When the expectant mother feels the movements of the fetus, it is wonderful: the pregnant woman knows that the baby is doing well. But it is impossible to assess the possible onset of intrauterine suffering in a child based on motor activity.
In order to detect and prevent problems in time, it is necessary to use ultrasound research methods (CTG, ultrasound and Doppler). Fetal cardiotocography (CTG) is a simple and accessible method for assessing a baby’s heartbeat, with which you can notice the initial signs of oxygen deficiency.
In addition, it is possible to identify changes in the muscle tone of a woman’s uterus, which can cause premature birth. CTG is a technique for recording uterine tone and heart rate on special calibration paper. That is, there are 2 graphs; some devices can record the child’s physical activity:
- heartbeats recorded by ultrasound
- uterine tone determined by a strain gauge
Is cardiotocography harmful to the fetus?
This is an absolutely safe procedure for both the fetus and the woman, does not cause discomfort and can be performed according to indications even daily (in case of fetal hypoxia), to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and make a decision on emergency delivery.
In what cases is CTG prescribed?
The study using cardiotocography is carried out for the purpose of early diagnosis of the pathological condition of the fetus. CTG examination is carried out starting from 28-32 weeks of pregnancy. However, to obtain high-quality and reliable results, the 32nd week is considered the best period. This period is associated with the cycle of fetal activity, when active movement is replaced by calmness. The baby is most active from 8 a.m. to 1-2 p.m. and in the evening from 8 p.m. to 12 p.m.
Indications for prescribing CTG:
- If a pregnant woman has negative Rh factor blood, there is a risk of hemolytic disease in newborn babies.
- In cases where miscarriages have previously occurred or pregnancy has been terminated artificially (abortion), also in cases of premature birth.
- When complications appear during pregnancy, for example, toxicosis is too severe, low-grade body temperature, multiple or post-term pregnancy appears.
- Various abnormalities in the development of the fetus and placenta, which were identified earlier during an ultrasound examination.
- When a pregnant woman has a history of disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, as well as systemic diseases (such as anemia, diabetes, heart and vascular diseases).
- If abnormalities are observed in fetal movements. Expectant mothers feel their baby and know his behavior. Some babies in their mother's tummy are very active and sleep for a very short period of time. And it happens when the baby sleeps during the day, and at night begins to actively move. If your baby's behavior suddenly changes, this may be a cause for concern.
- If a woman has suffered from influenza or ARVI, which had a bad effect on her general health.
- In the case where the unborn baby was previously treated for any complications. After completing the therapy, the pregnant woman is prescribed CTG for some time (from 2 to 4 weeks).
- During the manifestation of gestosis in a pregnant woman. This condition can contribute to disturbances in the blood supply to the fetus, which results in delayed development of the unborn child.
- Women who continue to drink alcohol during pregnancy and smoke. This group also includes pregnant drug addicts and those who are in remission.
- If the pregnant woman has chronic diseases.
Cardiotographic examination is carried out once, if the woman does not complain about anything. Sometimes the first study shows some pathology, then CTG is prescribed again.
Why is the assessment carried out?
The best period for carrying out the procedure is considered to be 30–32 obstetric weeks - this is due to the change in cycles of active movement of the child and calmness. Eg:
- active movements of the baby provoke the dominance of signals from the sympathetic system, which contributes to the acceleration of the heart rate;
- During sleep, impulses transmitted by the vagus nerve predominate, and the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle slows down.
These processes contribute to the formation of the so-called principle of antagonist unity - the main mechanism of the myocardial reflex. Its essence lies in the fact that the activity of the fetal heart muscle depends on its motor activity and ri. It is these factors that are taken into account to adequately assess the heart rate of the unborn baby and its intrauterine state.
With the help of one ultrasound examination, it is impossible to determine with high accuracy whether the child is receiving sufficient oxygen in the body, how he tolerates uterine contractions, and whether he can safely pass through the birth canal.
How does a CTG examination occur during pregnancy?
CTG examination of the fetus
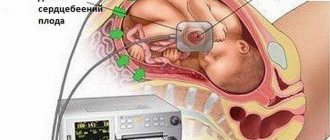
To conduct CTG, a specialized sensor with the effect of ultrasonic waves is used. This device is based on the Doppler effect. The CTG device is fixed on the stomach of a pregnant woman, in the area where the fetal heartbeat is most clearly audible. To correctly determine the area where this device will be strengthened, the obstetrician listens to the woman’s abdomen with a special obstetric stethoscope. A signal ultrasonic wave comes from the sensor, which reaches the child’s heart. After which, it, reflected from the heart, returns again to the same sensor.
The principle of operation of sensors during CTG examination
The information received as a result of this process is transformed into the results of the baby’s heart contractions in 1 minute. CTG results appear on a specialized tape using different methods: graphics, sound and light.
Cardiotocography results
If the pregnancy proceeds with complications and excellent indicators of previous methods of examining the fetus, CTG is performed about once every seven days.
CTG is not done on a full stomach. After eating food, blood sugar increases, and this affects the baby, provoking his activity and increasing sensitivity to environmental factors.
How are the final CTG indicators deciphered?
Decoding of the final CTG indicators is carried out by a specialist taking into account such data as: fetal heart rate variability, basal rhythm, acceleration, deceleration and fetal motor activity. Such indicators, at the end of the survey, are displayed on the tape and look like graphs of different shapes. So, let's take a closer look at the above indicators:
- Variability (or amplitude) refers to disturbances in the frequency and regularity of contractile movements of the rhythm and amplitude of the heart, which are based on the results of the basal rhythm. If no pathology of fetal development is observed, heart rate indicators should not be uniform, this is clearly visible through visualization by the constant change of numerical indicators on the monitor during a CTG examination. Changes within normal limits can range from 5-30 beats per minute.
- The basal rhythm refers to the average heart rate of the baby. Normal indicators are a heartbeat from 110 to 160 beats per minute when the fetus and woman are calm. If the child is actively moving, the heart rate will remain from 130 to 180 beats for one minute. Indicators of the basal rhythm within normal limits mean the absence of a hypoxic state of the fetus. In cases where the indicators are lower than normal or higher, it is believed that there is a hypoxic condition, which negatively affects the baby’s nervous system, which is in an underdeveloped state.
- Acceleration means an increased heart rate, compared to the level of basal rhythm indicators. Acceleration indicators are reproduced on the cardiotocogram in the form of teeth; the norm is two to three times in 10-20 minutes. Perhaps a slight increase in frequency up to four times in 30-40 minutes. It is considered a pathology if acceleration is completely absent over a period of 30-40 minutes.
- Deceleration is a decrease in heart rate compared to the degree of basal heart rate. Deceleration indicators take the form of dips or otherwise negative teeth. Within the normal functioning of the fetus, these indicators should be completely absent or very insignificant in depth and duration, and very rarely occur. After 20-30 minutes of CTG examination, when deceleration occurs, suspicions arise that the condition of the unborn baby is worsening. Of great concern in fetal development are the repeated and varied manifestations of deceleration throughout the examination. This may be a signal of the presence of decompensated stress in the fetus.
Carrying out non-stress and stress cardiotocography
To assess the parameters of the fetal condition, the number of movements of the baby is counted, its biophysical profile and the results of non-stress and stress tests are assessed.
The expectant mother calculates fetal movements on her own - she is given a remote control equipped with a button that must be pressed while the baby is active.
If there is a risk of developing intrauterine hypoxia, it is necessary to count fetal movements within one hour. Normally, they are recorded on CTG recordings at least 10 times in 60 minutes. The patient is warned that if the child’s motor activity decreases, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. When there is a high risk of oxygen deficiency in the mother's womb, sensitive methods are used to assess the condition of the fetus:
- Non-stress test - study of changes in fetal heart rate during its physical activity. The advantage of this technique is its non-invasiveness and short duration - the heartbeat rhythm is recorded in natural conditions.
- Stress test - assessment of changes in heart rate in response to uterine contractions caused by functional tests (oxytocin, mammary, atropine, acoustic). This technique is used in case of unsatisfactory results of non-stress CTG.
Importance of Fetal Health Indicators (FSI)
After the graphical results of the CTG study are ready, the specialist determines the value of the fetal condition indicators. For the normal development of the child, these values will be less than 1. When the PSP indicators are from one to two, this indicates that the condition of the fetus begins to deteriorate and some unfavorable changes appear.
Fetal condition indicator 4 points
When PSP indicators are above three, this means that the fetus is in critical condition. But if only such data is available, the specialist cannot make any decisions; first, the full history of the pregnancy will be considered.
You need to understand that not only pathological processes in the development of the baby can cause deviations from the norm; these can also be some conditions of the pregnant woman and the baby that do not depend on the disorders (for example, elevated temperature readings in a pregnant woman or, if the baby is in a state of sleep).
What is variability?
Variability is the amplitude of fluctuations that represent any deviations from the main line of the basal rate. In simple terms, it is the difference between the maximum (ascending) and minimum (descending) tines.
There are several main types of amplitude indicator (saltatory, slightly undulating, monotonic and undating), each of which requires a little explanation.
| Species name | Characteristic | Diagnostics |
| Monotonous | There are no drops or jumps on the line merging with the main straight line. | Fetal hypoxia, serious damage to the central nervous system, heart disease incompatible with life, etc. |
| Slightly undulating | The presence of microscopic waves almost adjacent to the main line. | |
| Undilating | Wavy. | Normal fetal development. |
| Saltatory | Similar to a discontinuous or broken line. |
In addition to the parameter under consideration, the cardiotocogram may contain additional indicators: STV (or short-temp variation) and LTV (or long-term variation) - short-term and long-term variability. They are decrypted only using special automated systems.
What CTG scores are considered normal when performing CTG, and is it considered a pathology?
The results of cardiotocography are assessed using a special Fisher point scale - assigning 0-2 points to each of the above indicators. Then the scores are summed up and a general conclusion is made about the presence or absence of pathological changes in the fetus. A CTG result from 1 to 5 points indicates an unfavorable prognosis - the development of hypoxia in the fetus, a 6 point value may indicate incipient oxygen deficiency.
What does a CTG score of 7 points mean in the conclusion?
CTG 7 points - this score is considered an indicator of the onset of fetal oxygen deficiency. In this condition, the specialist prescribes appropriate treatment to avoid the occurrence of hypoxia, as well as to improve the baby’s condition if it is present. With a score of 7 points at week 32, treatment measures begin without delay. The doctor who monitors the course of pregnancy can urgently send the woman to hospital treatment or limit herself to IV drips at the day hospital.
During the lighter stage of oxygen starvation, one gets by with more frequent and longer stays in the fresh air, weather permitting. Or taking medications to prevent this condition.
Even if, after deciphering the CTG examination, the specialist determines a result of 7 points, which is an alarming sign, you should not panic, because modern medicine can help the future baby get rid of this condition.
If pathological processes are identified in the baby’s cardiovascular system, which are a reaction to uterine contractions, it is necessary to urgently consult a gynecologist with the results of the study. After assessing the results, the specialist will be able to prescribe competent treatment, as well as send you for a second CTG examination.
CTG assessment value 8 points
Many expectant mothers are interested in the question of the 8-point CTG value, are these indicators a cause for concern? CTG 8 points shows the lower limit of normal, and this condition of the fetus usually does not require either treatment or hospitalization.
What is the significance of grades of 9 and 10?
Normal values are considered to be 9 and 10 points. These indicators can mean one thing: the development of the fetus is going well, without the development of pathologies. A score of 10 points indicates that the condition of the unborn baby is within normal limits.
Fetal CTG: interpretation of results. Fisher scale | please
There are some methods of ultrasound diagnostics of the condition of the fetus in expectant mothers, which are considered absolutely harmless to the baby.
One of these methods is cardiotocography ( CTG) during pregnancy; the norm or deviation from it according to individual indicators of this diagnostic method can be detected on various scales.
Based on the results obtained, the issue of the condition of the fetus can be considered and pregnancy management can be adjusted if necessary.
CTG is not a mandatory procedure, so the doctor may not refer the expectant mother for this test at all, but if any concerns arise, the procedure must be performed several times.
Features of the CTG procedure
This diagnostic method is used in the third trimester of pregnancy, usually from 32 weeks. Some doctors prescribe this test at 28 weeks, but the criteria for diagnosis are considered reliable from 32 weeks, since by this time the fetus’s activity-rest cycle has stabilized.
Fetal CTG is used to assess the condition of the unborn child during natural physical activity. If the baby does not show any signs of symptoms or is sleeping at all, most likely the procedure will be rescheduled or performed again - there is nothing threatening in this. Since the method is absolutely harmless to the child, it can be performed an infinite number of times.
If we consider the question in what cases or when is CTG performed during pregnancy , then this usually occurs in the following conditions:
- pathology of the placenta detected on ultrasound,
- suspicion of fetal growth retardation,
- uterine scar,
- possibility of premature birth,
- gestosis,
- post-term pregnancy,
- decreased fetal activity,
- concomitant chronic diseases in a pregnant woman,
- decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid or increase in the amount of amniotic fluid,
- abnormalities in the previous CTG,
- entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord detected on ultrasound.
There is no special preparation before the procedure. However, every woman wants to be prepared for what awaits her. If a CTG is prescribed during pregnancy, common sense will tell everyone how to prepare for it.
Since the study takes about 40-60 minutes, you should prepare yourself for a long time: take a light snack (apple, bread, chocolate), a blanket and a pillow for comfort.
Be sure to go to the toilet before the procedure, otherwise you will have to endure it for a long time, and the results will be unreliable.
The expectant mother will be placed on a couch or in a comfortable chair (you need to be in a reclining state or lying on your side, you cannot lie on your back), a sensor will be attached to your stomach, the information from which will go to the electronic unit. The doctor receives and studies all the data that is reflected on the curve. After the examination, the doctor writes a conclusion, which is given to the pregnant woman.
Fetal CTG results: interpretation
The most important issue of this method remains deciphering fetal CTG . There are several scales, the most popular are the 10-point Fisher scale and the 12-point Krebs scale. Typically, indicators are assessed on both scales and two ratings are written in the conclusion. It is worth considering that the data should not diverge on different scales by more than three points.
Below we will dwell in more detail on the Fisher scale. After performing a CTG, the results are deciphered according to the following parameters, which are individually scored from 0 to 2 points:
1. Basal rhythm (the average between the values of the fetal heartbeat, which does not change for 10 minutes or longer):
- less than 100 or more than 180 beats per minute – 0 points,
- from 100 to 119 beats per minute and from 161 to 180 beats per minute – 1 point,
- from 120 to 160 beats per minute – 2 points.
2. Variability (amplitude):
- less than 3 beats per minute – 0 points,
- from 3 to 5 beats per minute – 1 point,
- from 6 to 25 beats per minute – 2 points.
3. Variability (frequency per minute):
- less than 3 – 0 points,
- from 3 to 5 – 1 point,
- more than 6 – 2 points.
4. Acceleration (an increase in the fetal heart rate by 15-20 beats per minute relative to the base rate, occurring in response to fetal movement, umbilical cord compression, uterine contraction) in 30 minutes:
- 0 (absence) – 0 points,
- 1-4 (periodic) – 1 point,
- from 5 and above (sporadic) – 2 points.
5. Decelerations (decrease in heart rate in response to movement or contraction of the uterus) in 30 minutes:
- severe atypical decelerations – 0 points,
- mild to moderate decelerations – 1 point,
- absence or short shallow decelerations – 2 points.
To avoid subjectivity when deciphering fetal CTG data, in the modern world of medicine they are trying to create devices and computer programs that automate the decoding process as much as possible.
Normally, CTG during pregnancy according to the Fisher scale ranges from 8 to 10 points. A result of 6-7 points is considered pre-pathological, and doctors will most likely order a re-examination. If the CTG results are less than 6 points, this most likely means intrauterine fetal hypoxia and requires immediate hospitalization or urgent delivery.
Fetal health indicator (FSI)
Based on the results of the graph obtained from CTG, doctors find the value of PSP (indicators of the condition of the fetus), which during normal development is less than 1. If these values are in the range from 1 to 2, this may indicate the onset of abnormalities in the fetus. If the PSP value is greater than 3, this indicates a critical condition of the fetus.
However, no decisions are made based on these data alone; the entire history of the pregnancy is considered.
The reasons for deviations in indicators can be not only problems in the development of the fetus (heart failure, anemia, hypoxia), but also some conditions in the expectant mother and child that are not associated with disorders (increased temperature in a pregnant woman, sleep phase in a child).
It is worth noting that the CTG method is auxiliary or additional, therefore its results are relied upon only in conjunction with other diagnostic data. This mainly affects small deviations from the norm, so there is no need to sound the alarm in the event of diagnosing results different from the norm before talking and discussing the results with a gynecologist.
Source: https://BudLaska.ru/beremennost/ktg-ploda-rasshifrovka-rezultatov-shkala-fishera