In what cases is x-ray prescribed for frontal sinusitis?
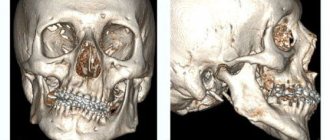
Frontal sinusitis in the image
An X-ray examination is prescribed to determine:
- the presence and localization of formations in the skeleton of the facial skull;
- visualization of the shape, size and condition of neoplasms;
- detection of atypical tumors;
- characteristics of the frontal bone above the eye sockets;
- determining the level of pathological secretion.
Frontitis is a disease of the adnexal cavities that can develop into a chronic course involving the periosteum and bone in the inflammatory process, followed by necrosis (brain abscess).
In addition, the pathology may be accompanied by the development of a purulent form, which can lead to the disease progressing to meningitis.
The clinical picture is due to a disorder of local circulation. Collateral edema prevents the natural self-cleaning of the nasal cavity, which leads to the accumulation of purulent contents and the development of characteristic symptoms.
Types of frontal sinusitis
Based on the nature of the disease, two forms of inflammation of the frontal sinuses can be distinguished:
- acute;
- chronic.
Acute frontal sinusitis is characterized by the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the frontal sinuses and nasal cavity. Moreover, due to swelling of the mucous membrane and blocking of the frontonasal canal, the inflammatory process progresses quite quickly. The duration of this form of the disease is 2-3 weeks.
The transformation of the acute process into chronic frontal sinusitis is facilitated by insufficient cleansing of the frontal sinuses . This often occurs due to a severe curvature of the nasal septum, as well as due to incorrect treatment of inflammation. The duration of chronic frontal sinusitis is on average 4 to 6 weeks.
According to the type of inflammatory process, they are distinguished:
- exudative frontal sinusitis - characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the frontal sinuses. It, in turn, is divided into catarrhal, serous and purulent frontal sinusitis;
- productive inflammation - tissue proliferation inside the sinuses (polyps, cysts). An example is polyposis frontitis.
According to the etiological factor (i.e., depending on the pathogen), inflammation of the frontal sinuses can be classified as:
- viral frontal sinusitis, caused by viral infections. Moreover, most often, this form of inflammation is not an independent disease, but a consequence of ARVI;
- bacterial frontal sinusitis - occurs when various types of bacteria join viral inflammation;
- Fungal frontal sinusitis occurs when there is a fungal infection. Most often, this type of inflammation of the frontal sinuses occurs in older people;
- allergic frontal sinusitis is a consequence of allergic reactions;
- mixed frontal sinusitis, including several different forms of inflammation.
Based on the localization of the process, two types of frontitis are distinguished:
- unilateral (right-sided and left-sided sinusitis) – the inflammatory process occurs only in one of the sinuses;
- bilateral - simultaneous damage to two frontal sinuses.
Why do you need an x-ray for inflammation?
The appointment of an x-ray helps to identify the first signs of pathology and diagnose it in the early stages of development. However, diagnosing frontal sinusitis has some disadvantages:
- based on the use of radiation;
- has low sensitivity;
- lack of high-resolution technical capabilities.
Despite the shortcomings of the diagnostic procedure, x-rays are a more informative method for detecting the inflammatory process. The study is prescribed at the stage of selecting therapeutic measures, as well as to assess the dynamics and effectiveness of the selected treatment method.
Consequences of frontal sinusitis
Timely contact with a specialist helps to avoid the undesirable consequences of inflammation of the frontal sinuses. Moreover, in this case, the disease frontal sinusitis will be completely cured. However, an incorrectly selected course of therapy or prolonged chronic frontal sinusitis can lead to very serious complications:
- meningitis – damage to the membranes of the brain and spinal cord;
- abscess (purulent inflammation) of the brain;
- blood poisoning;
- osteomyelitis (a purulent process that develops in the bone) of the frontal bone and many others.
As you can see, the consequences of frontal sinusitis can be extremely serious . Moreover, there are fatal cases. Therefore, you should not delay going to a medical practitioner, much less neglect treating the inflammatory process, at least at home, but certainly under the supervision of your attending physician.
What does an x-ray image show?
The disease is displayed as a darkening with an upper horizontal level.
Frontitis on an x-ray, carried out in a direct projection with centering on the frontal region, shows the following:
- shape and condition of the frontal sinuses;
- the presence of an inflammatory reaction;
- amount of exudate;
- darkening with cystic formations;
- decreased air cavity in the sinuses;
- degree of proliferation;
- displacement of individual walls or sections thereof.
With neoplasms, in particular cysts, darkening (white spots) of a round shape containing fluid are visible on the image.
A decrease in air density (pneumatization) occurs due to the accumulation of secretions in the upper horizontal zone. When the body position changes, for example, when the head turns, the infiltrate shifts.
X-ray is used not only to confirm the diagnosis, but is also an informative way to differentiate frontal sinusitis from other pathological processes.
Indications for testing and symptoms of sinusitis
The main symptoms that may prompt a doctor to examine the frontal sinuses to make a diagnosis are:
- difficult and sometimes almost impossible nasal breathing;
- purulent and profuse nasal discharge;
- swelling and redness of the eyes;
- headaches, dizziness;
- swelling, tension and pain when pressing on the soft tissues near the maxillary sinuses, in the forehead;
- nose bleed;
- fever, general deterioration of the patient’s well-being, weakness.
The difference between frontal sinusitis and sinusitis is the localization of inflammation. In case of sinusitis, the focus of inflammation is the maxillary sinuses, in case of frontal sinusitis - the frontal sinuses.
X-ray of the sinuses
Symptom of "horizontal level"
Such a concept as a “horizontal level” symptom on an X-ray image appears as a result of a violation of the outflow of infiltrate from the paranasal sinuses. When the patient changes position, the fluid moves to the side.
Normally, the contours have thin walls, so they are carefully viewed in the image. The absence of boundaries indicates the possible presence of an X-ray negative formation.
In some cases, additional instrumental research methods may be needed - MSCT or MRI.
The safest diagnostic method
Diagnosis of pathology
External manifestations of the disease can be noticeable to the naked eye (puffiness of the face, local swelling and redness of the skin with “swimming” of the eye from the side of the more inflamed sinus). Also, inflammation of the frontal sinuses in an acute state is quite easily determined by palpation and tapping - the patient winces from touch, percussion causes increased pain, as does finger pressure on the forehead.
Anterior rhinoscopy demonstrates the presence of copious purulent discharge, severe hyperemia of the mucous membranes, their swelling and thickening. More accurate and complete information about the condition of the sinuses is provided by X-rays in frontal and lateral projections, as well as computed tomography.
Obtaining data helps to better assess the patient's condition and make the right decision about the required type of treatment.
A blood test allows you to see an acute inflammatory process, which is manifested by leukocytosis, a shift in the blood count to the left and an increase in ESR. If the collected data is insufficient to obtain an accurate diagnosis, a diagnostic trephine puncture of the frontal sinuses may be prescribed.
Types of medications and their use
In uncomplicated cases of the disease, conservative treatment is usually used using several types of treatments and a variety of drugs.
To reduce swelling and reduce mucus formation, so-called high adrenalization of the mucous membranes is performed. To do this, they are often and generously lubricated or irrigated with the following drugs: Galazolin, Ephedrine or Adrenaline. Adrenaline-based drugs are also prescribed for instillation into the nose. As a result of their use, the thickness and looseness of the mucous membrane of the nose and sinuses decreases, a huge amount of mucus stops being produced and the patient feels relief from his condition.
A whole range of drugs is prescribed internally to the patient:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics, especially when a purulent infection develops, for example, Claforan, Klacid and others.
- Analgesics that help reduce pain in the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Antihistamines that alleviate the patient’s general condition (Tavegil, Suprastin, Claritin and others).
For frontal sinuses, warming and other physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, warm ones on the frontal sinus area, UHF sessions, laser and infrared therapy, are very helpful. Only a doctor prescribes such manipulations and only if they cannot worsen a person’s condition.
More information about frontitis can be found in the video:
If all conservative efforts do not produce results, and drug treatment does not bring relief, then the doctor recommends trepanopuncture, that is, of the frontal sinus in order to cleanse it of its contents and cure sinusitis.
When diagnosing frontal sinusitis in a pregnant woman, only a specialist can make a decision on drug treatment. He assesses possible risks for both the health of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. Based on his conclusions, he makes a decision. In most cases, treatment of frontal sinusitis in pregnant women comes down to rinsing the nasal cavity and warming it up, as well as using some harmless physiotherapeutic procedures. In rare cases, a puncture is prescribed
Recipes for nasal rinsing
The presence of a large amount of contents in the sinuses and nasal cavity creates serious discomfort for the patient and interferes with normal breathing, and this, in turn, causes a lack of oxygen, increased headaches and worsening of already poor health.
In order to remove mucous and purulent discharge and reduce inflammation of the frontal sinuses, the following is used:
- Most often, a solution of sea salt is used for rinsing. It has several advantages: salt helps to quickly relieve swelling, disinfects well and soaks possible crusts of dried pus, anesthetizes and has an antimicrobial effect due to the content of iodine and other healing microelements. After such rinsing, the patient feels much better, his nose is freed and air flows freely. In addition, this procedure helps reduce headaches due to decreased pressure in the sinuses.
- You can also rinse your sinuses with alkaline mineral water without gas. It should be warm. This water contains soda, which has a softening effect on irritated and inflamed mucous membranes. By alkalizing nasal mucus, it helps reduce the amount of discharge and makes breathing easier.
- Rinse the nose with decoctions of various medicinal herbs. Chamomile is especially good and gentle. With its warm decoction you can quickly rinse the nasal passages, relieving inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane and thereby simplifying the release of pus from the frontal sinuses. To prepare such a decoction, you usually take a tablespoon of dried chamomile flowers and pour a glass of boiling water. You need to leave for about an hour, then strain well and cool to a pleasant temperature.
The addition of infection and the appearance of purulent contents means the development of an acute infectious inflammatory process. You can cope with this condition only with the help of powerful ones.
If possible, it is highly advisable to conduct a sensitivity test to determine which group of bacteria caused the inflammatory process. In this case, it will be much easier to choose the ideal antibacterial drug, whose action will specifically “hit” the bacteria that cause the disease. However, such a study often takes too much time, and if the patient is unwell, it is contraindicated to hesitate.
Therefore, in acute frontal sinusitis, strong general antibiotics such as Claforan are most often used.
The duration of treatment and dosage, as well as the drug itself, are chosen by the attending physician. It is very risky to interfere with the treatment regimen he has adopted, since an advanced disease becomes chronic and can threaten with numerous dangerous ones.
Folk recipes
Among the people, inflammation of the frontal sinuses is often treated with heating:
- To do this, you can use a regular hard-boiled chicken egg. It is first wrapped in cotton cloth and applied to the affected area. As it cools, the egg is unwrapped and they begin to “roll” the frontal part of the sinus with it. This procedure is especially well received by young children. They do not regard it as a treatment, and after warming up they experience relief.
- It is also good to warm your forehead with bags of rock salt or coarse sand. They are made small and sewn from thick fabric. A heated bag is placed on the frontal sinus area and the inflammation is thoroughly warmed up. Since sand and salt retain heat well, the procedure is long and effective.
Surgery
If none of the methods of conservative and medicinal treatment has the expected effect, the doctor prescribes trephine puncture of the frontal sinus. This operation can be carried out in two ways:
- Through the frontal surface of the frontal bone.
- Through the orbital wall of the frontal sinus.
The second method is used much less frequently due to the high risk of deep perforation of the orbital socket and penetration of infection into it.
To perform this, special markings are used, which are performed using an x-ray of the skull in order to determine the thinnest area of the frontal bone above the sinus. It is in this place that a special mark is placed into which the drill is placed and a hole is made. A special cannula is inserted into it, the contents of the sinus are drained and it is washed. Through the same cannula, medications are injected into the cavity. Treatment usually lasts from 3 days to a week, rarely a little longer.
Surgical treatment is combined with medication to speed up recovery and completely eliminate the source of infection.
To speed up the healing of the injury, the patient is recommended to have a high-calorie diet high in vitamins and microelements. After recovery for some time, the patient needs to take special precautions and avoid hypothermia and colds.
In which institution can an x-ray of the sinuses be taken?
An X-ray examination of the paranasal sinuses can be done in a public clinic with a referral from an otolaryngologist or in a private diagnostic center.
If frontal sinusitis is suspected and it is necessary to take an x-ray, the patient needs to have a referral from an ENT specialist indicating the area to be examined.
A specialized doctor, an otolaryngologist, can make a final diagnosis and decide on treatment tactics for frontal sinusitis. The specialist evaluates not only the results of the x-ray, but also the general condition of the patient.
After taking a full medical history and studying the radiologist’s findings, the doctor decides whether to perform surgery or prescribe conservative therapy (taking antibiotics, secretolytic and anti-inflammatory drugs).
How to treat the disease frontal sinus sinusitis. Medicines and folk remedies
Frontal sinusitis is one of the varieties of such a dangerous disease as sinusitis, in which the pathological inflammatory process is localized in the sinuses located in the superciliary region, in other words, above the eyes.
Like almost all other diseases, it can occur in acute and chronic forms. It is on this that depends how to treat the disease frontal sinusitis, the choice of therapy that will be the most effective and will lead to a speedy recovery.
Inflammation of the frontal sinus during frontal sinusitis
If the development of sinusitis is only supposedly associated with atmospheric pollution, then this relationship has been proven in the occurrence of frontal sinusitis. After all, the diagnosis of frontal sinusitis is most often made to people living in the area of industrial enterprises.
Like sinusitis, frontal sinusitis is caused mainly by staphylococci, but streptococci, Haemophilus influenzae, some fungi and anaerobic microorganisms can also act as causative agents of inflammation. The inflammatory process provoked by them can be of varying intensity, while pus often accumulates in the sinuses.
Frontal sinusitis is characterized by not only local, but also general symptoms. This:
- elevated temperature (up to 40°C), which is a consequence of poisoning of the body;
- diffuse headache that appears as a result of liquor-dynamic disturbance and blood circulation;
- terrible weakness;
- pathological sensitivity to light;
- pain in the ears and teeth;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- blurred vision;
- headache concentrated in one place;
- lacrimation;
- dizziness;
- swelling of the eyelids and skin above the bridge of the nose;
- snot of various colors, but usually it is yellow or green;
- hyposmia/anosmia, etc.
If at least some of these signs appear, you must immediately contact an otolaryngologist, since the inflammatory process can spread to nearby organs and cause meningitis and other equally dangerous pathologies.
?
What is the pain with frontal sinusitis?
Headache with frontal sinusitis usually occurs before other symptoms. It is localized between the eyebrows.
With a unilateral acute process - from the side of the inflamed sinus, with a bilateral one - in the entire area, and with a chronic process it is diffuse. The mechanism of its appearance is quite complex, since the trigeminal nerve is involved.
Other reasons for a headache, especially in the morning, are:
- decreased pressure in the inflamed sinus due to oxygen resorption;
- dilation of the arteries and the resulting painful pulsation;
- increased pressure due to the accumulation of pus in the sinus;
- exposure to metabolic products of microorganisms.
Attention! A typical headache may disappear, but this is not always a sign of final recovery, since it can disappear only when the outflow of pus improves.
Both with acute inflammation and the next exacerbation of chronic discomfort in the forehead becomes bursting, the intensity of which increases significantly with any eye movements, with bowing of the head and with percussion of the forehead.
In addition, an extraordinary heaviness appears, felt as if behind the eyes.
Patients feel worst in the morning, which is due to the complete filling of the affected sinus with mucus/pus and a decrease in outflow from it.
Patients often complain of feeling pain not only in the eyebrow, but also in the temporo-parietal or temporal regions, and with unilateral damage, discomfort will also be present only on one side.
In people diagnosed with chronic frontal sinusitis, during periods of remission, the severity of pain is significantly reduced, but they are still constantly present and have a clear localization. It is dull, pressing, sometimes pulsating, intensifies in the evenings, after prolonged tilting of the head or physical stress.
At the same time, most patients can know in advance that an exacerbation is approaching by the appearance of a “tide” in the forehead, both when bending over and when completely at rest. Deterioration of the condition usually occurs in such cases within the first 24 hours. Source: nasmorkam.net?
Frontitis: drugs for treatment. Scroll
Since bacteria are almost always the causative agents of the disease, its treatment is carried out mainly with antibiotics.
Ideally, nasal discharge is initially examined and it is found out which microorganism caused the inflammatory process, as well as how sensitive it is to various antibiotics.
Until the results of this analysis are received, the patient is prescribed amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid. There are a number of drugs on the market containing these substances, these are:
- Augmentin SR;
- Amoklavin;
- Flemoklav Solutab;
- Amoxiclav and others
Subsequently, this penicillin antibiotic is replaced by another, to which the causative agents of the disease have shown greater sensitivity. Although, if frontal sinusitis occurs without the presence of discharge, it is fought with the medications presented above. In addition to penicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides can be used, in particular:
- Cefaclor;
- Summed;
- Cefuroxime;
- Azithromycin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Macropen;
- Cefotaxime, etc.
If acute frontal sinusitis is just beginning, you can try to cope with it with local antibiotics, for example:
- Isophroy;
- Polydexa;
- Bioparox;
- Levomicol.
In addition, the following are often prescribed:
These drugs are classified as vasoconstrictors and are necessary to eliminate swelling. Initially, patients are recommended to use mild agents, for example, ephedrine solution or phenylephrine in combination with dimethindene.
Nazivin , Noxprey , Nazol , etc.), naphazoline ( Naphthyzin , Sanorin , etc.), xylometazoline ( Galazolin , Xylobene , Dlyanos , etc.) may be recommended
1
Decongestants. Prescribing Furosemide or intravenous administration of a 1% CaCl solution to patients is necessary in the absence of any discharge.
2
Antihistamines. Zyrtec, Ebastine, Loratadine and others are also necessary to eliminate swelling of the mucous membrane, which significantly complicates breathing.
3
Homeopathy. Lymphomyosot, the popular Sinuforte, Echinacea compositum are used for exacerbation of chronic sinusitis and the acute form of the disease.
4
Antipyretic. Paracetamol and ibuprofen are used for fever above 38.5°C and severe, persistent headaches.
Often patients are prescribed Erespal , and rinsing of the nasal cavity is also indicated. In case of frontal sinusitis, it is recommended to carry out this procedure in a clinic.
Its essence is to administer, using a conventional blood transfusion system, 100–200 ml of saline solution heated to body temperature with lactoglobulin or an antibiotic, to which the pathogens have been found to be hypersensitive.
The patient is seated, his head is tilted so that the auricle touches the shoulder. The tip of the system is inserted into the nasal passage, which is on top, and the solution is poured in at a speed of about 40 drops/min. An indicator of the correctness of the procedure is pouring the solution from the opposite nostril.
?
Treatment of frontal sinusitis without puncture at home
Treatment at home is allowed only for mild cases of the disease. Patients receive a list of necessary medications and strict recommendations for their use.
In addition to the doctor's prescription, patients can rinse their nose and do inhalations.
But you cannot decide to warm your forehead on your own, even if certain folk methods recommend it.
This is explained by the fact that pathogenic microflora from the affected sinuses can spread to others, as well as penetrate into the brain and other organs, which will lead to the development of complications.
?
What folk remedies can be used for frontal sinusitis?
Traditional medicine offers many methods for treating this type of sinusitis. This:
1
Inhalations. The simplest way is to inhale the vapors over freshly boiled potatoes. To enhance the effect of steam, you can breathe over a hot decoction of medicinal herbs, for example, chamomile, bay leaf, adding a couple of drops of essential oil. It is best to give preference to tea tree or eucalyptus oils.
2
Rinse. Chop the onion and pour in 200 g of boiling water. Add a spoonful of honey to the cooled mixture and rinse your nose three times a day. You can also use chamomile decoction or saline solution prepared at home for this purpose. To do this, add a spoonful of salt and a couple of drops of essential oil to a glass of cooled boiled water.
3
Drops. Juice is squeezed out of peeled and grated black radish, which is instilled up to 4 times a day. You can also use the juice of cyclamen tubers, but only after preliminary dilution with water in a ratio of 1:4.
But you can start treatment with any folk remedies only with the permission of an ENT specialist, and exclusively as a supplement to antibacterial therapy.
?
Frontitis complications and consequences of the disease
In the absence of complete treatment of the acute inflammatory process, chronic frontal sinusitis develops.
If even after this the patient does not take any action, the disease can cause very unpleasant consequences.
Possible complications after frontal sinusitis include:
- meningitis;
- other sinusitis;
- otitis;
- phlegmon of the orbit;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- sepsis;
- neurological disorders, in particular pathologies of the facial nerves;
- brain abscess, etc.
?
Puncture with frontal sinusitis
How to treat frontal sinusitis depends on the severity of its course. If the course is persistent, treatment of frontal sinusitis with a puncture is required. If the sinuses are medium or small in size, they are cleaned by piercing their lower wall. The puncture is performed using a special device or, in extreme cases, a needle for blood transfusion.
In other situations, trephine puncture . The essence of the procedure is to insert a cannula through a hole made in the anterior (facial) wall of the sinus.
Every day, the sinuses are thoroughly washed, after which solutions of the selected antibiotic and hydrocortisone are infused. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia.
If acute purulent frontal sinusitis is diagnosed, patients may require surgery. Initially, the frontal recess is opened, the frontonasal canal is expanded, after which they move on to opening the affected sinus through the facial wall and removing the pus. If the inflammatory process affects both sinuses, it is recommended to remove the septum between them.
A new one is created from the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. Since the cleaned channel turns out to be quite wide, a drainage tube is inserted into it. It is left for about a month so that the anastomosis can become covered with epithelium.
Of course, many are interested in whether it is possible to cure frontal sinusitis without surgery? This is possible, but only in the early stages. If the inflammatory process is advanced and is accompanied by active formation of pus, then treatment can only be surgical.[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1] ?
After a puncture: what recommendations to follow?
After a puncture or surgery, patients may be prescribed the use of vasoconstrictor drops for 4–5 days, as well as careful wound care. In the future, patients need to beware of drafts and consult a doctor at the first symptoms of ARVI.
If pain persists after sinusitis, you should contact an ENT specialist to find out its nature. But in most cases, discomfort goes away within a few days after the procedure and is associated with the tissue healing process.
?
How a photo is taken
Radiography for inflammation of the nasal sinuses has the following algorithm:
- Before carrying out the procedure, you must remove all jewelry;
- the patient in the X-ray room is placed lying or sitting on a couch, which allows you to fix the position of the head while the X-ray machine is operating;
- the upper body is covered with an apron to minimize exposure to radiation;
- then the patient is photographed in four projections;
- in some cases, a contrast agent is used - a special solution containing iodine is injected into the patient’s sinuses.
Frontitis in the image is detected using four main positions.
- Side shot. The patient must open his mouth and touch the device screen with his chin. This projection demonstrates the boundaries of the frontal, maxillary and sphenoid sinuses.
- Chinocranial projection. Makes it possible to study in detail the walls of the frontal sinus.
- Waters' position. The patient presses his chin to the screen, throwing his head back. Allows you to analyze the fundus of the eye.
- Posteroanterior projection. The patient should lean his forehead and nose against the screen of the device.
Taken together, the projections allow you to see the full picture and help diagnose frontal sinusitis.