood cells. The first is their lack, then erythropenia, and the second is their excess. How does the male body react to the fact that the blood contains a small amount of red blood cells? Since the level of transport and nutrition of the cells will be disrupted due to the low level of red blood cells, they will not be able to receive the necessary amount of substances they need.
The consequences of such violations can be the following conditions:
- loss of consciousness, and sudden;
- state of apathy and constant fatigue;
- change in the skin towards a white color;
- excessive fatigue;
- with sudden movements and physical activity, pain in the head and frequent dizziness.
What is the body's reaction to surges in red blood cells? The above symptoms are considered the most harmless and do not cause concern for a man or the need for a medical examination. Frequent causes of erythropenia are the occurrence of cancer, which disrupts the general rhythm in the human body.
There is also a natural reason that affects the production of red blood cells - excessive consumption of protein foods . This phenomenon occurs in people who adhere to a vegetarian diet.
Red blood cells may not always be insufficient in the body. Sometimes it happens that there are too many of them in the circulatory system. This is due to many factors and can occur in both men and women. The most likely causes of excess blood substances include:
Article on the topic:
What is an APTT blood test? What should the indicators be?
- Oxygen starvation and tense environmental conditions affecting the level of these substances in the blood. People living near factories and other industrial enterprises suffer from this.
- An increase in temperature, which is associated with visiting saunas and baths.
- Smoking on a daily basis.
- Oncological diseases that metastasize to the brain.
- Lack of clean water, which must be available daily.
- Unbalanced diet, which is dominated by fats and contains few amino acids.
Important! Often, jumps in red blood cells are not associated with serious illnesses, but are manifestations of external factors.
So, if the red blood cells are not normal, then the doctor can talk about the development of erythrocytosis or erythropenia.
How to reduce the level of red blood cells?
The condition of elevated red cells in the blood is not a disease. To reduce the content of red blood cells, you should find the original cause - a disease or factor that affects the body, and fight it directly.
Doctors recommend following a diet by removing fatty and iron-containing foods from your diet. People who are overweight are advised to bring it back to normal. For those who are accustomed to cigarettes, give up this bad habit.
The hospital may prescribe phlebotomy (forced removal of blood from the body) or oxygen therapy. In the most severe cases, surgical intervention is an option.
This way you can determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Platelets
The main purpose of platelets is to ensure hemostasis, or, in other words, blood clotting. They take part in the human body’s immune response to infection. The normal value is from 180 to 320 * 109 per liter. A low platelet count may indicate severe inflammation or an autoimmune disease. An increased degree is typical for conditions after large blood losses (for example, after undergoing surgery), as well as for atrophy (decreased functioning) of the spleen and cancer.
What else does a general blood test reveal in an adult man?
Causes of low red blood cell concentration
A low concentration of red blood cells per liter of blood is called erythropenia - anemia. It appears as a result of large losses of blood, in the case of injuries, surgical operations, chronic bleeding, or occurs with a disruption in the creation of red blood cells.
Their number has decreased due to a lack of iron in the body, most common in young children and pregnant women.
The red blood cell count is also reduced by a lack of vitamins B12 and B9.
Infectious diseases (diphtheria, whooping cough, etc.) also affect the reduction of red blood cells in the body. Many diseases affect the deviation of red blood cells from the norm, so it is better to start any checks with a blood test. This will allow you to quickly establish a diagnosis and select the best treatment.
Biochemical blood test for women and men
A biochemical blood test in women and men shows how well certain organs function. It is from biochemical analysis that one can assume, for example, diagnoses such as renal failure, diabetes mellitus or viral hepatitis. A reduced level of total protein in the blood along with an increase in creatinine and urea levels may indicate kidney disease. Excess or lack of glucose may indicate diabetes.
Deficiency is also observed with prolonged fasting. Excessive amounts of bilirubin indicate liver problems. And an increased level of total cholesterol indicates the presence of a large amount of saturated fat in your diet or thyroid disease.
Biochemical blood test standards are common for both sexes:
- total protein - 63-87 g/l;
- urea - 3.4-8.6 mmol/l;
- creatinine - 15-75 µmol/l;
- total bilirubin - 8.49-20.58 µmol/l;
- ALT - up to 37 units;
- AST - up to 42 units.
Regular laboratory diagnostics can help you monitor your health and begin timely prevention of the most common diseases. But what to do if the clinic does not have a medical examination program? For your convenience, the online laboratory “Lab4U” has developed an Annual Medical Examination complex. It includes more than 30 blood parameters, reflecting the functioning of all body systems, and allows you to detect diseases at the earliest stages before the appearance of clinical signs.
Permissible deviations
The number of red blood cells in a man’s body is constantly changing. In this case, the change occurs both in the direction of exceeding (erythrocytosis) and in the direction of decreasing (erythropenia) normal values. Allowed deviation is /- 0.5*1012/l. The dynamics of indicators is due to the following factors:
- Dehydration. In this case, the so-called relative erythrocytosis is observed: the volume of circulating blood in the body decreases, but the number of blood cells remains the same. As a result, the blood “thickens” and there are more red cells per unit volume. This phenomenon may appear after intense physical activity, a long walk in hot weather, or in case of poisoning, accompanied by repeated vomiting and diarrhea.
- Being at high altitude (for example, in the mountains) will also provoke erythrocytosis.
- Domestic injuries. Adult men are more susceptible to household injuries than others: scratches, abrasions, cuts and other conditions that may cause bleeding. Sometimes this leads to a slight decrease in red blood cells.
Reasons for the downgrade
A decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood below normal in men is called erythropenia. This condition develops under the influence of certain causative (etiological) factors, which include:
- Severe blood loss after injury with damage to large vessels or extensive surgery.
- Long-term systematic loss of a small volume of blood (chronic blood loss), particularly against the background of heavy menstruation in women.
- Increased destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia), provoked by improper transfusion of blood components with the development of an immunological conflict, poisoning with heavy metal salts, and also developing in people with an artificial heart valve.
- Insufficient intake of iron from food into the body or impaired absorption of iron into the blood from the intestines against the background of various pathologies of the digestive system.
- Deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid, which are necessary for the normal process of formation and maturation of red blood cells in the red bone marrow.
There is also a relative decrease in the number of red blood cells in a man’s blood due to an increase in plasma volume against the background of a significant intake of fluid or volumetric intravenous infusion of various solutions.
Reasons for the increase
An increase in the number of red blood cells in a man's blood (erythrocytosis) is a fairly rare occurrence. It can accompany the development of a benign tumor of the erythrocyte lineage of the red bone marrow hematopoiesis, which is called erythremia. A physiological increase in the number of red blood cells may occur in residents of high mountainous areas, characterized by a reduced partial pressure of oxygen in the air.
Relative erythrocytosis also occurs, in which the absolute number of cells remains at the same level, but due to a decrease in the volume of blood plasma, their volume increases. This condition is accompanied by severe dehydration (dehydration) of the man’s body against the background of intense diarrhea, uncontrolled use of diuretics, as well as insufficient water intake into the body, as well as its loss through sweat.