How to raise platelet levels
First of all, it is necessary to establish the cause of the decrease in these blood cells and take measures to eliminate it.
The cause may be an allergic reaction (for example, to medications), an infectious disease (influenza, HIV infection, hepatitis), thyroid disease (thyrotoxicosis), acute lack of folic acid or vitamin B12, tumors, autoimmune diseases, etc. Get additional examination from hematologist, allergist, endocrinologist. When the cause has been established, treatment of the underlying disease has been prescribed and all contraindications have been identified, efforts can be made to increase the level of platelets in the blood. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable; usually, when prescribing treatment for the underlying disease, doctors simultaneously prescribe measures to increase platelets. Complex treatment is usually used: medications in combination with correction of nutrition and daily routine.
The most commonly prescribed medications to raise platelet levels in the blood are Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Sodecor, and Thrombopoietin. To increase blood clotting and prevent bleeding, Etamzilat, Vikasol, Derinat are prescribed. In case of acute deficiency of vitamin B12, vitamin complexes containing this vitamin are prescribed. You should keep a strict record of all the medications you take, for example, aspirin thins the blood, taking it will be undesirable, it is better to replace it with another medicine.
In order to quickly increase platelets in the blood, you should adjust your daily routine. First of all, be sure to get enough sleep, take breaks from work to rest, completely give up smoking and alcohol, and spend more time in the fresh air. Go for morning jogging, do morning exercises, avoid stress and nervous tension.
You should also make changes to your diet. First of all, eliminate coffee, alcohol and high-calorie foods, as well as blood thinning foods (raspberries, blueberries, citrus fruits, ginger, olive oil). Try not to overeat at night. Eat more vegetables and fruits; sour apples, beets, bananas, melons, persimmons and pomegranates are especially good for you. Also, to increase platelets, it is recommended to eat sea fish, beef, liver, kidneys, legumes, walnuts, parsley and dill, rice, buckwheat, sesame, green tea.
How to increase during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman regularly undergoes blood tests, so a decrease in platelet levels can be detected fairly quickly. A decrease in platelets in the blood of a pregnant woman can lead to miscarriage, premature birth or large blood loss during childbirth.
Therefore, when conducting an examination, great attention should be paid to the platelet level. The reason for the decline in this indicator should be determined as quickly as possible and work should begin to eliminate it.
During pregnancy, platelets can be increased only under the strict supervision of a doctor. Typically, immunoglobulin, vitamin B12 injections, folic acid tablets are prescribed, and for severe bleeding - aminocaproic acid. The diet should be filled with foods rich in proteins and vitamins. Consume natural juices, sea fish, beef, walk more in the fresh air, and avoid stress.
Additional articles on this topic:
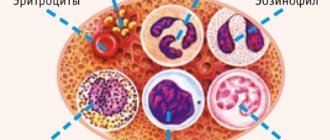
Platelets as blood cells
Nuclear-free blood plates are formed in the bone marrow from the semi-liquid content of its giant cells (megakaryocytes).
The process of thrombocytopoiesis (formation of blood platelets) is regulated by the hormone thrombopoietin, synthesized in the liver, spleen and kidneys. Approximately one third of all platelets produced are contained in the spleen, the rest circulate throughout the body in the bloodstream. The lifespan of flat cells is ten days, after which they are utilized (digested) by tissue phagocytes of the spleen.
Functional responsibilities of platelets include:
- Providing primary hemostasis (vascular-platelet response to blood loss). When microtrauma of capillaries or rupture of large vessels occurs, a significant number of platelets quickly move to the site of damage. Due to aggregation (the organic ability of flat cells to stick together), a blood clot is formed, stopping bleeding.
- Maintaining the integrity and trophism of the endothelium (the inner layer of the vascular wall). For the endothelium, platelets are both suppliers of nutrients and objects of nutrition (1/15 of the total cell volume is absorbed by the inner layer of the vascular wall).
Important! The main responsibility of platelets is to protect blood vessels from damage and ensure the process of normal coagulation (blood clotting).
Normal platelet count in a general clinical analysis (CCA) of blood
| For women | For men | For children |
| 180–320 (*109 cells/l) | 200–400 (*109 cells/l) | 180–380 (*109 cells/l) |
The general blood test takes into account the platelet count (PCT) - the percentage of platelet mass to the total blood volume. Reference thrombocrit values for adults and children range from 0.22 to 0.24%. PLT and PCT are closely correlated, their indicators in the OKA increase and decrease in proportion to each other.
A feature of platelet parameters is their variability under the influence of physiological factors and climate:
- In women, in the first week of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, the level of PLT and PCT can decrease by half, which is associated with blood loss. Thrombocytopenia during the perinatal period is due to the natural protection of the expectant mother’s body from the risk of thrombosis. The normal platelet count for a pregnant woman ranges from 100–310 (*109 cells/l).
- PLT and PCT indicators decrease slightly at night and in the spring season. This is not an anomaly, since the body does not show physical activity at night, and in the spring it often experiences a state of vitamin deficiency.
- A reduced platelet count is a clinical sign of underweight in newborns.
Deviation of PLT values from the norm is not a basis for diagnosing a specific pathology. The doctor must evaluate the comparative characteristics of all indicators of OKA and refer the patient for an extensive examination (analysis of venous blood for platelet indices and biochemical composition, ultrasound, MRI, CT).
Complex therapy, including:
- medications and vitamin-mineral complexes;
- nutrition correction;
- traditional medicine.
Treatment of thrombocytopenia is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosed cause of deviation from the norm. To restore normal values of platelet parameters, it is strongly recommended to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and maintain a drinking regime (at least 2 liters of water per day).
Medicines
To raise platelet levels, your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
Prednisolone. It belongs to the steroid hormones and is the main drug for the treatment of thrombocytopenia. With an initial daily dosage of 1-2 mg/kg, hemorrhagic rashes disappear within 7-1 days.
- Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the drug and systemic fungal infections. It is not advisable to use during pregnancy, as there is evidence of the danger of the drug for the development of the fetus;
- Price – from 67 to 108 rubles.
Etamzilat. Refers to hemostatic agents, stimulates the production of platelets and their release from the bone marrow. When the drug is administered intravenously, the effect occurs after 5-15 minutes.
- Contraindicated in case of individual sensitivity, thrombosis, thromboembolism, acute porphyria and hemoblastosis in children. Safety during pregnancy has not been established; it can be used during this period at the discretion of the doctor;
- Price – from 21 to 36 rubles.
Immunoglobulin. Increases the platelet content in the blood up to 75% even in the chronic form of the disease. In half of the patients it is able to return the indicator to normal.
- Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity, allergies in the acute phase, diabetes mellitus, renal failure, anaphylactic shock to blood medications, or absence of antibodies to the drug. No studies have been conducted on the harm of the drug during pregnancy.
- Price – from 820 to 985 rubles.
Vincristine is used in the treatment of idiopathic purpura due to thrombocytopenia, but is not recommended as a primary treatment for this disease.
- Hypersensitivity to the drug, bone marrow suppression, the presence of infections, neurological disorders and after vaccinations are also contraindicated.
- Price – from 180 to 596 rubles.
Azathioprine is an immunosuppressant and is used for immune and symptomatic thrombocytopenia.
- Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the drug and pregnancy;
- Price – from 238 to 257 rubles.
Codecor. Prescribed when the platelet count in the blood drops. It is produced on the basis of natural ingredients (mixtures and infusions of herbs). Can be used during pregnancy.
- Contraindicated in case of individual intolerance and arterial hypertension;
- Price – from 67 to 216 rubles.
Dicynone. A prophylactic agent that increases blood clotting, strengthens the walls of blood vessels and increases platelet levels.
- Contraindicated in cases of thrombosis, acute porphyria, childhood hemoblastosis and hypersensitivity to the drug. During pregnancy, it is used only when the benefits of the medicine outweigh the potential risks for the mother and fetus.
- Price – from 372 to 541 rubles.
Normal platelet count in blood
You took a blood test, received the result, found a line with numbers about platelets, but how do you understand that they are low? In fact, you just need to compare your result with the following normal indicators:
- In adults – 180-320×10 9 /l.
- In newborns – 100-420×10 9 /l.
- In children over 1 year old – 180-320×10 9 /l.
- In pregnant women – 150-380×10 9 /l.
In women during menstruation, platelets may decrease due to blood loss. This figure also decreases in pregnant women or with large blood losses. In other cases, a decrease in platelets below 150×10 9 /l should be a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Proper increase in platelets
Every person knows that platelets, like leukocytes, play an important role in our body. How to increase platelets in the blood, read further in the article.
Normal platelet count in blood
Platelets are small, colorless bodies that circulate in large quantities in our blood. They are responsible for blood clotting. There were cases when, when bleeding, people died from blood loss. It is necessary to monitor the platelet count. The norm is considered to be 180 – 320 thousand.
When do you need to increase platelets in the blood?
Most often, a drop in platelets occurs:
- during chemotherapy;
- menstruation;
- pregnancy;
- when taking certain medications (aspirin, antibiotics).
If you have:
- wounds do not heal for a long time;
- bruises and hematomas appear for no reason;
- The bleeding does not stop for a long time.
How to increase platelets in the blood?
If you are faced with such a problem, then ask yourself the question: how to increase platelets in the blood?
First, you need to include iron-rich foods in your diet. They can also protect you from anemia. These foods containing iron include:
Meat. Include some beef, liver, offal, and chicken in your daily diet. To increase platelets in the blood, eat more cereals. It is useful to eat boiled lentils, peas, and beans. Don't give up green vegetables and fruits. Prepare salads from dandelion leaves, beets, parsley, spinach. Very useful to increase platelets in the blood, red fruits: pomegranate, apples, strawberries
You should pay attention to: cranberries, blueberries, persimmons.
How to raise platelets in the blood after chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a very important stage in tumor treatment. In addition to the fact that it destroys cancer cells, various unfavorable processes in the body are possible. One of them is thrombocytopenia.
How can platelets be raised after chemotherapy? After all, these are cells that ensure the normal process of blood clotting, and with thrombocytopenia, their number in the blood drops, which is why the blood cannot clot.
Causes of problems after chemotherapy
Many medications used to treat cancer have a toxic effect on the body's cells, particularly the bone marrow. It is known that its cells have a very high division rate. Violation of this process leads to a rapid drop in platelets in the blood.
All drugs that are used to treat cancer pathologies reduce platelet counts to one degree or another. According to the degree of toxicity, they are divided into five classes. Class zero drugs do not reduce the indicator below 100*109. The most toxic drugs lower the platelet count to 25*109 or even less.
The causes of thrombocytopenia after chemotherapy are not fully understood. The leading role in the drop in platelet count probably belongs to damage to the bone marrow by drugs for intensive cancer treatment. Chemotherapy drugs kill rapidly dividing cells in that organ, causing the number of vital blood cells to steadily decline.
The main danger of this problem
Platelets are the most important formed elements of blood. If their number decreases, liquefaction and clotting disorders naturally occur. Thrombocytopenia is said to occur if tests indicate a level of less than 180*109 tr. per liter of blood.
If the patient develops bruises and frequent nosebleeds, this indicates that the platelet count drops to 25 - 50 * 109 in one liter of blood.
The main danger of the disease is that it sharply increases the risk of bleeding. It often happens that such cases cause death. Due to the development of pancytopenia, intoxication associated with chemotherapy increases in the body.
Important
In addition, due to the severe form of the disease, there is an increased risk of effusion in the brain. There is a very high risk of development and internal bleeding.
If a person experiences severe bleeding, death may occur from blood loss. If there is a sharp drop in platelet counts during chemotherapy, patients may be given lower doses. Surgical treatment is postponed until thrombocytopenia is eliminated.
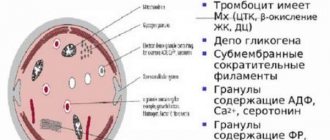
What are platelets, their norm and importance for the body
Platelets are blood elements that are small cells of irregular, flattened spheroid shape that perform the following tasks:
- cover the bleeding site;
- participate in the process of blood clotting;
- stimulate the regeneration of damaged tissues.
In the normal state, these cells are small in size (2-4 microns in diameter). When blood vessels are damaged, when platelets encounter something other than the tissue on the inner surface of blood vessels and the heart, they are activated. Outgrowths (up to 10 pieces) appear from the spherical cells; they greatly increase in size.
With these outgrowths, cells attach to other tissues and cover the site of injury. The appearance of a thick, and then completely dried, blood crust on skinned knees is the result of the work of platelets. The same mechanism operates during blood clotting - only active platelets in this case cling to each other.
After forming a plug that closes the damage, platelets begin to secrete growth factors that promote regeneration - accelerating the division and growth of new cells. The life cycle of a platelet is on average 10 days, after which the liver or lungs destroy it.
The number of platelets in the blood is determined in thousands per microliter of blood.
Normal indicators:
- in a baby within 2 weeks after birth – 100-420 thousand/µl;
- in an infant up to one year old – 150-350 thousand/µl;
- in a child under 12 years old – 180-390 thousand/µl;
- in women – 150-380 thousand/µl;
- in men – 180-400 thousand/µl.
During pregnancy or menstruation, the norm decreases to 130-400 thousand/µl and 75-220 thousand/µl, respectively.
Causes of problems after chemotherapy
Many medications used to treat cancer have a toxic effect on the body's cells, particularly the bone marrow. It is known that its cells have a very high division rate. Violation of this process leads to a rapid drop in platelets in the blood.
All drugs that are used to treat cancer pathologies reduce platelet counts to one degree or another. According to the degree of toxicity, they are divided into five classes. Class zero drugs do not reduce the indicator below 100*109. The most toxic drugs lower the platelet count to 25*109 or even less.
The causes of thrombocytopenia after chemotherapy are not fully understood. The leading role in the drop in platelet count probably belongs to damage to the bone marrow by drugs for intensive cancer treatment. Chemotherapy drugs kill rapidly dividing cells in that organ, causing the number of vital blood cells to steadily decline.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The clinical picture of this pathology cannot be called highly specific: the manifestations of the disease can be confused with anything. However, you should be aware of them in order to inform your doctor in time if there are warning signs of a disorder.
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia include:
- Tendency to internal hemorrhages;
- General fatigue, apathy, decreased performance;
- Constant formation of hematomas and bruises on the skin without objective reasons;
- Prolonged bleeding due to mechanical trauma to soft tissues;
- Bleeding of mucous membranes and gums;
- Frequently recurring nosebleeds;
- The presence of flat red spots on the skin of the legs and feet (their size usually does not exceed the diameter of a pinhead);
- Bloody inclusions in feces and urine (in especially severe cases).
If you experience similar signs and you already have an idea of the cause-and-effect relationships of thrombocytopenia in your case, be sure to consult a physician and voice your suspicions. The doctor will prescribe additional examinations for you, during which the exact cause of the changes occurring in your body will be determined.
Try to cooperate with your doctor. Typically, it takes time for platelet levels to return to normal. Especially if the reason for the decrease in their levels is pregnancy - in this case, taking certain drugs becomes dangerous. Find out from a specialist what folk remedies can help you cope with your problem.
Follow the diet that is recommended to you. Adjust your lifestyle and minimize harmful effects on the body and blood. For example, you should limit yourself to drinking alcohol and smoking.
Recommended products for low readings
The quality of nutrition greatly influences the composition of the bloodstream, so changes in diet can increase the number of platelets in the blood.
There are many products that work to increase the number of platelet cells, and they can all be bought in a regular supermarket; you don’t need to look for anything exotic or expensive.
Foods that increase the level of platelets in the blood include, first of all, meat. Beef is best suited for improving blood quality, but chicken also copes well with this task.
Organ meats such as liver and kidney, especially beef, also help increase cell levels.
Buckwheat is also a product that increases the number of platelets. Buckwheat and rice porridges introduced into the diet have a beneficial effect on blood flow.
Eating legumes, namely beans, peas and lentils, also helps increase platelet cell levels.
A properly formulated diet will help improve blood flow and solve the problem of how to increase the number of platelets in the blood.
However, it is not enough just to include healthy foods in the menu; you need to change your approach to nutrition and make food intake correct.
To do this, you need to follow simple recommendations compiled by medical professionals:
- reduce the amount of products containing artificial flavors;
- minimize the consumption of coffee and other caffeine-containing products;
- give up alcoholic beverages and excessively high-calorie foods;
- introduce into the diet fruits, vegetables and berries that have not been subjected to heat treatment.
At the same time, it is necessary to carefully monitor the consumption of dishes that may contain products that thin the blood.
There are few such products; the most common ones include ginger and olive oil.
Raspberries, blueberries, oranges, lemons and other citrus fruits can worsen clotting. Avoiding potentially dangerous foods will reduce the risk of a low platelet count.
Changes made to the diet will help if the decrease in platelets is recently detected and there are no complications associated with the decrease in the number of cells.
Nutrition for thrombocytopenia
It will be possible to increase the number of platelets using diet and folk remedies even with low levels in the blood, if you compensate for the lack of nutrients in the body such as vitamins C, K, B9, minerals calcium, iron, zinc.
The reason for the drop in platelets may be not only a lack of nutrients for the synthesis of new cells, but also a violation of the absorption of vitamins and minerals in the small intestine.
How to eliminate vitamin deficiency
A decrease in platelets is caused by a lack of vitamin C. 300 - 400 g of fresh herbs and fruits daily will help fill the deficiency. Quantitatively, this corresponds to two tangerines, an orange, two servings of a salad of tomatoes, cucumbers, and herbs.
Buckwheat, asparagus, spinach, green onions, tomatoes, beets will help increase vitamin B9 reserves in the body. Folic acid is a stimulator of thrombopoiesis - platelet production.
This vitamin is one of the most important for the production of new blood platelets. Just remember that folic acid is destroyed during heat treatment.
Vitamin K, known as an antihemorrhagic, helps increase the number of platelets in the blood. This compound is involved in blood clotting; if it is deficient, the prothrombin time, an indicator of blood clotting, lengthens.
The antihemorrhagic vitamin is synthesized by intestinal microflora and is supplied with food, but its absorption in the intestine may worsen due to inflammation of the gallbladder. The dinner table should include cabbage, spinach, eggs, liver, broccoli, kelp and other foods containing vitamin K.
How to compensate for mineral deficiencies
Calcium is required for platelet production. This macronutrient is found in sufficient quantities in dairy products.
There are conflicting opinions regarding the use of dairy products to increase blood platelets in thrombocytopenia. There is evidence that dairy products can increase the rate of autoimmune processes. This means that in cases of autoimmune thrombocytopenia, dairy products should be used with caution.
For hematopoiesis, it is necessary to obtain sufficient amounts of iron from food. This mineral is found in meat, offal, dried mushrooms, pumpkin seeds, chicken egg yolk, brewer's yeast, and cocoa.
The diet should contain omega-3 acid, which is abundant in fatty fish, eggs, and flaxseed oil. But in this regard, it is important not to overdo it. Excess omega-3 interferes with platelet aggregation (sticking together), which increases bleeding and the risk of internal bleeding.
Diet features
The diet should contain foods that increase platelets in the blood:
- rabbit, turkey, beef;
- offal - liver, kidneys;
- white fish;
- buckwheat;
- whole grain;
- legumes – peanuts, beans;
- nuts – hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds, pine nuts.
The diet should contain sources of vitamin C, which is abundant in leafy greens, fruits, and vegetables. Carrots, green apples, lingonberries are useful. Drinking green tea is useful for raising platelets.
Eating 2 kiwi fruits daily will help increase the number of blood platelets in conditions such as anemia, infection, vitamin B deficiency.
With dengue fever, residents of Southeast Asia and Africa who have suffered from this viral disease resort to eating pitaya fruits in order to increase platelets.
What foods increase platelets in the blood and their use is harmless to health?
- Chokeberry berries are consumed daily for 3 weeks in the amount of 50 pieces.
- A mixture of lemon and honey strengthens blood vessels and generally has a positive effect on hematopoiesis, as it contains a large amount of vitamin C (lemon), fructose, as an energy supplier.
- You can drink pomegranate juice every day, and in order not to harm the stomach, it is diluted with water in a ratio of 2:1.
How to increase platelets in the blood
However, you can try to raise your platelet levels on your own using folk remedies and nutritional correction. But in general, even these “mild” self-medication options should be under the strict supervision of a doctor.
It is important not to overdo it in this matter: you must understand that platelets can be increased excessively, which will also entail certain problems with hemodynamics. Excessive blood thickness is no less dangerous than poor blood clotting
People with excess platelets experience vascular occlusions and other potentially dangerous pathologies of the circulatory system. Therefore, if you decide to use certain pharmaceutical drugs, be sure to check with your doctor about the regimen, duration, frequency and dosage that is optimal for your case.
Reasons for low level
It is believed that a low level of platelets in the blood is an indicator below 100∙109/l, despite the fact that the lower threshold in the above standards often does not coincide with this value.
A condition in the body in which platelets are lower than normal is called thrombocytopenia. Factors of thrombocytopenia can be divided into two groups:
- Infectious diseases.
These include
Pimples that may appear on the lips, nose, and genital area.
- ARVI, acute respiratory infection
- Hepatitis of various groups
- Mononucleosis
An acute viral disease that is transmitted through human saliva, blood and sweat glands.
HIV AIDS
Violation of the immune state of the body.
Autoimmune diseases
In them, body cells are mistaken for pathogens and destroyed as hostile (for example, lupus).
- Oncological diseases
- Gaucher disease
With this congenital pathology, organs that affect the normal functionality of platelets can be depressed.
Taking certain medications
Blood thinners (such as Aspirin and Heparin) can cause low blood platelets.
Including blood thinning foods in your diet
Of course, this reason will have a slight effect on the decrease in platelets in the blood, but it also must be taken into account when making a diagnosis. Foods that thin the blood include lemon, garlic, cherries, ginger, onions, etc.
- Non-infectious causes
- Pregnancy;
- Period of menstruation;
At this time, the woman loses a significant amount of blood, which is what causes low platelets.
- Avitaminosis;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Heavy metal intoxication;
- Disruption of the spleen or even its removal.
In addition to the fact that when platelets in the blood decrease, blood viscosity decreases and it becomes more difficult to stop bleeding from an open wound, the real threat to life is the following: the vessels become more fragile, lose their elasticity and internal bleeding may occur.
How to increase with unconventional methods
You can normalize the level of platelets in the blood using folk remedies. But it is important to remember that any self-medication is fraught with complications.
Nettle
Nettle is ideal for increasing platelets. It is recommended to make and consume nettle drink, nettle decoction, and verbena infusion.
Sesame oil
This natural remedy will help increase your platelet count. Sesame oil contains all the substances necessary for the normal functioning of the hematopoietic system. The product is consumed 1 spoon 30 minutes before meals.
The duration of the course depends on the amount of oil consumed.
Chokeberry
Berries improve blood clotting, normalizing its enzyme composition. The treatment is simple. You need to eat 50 g of berries after eating in the morning. The course lasts no more than 3 days. Do not increase the time of therapy or consume red rowan.
On a note! It is important to remember that it is impossible to increase platelets in the blood using non-traditional methods in the presence of hemorrhagic complications.
It is necessary to urgently contact the clinic.
How to diagnose thrombocytopenia
If a person’s platelet count decreases and an illness begins to develop, then the risk of developing both minor and life-threatening diseases increases. Due to the peculiarities of the course of thrombocytopenia, it is necessary to follow several steps to identify the disease. The first thing is to go for a consultation with a doctor, then analyze the atypical symptoms that have arisen, these include:
- regular nosebleeds;
- inability to stop minor bleeding from a cut for a long time;
- bleeding gums;
- blood spots in the urine, as well as in stool;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- the appearance of petechiae, that is, red spots on the skin or the causeless appearance of bruises.
Composition of human blood
Reasons that provoke a decrease in platelets
- Diseases of a hereditary nature.
- Leukemia or bone marrow dysfunction.
- Disorders of the spleen.
- Consequences of chemotherapy or taking potent drugs.
- Autoimmune diseases (including AIDS).
- Bacterial blood infection.
- Pregnancy and postpartum period.
- A dangerous but rare disease is thrombocytopenic idiopathic purpura (high level of clots).
Several recipes to quickly increase platelet levels
An excellent natural platelet stimulator is nettle. There are several simple recipes.
Recipe 1
To prepare a medicinal drink you need to take 5 ml. nettle juice per 50 ml. milk. The components are mixed and consumed three times a day for three weeks. If a person has lactose intolerance, then take boiled water instead of milk.
Recipe 2
For 250 ml. only 10 g of dry nettle is required. The ingredients are mixed and boiled for five minutes. Then the broth is infused for two hours. You need to take 125 ml of the finished product. daily three times a day. The duration of treatment is 21 days.
Treatment with sesame oil
The product copes well with thrombocytopenia. The course of treatment involves taking the oil three times a day, one tablespoon thirty minutes before meals. The duration of treatment is determined by the amount of sesame oil consumed (full course - 2 liters)
It is important to note that additional drug therapy is excluded.
Folk remedies
With minor deviations in the platelet count, you can limit yourself to adjusting the diet and folk remedies. Recipes for increasing platelets are prepared from natural and inexpensive products.
Recipes for increasing platelets in the blood using folk remedies:
- Nettle. This recipe is effective after chemotherapy. Take 5 ml of nettle juice and mix with 50 ml of milk. Take three times a day, before meals. Course – 2 weeks.
- Oak bark. 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the raw materials and leave for 2 hours. Helps with bleeding gums and wounds.
- Honey and lemon. This is a means to improve blood composition and strengthen the walls of blood vessels. Mix the ingredients in equal parts and consume a tablespoon in the morning. To enhance the effect, add sesame or flaxseed oil.
- Pomegranate juice. For drinking, use diluted juice in a 2:1 ratio. People with stomach diseases should not drink without eating first.
Thrombocytopenia
A decrease in the level of platelets in the blood is called thrombocytopenia. Platelets perform many functions in the human body, and the main one is stopping bleeding. It is due to these cells that when damaged, a blood clot forms, which clogs the wounded vessel and eliminates blood loss.
Under normal conditions, the platelet level can vary significantly, but should not be less than 150 thousand/μl of blood and exceed 400 thousand/μl of blood. Quite often, thrombocytopenia occurs without any symptoms until the patient’s condition worsens.
What causes a drop in platelet levels in the blood?
There are several reasons for a decrease in platelet counts. Doctors name the main provocateurs of the disease:
- disturbances in the production of platelets - if there are disturbances in the functioning of the bone marrow, the composition of the blood is disrupted, and platelets can either be produced in insufficient quantities or die ahead of schedule, continuing to be produced according to the natural rhythm;
- radioactive damage;
- excessive alcohol consumption - under the influence of toxic substances contained in alcoholic beverages, a disruption occurs in the circulation of platelets in the blood: they settle in the spleen, without leading to its significant increase, and do not enter the blood circulating in the vessels and veins in the required quantities;
- genetic disorders in hematopoietic processes;
- transmission of severe infectious diseases;
- use of a number of medications;
- eating too many blood-thinning foods;
- heavy blood loss;
- undergoing hemodialysis.
Thus, there can be many reasons for the development of a condition with a reduced volume of platelets in the blood.
What can a low platelet level cause?
A decrease in platelet levels in the blood is not a harmless condition and can lead to serious consequences, and sometimes, in the absence of urgent medical assistance, to death. Complications of platelet deficiency include:
- internal bleeding;
- acute hemorrhage in the brain;
- hemorrhages in the retina of the eye even with a slight increase in blood pressure;
- heavy blood loss even with not very severe injuries.
Leaving this condition untreated is unacceptable. It is necessary to start therapy immediately after identifying this pathology.
Medicines used to increase platelet levels in the blood
Today, various medications come to the aid of patients. Most often, patients are prescribed the following medications to treat pathology:
- prednisolone - this hormonal drug is prescribed if it is necessary to increase platelet levels after undergoing a course of chemotherapy;
- etamsylate - the drug increases blood clotting by activating the release of platelets from the spleen, which is the repository of these cells in the body;
- codecor - this herbal medicine helps to normalize the process of hematopoiesis;
- vikasol - this drug is prescribed for complex therapy of the disease to prevent the development of internal bleeding;
- thrombopoietin - the drug is very powerful and stimulates the active production of platelets by the bone marrow in an extremely short time.
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor. In no case should you allow the unauthorized use of medications, as this creates a risk of developing dangerous consequences of improper treatment.
Folk remedies for raising platelet levels
Traditional therapy, proven for many generations, is an excellent remedy for low platelet levels and is completely safe.
Reasons for the downgrade
A decrease in the level of blood platelets provokes various disorders in the body. In some cases, urgent treatment is necessary, in others the situation does not require medical intervention - just adjusting the diet is enough.
The condition is temporary, not dangerous, and does not require special treatment if it is caused by excessive consumption of certain foods.
A drop in platelet levels usually occurs due to:
- primary herpes;
- liver inflammation during hepatitis;
- infectious and viral diseases;
- mononucleosis;
- immunodeficiency;
- malignant tumors;
- vitamin deficiency;
- alcohol intoxication;
- pregnancy;
- Gaucher's disease;
- autoimmune conditions;
- abuse of anticoagulants and blood thinners.
Garlic, cherries, ginger, onions, and lemon help reduce platelets.
Is it possible to increase platelet levels on your own?
At home, you can stabilize the quantitative platelet count in three steps. Step 1. It is necessary to review your diet, since blood counts may depend on the food consumed and the vitamins that enter the body
Therefore, it is very important to eat foods rich in iron, as well as enough vegetables and fruits.Step 2
Pay attention to a proper diet and avoid fatty, spicy foods. A person suffering from low platelet levels should forget about eating sausages, lard, canned food, pates and other rich fish and meat dishes. Step 3
Consult a doctor who will prescribe special medications that will help normalize platelet counts if this cannot be achieved with proper nutrition.
Diet that reduces indications
When dieting to reduce platelet counts, the following rules must be followed:
- Eat meals at the same time every day.
- Eliminate from your diet foods that contain large amounts of fats and carbohydrates.
- Include foods containing iodine and organic acids in your diet.
The following foods are prohibited on this diet:
- drinks containing alcohol;
- cereals;
- smoked meats;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- various confectionery products.
The foods needed to lower platelet levels have been presented previously.
Interesting article: List of products that thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots