News on the topic of genetic blood testing during pregnancy
Read more
The presence of Down syndrome in an unborn child can be determined using a simple blood test
The birth of a child with Down syndrome is a huge tragedy for the family - a tragedy for the family. Unfortunately, even such a modern examination method as ultrasound cannot always accurately determine the presence of Down syndrome in a fetus in the womb. A more precise method, called amniocentesis (puncture of the amniotic sac), is traumatic and also carries a risk of miscarriage. Scientists from the island state of Cyprus claim that in the near future they will complete the development of a new “bloodless” method for determining whether a fetus has Down syndrome. To do this, a pregnant woman will only need to take a blood test.
A new method for detecting genetic abnormalities of the fetus in early pregnancy that does not require puncture of the amniotic sac
The new method allows the DNA of the embryo to be extracted and studied using a routine blood test from the mother. Until now, doctors used puncture of the amniotic sac to identify genetic disorders.
Read more
Blood tests required for pregnant women can now be done at home
Since the beginning of autumn, the Sinevo network of medical laboratories has been providing a new service. Expectant mothers, residents of the capital of Ukraine, can be tested for gestational diabetes at home - this test is included in the list of mandatory tests.
Read more
A new method for diagnosing Down syndrome in a fetus has angered human rights activists
European human rights activists are protesting against the widespread introduction of a new method of testing pregnant women for the presence of the severe genetic disease Down syndrome in the fetus. According to human rights activists, this method will lead to an increase in the number of abortions.
Read more
Prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome will become safe
Some pregnant women have a high risk of giving birth to a child with an incurable genetic disease - Down syndrome. It is very important to have methods to recognize such a pathology in the fetus as early as possible, so that termination of pregnancy causes minimal harm to the woman’s health. Currently existing techniques are quite invasive, that is, traumatic, in addition, they lead to miscarriages in an average of 1 case per 100 procedures, and this can become a real drama for a woman, especially when it turns out that a completely healthy child died. Scientists from Hong Kong have developed a completely safe test - a mother's blood test shows the presence or absence of Down syndrome in the fetus.
Read more
A new simple test will quickly determine the presence of Down syndrome in a fetus
The birth of a child with Down syndrome is a tragedy for the family. Unfortunately, even such a modern examination method as ultrasound cannot always accurately determine the presence of Down syndrome in a fetus in the womb. A more precise method, called amniocentesis (puncture of the amniotic sac), is traumatic and also carries a risk of miscarriage. Dutch scientists claim that in the near future they will complete the development of a new “bloodless” method for determining whether a fetus has Down syndrome. To do this, a pregnant woman will only need to take a blood test.
Read more
Herpes is a cause of premature birth
Researchers from the University of Adelaide's Women's & Children's Hospital in Australia have made the world's first discovery of the relationship between viral infections, high blood pressure and the risk of preterm birth in pregnant women.
Read more
Ebola fever: a rapid test for diagnosing a dangerous disease created in France
A scientific breakthrough made by French scientists will make it possible to identify patients with Ebola virus fever much faster - perhaps this will finally help stop the epidemic of a dangerous disease raging in West Africa.
Why is analysis needed?
Genetic diseases are associated with chromosomal mutations and lead to the formation of a fetus with severe abnormalities. A gene is a DNA particle that determines the characteristics of an organism: eye color, blood type, etc. Each person is the owner of certain genes that are contained in chromosomes. Damage to their structure leads to mutations, which manifest themselves as deviations in physical or mental development. For timely detection of possible pathology, genetic analysis is prescribed.
An error in the set of chromosomes is often incompatible with the further development of the fetus and leads to miscarriage or stillbirth. If a woman carries the fetus to term until the end of pregnancy, a child with severe pathologies is born. In addition, if the reason for this development of events is not established, subsequent pregnancies will end in a similar way.
Often, the risk of a genetic disease can be minimized by contacting a geneticist at the planning stage of conception. If the fact of pregnancy has already been confirmed, then you should not refuse the examination. In some cases, if the problem is detected early, necessary steps can be taken to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
How is genetic screening of a newborn done?
Often, genetic screening requires only a blood sample. A needle is inserted into a vein in the arm and blood is drawn. In newborns, blood is taken from the heel. Sometimes scraping of the inside of the cheek may be necessary. Rarely, a skin or muscle biopsy is required. Samples are sent to the laboratory for analysis.
In some genetic tests, where both parents must be carriers for the disease to occur, one partner is tested first. If the results are normal, the other partner is not tested. If testing of the first partner reveals an anomaly, the second should be tested as well.
How is biochemical screening performed?
For this type of screening, a biochemical blood test is performed. This is an absolutely ordinary manipulation - taking venous blood. Most often, a biochemical blood test is taken on the same day as an ultrasound examination of the fetus at 11-14 weeks. Next, the pregnant woman’s blood test is sent to a specialized genetic laboratory. On average, maternal serum biochemistry takes 7-14 days to prepare, given the complexity of the analysis.
What is genetics?
- Genetics is a science that studies hereditary dependence at the molecular level and the reasons leading to gene mutation. The science is vast and is divided into many branches, one of which is called medical genetics. With the help of this subsection, diseases of parents are identified, which can subsequently be transmitted to subsequent generations.
- Genetic medical examinations are intended to prevent such diseases, while prenatal diagnosis identifies hereditary diseases in the early stages of fetal development.
- This science achieved especially outstanding achievements in the last century, when scientists created the first genetic tests. With their help, people have learned to identify the causes of many hereditary diseases, thereby preventing the birth of a child with a predisposition to a particular disease. Therefore, it is advisable to carry out genetic examinations at the initial stage of pregnancy.
- A couple planning to have a child cannot help but worry about the health of the unborn baby, so many consciously seek advice from a geneticist about possible hereditary diseases of the future child. A medical examination will predict the result of the connection of the parents’ chromosomes and, in case of unfavorable prognosis, will allow timely protection of the child from possible illnesses.
- This approach is especially relevant for parents suffering from diseases such as epilepsy, hemophilia, asthma and other difficult-to-treat ailments. The desire to have children is great, however, the fear of giving birth to a child doomed to such suffering prevents them from deciding to conceive.
- It is not too late to conduct genetic testing, even if pregnancy has already occurred. First of all, this is necessary to realize that everything is in order with the health of the future child.
Decoding the results
The results obtained are compared with reference samples. Then, based on the absence or presence of the desired genes, the presence of changes or mutations in them, the geneticist makes a conclusion about the state of the chromosomes and enters the results into a genetic passport . Afterwards, the doctor assesses the risk of developing or the presence of a particular disease and makes recommendations aimed at preventing or eliminating the disease.
If a paternity test was done, in case of a positive result, the geneticist gives a conclusion with a probability of 99.9%. These numbers are explained by the fact that a father can always have a twin brother who has an almost identical set of chromosomes. In practice, this happens extremely rarely, but the situation cannot be ruled out. If the man is not the father of the child, the result is categorical - 100%.
About genetics
The term “genetics” comes from the Greek word “γενητως” - to generate, to descend from someone.” Genetics studies the laws of transmission of biological information (heredity) from generation to generation, as well as the process of changing this information under the influence of one factor or another.
Modern genetics is the possibility of curing previously incurable diseases, improving the capabilities of living organisms (eugenics), developing uninhabitable territories, solving the problem of garbage and ecology in general. Genetics began to be counted on as a means capable of advancing the interests of humanity into the distant future.
Basic Genetics Terminology
Biological information is transmitted using DNA and RNA macromolecules - complex organic formations consisting of blocks of nucleotides. The part of DNA or RNA that is responsible for making a particular type of protein is called a “gene.” Genes form alleles (they determine the order and sequence of creation of protein formations).
DNA and RNA molecules are stored in chromosomes, special biological structures found in eukaryotic cells. The internal contents of a chromosome are called chromatin.
Each species has a limited number of chromosomes. For example, a person has 46 of them, a dog has 68, a turkey has 82, and a fruit fly has 8. The chromosome of every living creature, even of the same species, has its own unique characteristics in shape, contours, and sizes. These features are so characteristic that they can easily be used to identify a specific biological individual, which, by the way, is successfully used by forensic experts. To indicate the uniqueness of the chromosome set of each individual, the Soviet scientist G.A. Levitsky introduced the term “karyotype”. Later, medical science learned to determine the norm, anomalies and pathology of the gene set by karyotype. A visual representation of the chromosome set is called a “karyogram”. It is this that serves as the starting point for human genetic analysis, including pregnancy planning.
Genetic abnormalities in WHO data
Genetic anomalies are morphofunctional disorders in the body that arise as a result of gene and chromosomal mutations.
WHO data on the health of millennials is extremely concerning. According to statistics from European medical institutions, only 14% of graduates of secondary educational institutions can be considered healthy.
Poor ecology, various addictions, and an unreasonable lifestyle have led to a significant increase in the number of newborns with genetic disorders. The number of such children reaches 17%. Meanwhile, studies conducted by WHO experts indicate that already at a figure of 10%, the degeneration of the human species begins. This, without a doubt, cannot but cause concern among the sensible part of society.
Thus, control of genetic health is the path to improving society as a whole!
Prevention of genetic abnormalities of the fetus
Genetic tests are recommended for all married couples planning to have a child, since gene mutations can occur even in practically healthy people.
Very often, a person does not have any signs and symptoms of genetic pathologies, but at the same time he may be a carrier of a defective gene.
If there are cases of hereditary pathologies in the family of at least one of the spouses, contacting a geneticist and undergoing a comprehensive study is mandatory. Such pathologies include primarily:
- thrombophilia;
- cystic fibrosis;
- hearing loss;
- hemophilia and many others.
Modern methods of molecular genetic studies of married couples make it possible to determine not only gene mutations and the presence of hereditary diseases, but also a predisposition to many severe pathologies at the genetic level.
These are diseases such as:
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine disorders;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- oncological diseases;
- osteoporosis and many others.
It is especially important to undergo genetic testing for couples who decide to conceive a child in adulthood. A person does not always have an idea about the health status of his relatives and may not even suspect that he is a carrier of a damaged gene
Consulting a geneticist during pregnancy and conducting genetic research in the early stages will help avoid many risks for the mother and unborn child and allow you to plan your pregnancy correctly
A person does not always have an idea about the health status of his relatives and may not even suspect that he is a carrier of a damaged gene. Consulting a geneticist during pregnancy and conducting genetic research in the early stages will help avoid many risks for the mother and unborn child and allow you to plan your pregnancy correctly.
Why do “breakdowns” occur in the genetic apparatus?
It would seem that Mother Nature is wise, so information is passed on from generation to generation without failure. However, unfortunately, a defective gene or chromosome can also be passed on to offspring.
In addition, the hereditary apparatus is fragile and subject to changes under the influence of damaging factors before pregnancy:
* Environment, parasites, food, food coloring and additives. * Beam or ionizing radiation. * Medicines and many others.
Agree that we have more of this “baggage” with age. Therefore, the likelihood of “breakdowns” in genes and chromosomes increases as we get older.
| In most cases, breakdowns occur at the cellular level. Under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors, cells stop working normally and lose their ability to self-heal. Regulatory peptides are responsible for the transfer of information between cells - protein substances that carry specific “instructions” for cells on how to work correctly. Scientists have found that regulatory peptides isolated from animal tissues are perceived by the cells of the human body as their own. This is how Ovariamin was created - a natural bioregulator, a representative of the Cytamine class. Ovariamine naturally restores the normal functioning of ovarian cells, has a mild normalizing effect and does not accumulate in the body, which significantly reduces the likelihood of side effects. Taking Ovariamine helps with ovarian dysfunction, hormonal infertility, and exhausted ovarian syndrome. Ovariamine promotes pregnancy and the birth of a planned healthy child. |
On a note! Hereditary diseases should be distinguished from congenital developmental anomalies, which arise as a result of intrauterine damage to the fetus by various factors. For example, infection (syphilis, toxoplasmosis, rubella), medications and others.
What mutations are there?
* In chromosomes - transfer of individual sections to the other side, changes in structure and number. * In genes - a change in number, location or structure.
With pronounced mutations, when the child is obviously not viable, a miscarriage occurs in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 7-8 weeks). Wise Nature follows her law: “All or nothing.”
Is it possible to control genes and chromosomes?
Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to eliminate the “breakdowns” that have already occurred. However, it is possible to identify defects using modern diagnostic techniques in a single family. Research is carried out both before conception and during pregnancy.
Photo: https://ru.depositphotos.com
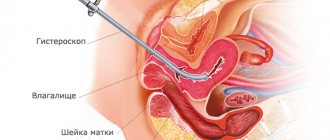
Perinatal diagnosis
Perinatal diagnosis is an intrauterine examination of the fetus aimed at identifying hereditary diseases and developmental defects. There are two types of perinatal diagnostics: non-invasive and invasive methods. If non-invasive methods are absolutely safe (ultrasound, blood biochemistry) for the mother and for the unborn child, then invasive methods involve some “invasion” into the uterine cavity in order to take material for research and determine the karyotype of the fetus with high accuracy. This allows us to exclude pathologies such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome and other equally dangerous genetic diseases. Invasive methods: • chorionic villus biopsy - obtaining cells from the future placenta using a puncture through the anterior abdominal wall; • amniocentesis – taking amniotic fluid at 16–24 weeks of pregnancy (the safest method, since the risk of complications does not exceed 1%); • placentocentesis (taking a sample of placental cells containing fetal cells for examination, the risk of complications is 3-4%); • cordocentesis (fetal umbilical cord puncture and cord blood collection). All these procedures are associated with a risk of complications, so they are carried out according to very strict doctor’s instructions. In addition to patients at genetic risk, pregnant women will be subjected to invasive testing methods in case of a high risk of a genetic disease for the fetus or to determine sex in diseases whose inheritance is associated with sex. A striking example of this is the hemophilia gene. If the mother is a carrier, she can only pass the disease on to her sons
Examination can determine the presence of a mutation. It is important to understand that all these methods are carried out by experienced specialists under ultrasound supervision in a day hospital. After the procedure, the pregnant woman remains in the hospital for several hours for observation.
She may be prescribed medications to prevent possible complications. Currently, the developed diagnostic methods are sufficient to identify 300 out of 5,000 genetic diseases. In any case, the issue of invasive diagnostics is decided in each case individually and only with the consent of the expectant mother. But it is still advisable for all pregnant women to undergo non-invasive methods at the specified dates, since the health of the unborn child may depend on this.
You can prevent your child from getting sick
Heredity plays a huge role in the formation of a person.
We all borrowed certain appearance, character and health characteristics from our parents and grandparents from different generations. Genetics is a science that studies the mechanisms of diseases transmitted by inheritance. Currently, pregnant women are recommended to undergo examination by a geneticist in order to exclude pathologies or to detect them in a timely manner. How does this procedure happen and is it so important?
Genetic analysis during pregnancy
From the moment you are convinced that you are carrying a child under your heart, his health should become your main concern. The formation of the fetus, especially in the early stages, is subject to the influence of various unfavorable factors and the mother, as a barrier, must protect her child from environmental aggression until the baby gets stronger.
There are categories of pregnant women for whom consultation with a geneticist is indicated to exclude pathologies in the child. These include:
- women under 18 years of age or over 35 years of age;
- future mothers suffering from hereditary diseases;
- women who have ever given birth to children with developmental disabilities;
- representatives of the fair sex with tobacco, alcohol or drug addiction;
- parents who are HIV-infected, have hepatitis, or have had infectious diseases at the beginning of pregnancy (rubella, chickenpox or herpes);
- women taking medications that are contraindicated for use during pregnancy;
- expectant mothers who have received a dose of radiation (fluorogram or x-ray examination at the beginning of pregnancy);
- female athletes who participated in extreme sports in their youth;
- women who have received a large dose of ultraviolet radiation.
Since signs of pregnancy do not appear immediately, any woman is likely to be at risk.
Why and how is CTG done during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is an unusually joyful time for every woman who is preparing to meet her baby. But, in addition, pregnancy is also a very important period, because any mother wants the baby to live “comfortably” in her tummy, without experiencing any inconvenience or lack, so that he develops and is formed according to all indications.
In order to monitor how comfortable the baby is in the womb, in order to promptly identify and correct any “problems” in this regard, the pregnant woman has to take tests and, if necessary, undergo certain examinations.
Doctors call CTG one of the most valuable examination methods during pregnancy, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the fetus.
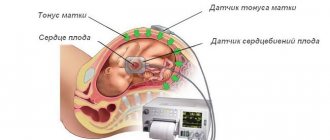
CTG (cardiotocography) during pregnancy is carried out in order to obtain results regarding the child’s cardiac activity and heart rate, as well as its motor activity, the frequency of uterine contractions and the baby’s reaction to these contractions.
CTG during pregnancy, together with doppleometry and ultrasound, makes it possible to timely determine certain deviations in the normal course of pregnancy, study the contractile activity of the uterus and the reaction of the baby’s cardiovascular system to them.
Using CTG during pregnancy, you can confirm (or refute) the presence (or absence) of conditions dangerous for the mother and baby, such as fetal hypoxia; intrauterine infection, low or polyhydramnios; fetoplacental insufficiency; abnormalities in the development of the fetal cardiovascular system; premature maturation of the placenta or threat of premature birth. If suspicions of one or another abnormality are confirmed, this allows the doctor to promptly determine the need for therapeutic measures and adjust the management tactics of the pregnant woman.
When is CTG performed during pregnancy?
To conduct CTG during pregnancy, a special device is used, which consists of two sensors connected to a recording device. Thus, one of the sensors takes readings of the fetal cardiac activity, while the second records uterine activity, as well as the baby’s reaction to uterine contractions.
An ultrasound sensor for listening to the fetal heartbeat and a strain gauge sensor for recording uterine contractions are attached to the pregnant woman's abdomen using special belts. One of the main conditions for the most effective recording of readings is considered to be a comfortable position for the woman during CTG during pregnancy.
Thus, readings are taken when the pregnant woman is lying on her back, on her side or sitting; in any case, it is necessary to choose the most comfortable position.
In this case, the pregnant woman will hold a special remote control with a button in her hands, which she presses when the baby moves, which makes it possible to record changes in heart rate while the fetus moves.
The most appropriate time to perform cardiotocography is the third trimester of pregnancy, starting from 32 weeks.
In addition to the fact that at this moment the fetal cardio-contractile reflex is already formed and the relationship between cardiac activity and motor activity is established, the activity-rest cycle (sleep) is also established.
In principle, CTG can be performed earlier than the specified period, but the reliability of the diagnosis in this case is called into question.
Normal CTG values during pregnancy
CTG indicators during pregnancy cannot be a reason for making a diagnosis; this is just additional information about the condition of the fetus at a given time. Moreover, to form a complete and most plausible conclusion about the vital activity of the fetus, a one-time examination using CTG is not enough: cardiotocography must be carried out several times.
The results of CTG are displayed by a curve on the tape, assessing the readings on which (curves), the specialist can determine whether there is any deviation from the recommended norm. When performing CTG, several indicators are assessed:
- basal rhythm (average heart rate), indicated by the abbreviation BHR or HR. The norm is 110-160 beats per minute in a calm state, 130-190 – with fetal movements;
- rhythm variability (average height of deviations from the basal rhythm). The norm is 5-25 beats per minute;
- deceleration (or deceleration, slowing down the heart rate). They appear on the chart as significant depressions. There are no norms, and if they do occur, they are very short and shallow;
- acceleration (or acceleration, acceleration of heart rate). They appear as teeth on the graph. The norm is 2 or more accelerations per 10 minutes;
- tocogram (uterine activity). The norm is no more than 15% of the frequency of fetal heart contractions of uterine contractions lasting from 30 seconds.
Interpretation of CTG during pregnancy is carried out using a 10-point system, each of the criteria (with regard to variability, the amplitude of deviations and their number is assessed) scores from 0 to 2 points. The result is a holistic picture according to which:
- from 9 to 12 points – the condition of the fetus is normal;
- from 6 to 8 points – the presence of hypoxia, but without high threats, a repeat procedure is required;
- 5 points or less – severe hypoxia, requiring urgent delivery.
If the CTG results are extremely negative, the doctor makes a decision to artificially “force” events - induce labor.
Is CTG harmful to the fetus during pregnancy?
CTG is a completely safe procedure that has no contraindications. Therefore, if an expectant mother is concerned about the question of whether CTG is harmful during pregnancy, the answer in this case is always categorical - not harmful. If necessary, examinations can be carried out over a fairly long period of time, even daily.
Moreover, the examination is very, very informative, it allows you to identify possible threats to pregnancy and the fetus in a timely manner, and take the necessary actions in a timely manner.
But, in any case, the obtained tests should be considered only in the context of the general course of pregnancy and in mutual connection with the results of other examination methods, in particular ultrasound and doppleometry.
Especially for beremennost.net – Tatyana Argamakova
Source: https://beremennost.net/ktg-pri-beremennosti
News on the topic of blood tests for genetics
Read more
DNA test will become easier than blood test
Scientists from Hong Kong managed to create the world's first miniature chip, which is necessary for carrying out the polymerase chain reaction - a highly sensitive testing method used in molecular genetics
Read more
Genetics against drug side effects
Millions of people around the world take medications that lower the level of bad cholesterol in the blood and blood pressure. But for some patients, taking these medications causes serious side effects. British scientists are working to solve the problem.
Read more
Genetic analysis or entertaining genomics?
Commercial genetic tests that can determine the risk of disease in offspring have become widely available in Western society. But, according to scientists, their value is no higher than the value of a visit to an astrologer
Read more
A unique genetic analysis method will save the lives of premature babies
Scientists from the USA have developed a new method for sequencing the genome of a newborn baby - thanks to this technique, results can be obtained within just one day. This greatly increases the chances of saving many premature babies.
Read more
Favorite smells are determined by genes
We may like the aroma of some foods more than others. It turns out that it has to do with genetics.
Read more
The secret to the super survival of American bedbugs is “incest”
Over the past decade, cities across the United States have experienced unprecedented infestations of bed bugs. Even the strongest pesticides no longer affected insects. Finally, American geneticists have unraveled the secret of the invulnerability of the new generation of bedbugs.
Read more
Those who love being late received an “indulgence” from geneticists
Those who are regularly late for work in the morning have the opportunity to justify themselves to their stern boss with “bad genes.” But it is unlikely that he will be lenient towards being late, even if caused by bad heredity.
Read more
Cancer in one of the “twins” is a reason to examine his brother or sister
Even the knowledge gained in biology lessons at school is enough to understand: the appearance of cancer in one of the identical twins is a danger signal for the other. But a similar danger exists for fraternal twins.
Read more
Australian woman gives birth to baby - bone marrow donor for older child
A married couple from Australia had to “out of plan” to have a second child. The reason for the unplanned addition to the family was a hereditary disease of the older boy - a bone marrow transplant of the younger child will help save his life.
Blood genetics are very important to study
The most important section of all genetics as a whole is represented by blood genetics. By studying its properties and qualities, scientists will finally be able to develop new ways to prolong and preserve human life, in addition, the study of the genetics of blood and its groups helps to understand the main cause of diseases and find effective methods fight them. As you know, the blood of each person has many differences, first of all, it is divided into groups, therefore, by conducting various experiments and studying the genetics of blood, scientists can see the different reactions that occur when the blood of completely different people is mixed.
The blood of living organisms contains fibrogen, which is a coagulating agent, and if it is removed during a blood test for genetics, the result will be only serum. During the experiments, red blood cells were isolated from the blood and placed in the same serum isolated from the same blood; instead of gluing and forming lumps, the red blood cells were evenly distributed in the serum. However, if you simply combine red blood cells from one person with the blood serum of another, you can observe two types of reactions: either the red blood cells will stick together, or this will not happen.
The main task of scientists studying blood genetics is to discover new possibilities for treating blood diseases and prolonging human life. Already, serious discoveries have occurred in blood genetics that help scientists in the study of this science. Largely due to the in-depth study of the genetics of blood groups, the basic systems of blood groups in various people were discovered. Nowadays, about a thousand blood groups and subgroups have already been discovered, and agglutination reactions have been studied, which have made it possible to better study not only the properties of red blood cells, but also the serum itself.
A thorough study of the genetics of blood groups has shown that each person can be the owner of unique combinations of these blood groups. Scientists have been studying blood genetics for several years now, but each time they discover more and more complex blood groups, which are now considered systems in general terms. Long-term studies of the genetics of blood groups in different people have once again proven a special connection between a number of diseases, for example, those with type A blood can get stomach cancer, but those with type 0 blood are not immune from stomach ulcers.
Modern medicine has made great progress; now it is enough to donate blood for a genetic analysis to identify dangerous pathologies and serious diseases in the early stages, especially when there are no symptoms. In addition, a genetic blood test during pregnancy allows you to find out the blood type of the unborn child; in addition, by donating blood for a genetic test, parents will be able to find out exactly what diseases may occur in the newborn and prevent their manifestations in time. For many young mothers, the question arises: where to donate blood for genetic testing in order to be sure to establish not only the inherited blood type of the unborn child, but also to identify possible pathologies.
First of all, you can donate blood for genetic testing at any specialized clinic that studies possible problems of hereditary diseases, as well as establishing a predisposition to them in future children. Nowadays, the study of blood genetics helps many couples give birth to a completely healthy baby, or at least obtain the most accurate information about the problems that may arise after the birth of a child. Blood genetics has become especially relevant for couples who decide to have a child at a later age. Therefore, with such a late pregnancy, the likelihood of gene changes in the fetus is very high. Therefore, only timely diagnosis of blood genetics will help to avoid the occurrence of such unfavorable conditions, which can lead not only to spontaneous abortion, but also to further infertility.
It is the study of these factors that is the main task in blood genetics; only by studying and understanding the cause of certain diseases, scientists will be able to save humanity from serious diseases. And these are not empty words, because the discoveries made now have already made it possible to save many babies born with hemolytic jaundice; continued research in blood genetics will certainly allow us to discover new methods that help in medicine. This is how the opportunity to save people with a simple blood transfusion was discovered at one time. But this would have been impossible if scientists had not discovered and carefully studied various blood groups; it was these discoveries in blood genetics that allowed medicine to move to a completely new level.
Where to do the analysis?
A genetic test during pregnancy can only be done in specialized medical genetic centers, as well as in some clinics. If performed incorrectly, these studies may simply not identify the risk of early termination of pregnancy and ultimately seriously affect the physical and mental health of parents. That is why, before analysis, it is important to choose the right center, learn as much as possible about it and the professionalism of its workers.
It should be noted that the price of genetic analysis is quite high and greatly exceeds the cost of conventional medical tests. However, the results obtained can ultimately save much more money, since timely detection of the disease or the possibility of its development will help to cope with the disease most effectively. Take care of your child's health in advance!
Evaluation of results
The tests are deciphered by a geneticist who, if a pathology is detected, will tell you about the risks of complications and methods for solving them.
In the 1st trimester, studies are carried out to diagnose Down and Edwards syndrome in the fetus. During an ultrasound, the doctor examines the thickness of the nuchal translucency. When TSV exceeds 3 mm, there is a huge threat of pathology.
Determination of the level of hCG and the beta subunit of hCG is also used. In the normal course of pregnancy in the early stages, every 3 days by the 4th week the hormone content increases until the 9th week, and then falls. If the amount of hCG beta subunit is higher than normal, there is likely an increased risk of developing Down syndrome, if lower, Edwards syndrome.
During gestation, PAPP-A values should increase. If the level is below normal, there is a risk of Down or Edwards syndrome. Experts do not consider an increase in PAPP-A a violation: with such content, the likelihood of the baby becoming ill is no greater than with a normal amount.
To calculate the risk correctly, do the research in the laboratory where the risk is calculated. The program is built on special parameters, individual for a particular laboratory, and draws up a conclusion in fractional form. For example, 1:250 means that out of 250 pregnant women with identical indicators, 1 baby is born with Down syndrome, and the remaining 249 are healthy. If you receive a positive result, you will need to be screened again in the 2nd trimester.
Norm
When calculating the results of the study, the doctor uses a special program. All biochemical screening indicators are entered into it. The program plots deviations of these data from the norm. In this case, the MoM coefficient (multiple of median) is calculated.
The norm for a genetic double is considered to be MoM from 0.5 to 2.5. The patient is given a form containing the following information:
- risks associated with a woman's age;
- beta-hCG and PAPP-A values;
- risks of genetic mutations;
- MoM coefficient.
Normal values for beta-hCG range from 13.4 to 130.4 ng/ml, and PAPP-A range from 0.79 to 8.54 mU/ml. The exact reference values of markers depend on the stage of pregnancy.
It is very important to undergo biochemical screening on time. In the second trimester, the PAPP-A indicator returns to normal, even if the fetus has mutations.