Concept of the uterine epithelium. What it is
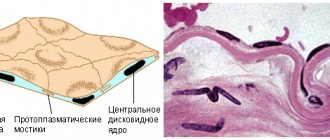
The epithelium in the smear, the norm in women is 5-10 cells, is classified into 2 types: single-layer and multilayer. A detailed examination under a microscope shows that the tissues of the first type have a variety of shapes. A characteristic feature is that their size is approximately the same. Multilayer epithelium contains cells of different shapes with uneven edges.
The main function of the lining membrane is to protect the genitourinary system from penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, all tissues are tightly connected to each other, and there is no intercellular space.
The life cycle of cells is short, but due to the fact that they are quickly regenerated, they are timely replaced with new ones. If the layer is damaged during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, it is also quickly restored. In addition to its protective function, the epithelium takes part in the metabolic process.
How does this type of cell change depending on age?
A woman goes through different stages of development in her life, depending on her age, internal organs and cells change. The squamous epithelium was no exception (in the smear it is designated as “Ep”). In women of reproductive age, the boundary between the arrangement of cylindrical epithelial cells and flat ones is clearly visible. They have a typical appearance, and the analysis results will be reliable due to their correct location. During life, this clear boundary moves into the cervical canal. In women before and during menopause, squamous epithelial cells are no longer as large as they were before. They become thinner, and a gap appears in the vessels.
Types of epithelial cells
The female organs responsible for the normal functioning of the urinary and reproductive systems have a complex anatomical structure, which includes a lining membrane. Its main constituent element is epithelial cells of several types (flat, glandular, cylindrical).
When performing a microscopic examination of a smear in a small amount, their presence is considered normal (does not exceed 10 units).
In anatomy, there are 2 types of uterine epithelium:
- Multilayer flat. The thickness is 150-200 microns, consists of basal, superficial and intermediate cells, which are regularly renewed (the desquamation process occurs once every 6-7 days). The presence of this type of epithelium in a smear in women is considered normal.
- Single-layer glandular or cylindrical. Located on the walls of the cervical canal. This layer is responsible for the production of mucus, which prevents pathogenic bacteria or infection from entering the reproductive system.
Flat epithelial cells of the uterus have a similar structure to those located on the skin. The only distinguishing feature is that they do not become horny. In a situation where tissues begin to harden and turn into horny substance, gynecologists assume the presence of a pathological process.
What is squamous epithelium
A woman's vagina is covered with a mucous membrane, which consists of squamous epithelium. Over the course of a month, the reproductive system goes through 3 phases of the menstrual cycle, during each of which cells may undergo minor changes in shape and size. There is epithelium that becomes horny and that does not have this ability.
Depending on the current phase of the menstrual cycle, the ratio of cells of the 2 types will change. This must be taken into account when performing a smear analysis in order to understand whether deviations from the norm indicate pathology or not. In a healthy woman, the presence of no more than 10 cells in the biomaterial is allowed.
If their content is exceeded in the field of view, then additional studies are carried out to help determine the inflammatory process or infectious lesion of the genitourinary system. In the case of structural changes in cells, there is a possibility of the formation of a tumor of a benign or malignant type.
What is columnar epithelium
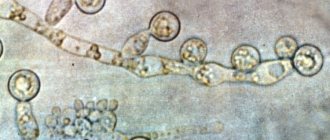
A characteristic feature of the cylindrical cells of the epithelial layer is that they are entrusted with the function of producing a special mucous secretion on the uterine cervix. If we look at a smear from a healthy woman, the cells in it will have a honeycomb-like or linear structure.
It is not considered a deviation if they are shaped like a glass, which is due to their stretching when filled with cytoplasm. Sometimes granules of mucous secretion are found in them. If the cylindrical epithelium is displaced, and flat surface cells form in its place, then the patient is expected to develop ectopia.
Atypical epithelial cells
The epithelium in the smear, the norm in women is 5-10 cells in the field of view, can be detected in the form of atypical cells. In this case, a repeat study is often prescribed, which eliminates the possibility of a diagnostic error. Modified cells of the lining of the vagina and cervix indicate the development of dysplasia or oncology.
Dysplasia transforms into cancer in only 1% of patients, but if you are constantly registered and also follow medical prescriptions, then after 2-3 years you can completely get rid of the disease.
Epithelium in a smear in women is normal and with dysplasia
If therapeutic measures are ineffective and there is an increased likelihood of cancer cells appearing, a procedure for removing the cervix and the main reproductive organ is indicated. The operation is performed mainly on menopausal patients or those who are not planning a pregnancy.
Medical terms that scare you
Dystrophy or dystrophic epithelium - occurs with true erosion of the cervix or pseudo-erosion, which is also called ectopia. In a word, when there is a wound on the cervix. When it heals, cell degeneration will no longer be detected.
The medical term “metaplastic” is often present in the cytogram. Many people think that this indicates a malignant process. But no - metaplastic epithelium is a good smear result. This indicates that the cells were taken exactly from the desired zone - the junction of two types of epithelium - from the endocervix (cylindrical) and exocervix (flat). These are the cells of the transformation zone, where atypia, precancerous or cancerous changes are most often found.
Acetowhite epithelium (ABE) is not an indicator that can be displayed on smears. ABE is visible during extended colposcopy after exposure of the cervix to acetic acid. If there are pathological areas on it, the epithelium will begin to turn pale. Next, the doctor draws conclusions based on how quickly the whitening occurred, how bright it was, how long it lasted, whether it had boundaries, whether there was a sign of a ridge, etc. If the reaction was not pronounced, most likely women have chronic cervicitis (inflammation ), HPV or LSIL (mild dysplasia). In case of severe ABE, HSIL is diagnosed - severe dysplasia.
In appearance, the cervix, even with severe dysplasia, can be quite healthy. And only the vinegar test shows what is not visible to the eye.
Not every gynecologist is a good colposcopist. An experienced specialist monitors the cervix during extended colposcopy after treatment with vinegar and iodine, literally without taking his eyes off, and makes very accurate diagnoses. By the way, in some countries it is the vinegar test, and not the PAP test, that is a screening method for diagnosing precancer. If coarse acetic-white epithelium is detected, the woman is taken under control and treated.
Hyperplastic epithelium is usually synonymous with cervical canal polyp. Needs removal and histological examination.
Cells with signs of keratosis, keratinization - most often these words can be seen in the reports of women with suspected leukoplakia. But the same signs (features of epithelial cells) occur in precancer and cancer.
Pronounced reactive changes are an inflammatory process in the cervix.
Signs of mild dysplasia - lsil. If there are pronounced, deep changes, we are usually talking about HSIL - severe neoplasia, in which surgical intervention is necessary - conization of the cervix.
Koilocytosis is a feature of epithelial cells most characteristic of PVI (human papillomavirus, HPV). Viral infection.
Reparative changes in the epithelium are benign changes in cells, a variant of reactive changes (see above).
Degenerative changes are not cancer; they occur during a chronic or acute inflammatory process. In the same category, reactive changes include the following concepts: inflammatory atypia, squamous metaplasia, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis.
Atypia, atypical changes - dysplasia (precancer) or malignant neoplasm.
Atypical squamous epithelial cells of unknown significance - asc-us. These are cells of unknown significance. The cytologist sees that they look unusual, changed, but cannot accurately determine what was the cause - inflammation, dysplasia, infection or irritation. There is no need to be afraid of this formulation. It does not raise the doctor's suspicion of cancer. However, it is a reason to take smears from the cervix for HPV of high oncogenic risk (required types 16 and 18). And if they are detected, you need to undergo an extended colposcopy.
Proliferation of squamous epithelium - that is, proliferation or in medical terms - mitosis. Normally, this process proceeds slowly. Its purpose is to renew the upper layer of the cervical mucosa. During pregnancy, the process is more active, but normally moderate.
If, according to the results of scraping, proliferation is pronounced, then this happened for one of the following reasons:
- cervicitis (inflammatory process on the cervix);
- tissue trauma resulting from diagnostic curettage, abortion, difficult childbirth, conization;
- tumor growth - benign or malignant (cervical canal polyp, mild or severe dysplasia, cancer, papilloma).
That is, proliferation can be hyperplastic, inflammatory or post-traumatic.
Dyskaryosis is an enlargement of the cell nucleus. The cause is gynecological diseases (colpitis, cervicitis, vaginitis) or dysplasia.
Back to contents
Indications for the purpose of analysis. When necessary
The epithelium in the smear, whether normal or abnormal in women, is detected during a microscopic examination of biological material obtained during a gynecological examination. This type of diagnosis provides data on the composition of the microflora of the patient’s genitourinary system.
It is recommended to perform a smear in the following situations:
- the woman is planning a pregnancy soon;
- in the lower abdomen the girl periodically feels pain that is not related to menstrual bleeding;
- the secretion released from the genitals has changed its color, smell or consistency;
- there is a constant feeling of itching and burning in the genitals;
- the patient recently underwent a course of drug therapy, including antibiotics;
- annual preventive examination by a gynecologist.
In a healthy girl, the cells of the lining layer are practically undetectable in a smear. An active increase in the amount of epithelium in the biomaterial is observed only with the development (hidden course) of infectious or inflammatory diseases that require medical intervention.
Cytology smear
An external examination of the female genital organs, even with the help of modern technology, does not provide the same guarantee in diagnosing the disease that analyzes of biological material provide. One of them is a cytology smear, which has several names, including a smear for atypical cells.
Cytology is a science whose object of study is the cell, its composition, physiological activity and behavior
.
It is interesting that each age has its own characteristics and changes in cellular composition. The material for study is taken using a small disposable brush from the surface of the uterus. Several cells taken from a woman will tell you about the condition of the genital organs in a simple and accessible way. They take into account what size, what shape the cells are, how many there are and how they are located. The main goal is to detect atypical cells in time
in order to identify malignant tumors at an early stage. Therefore, this analysis is often called oncocytology.
You have taken a smear and within 24 hours the result will be known, which may or may not please you. After all, it is after cytology that the terrible diagnosis of cancer is made. But if you have an atrophic type of smear, what does this mean?
”
Rules for preparing for research
The process of obtaining biological material for microscopic examination itself does not involve any difficulties. However, gynecologists strongly recommend that their patients prepare for the analysis in advance, which will avoid receiving uninformative or false results.
- For 2 days before the analysis, genital hygiene is carried out with warm water, without using soap or shower gel.
- For about 3-4 days you should abstain from any type of intimacy.
- The day before the smear, douching is prohibited.
- To avoid possible changes in the composition of the microflora, 1 week before the study you should stop using vaginal suppositories, creams, gels, and lubricants.
You can take the test at any phase of the menstrual cycle, with the exception of bleeding. It is better if it is 2-3 days after the end of your period.
Tips on how to prepare for analysis
Preparation is necessary to obtain the most reliable results and eliminate diagnostic errors.
Tip #1
2 days before the procedure, it is necessary to avoid sexual contact, douching, and the use of any vaginal forms.
Tip #2
1-2 days before the study, it is not recommended to visit the pool, swim in open water, or take a bath. You can wash in the shower.
Tip #3
1-2 hours before the test, you should refrain from urinating, as urine can wash away some of the cells, which will lead to false negative results.
Technique for taking a smear. How is the analysis performed?
The epithelium in the smear, the norms of which in women are the same in different parts of the reproductive system, is determined in the urethra, vagina and cervical canal. A vaginal sample is obtained by placing a sterile swab on the affected area, or if the pathological area is not visualized, then on the posterior fornix.
The urethra (urethra) has a narrow opening, so a sterile swab placed on a thin wire or a special medical disposable loop is used to obtain a sample. The instrument is inserted to a depth of 1-2 cm, lightly pressing on the back and side walls.
Material from the cervical canal is obtained using a small brush. It is inserted to a depth of no more than 2 cm, rotated, and then carefully removed. After all the manipulations, the resulting sample is placed on a glass slide, signed and sent to the laboratory.
What is determined in a smear in men?
The analysis is deciphered by your attending physician or laboratory employee. The results form has a line in which all components of the analysis are indicated, and opposite them there may be an o or “-”. A smear from the urethra, in addition to the epithelium, determines:
- mucus in the smear - indicates urethrorrhea and urinary tract infection, such as cystitis or urethritis;
- leukocytes - the norm of leukocytes in a man's smear is 1-5, more than 5 cells, evidence of an inflammatory process - prostatitis, urethritis. If there are more than 100 leukocytes - gonorrhea or trichomoniasis, 20 to 80 leukocytes - chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis and gardnellosis;
- red blood cells - can be a sign of traumatic urethritis, tumor growths in the urethra, crystalluria, ulceration of the mucous membrane. Normally, no more than 3 red blood cells are allowed per field of view;
- key cells in the smear—gardnellosis urethritis or bacterorrhea;
- lipoid granules-prostatorrhea, chronic inflammation of the prostate, sexual dysfunction - excessive activity or prolonged abstinence;
- spermatozoa are a sign of spermatorrhea; normally these components should not be present in the smear;
- eonophils are a sign of an allergic reaction or urethritis that was caused by a specific allergen.
Based on the information received, the doctor selects a treatment regimen and selects medications that can improve the patient’s well-being and relieve inflammation, if any.
The norm of leukocytes in a smear in women
How is a man swabbed?
Analysis from the urethral canal in men is taken with a special instrument that resembles a wire with a kind of probe at the end. The instrument is inserted into the opening of the urethra several centimeters, and with two rotational movements the biomaterial that is present on the walls of the canal is collected. During these movements, the patient may feel slight pain and burning; this is a normal reaction of the body. Next, the instrument is removed, and the withdrawn liquid is applied to a glass slide and sent for microscopic examination.
After a few days, the man will still feel a burning sensation in the genital area, sometimes there is even blood in the urine, but this condition does not require medical intervention, it goes away in three to four days.
Epithelium norms
After receiving the biological material, it is sent to the laboratory, where it is examined microscopically. All results are recorded on a special form, after which they are transferred to the leading gynecologist for their interpretation and making a final diagnosis or prescribing a repeat smear.
Normally, a healthy woman should have no less than 5 and no more than 10 epithelial cells that are in the field of view. Any deviations indicate the development of the disease. In the menopausal period, an indicator that exceeds the standard values by 1-2 units is not considered pathological.
The meaning of the letters on the analysis form. Decoding the results
The norms of epithelium in a smear in women are not the only parameter that gynecologists pay attention to. A microflora study shows which representatives of beneficial, pathogenic and opportunistic organisms, as well as their number, inhabit the genitourinary system.
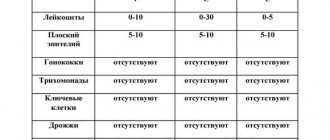
In a healthy patient, the analysis results will be identical to the indicators indicated in the table:
| Index | V | C | U |
| L | 0-10-15 | 0-30 | 0-5-10 |
| Ep or Pl.Ep | To 10 | To 10 | To 10 |
| Slime | No or moderate | No or moderate | No |
| Key cells | No | No | No |
| Gn | No | No | No |
| Trich | No | No | No |
| Other flora | A large number of gram+ Dederlein sticks | No | No |
| Candida | No | No | No |
It is clear from the table that gynecologists use abbreviations in some cases. They correspond to the first letters of the indicators being studied.
The explanation of the short parameters is as follows:
- V – vagina.
- C – cervical canal.
- U – urethra.
- L – leukocytes.
- Ep – epithelium, Pl.Ep – squamous epithelium.
- Gn – gonococci.
- Trich – Trichomonas.
If mucus is detected in the smear, this indicates that a favorable environment remains in the vagina and cervical canal. Normally, the main part of the microflora (up to 95%) consists of gram-positive Doderlein rods, which are called lactobacilli. Other microorganisms must be absent, and their presence indicates a disease.
Why do you need a cytogram and how to get tested?
The pelvic organs are made up of different types of cells, sometimes several layers. When inflammatory or other pathological processes occur, cells uncharacteristic for this area may be detected. This is one of the first signs that the disease is developing. The sooner a problem is detected, the faster and more effectively it can be eliminated with minimal negative consequences.
In order to take a cytogram, a woman must prepare. This is very important to ensure that the data obtained is as reliable as possible. The preparation is not difficult, but it must be approached as responsibly as possible. This is in the interests of the woman herself. When a gynecologist prescribes a cytogram for a woman, he informs her about how to prepare for this:
- a woman should not use hormonal contraceptives for some time before taking the test;
- within 2 days before taking the cytogram, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse, both protected and unprotected, because this will also affect the results of the analysis and their reliability;
- you can’t douche, because this will also distort the picture;
- it is undesirable for a woman to undergo gynecological examinations on a chair shortly before taking the test, because such “external interference” can also distort the results;
Severe inflammation of the vagina can also cause distortion of the results.
How is a smear taken? Samples are collected using a special gynecological “brush” in the area of the cervix and cervical canal. That is, two smears are taken, because it is in these places that vaginal epithelial cells accumulate. To do this, the doctor uses a special mirror to take samples exactly where it is required, and then applies a smear to the glass for examination.
A cytogram can help identify various diseases:
- abnormal development of the cervix;
- STI;
- inflammatory processes of the uterus and cervix;
- changes that occur in tissues after menopause;
- neoplasms in the cervix;
- cervical erosion, etc.
Of course, if you suspect the presence of one of the above diseases, additional tests and examinations will be required.
During laboratory research, cells are stained using special methods. This allows you to identify the nuclei and cytoplasm of cells. It is very important that the analysis is carried out by a qualified cytologist, and that modern techniques and equipment are used to obtain the most reliable information. Usually, when sending for a cytogram, the gynecologist indicates in his direction the disease he suspects. The cytologist, after performing the analysis, confirms the diagnosis or refutes it. But, even if the diagnosis suggested by the gynecologist was not confirmed, but the cytogram reveals other problems, the cytologist indicates this in the conclusion.
A specialist in the laboratory under a microscope studies the type of cells, examines the epithelial cells on different layers, counts their number, pays attention to the shape, shape and size of the nucleus, the clarity of the boundaries, etc. All this can provide information about the presence of a particular pathology, viral or infectious process. As a result, one of the options is indicated in the transcript for the cytogram: negative or positive. If this is a negative option, then there are no problems and everything is within normal limits. If the result is positive, this indicates the presence of abnormal cells in the epithelium, which may differ in size, shape, nuclear size or some other non-standard structural features.
Atypical epithelial cells in a smear
Atypical epithelial cells differ in structure from normal ones; they may have a different size or shape, that is, they have undergone changes. There are only two reasons for their appearance in a smear - the development of an inflammatory process or the onset of cancer. Often doctors are faced with the first problem.
It can occur as a result of infection of the genital tract or bacterial infection. Much less often, atypical cells confirm the development of a tumor process. But even this does not always indicate the development of cancer, because the human immune system is capable of destroying the altered cells from which the tumor grows.
If the results of the smear confirm the presence of atypical cells, the woman must undergo testing to determine sexually transmitted infections. In addition, a biopsy and colposcopy may be prescribed. There is no cause for concern if the form does not indicate the degree of atypia. In this case, there is only inflammation.
What additional studies are prescribed if the squamous epithelium does not correspond to the norm?
If a single squamous epithelium is detected in the smear, but there are no changes in the cervix, then the analysis is considered normal and does not require any additional examinations or studies. But there are some situations when it is necessary to carefully look at the epithelial cells in an enlarged form. This happens when there is suspicion of cervical erosion, dysplasia, or the development of cancer. In this case, colposcopy or cervical biopsy is prescribed. Such studies are carried out by a highly professional specialist, since the patient’s life may depend on the diagnosis as a result of the examination. If moderate to severe damage to the cervix is detected, treatment methods such as cauterization or removal of the affected area are prescribed.
Prevention, regular examination and examination, timely treatment of pathological processes can prolong your life for a long time. Take care of yourself and don't get sick!
What doctors don't see with microscopy?
When performing a microscopic examination of a smear, there are conditions that laboratory assistants are not able to see. It is impossible to diagnose cervical cancer. This requires cell histology. The procedure can only be performed during separate diagnostic curettage.
It is impossible to understand from the results of the study whether a woman is pregnant or not. To do this, she needs to take a blood test to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, perform an ultrasound screening of the uterine cavity (not advisable in the early stages), and also undergo a gynecological examination using speculum.
Cervical cancer, erosion, leukoplakia, koilocytosis, human papillomavirus are not determined by the presented study. They are diagnosed only after cytological analysis of the biomaterial. The smear also does not show herpes, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, HIV.
Cytogram without features: what does it mean?
This means that the number of epithelial cells, their shape, size and other characteristics are within normal limits. All this suggests that there are no problems. Although, this also cannot be a 100% guarantee that there are no problems at all. Sometimes cytology results can be distorted if an incorrect smear was taken, or the woman ignored the rules for preparing for the test.
Usually, in the case of a cytogram with signs of inflammation with reactive or degenerative changes in the epithelium, based on one analysis, a diagnosis is not made, because the disorders can be complex. For example, if it is a herpes or papilloma virus, the nucleus of the epithelial cells may be increased in size.
But such changes can also be detected with other problems. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, the gynecologist takes into account not only the results of the cytogram, but also the patient’s age, the phase of the menstrual cycle when the smear was taken, concomitant diseases, anamnesis, complaints, other symptoms and the results of a visual gynecological examination on the chair. Therefore, treatment is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis made on the basis of all the above factors.
Deviations from the norm, what they talk about
If, when receiving the results of a gynecological smear examination, the form contains significant deviations from the norm, then you need to see whether they are lower or higher. An insufficient amount of squamous epithelium indicates a hormonal imbalance, and an excessive amount indicates an inflammatory or infectious lesion.
Vaginitis
One of the common causes of deviations in a smear from the norm is a disease such as vaginitis or colpitis. It does not pose a strong threat to a woman’s health, but if not treated, the inflammatory process will spread to all pelvic organs.
This leads to the development of serious complications in the form of problems with conceiving a child and an increased risk of urinary tract infections.
Vaginitis can be caused by:
- Conditionally pathogenic representatives of the flora. They are present in small quantities in the vaginal system, but do not cause diseases, and when favorable conditions occur (reduced immunity) they begin to actively multiply. The causative agents are: streptococci, staphylococci, fungi of the genus Candida, gardnerella, E. coli.
- Infectious microorganisms. They are spread sexually and are not normally found in the body. Among the pathogens noted: chlamydia, mycoplasma, trichomonas, gonococci, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus and HPV.
Depending on the cause of the disease, specific and nonspecific vaginitis is distinguished. If we look at medical statistics, we can find out that 90% of all colpitis develops against the background of gonococcal infection entering the body or as a complication after candidiasis.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra (urethritis) is more often diagnosed in men, which is associated with the anatomical features of the structure of the organs. In women, this disease almost always occurs in combination with cystitis. If in such a state you take a bacteriological culture for flora, an additional increased content of leukocytes will be detected.
Urethritis develops against the background of other pathologies (usually with gonorrhea), when, during intimate intimacy with a carrier of the infection, the pathogen moves upward through the urethra. Herpes simplex, chlamydia and poor genital hygiene are also considered provocateurs.
Background diseases of the cervix
This category of diseases includes pathologies in which the normoplasia of the epithelium is completely preserved, while certain changes occur in the vaginal part of the cervix. The lining cells divide, differentiate and mature correctly.
The main representatives of pathologies are:
- pseudo-erosion;
- ectropion;
- polyps;
- endometriosis;
- leukoplakia;
- erythroplakia;
- papillomas;
- cervicitis;
- true erosion.
All these diseases are characterized by a benign course and cannot provoke the development of oncology. However, to preserve the reproductive abilities of the female body, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations and treatment.
Columnar epithelium
Normally, the number of columnar epithelial cells in a smear ranges from 4 to 15 per field of view. If there are fewer of them, this indicates hormonal disorders, and a complete absence indicates the development of dystrophy of the cervix or cervical canal. In this case, the woman is diagnosed with infertility.
An increased amount of columnar epithelium precedes the appearance of atypical cells and requires cytological examination and biopsy. After determining the cause of abnormalities in the smear, treatment must be prescribed.
It is often medicated and includes anti-inflammatory medications that kill the infection.
Other reasons
The main factor that provokes an increased content of epithelium in the smear, which is a deviation from the norm, is inflammatory diseases that affect the organs of the genitourinary system. This category includes: vulvitis, bartholinitis and endocervicitis.
A thorough determination of the number of leukocytes, mucus and key cells is required. It is possible that the increased cell content is a physiological norm. This is observed during menstrual bleeding, when a complete replacement of old epithelial cells with new ones occurs.
Norm
The inner surface of the uterus is covered with mucous epithelial tissue. Epithelial cells can be flat or cylindrical. If squamous epithelium is detected in a smear, one can conclude that an inflammatory disease of the reproductive system has developed.
The proliferation of columnar epithelium can have more dangerous consequences. A lot of columnar epithelium in a flora smear indicates the presence of cancer. If the epithelial cells in the smear are less than normal, then the patient is diagnosed with hormonal imbalance.
During a laboratory examination of a smear, doctors can detect from 3 to 15 epithelial cells in the visible area. Such indicators are not dangerous and are considered normal. When the epithelium increases, a diagnosis is made of urethritis, cervicitis, etc. Cells are located in the biomaterial separately from each other or in groups.
It is worth noting that failure to comply with hygiene rules on the eve of taking a smear can distort the results of the study. That is why it is very important to properly prepare for such a medical procedure.
Further diagnostic measures
After receiving a poor smear result, the interpretation of which indicates the development of an inflammatory or infectious disease, additional diagnostics are required. First of all, the woman should visit the leading gynecologist, who will re-examine.
Next, the following tests are prescribed:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) study to determine sexually transmitted infections.
- Bacteriological culture to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Ultrasound screening of the pelvic organs.
When all the tests are completed and the results are received, the patient again needs to visit the gynecologist. Often this complex is enough to make a final diagnosis and develop an individual therapeutic regimen.
Cytogram of inflammation
So what is an inflammation cytogram? This is the result of a study of multiple changes in the vaginal epithelium, which indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the cervix.
If the cytogram does not identify the causative agent of a particular disease, and the inflammation progresses, a test is necessary for the presence of other sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, gonococci, ureaplasma. If the test result is negative, culture from the cervix is performed and the isolated microorganism is treated.
Inflammation of the genital organs has a mild pain syndrome and only causes discomfort. Often they are not treated at all, the process becomes chronic, progresses and spreads to other organs. The presence of an inflammatory process in women may be a symptom of some other disease.
As inflammation progresses, so does the disease. It is impossible to identify an infection on your own and predict the consequences of inflammation. Self-medication will lead to complications. Only a specialist should determine the treatment method and make prescriptions.
Treatment of abnormalities
A deviation from the norm is the presence of epithelial cells in biological material of less than 4 units and more than 10 units in the field of view.
It is impossible to determine the underlying disease using this indicator alone, so additional examinations are always prescribed. Only after determining the reason why deviations from the norm were found in the smear will the doctor prescribe treatment.
Methods for eliminating atypical cells
If the results of the analysis revealed an increased content of atypical cells, the doctor will recommend undergoing procedures to remove them - diathermy, cryothermy and laser therapy. During the recovery period, the epithelium in the smear differs for each patient, so you need to regularly visit a gynecologist and submit biomaterial for research.
In diathermy, the mucous membrane is cauterized with electricity. If after the procedure multiple scars form on the cervix, infertility will develop.
Cryothermy is characterized by treating the epithelium with low temperatures, but treatment is effective only in unadvanced cases. Laser therapy is considered the most effective because, in addition to removing atypical cells, it allows one to examine all layers of the epithelium.
Therapeutic procedures
Treatment tactics and a set of therapeutic procedures are determined individually for each patient, depending on the cause of the increased or decreased content of epithelial cells in the smear. If the results of flora culture indicate the presence of fungal microorganisms, bacteria or parasites, vaginitis is diagnosed.
This disease can be treated with medication, by taking antibiotics or antimycotic drugs, or a combination of both. In case of hormonal imbalance, the woman is offered to undergo replacement therapy to restore it. It involves taking medications that replenish the amount of the missing hormone in the body.
When the cause of abnormalities in the epithelium in the smear is an infectious lesion, urethritis is often detected. The disease is treated with antibacterial medications in combination with analgesics. If the doctor suspects the development of an oncological process, then after additional examinations it is possible to prescribe a course of chemotherapy, radiation, and, in extreme cases, removal of the uterus.
Drugs
Prescribing medications is the competence of the leading gynecologist. The doctor, based on the diagnosis, prescribes the patient appropriate medications, their regimen, dosage and course duration. The drugs can be in the form of suppositories, tablets or ointments.
The following remedies are effective:
- Metronidazole. Tablets whose action is aimed at combating simple microbes. The average duration of treatment is 10-15 days.
- Polygynax. Capsules for vaginal administration. For the acute stage of the disease, 12 days are used, and for prevention – 6. Administration is carried out 1 time before bedtime.
- Femoston. Tablets to restore disturbed hormonal balance. They contain synthetic estrogen. The course and regimen of admission are determined individually.
- Furazolidone. A medicine from the group of antibiotics in the form of tablets. They are also used to prepare antiseptic solutions for vaginal douching.
- Enterofuril. Antimicrobial drug in tablet form. The average duration of treatment is 10-12 days.
The normal epithelium in a smear in women is 5-10 cells per field of view. If the indicator is increased or decreased, this indicates the presence of pathology, so it is necessary to undergo additional examination. If any diagnosis is confirmed, you should adhere to the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Author: Chernyshova Victoria Konstantinovna (vikyxa88-etxt)
Article design: Mila Friedan