Hormones
05/21/201801/24/2019 Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova) 1538 Views hormonal studies, TSH
The test results show elevated TSH, what does this mean in women and how to treat it? Now we'll tell you everything.
High thyrotropin levels are a sign of pituitary or thyroid dysfunction. When establishing the causes of a pathological condition, special attention should be paid to the correct preparation of the patient for the donation of biomaterial.
It is possible to obtain false positive results due to taking medications, emotional or physical fatigue, as well as the wrong time of blood collection. In case of overestimated or underestimated TSH results, excluding the above factors, the doctor determines additional diagnostic methods.
You should understand the main reasons for exceeding the permissible norm of thyroid-stimulating hormone and how to lower TSH in women to normal.
- 1 What is the TSH hormone and why is it needed?
- 2 What is the normal TSH level, and what does it affect?
- 3 Symptoms of elevated TSH
- 4 Causes and consequences of elevated TSH in women
- 5 Why is thyroid-stimulating hormone elevated? Pathological causes
- 6 Consequences
- 7 How to reduce TSH without hormones using folk remedies?
- 8 Diet for elevated TSH
What is TSH in a blood test?
TSH, in its chemical structure, is a representative of the family of glycoprotein hormones and belongs to the group of protein-peptide compounds. For its role in the body it is called regulating. Synthesized by the pituitary gland. Its full name is thyroid-stimulating hormone. Synonyms thyrotropin, thyrotropin are also used. Stimulates the thyroid gland. Determines the content of the main thyroid hormones in the blood: thyroxine (T4), converted into a more active form - triiodothyronine (T3).
In the functioning of the pituitary gland, there is a phenomenon of interaction between TSH, T4, T3, and the feedback principle operates. It is expressed as follows: if the level of T4 decreases even slightly, the pituitary gland immediately reacts to this with a multiple increase in TSH in the blood. It, in turn, activates the thyroid gland, causing it to increase the production of vital thyroxine.
If the thyroid gland releases a lot of thyroxine, and its concentration exceeds the norm, then the excess is suppressed by inhibiting the release of TSH. Suppression of synthesis is carried out by the action of the isolated thyrotropin on the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Based on this interconnected production mechanism, based on the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in a blood test, diagnosticians and endocrinology specialists:
- judge the functional activity of the thyroid gland;
- study the production of hormones, the body’s needs for thyroxine;
- assess the quality of compensation for the condition caused by persistent hormone deficiency (primary hypothyroidism);
- determine the hormonal background of a woman - without TSH, a diagnostic examination for hormones will not be complete;
- develop diagnostic and treatment tactics;
- monitor the effectiveness of treatment
How to stabilize TSH
So, the TSH blood test is elevated, what does this mean and what to do in such a situation. For starters, don't panic. Therapy is prescribed only by a doctor who will first conduct an examination and identify the exact cause of the increase in TSH in women. If the etiology is associated with pathological processes in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, then drug correction of the activity of these organs is carried out. For tumor formations, surgical removal is indicated.
Most often, the causes of elevated TSH in women are due to thyroid pathologies, therefore therapy is prescribed in accordance with the severity of the disorders. How to lower TSH in women:
- If TSH levels are slightly elevated in women, women are usually prescribed a corrective diet, reduced physical activity, and discontinued taking certain medications (estrogens);
- If the indicators are very high, then a serious deficiency of T4 and T3 hormones develops in the body, i.e. hypothyroidism is diagnosed;
- If the deviations of hormonal substances are critical, then hormone replacement therapy is prescribed;
- Usually, when there is a significant decrease in thyroxine and T3, analogues of thyroid hormones of synthetic origin, such as L-thyroxine, are prescribed. The woman will have to take these drugs for the rest of her life.
In addition to using medications, a woman needs to eliminate unhealthy habits, stop smoking and minimize alcohol consumption. If TSH levels are elevated, you need to take certain medications with caution. The selection of the drug and calculation of the dosage in this case is vital. Therefore, the independent use of any drugs can pose a threat to health; it is better to entrust the issue of prescribing medications to qualified doctors of the appropriate profile.
It is unacceptable to use herbal tinctures or any preparations in treatment. There are no plants in nature that contain T4 or T3, and therefore it will not be possible to compensate for their deficiency using folk remedies. However, in addition to basic therapy, you can use some home techniques.
Folk remedies
Are there ways to lower TSH using folk remedies? There are herbs that can normalize the content of thyroid-stimulating hormone. These include St. John's wort or parsley, rose hips and chamomile inflorescences, celandine, etc. These components are available for sale in pharmacies. You need to prepare infusions from them and take them half an hour before meals. Every month it is recommended to change the decoctions, alternating them with each other.
Beetroot juice is also useful for normalizing thyroid-stimulating hormone in women. You need to take a raw root vegetable and grate it. You should squeeze the juice out of the mass; you will need 100 ml. Add 0.2 liters of good quality vodka to the juice, mix well and put it in a dark place to infuse for two days. The resulting medicine should be taken three times a day, 25-30 ml, with water. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
These funds will be a good help to the main hormone therapy prescribed by the endocrinologist. In addition, you should follow certain dietary recommendations that will help quickly bring your thyroid-stimulating hormone levels back to normal. These include eating fatty fish, algae and coconut oil, sauerkraut and bone broths, fiber-rich cereals, etc. It is recommended to exclude broccoli and radishes, milk and fresh cabbage, foods with gluten and sugar from the diet.
Functions of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the female body
The first thing that elevated TSH means is a low concentration of triiodothyronine and thyroxine in the bloodstream. The role of thyroid-stimulating hormone is to ensure an increase in the production of T4 by the gland, which is achieved through its effect on receptors that are located on the membrane of the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. The result of this effect is an increase in iodine consumption by thyrocytes (thyroid cells), which trigger the process of synthesis and secretion of the most important regulators of differentiation of tissues, organs and systems - the hormone T4 (about 80%) and the more powerful T3 (about 20%). The effect appears within 1-2 minutes. Regulation of the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones is the main, but not the only task of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
In a woman’s body, it is also responsible for:
- quantitative change in phospholipids, nucleic acids;
- lipolytic effect (lipolysis) – enhances the breakdown of fat molecules into glycerol and fatty acids;
- production of proteins, support of energy balance;
- maintaining the normal structure of the thyroid gland (when TSH is increased, the size of the woman’s thyroid gland also changes - tissue growth, an increase in volume and a change in the contours of the thyroid gland are observed, which can be identified visually or determined by touch);
- an increase in the number and size of hormone-producing cells;
- sensitivity of hormonal receptors - prepares tissues for the action of triiodothyronine and thyroxine.
What diseases cause an increase in the hormone TSH?
TSH levels increase with hypofunction of the thyroid gland. An increase in TSH levels can be observed in the following cases:
- Secondary or primary hypothyroidism (most common cause).
- The presence of a tumor in the pituitary gland such as thyrotropinoma or basophilic adenoma.
- Preeclampsia during pregnancy.
- For some mental disorders.
- After acute lead poisoning.
- When Hashimoto's thyroiditis occurs.
- With syndrome of unregulated thyrotropin secretion.
- In acute adrenal insufficiency.
- Tumors in the lungs that secrete thyrotropin.
Indications for testing are the presence of specific symptoms that may indicate a dysfunction of the thyroid gland. Also, for the purpose of thorough diagnosis, a test for antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors (TSHR) is prescribed. Antibodies to the TSH receptor detect the presence of autoimmune disorders.
Sometimes there is a syndrome of euthyroid pathology, in which thyrotropin levels are increased, but only slightly, against the background of normal T3 and free T4.
Features of thyroid-stimulating hormone
When trying to independently determine what to do if the TSH test is elevated, you should take into account the normal daily variability of its level. The range of physiological fluctuations in values can be 1-3 mU/l. The highest concentration is observed late at night - at 2-4 o'clock. Then a slight decrease occurs. Thyrotropin is secreted in a pulsating manner.
The highest concentration is also observed at 6 am, and the lowest - in the period of time preceding the evening (17-19 hours). If a woman’s standard sleep-wake pattern is disrupted, the rhythm of secretion changes and a shift occurs to a later date. The circadian rhythm normally persists in old age and during pregnancy.
Individual variability (variability) of indicators, due to the use of different methods and test systems by laboratories, is of clinical importance. When interpreting the result of the study, it is important to exclude the influence of drugs that can increase the concentration of thyrotropin.
Causes and consequences of elevated TSH in women
Daily fluctuations in the hormone content in human blood have been noted. The maximum elevated level of thyrotropin in men and women is recorded between 2 and 4 am. Then there is a slight decline, which persists until 8-9 am.
Therefore, if the results of the analysis in patients indicate that the thyroid-stimulating hormone is higher than normal, then you should first remember what time the biomaterial was submitted for analysis. And if these increases are insignificant and the blood was donated before 9 am, then it is recommended to retake the test. It should be noted that the minimum amount of the hormone is typical for 17 - 19 hours.
What factors affect TSH levels?
High levels of the hormone TSH – this may be due to:
- long-term iodine deficiency, defects in its absorption;
- intense physical activity, prolonged training on an exercise bike (overload can provoke a 4-fold increase in concentration);
- taking radioactive iodine;
- lead poisoning;
- use of medications, hormone therapy;
- medical actions - thyroid surgery, gallbladder removal, ECT, blood purification;
- hypocorticism;
- diseases associated with aging women, gynecological problems;
- absence of menstruation (from 6 months) in a woman of reproductive age;
- to give up smoking;
- psycho-emotional overload.
The age of a woman does not have a significant effect on thyrotropin levels - it increases slightly, and concentration peaks at night become less pronounced.
Causes of low thyrotropin
If the TSH hormone test shows a low result, this may indicate the following diseases:
- Diffuse toxic goiter.
- Severe exhaustion of the body.
- TSH-independent thyrotoxicosis.
- Thyrotoxic adenoma.
- Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis with symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
- Some mental disorders.
To clarify the diagnosis, you also need to take additional blood tests, including AT to TSH receptors, to exclude Graves' disease.
Reference range for women
This term is the most correct and correct. It replaced the concept of “TSH norm”, which cannot fully reflect all the results. Clearly defining the norm when it is necessary to take into account the influence of many factors (gender, age, race, weight, previous diseases, health status, etc.) is not an easy task. In healthy women, the content of thyrotropin varies widely.
Compared to men, women have higher TSH concentrations (approximately 20%). Some laboratories accept the range of 0.4-5.0 mIU/l as normal (this is the same as the unit of measurement mU/l), other clinics consider values in the range of 0.3-4.5 normal. In a situation where the analysis form says, for example, “TSH 4.8,” you should focus on the normal parameters that were determined and approved by the specific laboratory that conducted the blood test.
It is important to know, according to the latest data, patients whose TSH concentration in the analysis goes beyond the values of 2.5-3 are considered to be at an early stage of hypothyroidism (mild form). Such women are recommended to undergo repeated tests, because even at relatively low concentrations, various dysfunctions of the endocrine gland can manifest themselves.
Thyrotropin during pregnancy
Most often, TSH norms differ in women by age, but their parameters are also accepted for women carrying a child.
| Trimester of pregnancy | TSH level in µmol/l |
| I trimester | 0,1- 0,4 |
| II trimester | 0,3 – 2,8 |
| III trimester | 0,4- 3,5 |
During this period of a woman’s life, the amount of TSH is determined by the fact that up to a certain point it is the mother’s body that provides the fetus with all the necessary substances. From conception to the age of 12-13 weeks, thyrotropin is involved in the regulation of the formation of the baby’s internal organs and their development.
Starting from 15-16 weeks, the level of thyrotropin gradually increases.
It should be taken into account that the concentration of TSH in women bearing a child is important precisely in the first trimester, when the fetus is just forming, and a lack or excess of pituitary gland derivatives can cause congenital malformations.
Decoding indicators
According to the study, the concentration of the substance may meet the standards, exceed them, or be lower. All standards are relative, and in each laboratory they may differ slightly, so when deciphering, the specialist always adheres to the parameters specified in the research form.
It should be noted that the level of the hormone TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) - this is the name of the substance in Latin, can fluctuate in women depending on the time of day, and in order for the result of the study to reflect the true picture of the state of health, it should be taken again to study dynamics in the same laboratory and at approximately the same time of day.
High TSH - what does it mean?
Elevated TSH in women does not always require treatment. It is possible to diagnose a pathological process only after excluding the influence of temporary and random factors. The level of serum free T4 is also taken into account. Treatment is prescribed for elevated TSH in combination with low (suspect hypothyroidism in a woman) or high (check for hyperthyroidism) concentration of thyroxine and/or triiodothyronine.
If the level of free T4 is normal, the functions of the thyroid gland are not impaired, then repeated tests are carried out at certain intervals, incl. using other test systems.
Deviations in the TSH level to a greater extent are detected quite rarely - only in 8% of patients (men and women) the indicator exceeds the normal value of 2.5-3 mU/l. Among patients with hypothyroidism, only 24% have levels of 10 mU/L or higher. This is a pathological increase.
Such high values occur in women with serious ailments:
- a malignant tumor that arises in the cells of the thyroid gland;
- congenital anomalies of the thyroid gland;
- tumor proliferation of pituitary cells (TSH-secreting adenoma);
- hormone-secreting neoplasms (in lung tissue, glandular tissue of the mammary gland);
- hereditary insensitivity to thyroid hormones;
- severe somatic pathology in the recovery stage;
- inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland – autoimmune or subacute thyroiditis.
If the upper limit of the “norm” is not exceeded to this level, the TSH indicator is 7.5, a little less or more within the range of 5-10 mU/d - what to do in this case? You should immediately consult a doctor - only a qualified endocrinologist can find the cause of the deviation and make a diagnosis. To confirm or exclude pathology, a number of diagnostic measures will be required.
TSH - what is it and what are the norms?
TSH is the abbreviation used for a blood test for thyroid hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) is synthesized in the pituitary gland. Why is a TSH test prescribed when thyroid disease is suspected? It's simple: thyroid-stimulating hormone regulates the level of T3 (interpretation: triiodothyronine) and T4 (full name: thyroxine), synthesized in the thyroid gland.
If these active substances are not produced enough, for example, with hypothyroidism, the pituitary gland increases the production of TSH. Thyrotropin “stimulates” the thyroid gland for active synthesis of hormones. If the level of T3 and T4 in the blood is too high (thyrotoxicosis, diffuse goiter), then the pituitary gland, inhibiting the synthesis of TSH, “removes” the thyroid-stimulating factor.
A clear relationship - thyrotropin is increased, T3-T4 is decreased and vice versa - is recorded only in the absence of pathology of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. These two glands, located in the brain, act as the main “controllers” of the thyroid gland.
The level of thyrotropin is maximum in newborns (1.1-17.0) and gradually decreases until 14 years of age. From this age, in women, the normal TSH level varies between 0.4-4.0 mU/l. The value of thyrotropin, even in a healthy woman, changes during the day, so it is recommended to take a test for the hormone in the morning, on an empty stomach. The day before donating blood, it is recommended to give up fatty foods, alcohol, and even take vitamin complexes. If the patient receives hormone replacement therapy, the course is usually interrupted within 2 weeks. before taking the test as directed by your doctor.
Important! A woman can take a TSH test on any day of the menstrual cycle. The phase of the menstrual cycle does not affect the level of thyrotropin.
Slightly elevated TSH of the thyroid gland, inconsistent over time, is not considered a pathology. This condition can occur after heavy physical activity or is triggered by taking anticonvulsant medications. However, a single case of deviation is not accompanied by organic disorders of the thyroid gland. A temporary increase in TSH is not accompanied by abnormalities recorded on ultrasound.
TSH and pregnancy
It is recommended for women to check their TSH level at the stage of planning a child. The functions of the thyroid gland are closely related to the activity of the reproductive system. For women who want to become a mother, the optimal value is in the range of 0.2-2.5 mIU/l. If the TSH value in women exceeds this figure and is at the upper limit of normal, then treatment may be required. It is prescribed by a doctor based on the results of a complete examination. To correct hormonal balance, patients may be advised to take synthetic thyroxine preparations.
If pregnancy has occurred, then it is especially important to monitor the condition of the endocrine glands. Tests are taken throughout the entire period of pregnancy, as well as after childbirth. After conception, hormonal changes begin in a woman’s body, which is expressed by an increase in the secretion of thyroid hormones and a decrease in TSH levels (when twins or triplets are expected, the TSH level tends to zero). In the middle or end of the term, the indicator may return to normal values.
If these physiological mechanisms are disrupted and thyrotropin concentrations remain high in the first trimester, then urgent action will be required to avoid adverse consequences. What to do if a pregnant woman has elevated TSH: a treatment plan is drawn up in accordance with the established diagnosis. Drug therapy usually includes drugs containing levothyroxine sodium as the active substance.
Signs of increased hormone levels
Changes in thyrotropin concentration in the first days occur without obvious symptoms. The woman has no complaints, her condition is satisfactory. With a prolonged increase in TSH, the concentration of thyroxine and triiodothyronine decreases.
In this case, the following clinical signs appear:
- performance decreases, general well-being worsens, weakness appears in the body;
- it is difficult for a woman to concentrate, memory deteriorates, and the thought process slows down;
- sleep disturbance leads to increased irritability;
- apathy towards the outside world periodically appears;
- Appetite worsens, sometimes disappears completely;
- the functioning of the digestive system is disrupted, nausea, vomiting, and constipation occur.
During the examination, the endocrinologist notes noticeable pathological changes:
- the skin swells all over the body;
- body weight increases, the likelihood of obesity is high;
- body temperature is constantly low;
- the skin becomes pale.
When clinical signs appear, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner to determine the cause of the pathological changes and establish an accurate diagnosis. Correctly selected treatment increases the chances of a full recovery without serious complications.
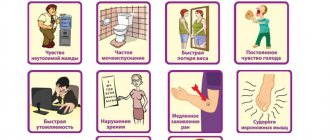
Symptoms of elevated TSH
In most cases, the development of the pathological process can be recognized by characteristic signs. High thyrotropin makes itself felt:
- lack of vigor and energy;
- rapid fatigue;
- excessive sleepiness;
- deterioration of memory, intelligence;
- weight gain due to poor appetite;
- obsessive feeling of cold;
- swelling;
- sensation of crawling goosebumps;
- dry skin;
- deepening of a woman's voice;
- brittleness, splitting of nails;
- deterioration of hair condition, excessive hair loss.
The following symptoms will indicate that a woman has elevated TSH and T4 at the same time:
- noticeable enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- increased heat generation, sweating;
- eating large amounts of food, but experiencing weight loss;
- disorder of the myocardium, vascular system, high pulse;
- vomiting, diarrhea, discomfort in the abdomen, solar plexus;
- thinning hair, premature appearance of gray hair;
- irritability, anxiety, instability of attention;
- menstrual irregularities;
- decreased muscle tone, general weakness.
Main symptoms
Elevated TSH is the main clinical sign of hypothyroidism, a syndrome caused by a lack of thyroid hormones, which manifests itself as a complex of symptoms in the form of disruptions in the functioning of all body systems.
| System | Symptoms |
| Reproductive | Decreased fertility, disruption of the menstrual cycle, absence of critical days (amenorrhea) or prolonged uterine bleeding, polycystic ovary syndrome, infertility, early miscarriage |
| Cardiovascular | Bradycardia (heart rhythm disturbance), decreased heart rate, blood pressure (less than 60 beats/min), thickening of the heart muscle in the left ventricle, changes in the normal height of the teeth in the cardiogram, increased atherogenicity coefficient, formation of blood clots in the vessels. Cold hands and feet, indicating poor circulation |
| Nervous | Deterioration of memory, attention and performance, tendency to depression, drowsiness and slowness, weakness of reflexes, hearing impairment. Sleep disorders manifest as insomnia at night and feeling tired during the day |
| Digestive | Constipation, deterioration of intestinal motility, nausea, development of biliary dyskinesia, lack of appetite |
| Urinary | Decreased filtration and absorption of fluid, which causes swelling of the face and extremities |
| Musculoskeletal | Muscle weakness, retardation of movements, cramps, fatigue, swelling of the knee joints |
| Endocrine | Enlarged thyroid gland, periodic dryness and sore throat |
| Skin covering | Dry and yellow skin, hair loss, brittleness and dryness, splitting of nails, reduction in eyebrow length. Hyperkeratosis (darkening) of the epidermis in the elbows, knees, armpits |
When is the test ordered?
A local physician, general practitioner, gynecologist, or endocrinologist can issue a referral for a blood test.
The indication is:
- detection of alarming symptoms;
- suspicion of deterioration in the functional state of the gland or cancer;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
In clinically asymptomatic women, hormonal blood tests to detect the disease are recommended every 5 years after reaching 35 years of age. Patients diagnosed with hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism - congenital or acquired - are examined annually throughout their lives.
Functions of TSH
TSH is produced by the pituitary gland to control the functioning of the thyroid gland. Entering the thyroid follicles from the blood, thyroid-stimulating hormone affects thyrocytes (cells) as follows:
- activates glucose absorption;
- increases oxygen absorption;
- affects the rate of protein synthesis;
- stimulates the absorption of fatty acids from the blood;
- activates the transport processes of iodine ions;
- increases the rate of iodization of thyroglobulin (precursor of T4);
- promotes the rapid release of thyroxine and triiodothyronine from thyrocytes into the bloodstream.
Also, under the influence of thyrotropin, the thyroid gland grows and increases blood circulation.
As a result of the influence of TSH, intense release of T3 and T4 occurs. At the same time, if there is a sufficient amount of thyroid hormones in the general bloodstream, then the production of TSH decreases.
Donating blood for TSH hormone
This is a laboratory test. Conducted in standard mode. It involves examining biomaterial taken from the patient using specialized equipment. Each medical laboratory has its own methodology, equipment, reagents, rating scales, which causes some discrepancies in measurement results. This is important to consider when visiting different clinics.
Repeated annual checks are recommended to be done in the same institution and at the same time, because daily and seasonal fluctuations in thyrotropin levels are possible. Its concentration in the blood can be determined as part of a separate study or as part of a set of tests. In laboratory diagnostics, chemiluminescent immunoassay is used to determine TSH.
Material for research
The biomaterial is blood serum. Hemolysis and lipemia may affect the test result. A woman's blood sample is obtained from a vein (forearm, cubital fossa). When drawing blood, the patient sits or lies. Venous blood collection is the simplest invasive procedure. The laboratory technician treats the injection site with a disinfectant. A tourniquet is applied to restrict blood circulation.
How do you prepare for the procedure?
It is advisable to collect blood in the morning.
Preparatory activities include:
- Exception on the eve of the examination of physical procedures and other methods of examination - X-ray, X-ray fluorography, ultrasound.
- Refusal to use hormone-containing drugs (7 days before) and medications containing iodine (3 days before). The exact timing of abstinence and the names of medications must be agreed upon with your doctor in advance.
- Avoiding alcohol consumption, stressful situations, overheating, hypothermia, minimizing emotional stress, physical activity (1 day).
- Limiting fatty foods, fried foods, not exercising (1 day).
- Elimination of any food before the session, pure non-carbonated water is allowed (the procedure is carried out on an empty stomach).
- Abstinence from smoking, keeping calm (1 hour).
Period of execution
The urgency of the analysis depends on the specific laboratory and its capabilities. After collecting the material, the study can be carried out independently or samples can be sent for analysis to another institution. In most cases, the result in the form of a special table on a laboratory form (indicating reference values) can be obtained on the same or the next day. By agreement with the contractor, the result can be sent by email.
How to decrypt
Specialists from a medical institution help to correctly interpret the final result, but for a more accurate interpretation, you will need to consult with the attending physician, who has all the necessary information about the internal picture of the disease, the woman’s health status, her physiological characteristics, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
How to bring the hormone back to normal?
Treatment for elevated thyrotropin is prescribed by an endocrinologist after a thorough medical examination and based on the diagnosis. In most cases, the cause is impaired functioning of the thyroid gland.
Considering the degree of damage by pathological processes, patients are prescribed special medications to adjust the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. If there are no serious contraindications, the use of folk remedies is allowed. It is also important to adhere to dietary nutrition and change your lifestyle.
Drug treatment
Elevated TSH in women (an endocrinologist will help determine the causes) is restored with the help of replacement medications:
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| "Levothyroxine" | The adult dosage ranges from 12.5 to 25 mcg per day. The medicine is taken 30 minutes before meals. |
|
| "Thyreotom" | Adults are recommended to start treatment with 1 tablet. Every 2-4 weeks the dosage is increased by 1 tablet. The medicine is taken for a long time 30 minutes before meals. |
|
| "Bagotirox" | The drug is taken in the morning before meals, 30 minutes, 1 tablet. |
|
In rare situations, in the absence of positive dynamics after using medications, the patient is offered surgical intervention.
ethnoscience
There are numerous recipes from healers and healers that affect the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. But the use of traditional medicine should be discussed with an endocrinologist.
The following recipes help restore the concentration of thyrotropin:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Herbal collection | Mix parsley, cocklebur and agrimony flowers in equal proportions. Pour 1 tbsp. from the resulting collection with hot water (200 ml). Place the resulting mass in a water bath and heat for 10-15 minutes. Cool and strain thoroughly. | Before use, the decoction should be diluted with liquid. It is recommended to take the medicine 1 tbsp. 3 r. per day. The course of therapy lasts 2-3 weeks. |
| Beet juice tincture | Mix fresh nectar (100 ml) with vodka (200 ml) and leave for 2 days. | The tincture is taken 20-30 ml 3 times a day. per day, washed down with water. The course of treatment is 14 days. |
| Herbal decoction | Mix equal amounts of chamomile, yarrow, mordovnik root, rose hips and chicory. Pour 1 tbsp. hot water, leave and strain. | It is recommended to drink the medicine 3 times a day. per day. |
Elevated TSH in women can also be reduced by tea with dandelion, chamomile, rose hips, St. John's wort or celandine. Therapy is carried out comprehensively; folk recipes alone will not help restore the functioning of the thyroid gland and eliminate the causes of pathological processes. You should not engage in self-treatment, as there is a high probability of causing serious complications.
Diet
A slight increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone can be restored with proper nutrition.
An endocrinologist recommends adding the following products to your diet:
- chicken;
- tofu;
- beans;
- whole grains, nuts, seeds can be added to salads;
- fruits and vegetables.
It is recommended to eat seaweed every day; it contains iodine. Low vitamin D levels have been linked to thyroid dysfunction. It is recommended to add foods containing it to the diet or go out into the sun every morning (20-30 minutes).
Lifestyle
During treatment, it is important not only to remember the doctor’s recommendations, but also to adhere to a healthy lifestyle:
- refuse strong physical and emotional stress;
- eliminate bad habits (alcoholic drinks, cigarettes).
Regular and moderate physical activity has a positive effect on metabolism. It is enough to exercise for 30 minutes every day. They mitigate side effects due to impaired thyroid function. Helps cope with fatigue, depression and prevent weight gain. You can run or ride a bike.
Favorite activities (drawing, knitting, painting) will help reduce stress and anxiety. Emotional stress can be relieved through breathing exercises or yoga.
Treatment of elevated TSH
If thyroid-stimulating hormone is elevated, the first thing a woman needs to do is visit an endocrinologist. The interpretation of blood parameters, the search for the cause of increased levels, and the determination of treatment strategies should be carried out by a qualified specialist.
He will conduct a thorough examination, and, if necessary, prescribe a repeat analysis and other specialized tests and samples, which together allow us to assess the functional state of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid system, which works on the principle of feedback. To bring the hormone back to normal, treatment requires predominantly conservative comprehensive treatment.
Drug therapy
The main effective direction of treatment is the method of therapy using hormonal drugs. A concentrated extract from the pituitary gland of cattle can be used as a medicine for elevated TSH. The drug Thyrotropin made on its basis is administered by injection, strictly according to indications, the course is 5-7 days. Several courses are held throughout the year.
But more often correction is carried out with synthetic thyroid hormones. Hormonal and replacement drugs include Levothyroxine, L-Thyroxine, Thyroidin, Euthyrox, Thyreocomb, Thyreotom, etc. Some women are wary of hormone replacement therapy regimens, citing side effects and changes in hormonal levels.
You should know that the dosage of medications is optimal and individual, selected by the doctor for each individual woman, taking into account the results of the examination and the clinical picture. The duration of the course is minimal.
ethnoscience
Using alternative therapy methods by independently selecting recipes is dangerous to health and is fraught with aggravation of pathological changes. With the approval of the attending physician, traditional medicine recipes can only be used as general tonics and as a way to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Most often, decoctions and infusions are prepared from medicinal plants (St. John's wort, licorice root, rowan fruits, rose hips, yarrow, coltsfoot flowers). To cover the lack of iodine, they resort to consuming kelp (sea kale), products derived from spirulina.
Diet and healthy lifestyle
For women with elevated TSH hormone, a therapeutic diet has been developed, which implies a complete, balanced diet. A sufficient content of fiber, proteins, and fats must be ensured (due to fatty fish, goat's milk, eggs, and fish oil).
Products containing this important element in large quantities will help compensate for the lack of iodine. Such as:
- products of marine origin (algae, fish, seafood, caviar);
- persimmon and black currant;
- organic cheese;
- chicken breast;
- milk products;
- buckwheat.
You should exclude from your diet foods that block the absorption of iodine - these are radishes, turnips, soybeans, cauliflower and red cabbage. Coffee, strongly brewed tea, chocolate and spices are harmful, because... they are stimulating. It is equally important to organize the correct drinking regime - drink enough clean water. You also need to change your daily behavior: ensure psycho-emotional comfort, avoid conflicts, overload, give up cigarettes and alcohol.
Treatment
Treatment of hypothyroidism, which is accompanied by elevated TSH, is carried out by compensating for T4 with levothyroxine-based drugs (Euthyrox, L-thyroxine, Levothyroxine), which are an analogue of the T4 hormone and are prescribed in individual dosages.
Levothyroxine is metabolized into triiodothyronine, which stimulates the growth and restoration of body tissues, increases oxygen consumption, activates the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and improves the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. During therapy with levothyroxine, it is necessary to undergo regular testing to monitor changes in TSH levels and health status.
For pathological enlargement of the thyroid gland caused by the development of Hashimoto's thyroiditis, nodular goiter, cyst growth or malignant cancer, surgical intervention may be prescribed in the form of:
- thyroidectomy;
- hemithyroidectomy (removal of one lobe of the thyroid gland);
- subtotal resection (removal of a node, cyst or benign tumor.)
Why is an increase in TSH dangerous?
An increase in thyrotropin secretion is observed relatively rarely; it manifests itself as hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis. Symptoms usually progress quickly. High concentrations of thyrotropin in women often cause infertility, difficulties with conception, spontaneous abortion in the early stages, severe toxicosis, bleeding, fetal hypoxia, developmental delay and even fetal death. The consequence of high TSH can also be problems with the heart, vision, mucous edema, thyrotoxic crisis, atherosclerosis, and disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system. Without medical care, a woman's quality of life can seriously deteriorate.
With timely, competent treatment and strict adherence to all medical recommendations, the prognosis is generally favorable.
Analysis of the level and norm of TSH according to the woman’s age
This study is of particular importance for diagnosing and prescribing correct treatment in cases with low TSH levels.
Symptoms for analysis:
- prolonged depression, apathy or persistent irritability, mood swings for no particular reason, insomnia and aggressiveness, decreased sex drive;
- baldness at an early age for no reason;
- the impossibility of conceiving a child when the spouses are in full health and at an optimal age;
- sore throat with the appearance of a tumor that can be felt with your fingers;
- mental and physical developmental delays in children compared to friends of a similar age;
- amenorrhea in women (if menstruation is persistently absent for several cycles at an early age);
- in cases where body temperature is often below 36 degrees;
- significant weight gain with normal meals, as well as uncontrolled appetite at the age of 25-30 years;
- frequent headaches that cannot be relieved with analgesics.
Not only the presence of pathological processes can become the basis for taking an analysis; there are also a number of other reasons for this:
- the study is included in mandatory screening when planning pregnancy at any age to determine the presence or absence of genetic diseases in the fetus;
- in infants, such an analysis is taken in order to exclude hereditary diseases and, if necessary, prescribe treatment in the early stages of the disease;
- for certain diseases, an analysis of the TSH level will help to determine the effectiveness of the treatment and (or) adjust it for each age;
- if thyroid pathology is determined in the early stages, then the analysis is carried out every six months as a control at any age of the woman;
- Such a study is especially important when diagnosing infertility or problems with conception. The sooner a woman’s deficiency of thyroid-stimulating hormone is detected from normal levels, the more effectively its level can be raised with the help of medications;
- suspected presence of autoimmune diseases.
A referral for an analysis of TSH levels is given by a general practitioner, but if necessary, it can be prescribed by an endocrinologist, gynecologist or cardiologist. This is done to determine TSH abnormalities in women at a specific age.
How is TSH level determined? Indications for the study
When determining the concentration of the hormone, doctors prescribe a study of TSH, thyroxine and antibodies to thyrotropin receptors in the blood. They are important components of the normal functioning of hormonal systems.
Among the main indications for conducting research are:
- the presence of a characteristic clinical picture, which is observed in diseases in the structures of the hypothalamic-pituitary system and the thyroid gland;
- assessment of the effectiveness of replacement treatment with products containing hormonal substances;
- infertility;
- pregnancy planning;
- hypertrophy of follicles in the thyroid gland;
- discomfort and sore throat of unknown etiology;
- nervous system disorders.
To effectively diagnose the concentration of thyrotropin in the female body, you must follow the rules for preparing for tests. In another situation, distorted research results may be obtained.
TSH during pregnancy: normal
As mentioned above, during pregnancy, thyroid-stimulating hormone can be increased compared to a woman’s normal state. Its indicators depend on the trimester:
Each trimester of pregnancy has its own indicators of thyroid-stimulating substance
Important: Only a doctor should evaluate the results of the study!
An increase in the pituitary substance in pregnant women is dangerous, especially in the 1st trimester of fetal development, since it is at this time that the important systems of the child begin to emerge. The most dangerous consequence of such a deviation in the expectant mother is brain dysfunction in the baby.
Important to know: Low levels can also lead to the development of various diseases. Therefore, if you are concerned about some unpleasant condition of the body, be sure to tell your doctor about it.
You should not diagnose yourself and worry if it seems to you that the indicators differ from the norm, since the general condition of the woman and her body should be assessed, and only an experienced doctor can do this.
Traditional methods of normalizing TSH levels
The level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in women is restored using traditional medicine due to the low level of active components in plants and herbs. There is no possibility of overdose and poisoning with infusions or decoctions. In addition, many women are attracted by the low cost of prescription components, which are much cheaper than pharmacological drugs.
The most effective means of alternative medicine are:
- Infusions of meadow clover, thyme or wormwood herb, lobaznik root, chamomile flowers, dry violet leaves, chamomile petals, oregano, linden buds and oak bark.
- Decoctions of fig fruits, elecampane flowers, nettle leaves, motherwort herbs, wormwood, thyme, chamomile, seaweed and yarrow. No less effective are products based on lungwort, elecampane flowers, and common oxweed.
- Tinctures of chaga mushrooms, nettle leaves, celandine or toadflax herbs, wheatgrass roots, sweet grass, male fern, valerian rhizomes, Icelandic cetraria and watercress.
Minor disturbances in the concentration of thyrotropin in the female body can be eliminated without the use of potent drugs. Many alternative medicine recipes can normalize thyroid-stimulating hormone levels with minimal risk of complications.
Long-term and regular use of these drugs allows you to achieve an optimal balance between thyrotropin and hormonal structures in the thyroid gland.
The normal level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in women is an important factor that reduces the likelihood of developing many diseases. If you detect any symptoms of changes in the level of thyrotropin in the female body, you should consult with specialized specialists. Timely detection of pathological processes allows the doctor to choose the most effective treatment tactics.
Author: saberlight
Article design: Mila Friedan
When the answers are ready. Decoding the results
The results of diagnosing TSH concentrations can be obtained the next day after the diagnosis. They are deciphered by the attending physician, who issued a referral for laboratory diagnostics to determine the level of thyrotropin.
| Pathologies | High performance | Low performance |
| With damage to the thyroid gland structures | Hypothyroidism, surgical interventions aimed at removing part or all of the gland, thyroiditis of infectious or autoimmune etiology at the stage of hypofunction, therapy using radioactive iodine. | Thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis of infectious or autoimmune etiology at the stage of hyperfunction, some types of benign and malignant neoplasms in the thyroid gland. |
| Without thyroid damage | Lack of iodine in the body, tumors in the hypothalamus, disruption of feedback processes in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, disorders of the adrenal glands, hypersecretion of prolactin, development of acute toxicosis in the last trimester of pregnancy. | Tumors characterized by the production of human chorionic gonadotropin, insufficiency of the hypothalamic-pituitary system due to trauma, meningitis, encephalitis, postpartum necrotic changes in the pituitary gland, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, exhaustion of the body, overdose of medications based on L-thyroxine. |
To obtain a more accurate idea of the etiology of TSH abnormalities in the blood, doctors prescribe additional research methods. They allow differential diagnosis between different pathologies and a clinical diagnosis.
Preparing and conducting analysis
In order to obtain a reliable diagnostic result for TSH concentration, you must adhere to a number of rules for preparing for the analysis. The highest concentration of thyrotropin is observed at night and persists until the morning.
Then the hormone level begins to fall and reaches its minimum by 18-20 hours. In this regard, the procedure for collecting blood for testing is carried out in the morning.
The material is taken on an empty stomach. You should not eat food 8-12 hours before the test. A low-calorie diet, prolonged fasting, or the use of chewing gum may affect the final result.
3-4 days before the study, to obtain data on the concentration of TSH in the body, it is not recommended to overeat and drink alcoholic beverages. You should not smoke on the day of the diagnosis.
The level of thyrotropin directly depends on the mental state of the woman. Emotional turmoil at work or in the family can negatively affect the final diagnostic results. Therefore, a few days before the study, you should not expose your body to stress and heavy physical activity.
2-3 days before the procedure, it is recommended to stop taking certain medications. In situations where the course of treatment with these drugs cannot be interrupted, the doctor indicates this in the direction of analysis in order to correctly decipher the study results.
Before the diagnosis begins, the woman should relax and sit or lie quietly for 30-40 minutes. The material is taken from the ulnar vein. The hand doesn't matter. Blood is drawn into a 5 ml tube and sent to the laboratory.
Data on the concentration of thyrotropin are entered into a special form. It contains a table with the names of indicators, their actual values, norms and interpretation.
If a repeat study is necessary to assess the dynamics of changes in TSH levels, blood is donated at the same time in the same laboratory. This is due to the fact that different institutions use different methods for obtaining data on the level of thyrotropin in the blood, as well as different equipment. Ultimately, the test results may have certain differences.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (the norm in women), subject to the rules of preparation and instructions of a specialist for laboratory diagnostics, is determined with minimal risk of data distortion. This allows the doctor to adequately assess the woman’s condition and take the necessary measures aimed at stabilizing the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Symptoms and treatment of hyperthyroidism
Elevated TSH hormone in women manifests itself:
- feeling tired;
- rapid fatigue;
- dryness, peeling and irritation of the epidermis;
- deterioration of joint functions;
- constant drowsiness, even after a full night's rest;
- the formation of edema in the arms and legs;
- development of iron deficiency anemia;
- frequent mood swings;
- causeless irritation, short temper;
- depression;
- apathy towards the outside world;
- inhibition of thought processes;
- decreased concentration;
- memory impairment;
- sudden weight gain;
- stool disorders (more often constipation);
- nausea;
- decrease in body temperature.
All of the above-described symptoms of elevated TSH in women can manifest themselves both in combination and individually. But in any case, they should not be ignored, as this can lead to very serious and unfavorable consequences.
Principles of treatment
How to lower TSH in women, what measures need to be taken for this, and is it possible to get rid of the ailment on your own? First of all, it is necessary to establish the reasons for the deviation and direct all efforts to eliminate them.
Thus, drug treatment for elevated TSH in women can be prescribed exclusively by an endocrinologist (or another specialist, if the problem does not lie in diseases of the thyroid gland). If a diagnosis of hypothyroidism has been made, it is advisable to use synthetic analogues of hormones produced by the thyroid gland. The drugs “Euthirox” and “L-thyroxine” are quite effective. Their use has a particularly beneficial effect on the body of women during menopause.
A very responsible and important point in the treatment of hypothyroidism with medications is dosage calculation. Since it is almost impossible to do this yourself, it is better to entrust this issue to a qualified specialist. An overdose of hormonal drugs can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the body!