A blood test for liver disease is mandatory. This body is involved in the most significant distribution and transport flows. Here, the neutralization of toxins and other harmful substances that enter the body along with consumed food, as well as inhaled air, occurs.
The liver is also involved in the digestive process; it converts consumed foods into energy and beneficial nutrients. Here is a repository of microelements and all the vitamins that may ever be required for life.
The organ participates in the chemical process associated with the processing of fat; it carefully controls the provision of the required level of this substance in the body. At the same time, the liver synthesizes the proteins required by the human body so that the blood clots properly and infections do not damage health. Even this extensive list does not describe all the functions assigned to this important body.
Indications for the study
There are certain signs that indicate liver damage. As a rule, characteristic symptoms appear already in advanced stages, which complicates the treatment of the pathology. Blood biochemistry to check the liver is prescribed in the following cases:
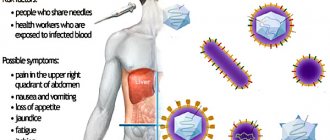
- Yellowness of the skin. A typical sign of increased bilirubin levels. Yellowness of the skin/eye sclera indicates long-term inflammation.
- Increase in organ size. Deviations can be detected at the initial stage using an ultrasound examination. With a strong enlargement of the organ, the patient experiences a growth of the abdomen against the background of no changes in overall weight.
- Losing weight. For liver pathologies, nausea and refusal to eat are typical, which leads to weight loss.
- Bitter taste in the mouth. Liver disease is characterized by a bitter taste in the mouth, a coated tongue, a thick yellow-brown or white coating, and cracks on the surface of the tongue.
Key indicators for liver diseases
The condition of the liver allows you to track certain enzymes. This:
- albumen;
- bilirubin;
- aminotransferases (AST and ALT)
- alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- glutamate dehydrogenase (GlDH)
- sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH)
- γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT)
- fructose monophosphate aldolase (FMPA).
Albumen
It is the main protein produced by liver tissue. A healthy organ produces 150–250 mg/kg albumin within 24 hours. The norm for an adult becomes 35–53 g/l. If the study showed a decrease, then the cause may be: liver failure, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis.
Bilirubin
This is a yellow pigment formed as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin. The resulting indirect bilirubin enters the liver, is neutralized and excreted naturally. Normally, 250–300 mg (total bilirubin) is formed in the human body during the day. Indicators of direct bilirubin are of diagnostic interest. The norm is not higher than 5.1 µm/l.
Exceeding the permissible values in a blood test indicates the following pathologies:
- inflammation of the gland of viral origin;
- cirrhosis;
- alcohol intoxication;
- cholangitis;
- stones in the bile ducts.
An increase in direct/indirect bilirubin fractions can be caused by:
- toxic/viral inflammation of the gland;
- suppuration, malignant neoplasms in liver tissue;
- cirrhotic organ damage;
- mononucleosis;
- echinococcosis.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, AlAT)
ALT norms depend on the gender of the patient: for men – 10–40 units/l, for women – 12–32 units/l. An increase in enzyme levels in the bloodstream can accompany acute hepatitis and obstructive jaundice. An increase in the ALT norm in relation to the permissible one is recorded in cirrhosis and during treatment with hepatotoxic drugs.
An increase in enzyme activity by 4-6 times or more indicates severe liver disease. The deviation is detected before the appearance of typical symptoms - jaundice, pain syndrome and others - in about 1-4 weeks. After the clinical picture develops, elevated ALT levels persist for no longer than 2 weeks, which is a sign of significant organ damage.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, AST)
The norm depends on gender: for men – 15–31 units/l, for women – 20–40 units/l. Increased AST activity is recorded in the event of hepatocyte death. Moreover, the more significant the damage to the organ, the higher the enzyme levels. An increase in quantitative indicators also occurs in acute infectious and toxic hepatitis.
Diagnosis of liver pathologies involves calculating the de Ritis coefficient - the ratio of AST/ALT numbers. Normally, it is equal to or exceeds the number 1.3. A change in numbers towards the lower side of the indicator indicates damage to the organ.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Enzyme activity depends on gender and age group. In a healthy adult – 30–90 units/l. An increase in alkaline phosphatase occurs in adolescents (up to 400 units/l) and expectant mothers (up to 250 units/l). A significant increase in the alkaline phosphatase level - 10 times or higher - occurs with the development of obstructive jaundice. If the excess is not so significant, one of the forms of hepatitis can be suspected.
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GlDH)
Normally, a biochemical blood test shows a low content of GLDG. The reason is that it is one of the liver enzymes located inside the cell. And an increase in its activity makes it possible to determine the severity of damage to the organ. Increased results indicate the onset of degenerative processes in liver tissue, caused by both external and internal factors.
- neoplasms;
- liver metastases;
- toxic substances;
- infectious pathologies.
How to take liver tests
Your doctor will tell you in detail how to take liver tests. But there are uniform rules for preparing for a biochemical blood test for liver tests.
How to take liver samples from an adult:
- It is recommended to donate blood for liver function tests on an empty stomach. It is advisable to follow the diet for about a day before taking the test.
- Before donating blood, it is better to rest a little (20-25 minutes).
- The day before taking the test, you should not drink alcohol, take medications, or engage in intense physical activity.
When taking a liver enzyme test for children, doctors recommend giving the child 150-200 ml of water for half an hour.
Blood test for malignant neoplasms
Liver cancer and hepatitis are determined by identifying antigens to certain diseases. Hepatitis markers: A (HAV) – Anti-HAV-IgM, IgM class antibodies to virus A; B (HBV) – Anti-HBs antibodies to the HBs antigen of the B virus; C (HCV) – Anti-HCV-total antibodies to C virus antigens.
The tumor marker AFP becomes a marker for cancer. The disease is confirmed by a result of more than 10 IU. An increase in the indicator may indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm in the organ itself, the presence of metastases, or embryonal cancer.
If there is a slight excess, you can suspect:
- cirrhosis;
- hepatitis;
- renal failure.
Preparing for the test
Blood biochemistry is prescribed if it is necessary to check liver function. Proper preparation for donating blood will help you get the most accurate results. Two to three days before visiting the laboratory, you need to exclude fatty, fried foods, fast food, sweets, smoked foods, cocoa, coffee, and marinades from the menu.
You should stop drinking alcohol a week before the test. Ethyl affects not only the condition of hepatocytes, but also the blood clotting rate. On the morning of blood donation, the patient should not smoke. But it is better to give up nicotine 10–12 hours before visiting the laboratory.
7 days before the test, you must stop taking any medications, including vitamin complexes. If this is not possible, then you need to stop taking the pills at least on the morning of blood donation. A woman must be sure that she is not pregnant. Due to gestation, it is possible that the permissible norms may be exceeded. And this cannot be considered as a symptom of a pathological condition.
On the morning of donating blood, you should avoid doing morning exercises, since increased physical activity can affect blood counts. The donation of biomaterial is carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. The last meal should take place the night before. Dinner should be light.
Blood is drawn from the ulnar vein. The procedure is painless, but may be accompanied by slight dizziness. The interpretation of the resulting analysis should be carried out by the attending doctor, since only a qualified specialist is able to compare all the data received and determine the presence or absence of pathology.
Blood tests to evaluate your liver and gallbladder are laboratory tests used to evaluate their condition and function. The most informative and frequently used laboratory tests of blood serum are called basic biochemical indicators . These biochemical indicators can be divided into three categories:
- studies whose results reflect damage and death of hepatocytes (liver cells) (ALT, AST levels);
- studies, as a result of which we obtain information about the liver’s ability to synthesize (produce) certain substances (level of proteins and cholesterol in the blood serum, coagulogram);
- studies that provide information about the state of the excretory function of the liver, as well as the presence of cholestasis (reduced flow of bile into the duodenum) caused by obstruction of the intra- and extrahepatic biliary tract (bilirubin level, alkaline phosphatase, GGT).
As a result of the examination, the patient will receive
Determining the value of biochemical parameters that will be interpreted by the attending physician taking into account the patient’s condition and will help make a diagnosis, determine the prognosis and make it possible to monitor changes in liver function when repeating the study.
What it is?
Liver enzymes are a group of biologically active proteins that can be produced exclusively by the cells of this organ. They can be found on the inner or outer membrane, inside cells or in the blood. Depending on the role of enzymes, they are divided into several categories:
- hydrolases – accelerate the breakdown of complex compounds into molecules;
- synthetases - take part in the reactions of synthesis of complex biological compounds from simple substances;
- transferases – participate in the transport of molecules across membranes;
- oxyreductases – are the main condition for the normal course of redox reactions at the cellular level;
- isomerases - necessary for processes of changing the configuration of simple molecules;
- lyases – form additional chemical bonds between molecules.
Prices for services
| Service | price, rub. |
| Blood sampling from a peripheral vein | 250 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | 200 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 200 |
| Total bilirubin | 210 |
| Direct bilirubin | 130 |
| Total cholesterol | 250 |
| Cholesterol – Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) | 300 |
| Cholesterol – High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) | 300 |
| Total alkaline phosphatase | 200 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT) | 200 |
| Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick). INR) | 300 |
| Coagulogram No. 2 (prothrombin (according to Quick). INR. fibrinogen) | 460 |
| Haptoglobin | 1090 |
| Fibrinogen | 280 |
| Serum albumin | 240 |
reference Information
ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase)
These are enzymes contained in the liver, as well as other organs and tissues of our body. Normally, both enzymes are present in the blood serum, and their activity does not exceed 40 units/l. An increase in ALT and AST in a blood test occurs with any damage to liver cells and hepatocytes caused by diseases and liver damage.
Whey proteins
Albumin, fibrinogen, haptoglobin and beta-globulins are synthesized by liver cells, hepatocytes, gamma globulins are produced by lymphocytes and plasma cells of the liver. In most liver diseases, the level of albumin and other liver proteins in the blood serum decreases, and the level of globulins, on the contrary, increases. Albumin levels below normal and globulin levels above normal may indicate chronic and progressive liver disease.
Coagulogram
This is a comprehensive study of homeostasis, which allows you to assess the state of the coagulation and other blood systems. The liver synthesizes almost all blood clotting factors; in addition, it removes these factors from the bloodstream and participates in the dissolution of blood clots. If the parameters included in the coagulogram deviate from the norm, it can be assumed that the synthesis of coagulation factors in the liver is impaired due to damage and death of hepatocytes in infectious liver diseases, cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, acute liver failure and other diseases.
GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase)
This is an enzyme found in the liver, pancreas and kidneys. Increases in diseases of the liver and pancreas, increases significantly in alcoholic liver damage;
ALP (alkaline phosphatase)
This is an enzyme produced in the liver and bile ducts, bone tissue and intestines. An increase in this enzyme is possible in case of obstruction of intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts and infiltrative liver diseases, in which substances, such as fats, or foreign cells, such as metastases, penetrate into liver cells. Bilirubin
This is a bile pigment, which is one of the most important components of bile and is formed as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin and other blood components, the resulting bilirubin is removed from the bloodstream by the liver and excreted in the bile. An increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood signals a decrease in the liver’s ability to remove bilirubin from the body and a violation of the outflow of bile; it occurs in acute and chronic liver diseases, chronic cholecystitis, blockage of the bile ducts and other diseases.
Video
Blood tests: LIVER FUNCTION (total protein/bilirubin/alkaline phosphatase/AST/ALT).
Liver tests are a biochemical blood test that measures the amount of liver enzymes and other substances that indicate liver dysfunction. Biochemistry helps to assess the condition of liver cells, identify existing and just beginning pathological processes in the liver, and the degree of their progression. The analysis can determine the presence of a hereditary predisposition to liver diseases.