Traces of hemoglobin in the urine of adult men, women, and children of all age groups are the first sign of a pathological condition of blood vessels, dysfunctional disorders in the hematopoietic system, kidney disease and other organs of the excretory system.
The appearance of signs of hemoglobin in urine indicates intravascular hemolysis of red blood cells, as well as a gradual change in the cellular composition of the blood. This is a dangerous symptom that can occur due to the presence of hematological factors, as well as due to the negative influence of external factors.
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a complex iron-containing protein of animals, humans, fish and birds, and invertebrates. In the lungs, under conditions of excess air, protein combines with oxygen, then, with the blood flow, red blood cells move to organs that lack this substance. Here hemoglobin is freed from oxygen, but binds to the waste products of gas exchange.
The normal levels of hemoglobin in the blood vary depending on the age, gender and condition of the person at the time of the examination. Lack of hemoglobin is accompanied by fatigue, pale skin, dizziness and loss of consciousness, and impaired growth in the child.
Quantity standards
The hemoglobin level is increased if there are serious abnormalities in the body, which indicates violations. Therefore, it is very important to know the amount of red pigment in urine. Moreover, up to 10 units in urine can be detected normally. This amount is physiological and is not a cause for concern. Increased levels of red blood cells also appear in women with monthly uterine bleeding.
Deviations from the norm
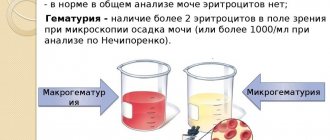
Even a slight appearance of red blood cells in urine is a reason to go to the hospital and undergo a series of additional tests. The detection of more than 2 red blood cells in the field of view of the microscope is already a deviation from the norm. Sometimes myoglobin is found in the urine, a substance similar to red blood cells, a structural component of muscles. This causes frequent errors in the diagnosis of hemoglobinuria.
Hemoglobin is more than 10
This condition is often associated with genitourinary tract infections. Sometimes it is a symptom of a blood disease. The appearance of a small number of red blood cells may be due to damage to the renal pelvis by a calculus or other disorders that are transient in nature. Therapy in this case is very rarely required.
Indicators 25 and above
Observed in hemolytic blood diseases. This condition is often found in cases of toxin poisoning. The hemoglobin level may be erroneously increased by the appearance of muscle proteins in the analysis or if leukocytes are isolated from the genitourinary organs. In addition, various genetic pathologies in the structure of blood cells lead to hemolysis in a patient.
Hemoglobin above 50
This phenomenon is observed in dangerous diseases, infectious lesions and muscle injuries, as well as extensive soft tissue hematomas. Most often, myoglobin appears in urine, which is not associated with damage to the kidneys or other urinary organs. Protein in urine is confused, since methods for its determination do not have high specificity.
Hemoglobin in urine: norm and pathology
A small number of red blood cells in the urine is normal. For women this indicator is up to 3 cells; in men it is normally absent. Hemoglobin is not normally detected in a urine test.
The body constantly breaks down red blood cells. Plasma contains up to 4 mg of hemoglobin. But excess protein combines with haptoglobin, forming a hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex. The molecule is too large to pass through the kidney filters.
If the death of blood cells is caused by pathological reasons, and an excess of this protein is formed in the vessels, then traces of hemoglobin are found in the urine.
What does it mean? This is a sign of a pathological process in the kidneys, bladder, bleeding in the urinary system and adjacent organs. It is called hemoglobinuria.
How and under what conditions is it formed in urine?
Traces of hemoglobin in the urine of men, women and children should be completely absent. The appearance of this substance in urine is called hemoglobinuria. In the bloodstream of healthy people, on average, about 10% of all red blood cells are destroyed, which release free hemoglobin.
In this regard, the blood plasma contains about 4 mg% of this protein compound. Free hemoglobin actively interacts with haptoglobin, forming strong biochemical bonds. This compound is not able to overcome the kidney filter, since its molecular weight ranges from 160 to 320 kDa.
The molecular complex, consisting of free hemoglobin and haptoglobin, enters the tissues of the liver and spleen, where it undergoes chemical decomposition with the formation of final metabolites of pigment metabolism.
If in the human body these biochemical processes proceed stably, and the kidneys, liver and spleen perform their functions, then hemoglobin molecules do not penetrate into the urine, as they break down into their constituent substances inside the body. Hemoglobinuria develops only when a critical amount of free hemoglobin (over 100 mg%) enters the blood plasma.
Haptoglobin, which is found in the bloodstream, is not able to bind excess concentrations of free hemoglobin, which entails its active reabsorption by kidney cells.
Absorbed hemoglobin accumulates in the epithelial tissues of the proximal canals, and then, through the process of chemical oxidation, can be converted into the substances hemosiderin and ferritin. Part of the absorbed hemoglobin enters the urine, which is subsequently detected during laboratory testing for biochemical parameters.
Traces of hemoglobin in the urine of women, men and children appear after prolonged or short-term exposure to external factors, or are one of the symptoms of a painful condition of internal organs. The table below details conditions the presence of which can lead to the formation of free hemoglobin in urine.
| Factors influencing the appearance of traces of hemoglobin in urine | Description of pathological processes |
| Nocturnal hemolysis of red blood cells | In this case, hemoglobin enters urine exclusively at night, when a person is sleeping and the pH of his blood is at a lower level. This pathological condition of the body is caused by the presence of a hematological disease in the form of acquired anemia, a type of which is extremely rare in medical practice. Mass death of red blood cells occurs in attacks. In the shortest possible period of time, a large amount of free hemoglobin is released into the blood plasma. The tissues of the liver and spleen are not able to ensure the rapid binding and breakdown of this substance. Such hemoglobinuria most often occurs in men and women whose age ranges from 20 to 40 years. Nocturnal hemolysis of red blood cells is associated with heavy physical activity, chronic infection, intoxication of the body, and the consequences of prolonged use of iron-containing drugs. After eliminating the negative influence of external and internal factors, urinalysis indicators stabilize, and free hemoglobin ceases to saturate the blood plasma. |
| Severe intoxication of the body | Contact with chemical or biological substances, overdose of potent drugs that have toxic properties can lead to massive hemolysis of red blood cells. In this regard, a sharp change in the cellular composition of the blood occurs, the death of red blood cells with the release of free hemoglobin. This is a dangerous condition of the body that requires emergency treatment measures. |
| Continuous static load | Traces of hemoglobin in urine can periodically appear in absolutely healthy people who have been on their feet for a long time or have traveled long distances on foot. Similar symptoms are often found in soldiers practicing marching formation, travelers, and athletes who engage in race walking or marathon running. In this case, hemolysis of red blood cells is associated with a static effect on the plantar part of the foot, the consequences of which are damage to red blood cells with the release of excess amounts of free hemoglobin. Traces of protein compounds are not found in urine after a short rest and recovery of the body. |
| Negative effects of cold | After prolonged swimming in cold water or hypothermia due to being in the open air, paroxysmal hemoglobinuria develops. The amboceptor hemolysin is formed in human blood, which binds to red blood cells, causing their premature hemolysis. The danger of the pathological process lies in the fact that with severe hypothermia, changes in the cellular composition of the blood can be irreversible. Once normal body temperature is restored, signs of free hemoglobin in urine disappear in humans. On average, this occurs after 24-48 hours. |
| Autoimmune reaction | This reason for the appearance of traces of hemoglobin in urine is very rare. The conditions for the development of a pathological state of the body are due to the fact that the cells of the immune system regard red blood cells as foreign and extraneous agents. Red blood cells are constantly under attack, which ultimately leads to an increase in the level of free hemoglobin, the detection of traces of it in the urine and the development of severe anemia. |
| Blood transfusion | In the case of transfusion of donor blood, which has an incompatible antigenic structure, acute hemolysis of red blood cells develops with the release of large amounts of hemoglobin. The protein compound saturates the composition of urine, and the symptoms of hemoglobinuria persist for several days. |
| Diseases of infectious origin | Bacterial pathogens of diphtheria, typhoid fever, syphilis, scarlet fever cause the death of red blood cells and the appearance of an excess amount of free hemoglobin. As the patient recovers, the biochemical composition of urine stabilizes. |
| Pathologies of the genitourinary system | Acute inflammatory diseases of the tissues of the kidneys, bladder and urethra can lead to destruction of their structure and the appearance of ulcerative formations. Hemolysis of red blood cells is caused by local secretions of blood and the breakdown of its cells. After eliminating the underlying disease, traces of free hemoglobin in the urine disappear |
Regardless of the conditions under which hemoglobin molecules appear in urine, its presence indicates a diseased state of the body. A person with a similar symptom should undergo a comprehensive examination aimed at detecting pathology.
Causes of hemoglobinuria
There are 2 options for this protein compound to enter the kidneys and urine:
- Penetration of whole blood cells due to the development of bleeding, inflammation in the urinary tract.
The reasons for the appearance of hemoglobin in the urine are urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, stones, tumors of various origins, and cysts in the kidneys. This condition is accompanied by a change in the color of urine.
If the recommendations for collecting and delivering the material to the laboratory are violated, then the red blood cells may begin to deteriorate. In this case, hemoglobin is released, and this is also detected during the study. In this case, we are talking about false hemoglobinuria.
- True hemoglobinuria - in this case, the breakdown of red blood cells in the vessels occurs. The causes of this condition are toxin poisoning, pathological processes in the spleen, allergic reactions, congenital damage to red blood cells.
With true hemoglobinuria, a significant amount of hemoglobin is released into the bloodstream. Some of it passes through the kidney filters and is found in the urine.
Accompanied by destruction of kidney tissue. With this form of hemoglobinuria, renal failure may develop.
The appearance of hemoglobin in the urine after a blood transfusion indicates that the biological fluid of the donor is rejected by the recipient, and the death of foreign tissue has begun.
After blood transfusion, the patient is under the supervision of medical workers for 24 hours.
Disturbances in the urinary system during pregnancy: what to do?
The normal level of heme protein in urine after conception is its absence. But it still occurs in women for several reasons:
- Rapid destruction of red blood cells in the acidic environment of urinary fluid.
- Heme passes through the renal filter due to its high levels in the blood.
- Hemolytic anemia caused by severe infections.
- Intoxication after poisoning the body with chemical/biological toxic substances.
- Impaired kidney function.
Pathology during pregnancy can be noticed by changes in the color of urinary discharge or oliguria. They take on a brown tint. If we talk about the development of such a symptom as lower back pain, then in a pregnant woman it occurs due to an increase in the load on the spine as the fetus grows. Therefore, as soon as the patient notices oliguria, she needs to see a gynecologist.
Types of hemoglobinuria
The classification of hemoglobinuria is based on the causes of the development of the pathological process.
The following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Paroxysmal nocturnal - develops against the background of defects in erythrocyte membranes.
- Toxic – poisoning with medications, reaction to an animal or insect bite, eating poisonous mushrooms.
- Post-transfusion – develops after blood transfusion due to incompatibility of the biological material of the donor and the recipient’s blood.
- Marching - after active and long training. Appears in athletes, military personnel - healthy people without signs of disruption of the functioning of other organs and systems. Hematologists note that most often this form is observed in people with lordosis, although a proven connection between these diagnoses has not been identified.
- Cold - when hypothermia, swimming in cold waters. This category also includes infection with pathogenic flora - pathogens of influenza, measles, mononucleosis, malaria, infection with Treponema pallidum, and bacteria that provoke the development of sepsis.
- Haffa disease - a positive urine test for hemoglobin is caused by intoxication caused by eating fish.
- Traumatic form - develops against the background of prolonged compression of tissues.
In addition, there are symptomatic, or one-time, and recurring forms of the pathological process.
Preparing and conducting analysis
In order for the results of a general urine test to be as reliable as possible, it is recommended to follow the following preparation rules before giving urine:
- on the evening before donating urine, do not eat vegetables and fruits, the natural pigments of which can change the color shade of urine (carrots, cranberries, beets);
- 24 hours before visiting the laboratory, stop taking medications with diuretic properties;
- 3 days before the test do not drink alcohol;
- 12 hours before the examination, do not eat food with a high content of hot spices, the presence of which can lead to irritation of the mucous membrane of the urinary system;
- 5 days before diagnosis, stop taking medications, the side effects of which can lead to hemolysis of red blood cells.
These are the basic rules for preparing for a urine test for signs of traces of hemoglobin. Otherwise, a person must lead a normal lifestyle so that the results of a urine test are objective.
The step-by-step process for taking a test to detect traces of hemoglobin is as follows:
- After waking up from sleep, you must perform thorough genital hygiene using soap, warm water and a clean, dry towel.
- Take a sterile container for collecting urine, which can be purchased directly from a laboratory or pharmacy.
- Flush a small amount of morning urine down the toilet to cleanse the urethra, and then fill a jar with urine for testing.
- Close the container with a lid, and then deliver the biological material for laboratory testing within 1 hour.
On average, at least 50 ml of urine will be required. This is the minimum amount of urine required for this type of analysis.
Women are advised to refrain from donating urine during menstruation, as well as 2 days after the end of menstruation. This is necessary in order to minimize the risk of blood drops getting into the urine. Their presence will lead to distorted results.
Symptoms
Signs of a pathological process are revealed by visual examination of a biological sample. This is a change in the color of urine - from dark brown to black, and its separation.
Subjective symptoms of the presence of hemoglobin in the urine:
- weakness;
- arthralgia, lower back pain;
- fever;
- hyperthermia to pyretic values;
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera.
Other symptoms depend on the type of hemoglobinuria. An increased level of hemoglobin after prolonged physical activity does not cause fever or increase in temperature. Goes away on its own after rest.
How to get it back to normal
In order to normalize the biochemical composition of urine, as well as to prevent further release of free hemoglobin, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of intravascular hemolysis of red blood cells.
Hemoglobinuria caused by exposure to cold or heavy physical exertion does not require the use of drug therapy. The use of medications is advisable only in the case of intoxicated breakdown of red blood cells or acquired anemia.
Medications
In order to normalize free hemoglobin levels, the following medications can be used:
- Troxerutin is an angioprotective agent that strengthens the walls of veins and capillaries, prevents vascular damage and hemolysis of red blood cells (1 capsule is prescribed 2-3 times a day for 1 week, and the average cost of the medication is 165 rubles);
- Active iron is an organic drug that replenishes the physiological loss of hemoglobin while measures are taken to eliminate the causes of hemoglobinuria (the medication is taken at the same time, 1 tablet per day with food, and its cost is 105 rubles per pack);
- Activate iron with lactoferin is a drug that replenishes iron deficiency, and also stabilizes the level of hemoglobin in the blood, normalizes metabolic processes (take 1 tablet per day, and the average price of the drug is 550 rubles for 20 tablets);
- Detralex is a medicine that stabilizes the condition of capillaries, prevents vascular damage and hemolysis of red blood cells (1 tablet per day is prescribed, and the cost of the medicine is 230 rubles for a blister of 10 tablets).
The above drugs help prevent further breakdown of red blood cells, maintain the tone of the walls of blood vessels, and stabilize hemoglobin levels. Without eliminating the main causes that change the biochemical composition of blood and urine, the use of these medications will not have a lasting therapeutic effect.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is not able to influence the stabilization of free hemoglobin levels. Therefore, their use is not advisable.
Other methods
If it is necessary to carry out emergency treatment measures to stabilize the cellular composition of the blood, the method of hematological transfusion is used. The patient is given a transfusion of donor blood components to saturate the body with additional red blood cells.
The treatment procedure is performed in a hospital inpatient department. Hematological transfusion is indicated for use in patients who have experienced massive hemolysis of red blood cells with critical loss of hemoglobin and the risk of death.
Urine hemoglobin test
There is no specialized test for hemoglobin. Its indicators are determined during a general urine test.
Main diagnostic criteria:
- change in color of biological fluid - red, various shades of brown, black;
- stratification - the top layer is transparent, the bottom is a dense sediment.
To confirm the presence of hemoglobin, samples with ammonium sulfate are used, and research is carried out using the electrophoresis method.
The comprehensive examination includes:
- coagulogram;
- bacterioscopic examination of sediment;
- blood biochemistry;
- bone marrow biopsy, myelogram - if paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is suspected;
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- X-ray examination of the kidneys.
Diagnostics and necessary studies
Hemoglobinuria is an “alarm bell”, indicating the development of pathology in the body, which means the prognosis may not be the most comforting. To clarify the circumstances, a person needs to contact a urologist or therapist and undergo a thorough examination to determine the pathogenesis.
Medical research is carried out in several ways. This may be a general analysis of urine and its sediment, where, using ammonium sulfate, the exact composition of the liquid is determined. Both “paper” testing with electrophoresis and ultrasound examination, usually used on the youngest patients, are done. After receiving the tests, the doctor prescribes treatment with antibiotics, anticoagulants, anabolic, iron-containing drugs, and in severe cases, a blood transfusion is performed.
You can determine the presence of iron-containing substances using a paper test strip. They are sold in pharmacies. Express diagnostics will give a positive or negative result, reflected on the color indicator; its determination is almost 100% reliable.
Hemoglobin in children's urine
A child should normally have no hemoglobin in his urine. The reasons for its appearance are exacerbation of kidney diseases, burns, infectious diseases, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, phimosis.
The pathology will be accompanied by additional symptoms – pain in the head, joints, and increased body temperature.
If the color of the urine changes or sediment appears in it, the child should immediately be shown to a pediatrician. The doctor will prescribe a urine and blood test, additional studies, and an ultrasound of the urinary system.
Next, the pediatrician will offer appropriate treatment or refer you to a hematologist.
Possible complications
Patients with traces of hemoglobin in their urine should undergo a thorough examination with further treatment of the underlying disease.
The lack of qualified therapy can lead to the development of the following complications:
- rapid weight loss;
- decreased ability to work;
- erectile dysfunction in men;
- digestive dysfunction;
- development of hemolytic anemia;
- functional disorders in the kidneys;
- thrombosis of the great vessels;
- pulmonary hypertension;
- bone marrow failure;
- aplastic anemia;
- oxygen starvation of the tissues of internal organs caused by a constant deficiency of hemoglobin;
- progressive hemolysis of red blood cells with a radical change in the cellular composition of the blood;
- the onset of death caused by vascular thrombosis, impaired renal function and severe anemia.
Traces of hemoglobin in the urine of women, men and children are determined by biochemical examination of urine. The appearance of molecules of this protein compound indicates a disruption in the functioning of the organs of the hematopoietic system, kidneys, liver and spleen tissues, exposure to particularly dangerous toxic substances, heavy physical exertion or prolonged hypothermia of the body.
Traces of hemoglobin in the urine appear due to the massive death of red blood cells, the breakdown of which leads to the release of an excess amount of this protein compound into the blood plasma. The lack of timely examination and qualified therapy leads to the development of a large number of complications affecting the performance of internal organs.
Hemoglobinuria in pregnant women
Hemoglobin in urine during pregnancy requires urgent medical attention. This is a consequence of kidney disease, urolithiasis.
The appearance of a red pigment may indicate a relapse of a chronic disease or the addition of a bacterial infection.
The condition is accompanied by additional symptoms - lower back pain, hyperthermia up to pyretic levels.
If cloudy urine or other signs of an inflammatory process appear, you should contact a gynecologist and undergo a comprehensive examination. Hospitalization of the patient is recommended.
Self-medication is unacceptable. Many drugs are prohibited during pregnancy, and the kidneys experience increased stress. This is fraught with the development of kidney failure and the death of the child.
Hemoglobin during pregnancy
Despite the fact that the general condition of a pregnant woman’s body is radically different from that of an ordinary person, the composition of urine is almost the same. Differences can only occur at the hormonal level, but even this is not always observed.
In order to monitor and analyze the condition of a pregnant woman and the health of the unborn baby, the antenatal clinic advises regularly performing blood and urine tests.
Increased hemoglobin in the urine of a pregnant woman is possible with a high acid-base balance, this leads to accelerated destruction of red blood cells.
With some kidney diseases (certain forms of nephropathy, urolithiasis, trauma), they cease to fulfill their filtering role and allow hemoglobin to pass through. In such cases, a comprehensive urine test fully indicates the presence of the disease.
The expectant mother can notice the presence of hemoglobin by the color of the urine: it turns dark brown. Of course, this is the cause not only of hemoglobinuria, but also of some other kidney diseases, but this sure sign is definitely a reason to see a doctor and get tested in the laboratory.
Treatment
Treatment of hemoglobinuria depends on its type and the cause that caused the development of the pathological process. The cold, march form in the vast majority of cases resolves independently and does not require drug therapy.
After rest, the patient’s condition returns to normal, and the urine acquires a normal color.
In other cases, you need to consult a therapist. If necessary, he will redirect the patient to a nephrologist or hematologist. Possible treatment options are presented in the table.
Table. Types of hemoglobinuria and methods of treatment.
| Diagnosis | Treatment Options |
| Chronic cold form | Corticosteroid hormones, immunosuppressants. |
| Paroxysmal nocturnal | Transfusion of red blood cells – up to 5 sessions. The use of indirect anticoagulants. Medicines to prevent the development of anemia. |
| Bone marrow pathologies | Corticosteroid hormones, anabolics to accelerate the formation of new bone marrow cells, androgens, immunoglobulins. Splenectomy. Transplantation from a suitable donor. |
| Toxic form, Gaffa disease | The use of antidotes, symptomatic therapy to help remove poisons from the body. |
| Kidney diseases | Antibiotics, highly specialized or broad-spectrum, herbal preparations. Urolithiasis - fees for removing sand, increasing diuresis, lithotripsy if indicated. |
| Traumatic form | Stopping the entry of breakdown products into the kidneys, normalizing the patient’s condition, symptomatic therapy. |
The presence of hemoglobin in the urine requires adherence to a gentle diet. Spicy foods, marinades and preserves are excluded. Strong tea, coffee, alcoholic drinks are completely prohibited.
They increase diuresis and act as an irritant to the urinary system.
For kidney disease, it is recommended to reduce the amount of animal products, fatty meat and fish in the diet.
The diet should consist of easily digestible dishes; fresh vegetables and fruits should be included in the diet. Confectionery products and baked goods must be excluded.
Complications from cold or marching form rarely occur. Paroxysmal types provoke the formation of blood clots in the renal veins and other vessels.
When the hepatic vein is damaged, ascites develops, the organ increases in size, and signs of esophageal varicose veins appear.
The chronic form of hemoglobinuria causes the development of calcium nephritis.
Treatment of hemoglobinuria: basic methods
It is worth noting that high hemoglobin content in urine is currently successfully treated and in most cases gives a positive result of therapy. Medications are prescribed based on the severity of the disease, tolerability of the drugs and the general health of the patient. So, for nocturnal paroxysmal hemoglobinuria, blood transfusions are used.
In mild cases with uncomplicated courses of the disease, the following groups of drugs may be recommended:
- Anabolics;
- Antioxidants;
- Iron-containing preparations;
- Anticoagulants;
- Antimicrobial installations.
In addition, since the presence of a high content of heme protein is most often observed in cases of kidney dysfunction, patients are advised to adhere to a diet and give up bad habits. What is included in the set of rules?
Firstly , you need to eat more fruits and vegetables. It is advisable to reduce their heat treatment. In general, fruits are best eaten fresh. Also, to reduce the load on the urinary system, patients are not advised to drink a lot of fluids.
Secondly , stop smoking and drinking alcohol. It is worth engaging in moderate exercise without overloading the body.
Thirdly , protect the body from hypothermia. If an infectious disease develops, you may be advised to take antibiotics with diuretics.
And what is also very important is not to self-medicate. If heme is detected in the urine, this most often indicates the development of a serious disease. It should be treated by a professional doctor who can prevent complications from occurring.
Cylinders
The cylinder is a protein coagulated in the lumen of the renal tubules and includes any contents of the lumen of the tubules. In the urine of a healthy person, single cylinders in the field of view can be detected per day. Normally, there are no casts in a general urine analysis. The appearance of casts (cylindruria) is a symptom of kidney damage. The type of cylinders (hyaline, granular, pigmented, epithelial, etc.) has no special diagnostic value.
Casts (cylindruria) appear in a general urine test with: a wide variety of kidney diseases; infectious hepatitis; scarlet fever; systemic lupus erythematosus; osteomyelitis. See in more detail: why there are increased casts in the urine.