Normal blood iron levels for women
The most important indicator characterizing the effectiveness of the process of the necessary formation of blood cells in a woman’s body is the iron component.
The need for the required content of this element in the blood of the weaker half of humanity is determined by the monthly loss of a certain amount during menstruation.
A blood test will allow you to determine the percentage of useful metal content and take timely measures in case of its shortage or excess.
On average, the norm of iron in the blood for women is determined to be 3 g or 35 mg per kg, however, the criteria for the volume of its content also depend on the age of the women.
A deficiency of this element in the blood can cause anemia, disrupt the immune system, cause mental development problems, cause nervousness, changes in intracranial pressure, and also cause irritation on the skin.
Attention! If it is exceeded, inflammatory processes of internal organs and, in particular, the renal system, as well as the onset of leukemia, are possible.
The level of iron in the blood for women differs depending on age.
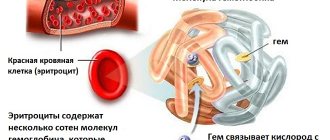
The calculation of the norm of hemoglobin, consisting of iron and protein, in a woman’s blood is determined in a special way and is expressed in grams per 1 liter of blood.
In this case, the average positive indicator of a healthy woman should be within the normal range of 120 to 140 g per liter.
During menstrual cycles, a decrease to 110 g per liter is considered normal. At a young age, the norm is from 115 to 135 g per liter. blood.
Under 40 years of age
Until the age of twelve, the content of hemoglobin in the blood does not depend on the gender of the child , and only upon the onset of puberty, as well as the beginning of menstruation in girls, does it decrease.
After this, as the system responsible for hematopoiesis develops, the level of hemoglobin in the blood gradually increases, reaching its stability, characteristic of a woman’s age range from 18 to 40 years.
In this case, the norm is from 117 to 155 g/l.
Under 60 years of age
After 40 years, a woman’s body changes dramatically, which is characterized by the passive functioning of the hormonal function of the ovaries, its decline, as well as a decrease in metabolic processes.
Often these circumstances lead to an increase in body weight, while the activity of the hematopoietic function decreases.
The level of hemoglobin in the blood begins to decrease , often falling outside the normal range, which is from 112 to 152 g/l.
This problem affects women who neglect protein foods at this age, due to their being on a diet, due to the desire to lose weight.
After 60 years
During the age period under consideration, the aging process is actively going on in the woman’s body, due to which there is a loss of fluid in the tissues , in particular, there is less liquid blood.
When it thickens, the level of hemoglobin in women's blood increases, in the absence of diseases associated with oncology and anemia. The norm is from 114 to 160 g/l.
During pregnancy
A special condition of a woman, called pregnancy, is accompanied by an increased load on the female body, which is caused by an increased need for essential microelements.
Iron is necessary for better oxygen supply to the unborn child, which is the key to its harmonious development.
In a pregnant woman, iron deficiency anemia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- increased fatigue and feeling of weakness;
- violation of the taste gamut;
- decreased blood pressure and significant pallor of the skin.
Note! Doctors recommend that if girls exhibit such symptoms, immediately consult a doctor to establish a possible pregnancy, in order to take the necessary measures aimed at preventing oxygen deficiency for the fetus, which can cause both premature birth and the manifestation of pathological diseases in the child.
The norm for pregnant women is from 110 to 140 g/l.
The relationship between iron and ferritin
Serum iron is increased (the reasons must be identified before starting therapy), and ferritin is decreased - this situation is often explained by a deficiency of the microelement. This prognosis is especially often found in people who abuse alcohol, as well as with infectious diseases or hepatitis.
If ferritin is elevated and total iron levels are within normal limits, this may indicate the presence of various causes, including: arthritis, malignant tumors, colds and much more. To avoid negative consequences, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Causes of iron deficiency in a woman’s body
The reasons why a woman’s blood level of iron does not meet the established criteria include its lack, due to increased consumption, as well as insufficient intake of the metal into the body.
On the contrary, a deviation from the established norm is an excess of this element, due to the possible influence of a number of external factors that influence the increase in hemoglobin levels.
Lack of iron in the body: symptoms in women
For this painful condition, as a result of which the required level of iron in a woman’s blood is disrupted, the following symptoms are inherent:
- muscle weakness;
- rapid onset of fatigue with minimal activity;
- drowsiness;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- increased heart rate when blood pressure drops;
- distortion of taste;
- loss of consciousness.
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin include:
- Incorrect diet containing insufficient amounts of foods that contain iron (liver, meat, mushrooms, carrots, watermelon, apples and others);
- Exacerbation of inflammation and infections (hemorrhoids, gastritis, gynecological diseases, etc.);
- Poor absorption of iron by the body , as a result of a lack of vitamins, as well as folic acid;
- Heavy blood loss as a result of surgery or heavy periods;
- A lifestyle without mobility;
- Poisoning at home with industrial poisons . In this state, the functioning of the human liver is aimed at increased production of enzymes, the synthesis of which requires iron, and therefore its consumption increases significantly.
Excess iron in the body: symptoms in women
This painful condition is dangerous due to the formation of blood clots and the deterioration of the natural movement of oxygen within the body.
Blood thinning medications are prescribed, and the consumption of foods containing a significant percentage of iron is minimized.
The cause of the increase in hemoglobin should be identified, and then immediate measures should be taken to eliminate it.
Factors that provoke high hemoglobin levels are:
- The actual residence of a person in high mountain regions, where the body, due to a lack of oxygen, makes attempts to replenish it, thereby increasing the percentage of red blood cells in the blood;
- Monotonous and prolonged physical activity, the consequence of which is an increased level of iron in the blood for women;
- Significant loss of fluid from the body, which is typical for places with a hot climate, as well as when performing work that causes profuse sweating;
- Dehydration of the body as a result of intestinal infections;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system, as well as diabetes;
- Long-term use of medications classified as diuretics.
- Pregnancy status;
- Abuse of tobacco products.
Signs of High Iron Levels
Serum iron is elevated, the reasons for which are often unclear to the patient, in 1/8 of the world's population. The pathology in the initial stage passes without symptoms. Expressive signs of the pathological process appear in later stages, especially if proper treatment was not started in a timely manner.
Signs of High Iron Levels
The most typical symptoms include:
- chronic fatigue and rapid fatigue;
- joint and abdominal pain;
- heart failure or bradycardia;
- changes in skin color including individual pigmented spots;
- loss of interest in sex;
- weakening and loss of hair;
- hypothyroidism or low thyroid function
- enlarged liver or spleen;
- active weight loss;
- inability to concentrate;
- joint pain.
If you have the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Timely treatment will help avoid many complications, including the chance of death.
What are the dangers of excess and deficiency of iron in the body?
A significant increase in hemoglobin in a woman’s blood is a dangerous problem for her body.
The blood becomes viscous, which is accompanied by rapid fatigue and insomnia, increased blood pressure, the appearance of spots on the skin, loss of appetite, heavy and prolonged periods, and disruptions in the genitourinary system.
A lack of iron microelements in a woman’s body also poses a danger to it , since it is directly related to the low content of hemoglobin in her blood, which in medicine is called anemia.
Anemia associated with iron deficiency in the body (anemia) is quite dangerous because it is accompanied by a significant decrease in immunity.
The appearance of an adult woman in this condition deteriorates, the hair on the head becomes brittle, the nails become brittle, and the skin becomes pale.
Blood test for iron: how to prepare for it
The level of iron in the blood for a woman must be constantly monitored , so it is necessary to conduct a timely study, which is a special procedure carried out in laboratory conditions and determining the amount of indicators contained in the blood.
The procedure is carried out as prescribed by the doctor, both during a general examination of the body, for preventive purposes, and when there is suspicion of specific diseases.
Medical criteria prompting this analysis are:
- acute and chronic infections;
- suspicion of iron deficiency in the body;
- various inflammations in the body;
- the need for differentiated diagnosis of anemia;
- suspicion of a lack of vitamins, as well as their imbalance;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines.
This blood test is carried out in the morning and on an empty stomach.
Despite this, you need to prepare for it several days in advance, for which you should follow a number of simple rules:
- 5 days before the test, you need to limit your intake of medications containing iron;
- For a week, you should limit your diet in relation to fatty and fried foods;
- Reduce physical stress on the body;
- Avoid taking oral hormones;
- At least 24 hours before the test, avoid tobacco and alcohol;
- Food consumption should be done 8-10 hours before the test;
- Before analysis, do not perform x-rays or fluorography;
- Avoid physical therapy procedures.
Analysis and preparation for it
Blood samples must be taken in the morning; the best time to take blood samples is 8-10 am. You should prepare properly for the examination:
- do not take dietary supplements containing iron for at least a week;
- Eliminate alcohol and fatty foods at least 24 hours before;
- if symptoms of ARVI or other infection appear, the test should be rescheduled for another time;
- warn the doctor if the patient is taking any medications, including contraceptives.
Reference values (in µmol/l):
- for infants under one year of age – 7.15 – 17.90;
- for children over one year old and adolescents under 14 years of age – 8.9 – 21.47;
- for girls over 14 years old and women – 8.9 – 30.44;
- for boys over 14 years old and men – 11.63-30.44.
How to increase iron in the blood: iron-rich foods
rich in these microelements will help get rid of acute iron deficiency in the body
The products under consideration are divided into two groups: animal and plant origin.
Animal foods include:
- meat dishes;
- fish dishes;
- offal;
- cream.
Plant foods, accordingly, include:
- buckwheat grain;
- beans;
- potato;
- carrot;
- tomatoes;
- apples;
- pomegranate;
- strawberry;
- blueberry;
- mushrooms;
- nuts.
The third group should conditionally include drinks such as juices from:
- drain;
- tomatoes;
- carrots;
- beets.
The table below shows examples of some products with the proportion of mg of useful metal in them per 100 g.
| Name | Amount mg/100 g |
| Beans | 72 |
| Nuts from the forest | 51 |
| Oat flakes | 45 |
| Buckwheat | 31 |
| Pig liver | 29,7 |
| Sea kale | 16 |
| Blueberry | 9 |
Flour products, strong coffee and tea, canned and calcium-containing products, vinegar and alcoholic beverages will slow down the increase in iron levels in a woman’s blood.
How to increase iron in the blood quickly
Raising the required blood level quickly enough is only possible with the help of special medications.
When the metal components in the blood decrease to the lowest possible limits, doctors, under constant supervision, carry out the necessary medical measures in a hospital setting, using medications containing synthetic iron compounds.
In addition to the above increase, you must adhere to the following rules for adjusting your diet:
- Coffee drinks and tea are contraindicated for consumption because they have the ability to wash iron out of the body;
- You should eat a large amount of foods that contain iron;
- Reduce heat treatment of food to a minimum, during which many microelements are destroyed;
- Meat products should be consumed together with fruits, high in vitamin C, for better absorption of the metal microelement;
- If there is a significant decrease in hemoglobin in the blood during the winter, doctors recommend additionally eating frozen berries, which will “slow down” the process of iron loss and also supply the body with additional vitamins.
Causes of increased iron
Even the slightest deviation of serum iron levels from the norm can lead to various diseases that indirectly affect human life. Therefore, it is important to know about the main reasons for changes in regulatory indicators.
The quantitative indicator of a microelement in the blood is characterized by the speed of its absorption through the colon. So, if the intestines lower natural regulation, the metal begins to quickly accumulate in the tissues of the body, leaking into other organs or tissues. In this case, hemochromatosis is diagnosed.
Hemochromatosis can be primary, resulting from genetic changes, or secondary, due to acute diseases or chronic conditions.
In any case, excess iron accumulates in the liver, heart, pancreas and other organs. The inherited type significantly increases the risk of cancer or heart disease. In some cases, diabetes may develop.
Anemia
Serum iron is elevated (the causes are difficult to detect in a timely manner) under the following circumstances:
- Hemolytic type anemia. It is characterized by the rapid destruction of blood cells, which allows hemoglobin to enter the tissue structure.
- Anemia of hyperchromic type. Leads to problems with the absorption of vitamin minerals and folic acid, without which protein synthesis of hemoglobin is impossible.
- Various kidney lesions in which the natural removal of iron from the body is disrupted. The most common disease of this type is nephritis.
- The presence of acute or chronic hepatitis diseases.
- Poisoning with various chemicals.
- Genetic thalassemia.
Excess metal in the human body can be detected due to blood serum transfusion or through excessive consumption of dietary supplements with a high content of microelements. An increased level is much less common than a decreased level.
Additional risk factors include social or territorial causes, such as cooking in iron vessels or significant metal content in water. Based on recent studies, alcohol intake is directly proportional to excess iron.
Risk factors include men, who develop elevated iron levels much more often than women. This is especially true for people aged 40 to 60 years. The chances of developing hemochromatosis in women increase during menopause, pregnancy or hysterectomy.
Drugs to increase iron in the blood: a review of the most effective
The level of iron in the blood for women is easily maintained by many drugs that have proven themselves and are widely used.
"Ferrogradumet"
The drug contains ferrous sulfate.
Indicated for use:
- with the onset of iron deficiency anemia;
- with a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood;
- during periods when a woman is carrying a child, as well as breastfeeding it;
- with Crohn's disease;
- with diarrhea;
- with enteritis.
Doctors recommend that adults take: 100-200 mg/day, for 30-60 days; children 3 mg/day.
For the purpose of preventive measures, take 325 mg/day ; when treating anemia, the indicated dose is doubled.
"Irovit"
It contains folic and ascorbic acids, components of iron and cyanocobalamin.
Applicable in the following cases:
- with iron deficiency;
- with a lack of folic acid in the body;
- with a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood;
- during pregnancy;
- for preventive purposes.
Adults are prescribed to take 1 tablet in the morning, afternoon and evening; children are prescribed individually in each individual case. The course of taking the drug is no more than 90 days.
"Heferol"
The drug contains ferrous fumarate.
Indicated for use in the treatment of:
- identifying symptoms similar to those described above;
- hypermenorrhea;
- polymenorrhea;
- hematuria.
Adults take 1 tablet per day, children are prescribed an individual dose. The course of treatment ranges from one and a half to two months.
It should be borne in mind that during treatment the general condition may worsen. This circumstance may be associated with a violation of the established daily dosages of medications, as well as individual intolerance to them by the body.
If such a situation arises, you should immediately inform your doctor about it so that he can adjust the dose and type of medication.
Increasing OHSS indicators
The most common cause of increased CVS indicators is iron deficiency anemia. It can be caused by chronic blood loss, adherence to a plant-based diet, alcoholism and impaired absorption of iron in the digestive tract. A similar, but less pronounced deviation of indicators from the norm is determined with latent iron deficiency. Other reasons for increased CVSS rates include polycythemia vera, acute hepatitis, and use of estrogens and oral contraceptives.
Vitamins with iron for women
For preventive purposes, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes containing iron elements.
When taking them, you should strictly follow the recommended dosages in order to avoid side effects.
The advantage of these complexes is that their intake is twenty times higher than the absorption of food metal.
To increase the level of iron in a woman’s blood, it is necessary to choose a vitamin complex, the concentration of iron in which will be able to replenish the body’s necessary need for it.
The most effective and time-tested multivitamin complexes of this group include:
- “Complivit Iron” - this vitamin complex contains the required dose of iron per day for a person, the basis of which is fumarate. In addition, it contains in a balanced manner other minerals and vitamins (A, E, B, C) necessary for the body. Doctors recommend using it as a biological supplement with food, 1 tablet and 1 time;
- "Vitacap" is a complex containing iron, prescribed by doctors to pregnant women and nursing mothers. In addition to vitamins E and D, its composition also includes: ascorbic acid, magnesium and potassium. Used orally, 1 capsule per day, in the morning, during breakfast;
- "Teravit" - on the contrary, unlike the previous drug, is not recommended for pregnant and nursing mothers. Contains a high concentration of vitamins: A, B, C, D, which can cause a feeling of nausea when taken, as well as allergies. This drug should be used exclusively as prescribed by the doctor, according to the dosage prescribed by him.
Ways to normalize elevated iron levels
Therapy for elevated metal levels in the blood should be aimed at reducing the total amount of the trace element in the body. The first thing the patient is prescribed is normalization of nutrition in accordance with dietary recommendations.
For the most effective and quick relief, various medications can be introduced into the patient’s body to reduce the amount of metal in the blood. In particularly severe cases, phlebotomy, a bloodletting process, may be prescribed.
Medications
There are currently no direct medications for high iron levels. Despite this, your doctor may prescribe certain medications that can reduce the amount of trace elements in the body.
Medications
Commonly used medications:
- heptapeptides of any group;
- zinc-based preparations;
- hepatoprotectors to protect liver function;
- food complexing agents.
The use of any pharmacological medications should be under the strict supervision of the attending physician. Otherwise, various complications are possible. Depending on the patient's condition, any other drugs may be prescribed. Antidepressants, immunomodulators, or fusion inhibitors are often used.
Diet therapy: general principles of nutrition
Based on the tests performed, certain dietary standards are discussed with the attending physician to significantly reduce the iron content in the human body. First of all, it is necessary to completely exclude any vitamin or mineral complexes containing metal.
This also includes almost all dietary supplements. Taking vitamins B and C is also undesirable.
The following foods should be excluded from your daily diet:
- most seafood, especially shellfish;
- seaweed;
- black chocolate;
- bread and legumes;
- strong green tea;
- pomegranate, persimmon, peaches;
- dried apples, prunes, dried apricots;
It is especially important to exclude eggs, fatty red meat and beef liver. It is prohibited to take any alcohol-containing drinks, including even the weakest cocktails. It is not recommended to take sweets, since the sugar they contain promotes faster absorption of various microelements and vitamins, including metal.
In the absence of contraindications, the doctor may introduce dairy products in large quantities.
Patients suffering from high iron levels should drink plenty of water, which can be diluted with lemon juice for variety. In the absence of contraindications, it is possible to take weak black tea, herbal tinctures or compotes. Any carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited.
Approximate daily diet:
- Breakfast. Steamed oatmeal with the addition of pineapple or strawberries. Black tea without sugar with various herbs.
- Lunch. Light salad of broccoli, cucumber and tomato. You can take 25-30 g of dried almonds or pumpkin seeds.
- Dinner. Boiled buckwheat, bread with low-fat cheese.
- Afternoon snack. Fruit salad (without adding apples) and drinking yogurt or kefir.
- Dinner. Boiled chicken meat with a light dietary side dish. Cocoa or weak black tea.
The basis of your daily diet should be raw food of plant origin. It is also advisable to consume large amounts of soy or legume products. It is best to cook and eat food from glass or ceramic dishes. Iron cans, pots or mugs must be excluded.
If the level of Fe in the blood is high, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the established diet. Any dietary requirements must be agreed with your doctor. In most cases, normalizing nutrition is quite enough to lower the level of metal in a person’s blood. Other products can be added to the products described above, which is also discussed with a specialist or nutritionist.
Phlebotomy
Phlebotomy or bloodletting is the most effective method of lowering a person's serum iron levels.
Phlebotomy
The method involves removing a certain amount of blood from a vein using various methods:
- An incision or puncture in the area of the arterial or venous system. The most dangerous use of phlebotomy, which can result in significant blood loss. The intervention is carried out slowly using a wide needle.
- Banking procedure. For this method, small jars are used, which the specialist places on the patient’s body. This allows blood to be quickly sucked out of the outer capillary or vascular surfaces, restoring natural circulation.
- Hirudotherapy. In this case, medicinal leeches are used, which are placed directly on the incision site. The main feature of this method is the collection of already unusable blood.
The main advantage of using phlebotomy is the rapid stabilization of the patient's condition.
In some cases, improvements in the cardiovascular system, as well as the elimination of unwanted joint pain, are possible. Under no circumstances should bloodletting be performed at home. If used incorrectly, complications may be dangerous to health. Contraindications are: low blood pressure, mental disorders or pregnancy.
Why iron is not absorbed in a woman’s body: reasons
The reasons for poor absorption of the element in question by the female body are an increase in calcium and phosphorus salts in it.
Excessive consumption of dairy products also interferes with the absorption of iron by the body, and therefore it is not recommended to consume iron-rich foods with milk.
In addition to calcium, manganese and zinc also affect the reduction in iron absorption.
In fairness, it should be noted that in case of abuse of foods rich in iron, a similar effect will be observed in relation to the above elements, which is also negative, so it is necessary to strive for a harmonious balance in the consumption of foods.