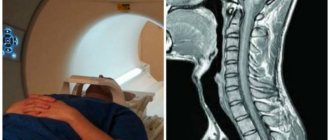
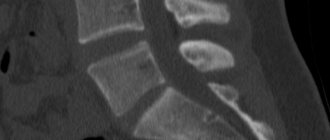
Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic method. It is carried out using a tomograph, which examines a certain part of the body and displays its image on the computer screen. CT scan of the lumbar spine allows you to see all sections, including the lumbosacral, in cross section.
Thanks to this diagnostic method, patients with a back injury have the opportunity to receive timely treatment, complete recovery and return to their normal lifestyle. Another undeniable advantage of CT is the ability to detect tumors in the spine when they are just beginning to emerge.
Indications
A CT scan is a diagnostic study using a special tomograph apparatus that performs a layer-by-layer scan of the body and produces the result in the form of a snapshot with an image. The following pathologies and conditions may be indications for computed tomography:
- Anomalies of the bone tissue of the spine.
- Infectious pathologies.
- Spread of metastases in the spinal column.
- Neoplasms of various etiologies.
- Preparatory stage for surgery on the spine.
- Pain in the back.
- Spinal cord compression.
- Damage to muscles and ligaments.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Spinal injuries and fractures.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Spinal deformity due to arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis.
- Hemorrhage in the spinal cord area.
- Congenital diseases of the spine.
- The appearance of a feeling of numbness in the limbs.
Computed tomography is the most informative method that allows you to quickly make a diagnosis.
Non-contrast tomography technique
The patient is placed on the tomograph table in a supine position, sometimes secured with belts, and asked to remain motionless. Then the doctor goes into the next room.
The table begins to move slowly through the tomograph ring. The ring rotates, cameras mounted on it take successive pictures with a distance of 2-5 mm between slices. The equipment makes a low noise. Native CT and SCT of the lumbar region last up to 5 minutes. During the examination, the doctor and the patient communicate via a two-way communication system.
Contraindications
The examination procedure is painless for the patient, but has a number of contraindications. You cannot do a CT scan:
- During the period of bearing a baby.
- While breastfeeding.
- If there are metal staples in the area being examined.
- If there are mental disorders.
- If you are allergic to iodine, if the CT scan is performed using a contrast agent.
- Computed tomography with contrast is contraindicated in cases of serious kidney pathologies.
- For diabetes mellitus.
- With high levels of creatinine in the blood.
- If the patient's weight exceeds 130 kg, but there is equipment that allows examination with a body weight of about 200 kg.
A relative contraindication is childhood, but if necessary, the doctor can prescribe such a procedure for the child. If the baby cannot lie still for the entire period of the study, the procedure can be performed under anesthesia.
What does it show?
CT scan of the lumbosacral spine shows:
- The structure of the bone tissue of the spinal column.
- The structure of the nerve roots and their condition.
- The lumen of the spinal canal.
- Condition of the spinal cord and existing compression.
- Disorders in intervertebral cartilaginous discs.
- Primary lesions with malignant cells.
- Prehernia defects.
- Hemorrhages in the lumbosacral region.
- Congenital and acquired anomalies of the spinal column.
After studying the received images, the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe therapy with 100% confidence.
Detectable pathology
CT allows you to evaluate bone (better) and soft tissue (worse) structures. Traumatic changes, spinal abnormalities, and tumors may be detected. The method makes it possible to determine the narrowing of the spinal canal and identify its cause: trauma, tumor, herniated intervertebral disc.
The adjacent soft tissues of the neck are always included in the scanning area. It is necessary to pay attention to pathological changes on their part. These are enlarged lymph nodes, space-occupying formations, vascular pathology, etc.
Preparation
If the procedure is performed as an emergency, then preparation for a CT scan of the lumbosacral spine is not required. But most often this study is planned, so there are some points that need to be taken into account:
- Three days before the test, follow a special diet. Do not eat foods that contribute to increased gas formation: cabbage, legumes, bread.
- The day before the CT scan, you should not drink alcoholic beverages or beer.
- It is better to carry out the morning examination on an empty stomach.
- If constipation is a concern, then before the CT scan you need to do an enema to cleanse the intestines.
- If the procedure is supposed to use a contrast agent, then first take an allergic reaction test and do not eat 4-6 hours before the procedure.
You must take past images with you for the study, if a CT scan has already been performed, so the doctor will be able to assess the dynamics of the process.
When can you do research and when not?
CT is indicated for patients with a history of trauma and severe neck pain radiating to the arm or shoulder blade. Tomography is indicated for the diagnosis of tumors, anomalies, and static disorders.
An absolute contraindication to the study is contrast intolerance (history of allergy episodes). Another contraindication is renal failure. Contrast cannot be administered if the vein is inflamed or thrombosed. CT scanning is relatively contraindicated for children, pregnant and lactating women.
If a study needs to be performed for vital reasons, it is done.
Contrasting
Contrast is rarely used when examining the cervical spine. Even with oncological pathology, contrast is usually not required. Non-ionic preparations with iodine are used: ultravist, omnipaque, iohexol, yomeron. They are injected into the vein of the elbow at high speed using an automatic device.
How is the procedure done?
The study is carried out in a specially equipped x-ray room. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- The patient lies down on a couch equipped with a tomograph.
- To ensure a stationary position, the arms and legs are fastened with belts.
- Medical workers go into another room and turn on the machine.
- The couch slides into a ring that is equipped with an X-ray tube and detectors.
- While working, the tomograph scans the body and takes a series of pictures that are displayed on the monitor.
- After the examination, the result will be ready in a few minutes.
It is important to lie still during the entire examination to obtain clear photographs.
If a CT scan is performed without contrast, then the entire procedure takes no more than 10 minutes if one part of the spinal column is studied.
For pathological neoplasms, the procedure is performed with the introduction of an iodine-based contrast agent. The drug is injected into a vein or subcutaneously into the spinal cord, it quickly spreads and accumulates in the tissues, which improves the clarity and quality of the images. After administration, the patient may feel:
- Warmth throughout the body.
- Mild nausea.
- Metallic taste in mouth.
While the tomograph is operating, the doctor is in another room, but through the glass he monitors the patient, who has an emergency call button nearby. He can use it if he suddenly becomes ill, then the procedure will stop.
With contrast, the duration of the study can be 30-40 minutes.
Decoding the results obtained
The diagnostician determines from panoramic tomograms whether there are violations of the integrity of tissues and bones. Detects the presence of protrusion, dystrophic lesions, osteochondrosis. The image shows stretching of the fibrous ring and intervertebral hernia. Based on the results of the image, the doctor can identify the causes of lumbago in the cervical spine, back pain, and numbness of the limbs.
Deciphering the results takes about an hour. The patient must wait until the diagnostic report is issued. Afterwards it is handed over to the attending doctor, who sent it for examination of the neck.
Actions after the procedure
The results of scanning the body using a tomograph are expressed in the form of images. The doctor analyzes them and makes a description, which is given to the patient along with them.
If pathology is noticeable, the specialist recommends visiting a doctor with a narrow specialization:
- If a fracture is visible on the picture, it is recommended to visit a traumatologist.
- If pathological disorders are detected in the spinal cord or nerve roots, you will have to contact a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
- The presence of tumors in the lumbar region requires urgent consultation with an oncologist.
- If other lesions are found, you need to visit a rheumatologist.
If the radiologist has not given specific recommendations, then you can contact your attending physician with pictures and descriptions, who will refer you to a specialist.
Computed tomography visualizes cartilage and bone tissue well, therefore it is often prescribed for diagnosing pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
A high-precision imaging method in addition to CT is MRI. The cost of this method is higher. Unlike computed tomography, it does not use ionizing radiation for diagnosis, therefore it is considered safer. In terms of information content, computed tomography of the cervical spine is better at viewing bone structures, but is inferior in examining cartilage and soft tissues. In case of injuries, breathing problems or bleeding, an MRI cannot be performed due to the serious condition of the patient; in such cases, a CT scan of the neck is indicated.
Advantages of the method over cervical radiography:
- The clarity of visualization of bone tissue is higher. Tomograms distinguish structures with a difference in density of 0.1% and sizes of up to 0.5 mm.
- Topographic accuracy, in contrast to radiography, in which the image is taken in a linear projection with layering of structures located in the same plane.
- Digital data processing: the ability to enlarge images of objects of interest, build a three-dimensional image and study the area from different angles.
Disadvantages of the method before radiography of the cervical spine:
- Low provision of tomographs in populated areas.
- Radiation exposure is 10-15 times higher.
- The cost is higher.
What is the price?
The cost of a CT scan of the lumbosacral spine ranges from 3,500 rubles to 12 thousand. The price depends on several parameters:
- Method of CT scanning.
- Tomograph models.
- Specialist qualifications.
- Clinic status.
- Providing additional services. If scanning is carried out using contrast, the price increases by 1500-3300 rubles.
- Areas of study, if not only the lumbosacral region is scanned, but also the thoracic region, then the cost will be higher.
- Recording the research results on a flash drive or disk will cost an additional 300-500 rubles.
Where to do it?
Computed tomography is an informative diagnostic method, but the cost of the procedure cannot be called humane. Patients often have a reasonable question: is it possible to undergo a CT scan for free? This is real, but you need to know some nuances:
- Get tested.
- Visit your primary care physician and get a referral.
- Make an appointment at the clinic for a tomography.
- On the day of the examination, have a referral from a doctor, a passport, an extract from the medical record confirming the need for a CT scan, and an insurance policy.
Getting a referral for a free CT scan from a doctor is half the battle, but the difficulty lies in the fact that public clinics have a quota for free examination, and it is always less than the number of people willing. Appointments are made a month or two in advance, but if you have oncology, the waiting time does not exceed two weeks.
If the cost of the procedure is not fundamental or an urgent tomography is needed, then a CT scan of the lumbosacral spine can be done in many private clinics and medical centers. Several clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg are represented.
| Clinic name | Cost of examination |
| Moscow | |
| Medical on 1st Kolobovsky Lane, 4. | 6400 rubles |
| Clinical Hospital on Yauza at the address: st. Volochaevskaya, 15, building 1. | 4900 |
| Clinic "MRI 24" on the street. Ordzhonikidze, 11. | 3200 |
| Saint Petersburg | |
| Clinic "Energo" on the street. Engelsa, 33 | 3200 |
| Medical at the address: 6th Krasnoarmeyskaya, no. 7 | 2450 rubles |
| Clinic “Seven Doctors” on 10th Sovetskaya Street, 4-6 | 3000 |
Before choosing a clinic for CT scanning, you need to look at patient reviews, compare the cost of the procedure, and consult with a doctor.