Pain during the procedure
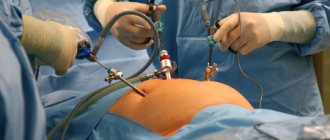
Laparoscopic surgeries are becoming popular. They are increasingly used in gynecology, when removing stones in the gall or bladder, as well as when removing abdominal organs. The operation is performed through several small punctures of soft tissue.
Progress of the surgical intervention:
- The patient is given anesthesia.
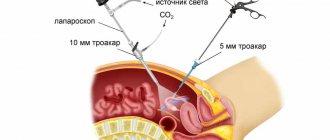
- 3-4 punctures are made on the anterior abdominal wall, through which a surgical instrument and camera are inserted.
- The abdominal cavity is filled with argon or carbon dioxide to expand the intra-abdominal space.
- An image is displayed on the monitor, the surgeon observes all his manipulations.
- After the operation is completed, the instruments are removed and sutures are applied to the punctures. If the surgical intervention is complex, for example, removal of the uterus, then drainage is left in the wounds for 1-2 days. In this case, sutures are applied for 5-6 days.
Before going on the operating table, patients are concerned about the progress of laparoscopy and whether it hurts. No. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, so the person does not feel any manipulation.
More often, general endotracheal anesthesia is used, in which the patient is put to sleep. He regains consciousness after the end of the operation. Local (epidural) anesthesia is done less frequently, only if there are contraindications to general anesthesia. An anesthetic substance is injected into the spine, the patient does not feel anything below the area where the anesthesia was injected. Very rarely discomfort is possible, but these are isolated cases.
Unlike laparotomy (cavity surgery), laparoscopy is much easier to tolerate. In some cases, the patient is discharged from the hospital the very next day. Analgesics, NSAIDs and lidocaine are used to relieve pain.
Laparoscopic operations
Laparoscopic interventions are characterized by the introduction of a laparoscope and additional manipulators into the abdominal cavity through small incisions on the anterior wall of the abdomen. Such access makes it possible to reduce the invasiveness of manipulation and ensure quick discharge of the patient from the hospital, while the effectiveness of treatment remains at a high level.
When can laparoscopy be used? Doctors prescribe this operation for the following conditions:
- Acute appendicitis, cholecystitis and other emergency abdominal surgery.
- Single and multiple uterine fibroids.
- Adhesions on the fallopian tubes or their obstruction.
- Ovarian cysts, etc.
Complications of laparoscopy are a rare event that can often be missed by doctors and the patient himself due to the mild severity of symptoms.
In addition, laparoscopy can be used as a diagnostic method when making a diagnosis using standard procedures is difficult. In this case, the attending physician has the opportunity to visually assess the condition of the abdominal organs and identify the pathological process.
Causes of pain after surgery
Painful sensations appear after surgery in all patients. Compared to laparotomy, the pain is minor and goes away much faster. The severity of pain largely depends on the patient's pain threshold.
More often, pain occurs in those places where punctures were made, as well as:
- in the abdominal area;
- near the navel (when filled with gas, the umbilical ring stretches);
- in the chest, in the side, under the ribs, in the shoulder area;
- in the throat;
- in the genital area.
During the first 12 hours, the most pronounced pain is observed. If epidural anesthesia was used during the operation, the person experiences pain in the lumbar region.
Pain after laparoscopy occurs for the following reasons:
- Injury to soft tissues and internal organs with a surgical instrument. In this case, pain is felt in the area of the incisions.
- Stretching, as well as irritation of the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide, which was introduced during the operation. Up to 3-4 liters of gas are pumped into the patient’s stomach. After the anesthesia wears off, the intensity of pain increases. The patient feels severe pain in the upper abdomen, in the back, under the ribs, and the shoulder may even hurt. Some people who have laparoscopy have difficulty breathing. This is caused by the compression of the diaphragm. It may be painful for a person to straighten up.
- The use of a tube through which the patient breathes during surgery. This tube is inserted into the throat and anesthesia is delivered through it. After using it, the patient feels a sore and sore throat, but does not experience any particular discomfort.
The intensity of pain depends not only on the pain threshold, but also on the indications for surgery. If the pain does not subside, the temperature rises after laparoscopy, the suture festers, and tension in the abdominal wall is felt, then you need to contact a surgeon. These are symptoms of an infectious process.
You should also seek medical help in the following cases:
- cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- redness of the seam;
- blood in the incision area;
- difficulty urinating;
- dizziness, headache, weakness;
- fainting.
Acute pain in the first 12 hours is not normal. This is a sign of a failed operation.
Basic principles of treating patients with cough after anesthesia
Immediately after identifying the cause of the cough, you need to start doing everything possible for the patient’s speedy recovery.
A throat aerosol will help the patient if the cough is caused by mechanical damage
Main methods and methods of treatment:
- For hospital-acquired pneumonia, massive antibacterial treatment is carried out with the latest generation antibiotics. Typically, hospital bacterial flora is insensitive to most antibiotics, so sensitivity testing is always performed. In addition to antibiotics, expectorants and sputum thinners are prescribed.
- If the cough is caused by mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, the patient is prescribed antiseptic aerosols in the throat, and the consumption of spicy, hot and solid foods is prohibited during the healing period.
- When aspirating gastric contents, it is necessary to do bronchoscopy, with which the doctor can remove pieces of food. Just as with pneumonia, antibacterial therapy is prescribed. If necessary, the patient is given oxygen to maintain proper blood gases.
- If the cough appears after the administration of atropine, nothing needs to be done. Over the course of a day, this symptom will go away on its own. If the patient’s cough is very bothersome, you can advise him to drink warm milk with butter, if it is not prohibited for him due to the general condition of the body.
Cough is a common complication of operations performed under general anesthesia. It may occur as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by the laryngoscope during intubation, or it may appear with the development of aspiration syndrome or pneumonia. In some patients, cough develops after atropine is administered. Treatment for cough should be prescribed after determining the cause of its occurrence, and should be aimed at the underlying problem. If this symptom occurs after the administration of atropine, no specific treatment is required; you can soften the throat mucosa with warm milk.
source
Abdominal pain
Patients often complain of pain in the upper abdomen, even if this area was not affected during the operation. The reason was described above. But you need to know how your stomach hurts after laparoscopy.
Painful sensations appear 2 hours after the operation, when the anesthesia stops working. The pain is severe, sometimes you cannot do without analgesics. More than 70% of patients rated the severity of pain at 30 points out of 100. Pain disappears after 12-24 hours.
It is impossible to determine where the pain is localized, whether the intestines, stomach or liver hurt. Sudden movements can cause abdominal pain. Unpleasant sensations should subside after three days, and disappear by 5-6 days. If this does not happen, you need to consult a doctor.
After laparoscopy, the area around the navel sometimes hurts, although there are no nerve endings there. The cause is injury to surrounding tissues.
Pain in the upper abdomen, side and under the ribs always occurs when internal abdominal organs are removed. The peritoneum is stretched, the walls are irritated by carbon dioxide, and therefore painful sensations appear.
Accordingly, pain after removal of the gallbladder is localized in the abdomen, hypochondrium, side, as well as in places of punctures and incisions. After surgery to remove an organ of the digestive tract, pain persists for more than a month until the functioning of the digestive system normalizes. The pain syndrome can be relieved with analgesics - “Spazmalgon” or “Ketanov”. If it does not go away 2-3 months after laparoscopy, then this indicates adhesions.
Basic characteristics of laparoscopy
The laparoscopy method is used quite often in modern medical practice, as it has more advantages than classical surgery (laparotomy). Firstly, the marks after laparoscopy are not so noticeable, and the healing process is much more intense. Secondly, the intervention is not so painful for the patient, therefore large doses of analgesics are not prescribed during the rehabilitation period, which significantly reduces the risk of side effects. After surgery, in the long term, adhesions form much less frequently, so there is practically no chronic pain as such.
So, the operation, as a rule, takes place under general endotracheal anesthesia. Local anesthesia is sometimes used. Local anesthesia is most often prescribed to elderly patients if there are any contraindications to other types of anesthesia. During the operation, pain is not felt, even if the person is awake. These are the properties of local anesthesia: the lower part of the body completely loses sensitivity.
Immediately after the administration of the anesthetic, several small incisions are made on the anterior abdominal wall, and then this area is expanded using a trocar. After this, surgical equipment is inserted into the open cavity, including a special video camera that displays the image on the screen. In addition, neutral or carbon dioxide is introduced into the cavity, due to which the space inside expands. Thus, the surgeon tracks his every action using images on the monitor. After all the manipulations have been performed, the doctor sews up the incisions. If pain occurs during the rehabilitation period, then special drugs are introduced into the cavity to reduce it.
Benefits of laparoscopy
- Injury is minimized;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Rapid recovery;
- No scars;
- There are practically no painful sensations.
Pain in the suture area after surgery
After the anesthesia wears off, patients most clearly feel pain in the area of the incisions. It decreases after 12-24 hours. The occurrence of severe pain several days after surgery may be associated with the development of complications. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
The puncture sites heal quickly, since their size is only up to 1.5 cm. They heal for 7-14 days, it all depends on the puncture site. The sutures in the navel area take a long time to heal, and the likelihood of suppuration is high.
During the first week after laparoscopy, the suture hurts. Normally, the following signs appear:
- It's a dull pain;
- abdominal pain;
- slight suppuration and redness of the incision site;
- bloating.
Such unpleasant sensations should subside within 7-14 days; it is during this period that the sutures are removed. If self-absorbable threads are used during the operation, they disappear within 5-7 days. The punctures heal completely after 30 days.
Is it painful to remove stitches after surgery?
If this is done on time, the wound does not fester, there are no complications, and the threads do not grow into the skin, then there will be no pain. The patient may experience discomfort from the instrument, but not pain.
Only a doctor should remove threads; you cannot do it yourself. It is important to go to the hospital within the specified time. If the suture material grows into the skin, then removing it will be painful.
Recovery after laparoscopy
The patient recovers quite quickly after laparoscopy. The next day, doctors allow the patient to get up, eat, and take care of himself.
Recovery after laparoscopy may take several weeks. During this time, it is forbidden to lift weights, wash in the bathroom, or actively engage in sports.
Until the seam heals completely, it must be treated daily with antiseptics, as well as basic hygiene procedures.
Shoulder and chest pain
This type of pain occurs very often because carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. It expands the peritoneum, but compresses the internal organs. Within 1-2 days after laparoscopy, there is pain in the collarbone, chest, left or right side, under the ribs. But the pain is moderate, it is easily tolerated without taking painkillers. It's more of an uncomfortable feeling.
After removal of the gallbladder or appendicitis, the shoulders hurt, the right side hurts, the back on the right side hurts, as well as the upper abdomen. The most pronounced pain is at the puncture sites.
Why does the shoulder and neck area hurt after laparoscopy? The neck, shoulders and chest hurt in almost all patients who have undergone this type of surgery. This is due to the introduction of carbon dioxide, which is released through the lungs for several days after surgery. This is why the neck, collarbone, throat and other parts of the body hurt. The most intense pain is the first two days after surgery, as well as during movement.
Right side hurts after gallbladder removal: diagnosis
To diagnose remote gallbladder syndrome, it is necessary to carry out the following list of examinations:
1. General blood test.
2. General urine analysis.
3. Collecting the patient's medical history.
4. Blood for bilirubin level.
6. Carrying out endoscopic retrograde manometry.
Sometimes, after removal of the gallstone, the stomach can hurt so much that the person will simply be unable to get out of bed. In this case, he needs to be hospitalized urgently, otherwise the inflammatory process can cause serious complications in the body.
Pain in the genital area
Women often have to undergo laparoscopy due to gynecological diseases. This type of surgical intervention is used for the following purposes:
- diagnosis of genital diseases;
- tube removal for ectopic pregnancy;
- treatment of endometriosis;
- removal of ovarian cysts, adhesions, fibroids or fibroids, as well as the uterus;
- treatment of inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy is also common among men with diseases of the genital organs. After laparoscopy of an inguinal hernia, men experience minor pain that goes away after 2-3 days. The pain radiates to the lower abdomen, side, lower back or sacrum.
After surgery, there is a high risk of complications. There is a risk of damaging nearby organs with the laparoscope. These are the intestines, liver and stomach.
Complications after laparoscopy are indicated by sharp cramping pain.
Pain in the lower abdomen after genital surgery in women is the most common. Other types of pain after laparoscopy in gynecology:
- the navel or the entire stomach hurts;
- pulling in the lower abdomen;
- the postoperative suture hurts;
- pain is felt in the right side, closer to the ribs;
- chest, shoulders, lower back hurt.
The localization of pain depends on the disease.
After laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst, pain in the lower abdomen and bloating occur. Painful sensations may bother the patient for 7 to 30 days. The most severe pain after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is felt in the first day. There is also severe pain at the puncture sites.
Do not be alarmed if your ovary hurts after laparoscopy. This is normal, since when a cyst is removed, soft tissue is injured. You need to be wary if the pain becomes cutting. It is acute, the pain in the ovaries increases. In this case, hospitalization is required.
Women who have undergone laparoscopic genital surgery have an increased risk of inflammation of the appendix, so it is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the pain. Painful sensations in the lower abdomen may be associated with menstruation, which usually begins a short time after surgery.
After laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes for an ectopic pregnancy, the lower abdomen will drag for at least a month. But such pain is mild. It should not cause discomfort or lead to loss of ability to work. Painful sensations may intensify with sudden movements. After laparoscopy of the uterus, it is painful to write and also to defecate.
After removal of the gallbladder, the right side hurts: treatment
Therapeutic therapy for this condition should be comprehensive and aimed at eliminating impaired functions of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and the stomach itself.
Drug therapy involves taking the following groups of drugs:
1. Painkillers (Drotaverine, Mebererine).
2. Enzyme-containing preparations to improve general digestion (Festal, Mezim forte, Pancreatin, etc.).
3. Prescribing antibacterial drugs to restore the patient’s disturbed microflora. Typically used for this purpose: Hilak forte, Furozoltdon). They need to be taken in courses of 5-7 days.
4. Taking antimicrobial drugs that help restore digestion and “build” healthy microflora (Linex, Bifidumbactrin, etc.).
5. Taking antipyretic medications (at high body temperature).
6. Prescription of anesthetics (it is better to administer them infusorally or intravenously, rather than take them in tablet form).
In the first six months after removal of the gallbladder, you may experience stomach pain and other unpleasant symptoms. This condition needs to be monitored, so the patient must have blood tested from time to time and be under medical supervision.
As a rule, 1-2 months after removal of the gallbladder, the patient’s body adapts to new working conditions and his digestive system improves. The liver begins to produce bile in normal quantities (depending on how fatty foods a person eats).
Despite this, there are isolated cases when drug therapy did not help to cope with inflammation and restore the functioning of the liver, stomach and intestines. A patient in this condition will suffer from high fever, vomiting and pain in the side. The only way out of this situation is to re-diagnose and perform another operation. The duration of recovery after it will be several months longer, since the patient will have to endure the entire rehabilitation cycle again.
Other characteristic pain syndromes
Very often, patients experience back pain. Pain syndrome occurs due to epidural anesthesia. The pain is mild and may bother the patient for several months after surgery. Sometimes my back hurts because of carbon dioxide.
After anesthesia, the whole body may ache, muscle weakness, dizziness and headache may be felt. If an anesthetic substance was injected into a vein, your arms may hurt, and after a couple of days your legs may hurt. Pain in the limbs can occur when carbon dioxide enters the vascular bed.
If a nerve is damaged by a surgical instrument, the patient's skin hurts or there is no sensitivity of the skin at all. The pain should go away over time. If this does not happen, then adhesions may be the cause.
Symptoms and diagnosis of hospital-acquired pneumonia
If the patient did not have a cough during the postoperative period, and then it appears and is accompanied by:
- elevated temperature;
- chills;
- body aches;
- weakness;
- secretion of sputum;
- shortness of breath;
- chest pain, we can assume the presence of hospital-acquired pneumonia.
When listening to the patient, weakened breathing and wheezing are heard, and upon percussion, dullness of sound is determined.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia poses a serious threat to the patient's life, so treatment must be started immediately.
Additional methods for diagnosing this dangerous disease include:
- general blood test for the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR);
- blood chemistry;
- sputum analysis (bacterial culture);
- X-ray of the chest cavity to identify infiltrate in the lungs, which appears during the inflammatory process.
These diagnostic methods will help establish an accurate diagnosis and begin immediate treatment.
Pain relief in the postoperative period
Laparoscopy is an operation with the least severe pain syndrome in the postoperative period. Immediately after surgery, the puncture sites are injected with an analgesic so that after recovery from anesthesia the patient does not feel severe pain.
Narcotic analgesics (opiates) are rarely used because they cause a number of side effects. They also quickly relieve pain, which interferes with the timely diagnosis of postoperative complications. If acute pain occurs after 12 hours, then this is not the norm.
In the first days after surgery, doctors may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They not only relieve pain, but also eliminate foci of inflammation. The most popular are “Ketanov” and “Ketotifen”. To relieve pain after laparoscopy to remove a cyst in the ovary, NSAIDs and non-narcotic analgesics are used simultaneously. But you shouldn’t get carried away with painkillers, they negatively affect your health. After laparoscopy, pain can be localized in different parts of the body, but it is not as severe as after abdominal surgery. This benefit is especially important for patients with a low pain threshold.
Exacerbation of chronic diseases
Some people may experience stomach pain after gallbladder removal, not just the right hypochondrium. Why is this happening? The restructuring of the biliary tract does not occur without leaving a trace for all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Changes in the composition of bile and the characteristics of its outflow often lead to an exacerbation of chronic diseases of the digestive organs that existed before the operation. Namely:
- Pancreatitis;
- Gastritis;
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- Hepatitis A;
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
Pain in the right side after removal of the gallbladder may be due to recurrent choledocholithiasis. It is caused by the repeated formation of stones in the bile ducts. Residual choledocholithiasis occurs against the background of stones that were already present but not detected during surgery. Pain is explained by this reason in 5-20% of cases.
During preparation for surgery, it is necessary to warn the doctor about all previously established chronic diseases. This will help to adjust treatment in time and avoid as many undesirable consequences as possible. For example, the doctor should know about the presence of diabetes mellitus, because it makes postoperative sutures heal worse.
Principles of treatment
Pain syndrome occurs for various reasons, so treatment tactics are strictly individual. They mainly resort to therapeutic methods. Surgery is considered only when absolutely necessary. Prescribed:
- Analgesics. If the operation went without complications, and the pain is only in the area of surgical wounds. Most often, ketorolac-based products are used (Ketoprofen, Ketorol).
- Antispasmodics. With excessive contraction of the bile ducts, sphincter of Oddi. One of the representatives is drotaverine (No-Shpa).
- Hepatoprotectors. To maintain normal functioning of liver cells.
- Enzyme preparations (Mezim, Pancreatin). Used to reduce the functional load on the pancreas during meals.
- Antibacterial therapy. Only if a bacterial infection is suspected. The type of drug is determined by the attending physician.
Diet
Nutrition correction plays almost the main role in preventing pain after cholecystectomy. Its principles:
- Reducing the consumption of cholesterol-containing foods (but not completely eliminating them);
- Limiting fried, fatty foods;
- Frequent split meals up to 4-6 times a day;
- Gradual, but not sharp reduction in body weight if it is excess;
- Increasing the proportion of plant dietary fiber in the diet (to stimulate gastrointestinal motility);
- Preference for baked foods (including fruits and vegetables), steamed dishes.
In what cases is diagnostics necessary and how is it carried out?
It is strongly recommended to consult a doctor if the cough does not go away on its own after 3 days, and also if it is accompanied by pronounced painful symptoms. At the appointment, the doctor will definitely get acquainted with the patient’s complaints, listen to the patient’s lungs and evaluate his external condition. But this is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis.
Additional examination methods include:
- General blood analysis. Its result can confirm the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- Radiography. A familiar procedure that displays the condition of the lungs;
- Sputum culture. If present, the patient may be scheduled to submit a sample for laboratory analysis. He is able not only to identify the presence of pathological pathogens, but also to select antibiotics to which they will be sensitive;
- Bronchoscopy. This is a fairly serious examination method, which consists of assessing the condition of the respiratory tract, trachea and bronchi using special equipment.
A general blood test is one of the methods of additional diagnostics.
After all the necessary procedures have been carried out, the doctor will be able to determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment therapy.