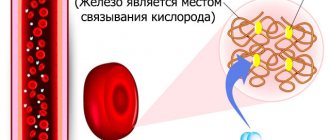
The phenomenon in which urine with blood appears in women is hematuria. This symptom manifests pathologies that require immediate intervention - therapeutic or surgical. In half of the cases, blood loss must be compensated. Substitution will prevent the development of anemia, avoid hemorrhagic shock and death. Without specialized medical care, it is impossible to determine the cause of hematuria and replenish the volume of lost blood. Calling a doctor is an indispensable condition for maintaining health and life.
Causes
There are over 10 conditions that contribute to the appearance of red blood cells in the urine. These pathologies are associated with disorders of the urogenital tract and dysfunction of the endocrine system. Hematuria can be caused by improper medication use or the presence of a tumor process in the body. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the symptom.
Infections of the genitourinary system
In infectious-inflammatory pathologies, the urine is slightly stained with blood. Factors contributing to the development of diseases of the urogenital tract in women:
- systematic exposure to low temperatures on the body
- lack of a regular sexual partner
- introduction of bacterial, fungal or viral microflora from instruments during diagnostic and treatment procedures
- insufficient implementation of hygiene measures
- neglecting to use pads when visiting a public toilet
- overuse of tampons during menstruation
If hematuria is caused by an infection in the genitourinary system, the woman’s body temperature rises and pain occurs. The localization of the unpleasant sensation is the lumbosacral region of the back, vagina, lower abdomen. The process of urine excretion is accompanied by cutting sensations inside the urethra; urine has an unpleasant fishy or acidic odor. At the same time as the woman, her sexual partner should undergo treatment.
Cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder develops due to hypothermia, poor personal hygiene, excessive activity during sexual intercourse, and alcohol abuse. Cystitis also occurs after recent medical manipulation with instruments that are not properly disinfected. Sometimes the bladder becomes inflamed after severe poisoning - acids, alkalis, medications, food.
Urine is stained with red blood cells mainly in the acute form of cystitis, and not in the chronic form. Additional symptoms:
- chills, increased body temperature
- power failure
- difficulty getting into a comfortable body position
- irritability, insomnia
But the main sign of the pathology is a frequent urge to urinate (up to 10 times in 1 hour), while the feeling of complete emptying of the bladder does not occur. The process of urine excretion is accompanied by a burning sensation in the genital canal. Urine is stained with red blood cells due to the fact that the inflamed bladder swells, the capillaries running inside the tissues of the organ are damaged. Hemorrhage occurs in the urine. Treatment of the pathology is predominantly conservative.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a urologist online
Endometriosis
It is a growth of the mucous layer of the uterus - the endometrium overcomes the limits of the reproductive organ and covers the pelvic cavity. The parts of the female reproductive system are located close. Although the initial focus of the pathological process is the uterus, the appendages are also susceptible to an unfavorable process. Along with the fallopian tubes and ovaries, the organs of the urinary system - the bladder, ureters, and urethra - are at risk.
In addition to the appearance of blood in the urine, women with endometriosis experience the following symptoms:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Failure of the menstrual cycle. Bleeding lasts up to 2 weeks; the discharged masses contain large fragments that externally resemble parts of the liver.
- Indifference to sex life.
- Decreased urine volume.
- Discomfort in the perineum while a woman is in a sitting position (the symptom occurs at stages 3.4 of endometriosis).
- Periodic increase in general body temperature.
- Weakness, decreased ability to work, sleep disturbance.
- Difficulty getting into a comfortable body position.
- Pressing pain during intimacy.
- Irritation inside the urogenital tract when urinating.
The progression of pathology takes a significant period of time - from six months to 2 years. With regular visits to the doctor, the disease can be identified at an early stage of its development and eliminated without consequences for health.
Urethritis
The mucous epithelium of the urethra becomes inflamed due to exposure to viruses, fungi, bacteria or protozoa. From the moment pathogenic microflora enters the body until the first signs appear, 1-3 days pass.
Factors that contribute to the development of urethritis:
- Weak body resistance.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules by a woman or her sexual partner.
- Wearing underwear that is too tight or chafing.
- Impact on the body of low temperatures and high air humidity.
- The presence of a urogenital disease, in which you have to scratch the itchy area, which exposes it to damage and the development of inflammation.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus. The disease causes irritation of the mucous membranes of organs, including urethral tissue.
- Recent diagnostic or therapeutic procedures on the urogenital tract (if the medical staff used non-sterile instruments when performing them).
Clinically, inflammation of the urethra is manifested by pain, increased body temperature, and the release of pathological secretions from the vagina. During an external examination, redness and swelling of the tissues are determined in the area of the external opening of the urinary canal. The patient complains of discomfort and burning when urinating. Urethritis quite quickly provokes the development of cystitis - the urethra in women is short and passes into the bladder. The proximity of organs is the reason for the rapid expansion of the spectrum of inflammation in the urogenital tract.
Urolithiasis disease
A common cause of the development of urolithiasis is the abuse of fatty, salty, sour, spicy foods, as well as unfiltered (contaminated) water. Concretions, or stones, form in the kidneys due to alcoholism and chronic drug intoxication. The metabolism of a woman’s body, the daily volume of physical activity, and heredity matter.
Urolithiasis is the formation of 1 or 2 stones at once - this is an individual factor. The neoplasm can independently leave the renal pelvis and move into the ureter. Sudden movement and physical activity predispose to this. Next, the calculus moves into the bladder, but in 80% of cases it still remains inside the ureter, blocking its lumen and causing urinary retention.
Stones differ in shape and structure - they can be smooth, streamlined, rough, with sharp or blunt edges. The severity of renal colic, an attack that occurs when the neoplasm moves, depends on the characteristics of the calculus. At this moment, simultaneously with hematuria:
- body temperature rises to subfebrile levels
- Nausea occurs, often progressing to vomiting
- sweat profusely
- Blood pressure levels rise to critically high levels
But the predominant symptom of renal colic is pain. The patient feels severe cramping discomfort in the lower back, moving to the lower abdomen. Spasms cause a high level of irritability, anxiety, and less commonly, fainting due to shock.
The appearance of blood during pregnancy
When urine is saturated with red blood cells in a pregnant woman, this is an alarming signal: you need to urgently contact the supervising gynecologist and call an ambulance. Hematuria in 80% of cases indicates detachment of the ovum - a threat of death of the child and mother (from massive blood loss). Additional signs are sharp pain in the suprapubic region, decreased blood pressure, and pressing discomfort in the back. Miscarriage can occur at different stages of gestation - due to stress, excessive physical activity, injury, or exposure to high temperature.
In addition to other symptoms, vaginal bleeding occurs. Other causes of hematuria in pregnant women are glomerulonephritis and increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity. With inflammation of the kidneys, in addition to blood in the urine, dull pain in the lower back, increased body temperature, weakness, lack of appetite, and a decrease in the volume of urine excreted occur. When intra-abdominal pressure increases, the pain syndrome covers the entire surface of the abdomen.
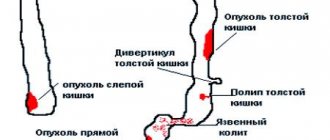
Oncology
Blood appears in the urine when a woman develops cancer of the bladder, kidneys, uterus, or ovaries. Common causes of the listed diseases:
- Hereditary predisposition
- Working under toxic conditions
- Regular exposure to stress factors
- Abuse of hormonal drugs
- Frequent cases of abortion
- Consumption of products with large amounts of stabilizers, dyes and other artificial ingredients
The degree of staining of urine varies from a faint pink color to an intense burgundy shade with large fragments of organ tissue. Saturation depends on the stage of the tumor process and the type of neoplasm. In addition to red blood cells in the urine, the condition is accompanied by discomfort in the lower back and lower abdomen, decreased appetite, and the release of blood clots from the vagina.
During intimacy, bursting pain occurs, libido is weakened, and the menstrual cycle is disrupted. A large tumor compresses the ureters and intestines: urine is released drop by drop, causing constipation. If hematuria is not relieved for a long time, general symptoms are supplemented by dizziness, nausea, weakness, and decreased blood pressure.
Functional hematuria
Pathology is the appearance of red blood cells in the urine after a short period of time after physical activity. Additional signs of the condition are pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of a foreign body in the back. Sometimes there is an increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels. Also, urine with blood occurs in women due to prolonged exposure to heat or cold on the body.
Glomerulonephritis
Inflammation of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys occurs as a result of hypothermia, exposure to a humid environment, or severe intoxication. The factor of genetic predisposition to glomerulonephritis is of no small importance. In addition to the saturation of urine with blood, the woman is worried about dull pain in the lower back, increased body temperature, lack of appetite, weakness, and decreased libido. Unlike a similar disease - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis is the leading cause of renal failure.
Injuries
Urine becomes saturated with blood when parts of the urogenital tract and abdominal cavity are damaged. The reasons are:
- falls, blows
- Road accident
- excesses during sexual intercourse
- careless actions of surgeons during intervention (accidental damage to organs located near the person being operated on)
- abnormal physical activity during work or sports training
- rupture of inflamed organs
- independent opening of the ovary or fallopian tube due to an enlarged ovum during an ectopic pregnancy
Symptoms of the listed conditions, in addition to hematuria, are pain in the lower abdomen and lumbosacral region; nausea, vomiting, weakness, decreased blood pressure. With massive blood loss, the patient loses consciousness, and the presence of red blood cells in the stool is also possible. Depending on a woman’s individual sensitivity, she can tolerate pain without realizing that internal organs are being damaged.
Taking hormonal medications
The use of oral contraceptives is complicated by the appearance of red blood cells in the urine in only 10% of cases out of 100. The side effect is caused by the significant load on the endocrine system that the drug provided. Discharge of blood from the vagina is a consequence of hormonal imbalance that has arisen in the female body. At the same time, accompanying symptoms - pain, increased body temperature - rarely occur. Given the anatomical proximity of the organs, when urinating, urine is colored by red blood cells released directly from the vagina.
Taking anticoagulants
The use of drugs that thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots can potentially lead to the development of hematuria. The symptom is one of the side effects from the use of Flenox, Heparin, Fraxiparin and their analogues. The reason for the development of complications is the oversaturation of the body with the active components of drugs. If a problem occurs, you should immediately inform the doctor who prescribed the anticoagulant. To stop the excretion of blood in the urine in 85% of cases, it is enough just to stop using the previously prescribed drug.
Possible complications
If the disease or condition that caused the development of hematuria is not eliminated for a long period of time, the level of hemoglobin may decrease and the formation of anemia. Other potential risks:
- Miscarriage, premature onset of labor. Develops due to partial or complete detachment of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterus.
- Hydronephrosis, or dropsy of the kidney, is the expansion of its membranes due to a stone blocking the outflow of urine. If the obstruction is not removed, the risk of organ loss increases.
- Infertility. Occurs due to adhesive disease. It develops against the background of prolonged inflammation in the urogenital tract, endometriosis, or previous trauma to the pelvic or abdominal organs.
In almost 100% of cases, these complications can be avoided.
Which doctor should I contact?
When red blood cells stain the urine due to endometriosis, it is necessary to contact a gynecologist. If hematuria in women is caused by urethritis, urolithiasis, cystitis, glomerulonephritis, you will need to consult a urologist. When the urine is bloody due to taking hormonal drugs or anticoagulants, you need to visit a specialist who recommended these medications. The doctor will conduct an examination, cancel the previously prescribed drug or replace it with an analogue.
When blood is excreted in the urine in pregnant women, you should contact an observing gynecologist. But if the hematuria is intense, you need to call an ambulance and limit physical activity until the doctors arrive. An oncologist should be visited if a tumor process is detected in the urogenital tract. Restoring the integrity of the parts of the genitourinary system is carried out by a urologist or gynecologist, depending on the damaged organ. If you have functional hematuria, you should make an appointment with a therapist. Then, taking into account the established underlying cause, treatment is carried out by a specialist.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a urologist online
Pathologies due to darkening of urine
Darkening of urine should be expected in case of oncology and severe diseases of the liver and kidneys. Dark color, increased content of red blood cells, mucus:
- For cholelithiasis;
- Kidney stones;
- Mercury poisoning;
- Hemochromatosis;
- Polycystic disease;
- Vasculitis;
- Glomonephritis;
- Shitostomiasis;
- The presence of Goodpasture syndrome;
- Malignant tumors in the liver, kidneys, genitourinary system, gall bladder.
Urine darkens in people suffering from anorexia, pyelonephritis, and malaria. An almost black color of the liquid when urinating indicates a liver injury.
Urine is brown in patients with liver cirrhosis, hepatitis, including viral and alcoholic. Brown coloration is observed in renal failure, when the filtration function is impaired and toxins are not completely eliminated from the body.
Urine becomes dark brown in people suffering from tyrosinemia. The disease is congenital. Therefore, from the first week it is necessary to pay attention to the color of the baby’s urine. If after several weeks the diapers remain wet and brown in color, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
Knowing everything about the peculiarities of urine color changes, everyone can monitor their health. The preservation of a dark shade, the presence of hematuria - signals about pathological processes in the body - gives reason to be wary. By seeking medical help in a timely manner, the chances of successful treatment of the disease that has arisen increase.
Diagnostics
To determine the cause of the development of hematuria, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the pelvic cavity, a laboratory test of blood, feces (to identify hidden red blood cells), and urine. Additionally, undergo an MRI or CT scan. The parameters of the stone and its exact location in case of urolithiasis are determined using a survey X-ray examination and subsequent excretory urography. If a tumor process is suspected, a biopsy of the affected organ is performed with further study of a tissue sample.
The normal content of red blood cells in the urine of women
The results of laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostics are interpreted by the attending physician. But patients should understand this issue at least in general terms.
- In a healthy patient, there should be no red blood cells in the urine, but, nevertheless, a small amount of them is allowed, not exceeding normal limits.
- Centrifuged urine can contain up to 5 units of formed elements, and liquid that has not undergone treatment can contain no more than three.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko considers the presence of up to 1000 red blood cells in 1 ml of liquid acceptable.
- A three-glass test allows you to determine the type of hematuria: initial, terminal or total.
There may be two types of elements present in urine: unchanged and leached. The first ones are “fresh”, that is, they have not undergone a change in structure, have a cylindrical shape and contain hemoglobin. The latter do not contain this component in their composition, therefore they are distinguished by a colorless or slightly greenish color and a “crumpled” appearance. In healthy fluid, the ratio of both types of red blood cells is 1:1.
Treatment
Stopping blood is performed with drugs such as Dicynone, sodium etamsylate, aminocaproic acid, calcium chloride. In case of injuries to parts of the genitourinary system, emergency surgical intervention is required. The doctor restores the integrity of the tissues, installs drainages (to prevent the accumulation of blood masses and subsequent inflammation of adjacent tissues). Glomerulonephritis is eliminated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and hemostatic agents.
Stones in the urogenital tract are removed conservatively or surgically. The type of treatment depends on the characteristics of the stones (size, composition, quantity), the likelihood of their independent removal. The patient’s age and blood pressure are also taken into account. If the calculus is subject to conservative removal, it is removed with the help of Fitolit, Urolesan, and water loading is performed.
The patient needs to drink 2 liters of water over 1 hour, after which she is injected intramuscularly with a diuretic drug - Furosemide or Lasix. After the injection, the woman should increase her physical activity - by walking, jumping, and exercising on a simulator. Physical activity will provoke the movement of the stone and its removal out. In order not to miss the release of a stone, when you have the urge to urinate only into a container.
When stone deposits cannot be removed conservatively, the patient undergoes surgery: contact lithotripsy. The method involves crushing the stone into sand and then washing it out of the urogenital tract. This type of operation does not require a skin incision and is aimed at rapid recovery of the body.
The tumor process is eliminated through chemotherapy, radiation exposure, the use of hormones, and surgery. Cystitis and urethritis are eliminated with the help of antibiotic therapy, uroseptics, antispasmodics, and sometimes diuretics. Additionally, it is necessary to regularly rinse the bladder and urethra with antiseptic solutions. In case of injuries to internal organs, a replacement blood transfusion is performed - transfusion of a volume of blood equal to the amount removed from the body.
In all of these cases, the patient is prescribed a diet. Depending on the factor that caused the staining of urine with red blood cells, nutrition involves increased consumption of vegetables, fruits, meat, and fish. The purpose of the diet is to increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, restore the body’s activity, and improve the overall well-being of the woman.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of conditions that are accompanied by hematuria, you need to:
- Avoid uncontrolled use of any medications and do not exceed the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
- Dress according to the ambient temperature and avoid hypothermia.
- Avoid damage to the body - at home, during sports training or work.
- Normalize the diet and quality of nutrition.
- Avoid significant physical activity and do not lift heavy objects.
- Carry out hygiene measures carefully and regularly.
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Improve or change working and living conditions, avoid staying near sources of intoxication.
If you have a hereditary predisposition to the development of any disease, you need to undergo regular diagnosis by a specialist in the appropriate field. Timely examination and, possibly, identification of pathology will allow it to be stopped without consequences for health. It is important to eliminate all diseases in the acute form of their development, preventing them from taking a chronic course.
Bloody urine always indicates health problems. The main reason may be disease or damage to the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity. To avoid the development of negative consequences and maintain reproductive status, a woman needs to visit a doctor and not deviate from his recommendations.
Classification of hematuria
The classification of hematuria is carried out taking into account the factors that led to its development and the amount of blood in the urine.
| Types of hematuria | Characteristics |
| Classification by factors of occurrence | |
| Postrenal | The symptom appeared as a result of kidney pathologies or injuries. |
| Extrarenal | The symptom appeared as a result of other pathological conditions. |
| Classification by the amount of blood in the urine | |
| Macroscopic | The amount of blood is enough for the urine to be colored red. In addition to blood, it may contain other impurities and pus. |
| Microscopic | The amount of blood is minimal, so it has virtually no effect on the color of urine. Abnormal changes can only be detected by special tests. |