Hematuria is a symptom characterized by the appearance of blood in the urine. It may not be noticeable upon visual examination, then it is called microhematuria; with a significant amount of blood loss, the urine becomes the color of meat slop or dark red clots are visible in it. The latter option indicates profuse bleeding, that is, the blood is released in large portions and coagulates.
The source of blood in the urine can be any part of the urinary tract, starting with the kidneys and ending with the urethra. It is important to note whether it is accompanied by any symptoms or not. The absence of symptoms does not mean that hematuria is harmless. Blood discharge can occur during or outside of urination. Hematuria can be pathological, that is, associated with diseases of the urinary system, physiological - as a variant of the norm, false (when red urine appears in a child, but there is no blood there), benign. What is the difference between these conditions, how do they manifest themselves and what to do about it, read on.
Causes
If your baby's urine turns pink or red, this may be caused by physiological or pathological factors.
Physiological
These include:
- Introducing some foods containing natural dye into the child’s diet.
- Taking certain medications.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Uric acid infarction with the following symptoms:
- the baby is no more than 2 weeks old;
- you can clearly see red dots (salt crystals) on the diaper;
- the baby’s general condition does not deteriorate;
- The baby's urine is red.
As soon as the baby begins to suck mother's milk, the kidneys will begin to remove uric acid salts from the body, and after a few days the urine will become straw-colored or transparent.
- Dehydration of the body. As a rule, such factors are considered harmless and after a short time the urine acquires a normal straw-yellow color.
In some cases, a child's urine turns red due to blood entering it. This condition is called hematuria and requires immediate consultation with a specialist.
Pathological
These causes of red urine are:
- Inflammation in the lower and upper urinary tracts
Inflammation in the lower tract is cystitis, and in the upper tract is lomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. Most often, infections such as cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis occur in girls (due to the shortened urethra and the close location of the anus to it). Diseases can also be the result of a recent illness:
- flu;
- scarlet fever;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis.
Symptoms of inflammation in the urinary system are: increased body temperature, nausea and vomiting, decreased amount of urine output, increased thirst, swelling of the face and limbs, dark red color of urine.
- Thrombocytopathy
The disease occurs due to a genetic disorder, as a result of which platelets do not function well in blood clotting. The development of the disease is influenced by some pathological conditions suffered by the mother while carrying the baby (sepsis, viral infections, injuries during childbirth, acidosis). Signs of thrombocytopenia are:
- presence of blood in urine;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- The navel may begin to bleed.
- Hemorrhagic diathesis
This disease is considered systemic and mostly congenital. With this pathology, blood clotting function and vascular tone are impaired. Symptoms of diathesis are:
- vomiting with blood clots;
- There are also blood streaks in the baby's stool;
- gums begin to bleed, this is especially noticeable during teething;
- urine is dark red;
- The whites of the eyes become red due to hemorrhage in the retina.
Pink urine in a child - safe factors
The normal color of urine in a newborn is red, deep pink. Urine contains a lot of urates - salts of uric acid. Colostrum contains little water, so little fluid enters the baby’s body and salts are not excreted.
But after a few days, the urine becomes lighter, and by 7-12 days of life it acquires a light yellow, straw color.
If you notice pink spots on your diaper, don't panic. Often this reaction occurs when urine comes into contact with materials that absorb liquid.
To reassure yourself, collect urine in a sterile container to evaluate the true color. If your urine is really pink, contact your pediatrician.
Symptoms
Red urine caused by consuming coloring foods is not a cause for concern and usually goes away within a few days. It is important to remember what the child ate and whether any medications were used. Vegetables such as beets cause a bright red tint to urine. It is very simple to check whether beets are the culprit of red urine: you need to first add a little soda and then vinegar to a portion of the child’s urine. If the urine acquired this color from a root vegetable, the urine will first lighten and then return to its previous color.
Other physiological factors only change the color of urine, but do not affect its turbidity. If the urine becomes cloudy, this indicates an admixture of blood in it and the beginning of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system.
Characteristics of urine and its properties
In order to understand whether urine is normal at home or not, everyone must know the main characteristics, namely:
- The normal daily amount of urine excreted should be 1.5 liters. More or less discharge may indicate problems in the body.
- Transparency. Cloudy urine indicates that the body is not getting enough water.
- Density.
- The smell is specific, but not pungent. If the urine does not fall under this characteristic, then most likely a disease develops in the body.
- Color – faded yellow. It tends to change throughout the day.
Treatment
Depending on the reasons, the following treatment is carried out:
- A condition such as uric acid infarction does not require any treatment; the child is carefully monitored for several days until the color of the urine returns to normal.
- Hemorrhagic diathesis requires treatment aimed at improving blood clotting and strengthening the walls of blood vessels. Use iron-containing preparations, ascorbic acid, vitamin K, rutin.
- Thrombocytopathy requires lifelong prevention of the disease, in which hemostatic drugs are used: sodium etamsylate, Adroxon, ascorbic acid, calcium gluconate.
- For diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, therapy with antimicrobial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs is used. At the same time, vitamin-mineral complexes and medications that support intestinal microflora are prescribed.
Danger of isolated hematuria
Although there are no additional symptoms with isolated hematuria, this does not mean that the condition does not pose a threat to the child. Associated symptoms may not be observed in the following pathologies:
- kidney cyst;
- initial stage of urolithiasis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- cancer of the urinary system.
Malignant tumors of the urinary system account for more than 5% of cases of hematuria detected in childhood and adolescence.
Prevention
To exclude diseases of the urinary system, you need to carefully monitor the child’s diet:
- Salt should be limited to a minimum amount.
- Protein foods should be limited.
- It is important to maintain the baby’s normal drinking regime; the child should regularly drink clean drinking water, herbal tea, compotes, and fruit drinks made from fresh fruits or berries.
- Avoid hypothermia, as this directly leads to diseases of the genitourinary organs.
- Take urine and blood tests regularly.
- Undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys.
At the slightest suspicion of an unnatural color of urine, only if it was not caused by taking medications or consuming coloring products, you should show concern and show the child to the pediatrician.
You can also watch a video about advice to parents about blood in urine.
Hematuria in older children
Blood in the urine in children 3 years of age and older most often indicates problems with the bladder and kidneys. In addition, experts also identify urolithiasis in adolescents. Stones, lingering in the bladder, damage its mucous membrane, which leads to bleeding. Also, red impurities in the urine of older children can mean injuries to the organs of this system, bruises in the lumbar area and abdomen.
In boys
A common cause of hematuria in boys is urolithiasis of the urethra, that is, stones are formed not in the kidneys, as is usually the case, but in the urethra. This pathology very often develops in childhood and is most typical for boys aged 5 years and older.
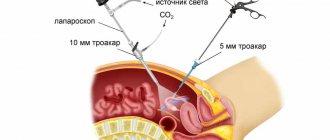
Associated symptoms include pain when trying to urinate, as well as problems with urine leakage. This is a dangerous and serious disease, so action must be taken as soon as possible. In most cases, you have to resort to minimally invasive types of surgery.
Another cause of blood in the urine in a child 7 years of age or older is injury to the groin area or kidneys. A child can be injured during play, in a fall, from a blow, and other, at first glance, harmless factors.
Only a specialized specialist can determine the cause of blood in the urine of a teenager. If such a problem is identified, consultation with a pediatric urologist is necessary.
For girls
According to statistics, they are most susceptible to diseases of the genitourinary system. If a girl has visible traces of blood after urinating, this may indicate the presence of kidney stones or the acute stage of hemorrhagic cystitis, which occurs due to poor personal hygiene, as well as a significant decrease in immunity.
It should be noted that in most cases, these are simply vain worries of the parents, and red traces in the urine are in no way related to pathological processes. If the problem is present in a girl 10 years old or older, we may be talking about premature onset of menstruation. As a rule, the timing of puberty in girls is highly individual and often depends on heredity.
Wrongful hematuria sometimes occurs due to the consumption of certain foods. For example, drinking beets or pomegranate juice may slightly change the usual color of the natural liquid.
Other manifestations
Blood in children can be a single symptom, as well as in combination with other manifestations. Depending on the disease, the following symptoms sometimes appear:
With severe hematuria, blood flakes appear. They block the urethra, which causes pain and the inability to urinate independently.
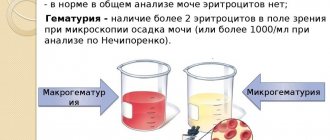
Diagnostics
Macrohematuria can be seen with the naked eye. However, with microhematuria, an ordinary person will not be able to see this, and mainly in children this symptom is discovered by chance during testing.
If hematuria is suspected, the following tests should be done:
- General urine analysis.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky.
- Urine culture.
- General and biochemical blood test.
In addition, additional studies may include ultrasound, cystoscopy, and radiography.
Periods of blood in urine
Sometimes blood is clearly visible to the naked eye of the parents. This indicates an excessive ingestion of red blood cells (according to test results, the presence of red blood cells may be higher than 10). Such a child needs immediate help. But in some cases, red blood cells are detected only as a result of laboratory tests; pathology cannot be determined visually.
Experts have determined that there are three periods for the appearance of red blood cells in the urine of children:
- If blood appears at the beginning of urination, then this is initial hematuria - damage to the urethra.
- If there is blood at the end, this is terminal hematuria, indicating damage to the urethra or bladder neck.
- Total hematuria - blood is released throughout urination - these are other pathologies in the urinary system.
How to properly collect urine for analysis
There are several simple and mandatory rules for collecting urine for laboratory testing, compliance with which will allow you to reliably judge the composition of the excreted liquid and protect against false results.
- The day before the test, exclude any coloring pigments and medicinal substances from the baby’s diet (warn the doctor about the treatment being carried out).
- Before collecting urine, wash your baby thoroughly.
- For the study, morning urine collected after a night's sleep is taken.
- Older children should be taught to collect for analysis the average portion of the stream, when the first and last two seconds of urination are carried out into the toilet or into a bucket.
Video on the topic