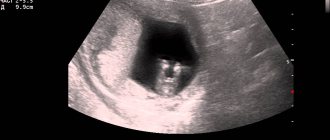
The coccyx-parietal size (CPR) is the greatest distance from the coccyx to the central point of the head (crone) of the fetus. This indicator allows you to very accurately, with an error of 1 to 4 days, determine the gestational age and date of birth. With an irregular cycle, this method will be more correct than determining the timing of pregnancy by ovulation, and with regular periods, the obtained values are usually simply compared with the obstetric period.
The shorter the gestational age, the more informative this indicator is. The embryo still has practically no limbs, but only a heart and body. Therefore, the size of the fetus allows us to assess its condition and monitor its development over time.
By measuring and tracking sizes over several weeks (dynamic study), it is possible to identify abnormalities in the baby’s development in the early stages. Doctors monitor CTE from 7 to 11 (less often 14) weeks of pregnancy, after which they use other values to monitor the baby - fetal fetometry. The ideal time to determine CTE is 11 weeks. , a routine ultrasound is usually prescribed .
Definition of the concept of CTE
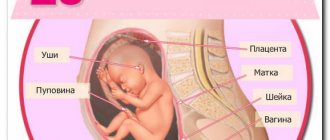
KTP - coccygeal-parietal size, this is the maximum indicator of the length of the fetus, at the greatest extension of the embryo, without taking into account the size of the limbs and the yolk sac.
A parameter that is determined at the first screening (ultrasound). The error of this indicator can be from 3 to 8 days, both up and down, in the first trimester. Further (in the 2nd and 3rd trimester), gynecologists no longer rely on this size, since during this period the error can be up to 2 weeks.
The CTE of the fetus by weeks of pregnancy can be determined already a month after conception, that is, at the 6th obstetric week. This is not so much the length of the embryo’s body, but rather an indicator that allows one to understand how viable the organism is.
Today, installing KTP is one of the most reliable methods that determines the exact duration of pregnancy, down to days.
It is practically the only one that helps assess the weight and development of the fetus in the first trimester , when other studies are either too early to conduct or they are not safe for the unborn child.
Since when is KTR no longer informative?
Starting from 13-15 weeks, data on fetal CTE is no longer informative. Other criteria for the development of the future baby become more important. From the second trimester, body parts are studied in detail, such as the length of the limb bones, the biparietal circumference of the head, the length of the nasal bone and the size of the nuchal space. Internal organs are also examined in detail, the structure of the heart and brain is assessed, and blood flow and the lumen of large vessels are checked using Doppler ultrasound.
These parameters cannot be assessed in the first trimester, since the fetus is still too small. But by week 16, the entire body is clearly visible using a sonography sensor. Therefore, after a full 15 weeks of pregnancy, CTE is no longer measured during ultrasound examinations of pregnant women.
Why is the CTE of the fetus determined by week?
Fetal CTE (measurements) are prescribed by a doctor in the first weeks of pregnancy (first screening), as a routine study, but there are cases when it is carried out earlier for medical reasons, since only this method can show abnormalities in the formation of the embryo.
It is done if:
- history of fetal growth retardation;
- congenital pathologies in previous pregnancies;
- bad heredity;
- previous pregnancy(ies) ending in miscarriage;
- history of the woman in labor, burdened by any other abnormalities;
- increased white blood cells or lack of hormones in recent blood tests.
Early in pregnancy, the ability to diagnose the general health of the fetus is limited.
The expectant mother undergoes many blood tests and this gives an understanding of the state of the internal organs and the development of the embryo as a whole, but these are only general principles, which for the most part reflect the deterioration of her organs and systems. While measuring CTE will tell you about the growth of the fetus.
The CTE of the fetus by week of pregnancy is a number that will reliably tell you about the age of the fetus and will help determine the date of conception, that is, correctly calculate the obstetric period and set the date of birth.
If a woman does not monitor her menstrual cycle, it is irregular, or she has doubts about the timing of conception, then measuring this indicator is the only and most accurate determining factor in pregnancy monitoring.
If you can find out this size at 6 weeks, you can monitor the embryo and subsequently the fetus over time and assess how correctly it is growing . Based on data on CTE, it is possible to reveal potential risks of retarded perinatal growth or genetic abnormalities (Dauna, Patois).
What CTE may require treatment?
When, on repeated measurements, there is an increase in CTE, but it is below normal (less than 1 mm per day), the doctor may assume a threat of termination of pregnancy. This can happen due to improper adaptation of the female body to bearing a fetus, under the influence of external and internal reasons, due to congenital genetic abnormalities of the embryo. The following medications may be prescribed to support pregnancy:
- gestagens to maintain the required level of the hormone progesterone;
- injections of the hCG hormone for better fetal development and preparation of the uterine cavity for gestation;
- antispasmodics to relax the muscles of the uterus;
- drugs that stimulate blood circulation and oxygen saturation of tissues.
Timely identified problems and prescription of drug therapy can normalize the course of pregnancy. Therefore, a woman should register with the antenatal clinic as soon as pregnancy is confirmed and visit her gynecologist in accordance with his recommendations.
Measurement methods
The CTE of the fetus by week of pregnancy is determined by an ultrasound diagnostic specialist, usually at 12-13 weeks of pregnancy. At the first screening, the body of the expectant mother is examined in three planes: coronal, axial and sagittal.
To find out the parameters of the coccygeal-parietal size, you should study the body of the embryo, in a fully extended state, using a sagittal scan. If the fetus is active, the ultrasound specialist waits until it is in a calm state and then takes a freeze frame.
Then the woman’s uterus is analyzed in different planes, a segment is visually measured, where the highest point is the parietal part of the head, and the lower point is the future tailbone. Measurements are carried out with a special sensor. The results obtained are compared with the standards displayed in a special table.
On average, the fetus grows by 1 mm up to the 13th week, but if growth does not occur for some period, there may be an increase in the following days.
Procedure indicators
Sometimes patients are prescribed several ultrasound procedures, during which it is necessary to pay close attention to the dynamics of changes in the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus. Since the child is in the process of growth until the very moment of birth, increasing in size by approximately 1-2 mm daily, you need to understand that comparison with established indicators is carried out literally on a daily basis.
| Term | CTE index (mm) | Term | CTE index (mm) |
| 6 weeks, 3 days | 7 | 10 weeks, 3 days | 36 |
| 7 weeks | 10 | 11 weeks | 40–41 |
| 7 weeks, 3 days | 12 | 11 weeks, 3 days | 45–46 |
| 8 weeks | 16 | 12 weeks | 52 |
| 8 weeks, 3 days | 19 | 12 weeks, 3 days | 58–59 |
| 9 weeks | 23 | 13 weeks | 66–67 |
| 9 weeks, 3 days | 26 | 13 weeks, 3 days | 73 |
| 10 weeks | 31–32 | 14 weeks | 79–80 |
It is worth noting that after a period of 14-16 weeks, there is no point in continuing to keep records of CTE, since it loses special importance at a further stage of fetal development. The emphasis is shifting towards other methods of diagnosing the child’s condition.
It is important to remember that only a qualified doctor has the right to decipher the results obtained, who, taking into account all possible subtleties, will make the right conclusion regarding the safety of the baby’s health. Lack of necessary experience among potential parents will hinder obtaining a reliable research result, which ultimately can lead to a sad outcome or unnecessary worry.
Table of norms
Data on the time from which CTE can be determined varies: some sources call the period 3 weeks, others 4. The same thing with information content at later periods: up to 13-14 weeks.
Table of fetal CTE in the 1st trimester by weeks and days of pregnancy
The table shows maximum values, so the size of the embryo should not exceed the given numbers. Until the 6th week, it is not possible to determine the minimum CTE indicators on ultrasound, or these indicators fluctuate.
These values are not influenced by individual characteristics, belonging to a particular race, or the sex of the fetus (statistically, these factors account for only 3% of cases); if strong deviations from the norm are observed, a consultation with a gynecologist is indicated.
Norms for fetal weight and height by week of pregnancy:
Why is it correct to measure CTE and not fetal growth?
The distance to the coccyx is measured, and not the full height, because the limbs of the embryo at this stage are still too small. It is impossible to correctly assess embryo growth before 8-9 obstetric weeks. In addition, the natural position for a baby in the womb is a sitting position, with its legs tucked under itself. Therefore, fetal growth is not measured at a later stage of pregnancy.
To correctly measure a child's full height, an ultrasound specialist would first have to determine the CTE, the length of the tibia and tibia, and then add all the results together. Such calculations have no diagnostic value and are impractical, because the rate of increase in CTE is directly proportional to fetal growth and quite accurately allows one to determine the embryonic gestational age.
Options for deviations from normal values
Towards lower values
What does the deviation of CTE from the norm (towards lower values) indicate?
The reasons why this happens can be divided into physiological:
- there is an error in setting the gestational age;
- hormone deficiency;
- multiple pregnancy.
And pathological:
- fetal death due to chromosomal changes;
- mental impairment in the fetus;
- viral or bacterial infection in the mother;
- neoplasms in the uterus (fibroids).
Physiological features can be eliminated. Sometimes ovulation occurs slowly - this leads to the fact that the date of the last menstruation cannot become a “starting point” for determining the exact date of conception and pregnancy.
In such a situation, the obstetrician relies on screening data and monitoring of the pregnant woman, based on the newly obtained data:
- If hormone deficiency is implied , then most often a woman’s body lacks progesterone. To identify this pathology, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination and, if such disorders are confirmed, hormone-containing medications are recommended. Such therapy can be carried out up to 30-35 weeks; the timing and dosage are prescribed and regulated only by a specialist monitoring the pregnancy.
- If the expectant mother has a multiple pregnancy , then CTE, at the initial stage, may also not meet the standards. If during an examination by a specialist and repeated examination no pathologies are identified, this suggests a similar picture.
- The fetal caloric index by week of pregnancy may not correspond to the average values. Often this reports a missed pregnancy or death. In this case, the obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes an ultrasound (10 days after the screening, which revealed abnormalities), where the uterus is scanned in different planes and the values of the yolk sac, fertilized egg, corpus luteum, as well as the heart rate of the embryo are monitored. If all other indicators correspond to the deadlines, then this pathology is excluded.
Abnormal changes are not always treatable. It should be remembered that if such deviations are noticeable at such early stages, then the risk of an unfavorable outcome is high.
- In the first trimester, slow growth of the embryo indicates genetic disorders in the mental sphere. To confirm the diagnosis and identify what exactly is wrong with the fetus, a consultation with a geneticist, determination of genetic markers, karyotyping, biochemical analysis, screening, collection of amniotic fluid and umbilical cord blood, and a DNA test are indicated. Already in the early stages, it is possible to isolate the embryo’s own red blood cells and determine what abnormalities the small organism is susceptible to. If a set of measures is carried out in full and on time, there is a chance to maintain the pregnancy or prevent the harmful consequences of a miscarriage for the woman.
- When the mother's organs are affected by infection, there is a threat of spontaneous abortion. A slow rate of fetal growth indicates a viral or infectious effect; any inflammation requires the most careful attention. The pregnant woman is examined for most known titers, including STDs, and treatment (antibacterial therapy) with the most gentle drugs is carried out immediately.
Such deviations can also result from:
- unbalanced diet of a pregnant woman;
- alcohol;
- tobacco products;
- excessive physical activity;
- exposure to chemicals.
Toward higher values
Possible reasons for deviations from the norm towards larger values:
- medication abuse;
- anatomical defects in the structure of the mother’s internal organs;
- neoplasms (especially in the reproductive system);
- acute respiratory viral infections and other infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy;
- diabetes mellitus or predisposition to it;
- hormonal defects (thyroid diseases);
- taking medications responsible for pregnancy;
- Rhesus conflict.
Due to neoplasms or congenital/acquired defects in the structure of a woman’s internal organs, the embryo may develop incorrectly. These pathologies affect not only the condition of the mother herself, but also the child, which leads to serious consequences, including the death of both.
Sometimes a pregnant woman, in pursuit of improved well-being or due to excessive worry about the health of her unborn baby, begins to uncontrolledly take multivitamins and increases the dosage of prescribed metabolic medications.
This leads to the fact that the embryo begins to actively grow. As a result, such growth can lead to the fact that the fetus becomes large (up to 4 kg) or even gigantic (more than 5 kg), which creates problems during pregnancy and childbirth, and can also lead to premature birth.
It rarely happens that the fetus is large due to individual characteristics, for example, both or one of the parents have height and/or weight above average, then the unborn child can also be large. In addition, errors in the operation of the equipment are possible, which leads to incorrect CTE indicators.
In order to exclude all these options, you should consult a gynecologist. It happens that CTE grows slowly, and it is necessary to distinguish between situations when the term is later and when the pregnant woman is 4 weeks or less.
If the fetus’s heartbeat is clearly audible, the volume of the pregnant woman’s abdomen and the fundus of the uterus are growing, but the CTE parameters do not correspond to the norm - this indicates that the embryo is growing spasmodically, then the pregnancy is observed in dynamics and there is a chance of saving it.
When all indicators do not develop and tend to decrease, then this, in most cases, indicates a frozen pregnancy.
There may be several reasons for this:
- congenital pathologies;
- Rhesus conflict pregnancy;
- undergone abortion.
If CTE grows slowly or development stops altogether, this is a pathology. When it is not possible to measure and observe other indicators on ultrasound, due to the short term or excessive activity of the fetus, a non-invasive DNA test is used. A DNA test can tell about the embryo’s predisposition to genetic pathologies or their presence.
The only disadvantage of this method is the cost, but if a woman has the opportunity and is ready for it, it is worth doing, since the earlier deviations are identified, the earlier, and therefore gentler, the treatment will be.
Rh conflict between mother and fetus is also a cause for concern , because even if previous similar pregnancies ended well (healthy children were born), then with a strong increase in the level of antibodies in the woman’s blood, this situation ends in miscarriage. In this case, the outcome will depend on the viability of the particular embryo and the degree of increase in titers.
A previous abortion also negatively affects the growth of the coccygeal-parietal size. Because of this, thinning of the endometrium occurs (it is responsible for securing the fertilized egg) and pregnancy does not develop.
It should be noted that this deficiency is dangerous as an independent deviation, but even more negative prognosis awaits a woman if a specific clinical example is aggravated by cervical erosion and ectropion (cervical inversion). Then the expectant mother is urgently hospitalized in a hospital, since only this measure helps maintain the pregnancy.
If there are any deviations from the norm, do not panic. You need to consult with an obstetrician who is managing the pregnancy , and if necessary, conduct additional screenings, blood tests and amniotic fluid tests. Only after understanding the full picture should a joint decision be made about the condition of the fetus and further actions.
If a doctor prescribes a curettage for a woman, she must decide to do so; refusal is fraught with irreversible changes, infertility and even death.
What to do in cases of deviation of the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus?
As can be seen from the table above, the numerical norms of CTE are constantly growing. If the values go beyond normal limits, then this is not a reason to panic at all: it’s just possible that a heroic baby will be born, weighing more than 4 kg. But if a woman in labor has a narrow pelvis, then she faces a cesarean section. Therefore, a pregnant woman should:
- Watch your diet. Do not eat foods that are too high in calories. But don’t go on a strict diet either;
- Avoid taking multivitamins, as well as some medications, such as Actovegin and its analogues. They help increase embryo growth
Situations when the indicator is less than expected:
- Incorrectly determined obstetric period;
- Late ovulation;
- Problems with a woman's hormonal levels. This is usually progesterone deficiency;
- Infectious diseases;
- Frozen pregnancy;
If a decrease in progesterone levels is expected, the patient is tested to determine it in the body. If confirmed, Duphaston is prescribed 2-3 times a day and Utrozhestan vaginally. These medications can be used either in tandem or separately, depending on how low the hormone is in the pregnant woman.
Infection is another way to deviate CTE. This could be detected chlamydia, etc. The gynecologist takes a smear of the flora and determines the degree of purity. Based on its results, Hexicon and Pimafucin suppositories can be prescribed. Therapy is selected very carefully due to the interesting position of the woman.
A frozen pregnancy is confirmed by ultrasound. This diagnosis will be supported by the absence of a heartbeat in the fetus.
In addition, external factors also influence the growth or underdevelopment of KTP: poor nutrition, lack of microelements, overexertion.
Causes
In any case, deviations from normal CTE values are a pathology caused by the following reasons:
- intoxication of the body of a pregnant woman (use of tobacco products and alcohol);
- diseases or neoplasms in the uterus (endometrial insufficiency, fibroids);
- hormonal deficiency (low concentration of progesterone);
- excess of metabolic drugs in the body;
- non-compliance with the diet by a pregnant woman;
- exceeding permissible physical activity;
- infectious diseases;
- Rhesus conflict;
- contact with chemical irritants;
- diabetes;
- congenital pathologies of the fetus;
- incorrect presentation of the fetus;
- sexually transmitted diseases (STIs);
- frozen pregnancy;
- abortion;
- hypoxia;
- insufficient provision of the embryo with nutrients due to impaired blood flow in the placenta;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle and, as a consequence, an error in setting the due date of pregnancy.
In addition, it is worth understanding that any specialist performing ultrasound may make a mistake when calculating the CTE or term , especially if the fetus is very active, in the process of diagnosis, or there is late ovulation, also due to inexperience.
The embryo grows spasmodically and therefore the parameters sometimes differ from each other, even if no more than 2-3 days have passed between screenings. Each individual device can give different results; they are affected by the sensitivity of the sensor and the “age of the equipment.”
The CTE indicator of the fetus is important in the growth and development of the unborn child, therefore, in order to avoid unnecessary worry, it is worth familiarizing yourself with its norms week by week, observing and drawing conclusions about the course of pregnancy, based on the results of studies only in tandem with an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist.
Author of the article: Bragonina Irina
Article design: Svetlana Ovsyanikova