Increased salts in urine - what does this mean? Urine is a liquid that is formed as a result of human activity and is its final product. Changes in the composition of these secretions are influenced by many natural and pathological factors. An increase in the amount of salt in the urine in women and men occurs due to a violation of the diet, taking certain medications, or infection with infectious pathologies. The climatic conditions in which the patient lives can also cause deviations in urine test results from the norm. “Why is there a lot of salt in urine? How to eliminate this phenomenon?” - the material in our article will help you find answers to these questions.
The salt content in the discharge has increased, what does this mean?
Most of the fluid secreted by the kidneys is water - approximately 94.5-95%.
The remaining 4.5-5% comes from other components - organic compounds (proteins) and inorganic elements (salts). In total, urine contains about 150 different substances. Salts in the urine of an adult may either be absent or present in the discharge in fairly small quantities. However, most of them are occupied by nitrogenous compounds. In a normal state, in humans, the percentage of ammonium salts should not exceed the following values: creatinine - 0.075% (an element formed as a result of the transformation of protein in the urine); urea – 2%; uric acid – 0.05%.
The following types of salts are also present in urine:
- sulfates;
- oxalates;
- urates;
- chlorides;
- phosphates.
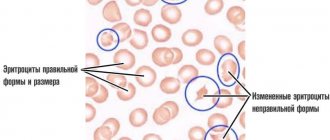
Absolutely all of these components are water-soluble compounds, so healthy urine does not form sediment. The process of crystallization of these substances can be affected by changes in the pH level of the secretions. In analyses, this indicator ranges from 5 to 7. Moreover, in the first case, the liquid has a weak acidic environment, and in the second, a weak alkaline environment. Increased salt content also causes a change in its composition. As a result of such a violation, these components begin to form microscopic crystals. These compounds then precipitate.
That is why calcium, ammonium and salts appear quite quickly in alkaline urine. As acidity increases, crystals of oxalates and urates begin to form in the secretions.
Classification
When microurolithiasis appears, it is necessary to classify the released sand according to its morphological type. This allows you to apply the correct treatment and prevent the appearance of stones. According to their composition, salts are divided into the following groups:
Phosphates
Their appearance provokes a shift in urine to the alkaline side (the normal pH of urine is 5-7 units). Below 5 the environment is acidic. Such salts can very quickly form into rounded conglomerates of a white or light gray hue. They respond well to conservative treatment.
Oxalates
These oxalic acid compounds are formed regardless of the pH status of the urine. Often observed in vegetarians due to excess consumption of tomatoes, rhubarb and other acidic foods. They form dark-colored stones with sharp edges, which lead to renal colic and injure the mucous membranes of the urinary tract. They are very difficult to lyse (break down) due to their high density.
Urats
They are uric acid salts formed as a result of a disorder in the metabolism of purines in the body, and often accompany a disease such as gout. Concretions of this type are rarely found and have a red tint. They can quickly dissolve under the influence of medications and urine alkalizers.
Characteristic manifestations in women
Women often exhaust their bodies with diets and remedies that get rid of extra pounds. This approach certainly affects well-being; usually, a woman refuses food on her own without consulting a doctor. This approach is fundamentally wrong, and has the wrong effect on the body, allows you to get rid of not only fats, but also useful substances, and also changes the qualitative composition of blood and urine.
Sometimes the reasons for the concentration of salt in the urine of women are the following:
- presence of gynecological diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- malignant neoplasms;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- chronic diseases.
A lot of salt may indicate severe intoxication of the body, which requires urgent hospitalization. During pregnancy, the indicators are unstable, but they are important diagnostic markers for determining the true condition of the mother and the unborn child.
Salts in the bladder in an adult are the result of various factors that only a doctor can determine upon examination.
What analysis shows the salt content
Crystals in urine are salt deposits consisting of phosphates, carbonates, oxalates, urates, etc. Normally, the liquid should not contain a protein-crystalline suspension. It consists of 99% water, and another 1% comes from:
- nitrogenous substances - creatinine, indican, urea, hippuric acid, urobilin;
- salts - oxalates, sulfates, phosphates, urates, chlorides.
To determine the composition of the sediment, a general urinalysis (UCA) is performed. Laboratory testing includes biochemical, organoleptic and physicochemical tests. If mineral inclusions are detected, a daily urine test for salts is performed.
During laboratory tests it is possible to determine:
- biochemical composition of sediment in urine;
- electrolyte concentration;
- level of nitrogenous substances;
- presence of bacterial flora.
To avoid errors in the results, it is recommended to collect biomaterial in sterile plastic containers. Urine samples are stored in the refrigerator for no more than 8 hours at 4°C.
OAM is a non-invasive way to assess the performance of the kidneys, thyroid gland, liver and metabolic abnormalities. If the concentration of salts in the biomaterial is high, additional studies are prescribed - ultrasound, excretory urography, CT scan of the urinary system.
Characteristics of oxalates in urine
Oxalates are formed when the acidity of urine increases, which is typical for diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- Crohn's disease;
- urolithiasis disease;
- cholecystitis;
- stomach ulcer;
- colitis.
The appearance of oxalates is always accompanied by pain during urination, spasms of the urethra and ureters, and increased temperature. Large crystals, when passing through the ureter, injure the mucous membrane, which increases the risk of an infectious and inflammatory process.
Treatment should be started as quickly as possible, since clinical manifestations will rapidly develop and the patient’s condition will worsen. Bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids and taking diuretics are indicated.
It is recommended at the time of treatment to completely abstain from consuming salt and sugar, smoked and fatty foods, as well as sweet carbonated drinks. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a specialist, the course of which depends on the specific situation.
Diseases that contribute to an increase in salts
High levels of salts in the urine may indicate the presence of pathologies such as:
- Kidney diseases - urates and oxalates increase, frequent urination, pain, pain, burning in the perineum appear, body temperature rises.
- Diabetes mellitus - the percentage of oxalates increases, but a number of additional studies are required to make an accurate diagnosis.
- Gouty arthritis – urate levels increase, which is accompanied by pain and aches in the joints.
- Urolithiasis – a persistent increase in creatinine and urate in the urine is recorded, which is accompanied by frequent painful urination and temperature.
The appearance of salts may not be associated with diseases, but indicate a dietary pattern and excessive consumption of salty, spicy, and sour foods.
Removing salts from the body
How to get rid of salts in urine and what needs to be done for this? Measures to remove salt varieties will depend on the reasons for their appearance. If the increase in the amount of salt inclusions in the urine results in a nutritional disorder, it is necessary to adjust, first of all, your diet.
Changing your diet
How to remove salt inclusions if the urate content is increased in urine? To reduce them, the following measures must be taken:
- foods rich in purine bases should be excluded from the diet;
- Foods rich in vitamins B and A should be included in your daily intake;
- adjust your fluid intake to 2 liters per day;
- systematic intake of alkaline mineral waters.
To prevent the formation of phosphate stones and reduce the level of phosphates in the urine, it is necessary:
- restriction in the intake of foods containing high calcium content;
- stimulate an increase in urine acidity by consuming acidic juices and fruits, as well as acidic mineral waters.
Reducing oxalate levels in urine involves:
- eating foods high in magnesium;
- taking fruits and foods high in B vitamins;
- compliance with the water regime of fluid intake up to 2 liters per day.
If there are pathological reasons for the appearance of a significant amount of salts in urine, symptomatic treatment is carried out to reduce them.
Folk recipes
How to treat increased salts in excreted fluid using medicinal herbs? To remove salts from the kidneys, the following traditional medicines are used, which are effective in removing sand:
- bay leaf decoction;
- decoction of pine cones;
- infusion of sunflower roots.
The following herbs help remove excess urates and oxalates:
- decoction of corn silk;
- infusion of birch buds;
- infusion of strawberry leaves.
The use of traditional medicine recipes is a good addition to the main treatment and is carried out only on the recommendation of a specialist.
Prevention
Preventing the accumulation of salts in the kidneys is, first of all, a healthy lifestyle and compliance with the following dietary rules:
- maximum reduction in alcohol consumption;
- consumption of processed foods by boiling, baking or stewing;
- increased consumption of vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins;
- mandatory compliance with the water regime of fluid intake up to 2 liters per day;
- increasing physical activity and combating physical inactivity.
Regular preventive examinations, including urine analysis, will allow you to promptly identify increased salt levels in urine and take measures to reduce them.
Exceeding the normal salt content in the body can be observed in pregnant women. As a rule, this occurs during toxicosis, when dehydration of the body is observed due to frequent vomiting.
General urine test for salt
This urine test shows the presence of one or another type of salt. This in turn indicates the correct functioning of the urinary system . To determine more accurate indicators, daily analysis is used.
As urine acidity increases, urate and oxalate crystals form. An alkaline environment promotes the formation of phosphates. In the case when the salt level is slightly increased, this can be attributed to dietary habits. Values that increase systematically over several studies are taken into account.
This requires a number of additional diagnostic measures to find the root cause.
Pathologies in women due to increased salts
The female body is structured somewhat differently than the male body. An increase in salts in the urine in women indicates the following ailments:
- diabetes;
- venereal problems;
- inflammatory processes of the urinary system, including the kidneys;
- infection and development of pathogenic microflora;
- oncology, namely the stage when necrosis of the tissue of the organ in which the tumor is localized occurs.
Frequent vomiting leads to dehydration of the body, as a result of which urate accumulates in the kidneys. If toxicosis drags on for a long time, there is a risk of stone formation. To prevent such developments, it is necessary to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day, follow a diet and not abuse meat products.
The next reason is considered to be an increase in the concentration of salts in urine. This phenomenon occurs due to the consumption of excessive amounts of foods enriched with proteins, as well as dehydration of the body (which increases the density of urine) and metabolic disorders (which is typical for uric acid diathesis, gout, xanthinuria, oxalosis and Wilson's disease).
The last common cause is a violation of the acid-base balance (pH) of urine. The manifestations differ depending on exactly how the pH is disturbed: when the acidity of urine increases, the solubility of salts worsens, and when the balance is more alkaline, the solubility of phosphates is impaired.
In this case, crystals of sediment (salts) present in the excreted urine almost always signal the development of serious diseases, which threatens a gradual deterioration of the condition and serious consequences, and this makes it necessary to quickly find out what such a change in urine means and how to get rid of it.
If the diet is not oversaturated with any of the listed types of food, but a high salt concentration in the urine remains, the following diseases may cause this:
- acute infection;
- diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- dehydration of the body.
24-hour urine salt test
If it is necessary to assess the total amount of salts excreted during the day, the doctor orders urine to be collected in a glass container, after which an analysis is performed. Typically, urine collection occurs at home, and the reliability of the results is influenced by several indicators:
- 3-5 days before the expected date of urine collection, you need to normalize your diet by giving up spicy, salty, sour and smoked foods, alcohol and sweet carbonated drinks.
- Reduce physical activity and consume enough fluid, at least 1.5 liters per day.
- Before each urine collection, it is important to disinfect the genitals by washing with baby soap.
After waking up at 6 am, the first portion of urine is not counted.
Next, the urine is collected in a glass jar with a volume of at least 3 liters. The last portion of urine should be at 6 am the next day.
The jar of urine is stored in a cool, dark place, but not in the refrigerator. The ideal option is a tiled bathroom floor.
After collecting the last portion of urine, close the jar tightly with a lid and shake vigorously. After this, 100 ml is measured into a urine collection container, which is taken to the laboratory. The container is signed, after which laboratory assistants study the quantitative and qualitative composition of the salts.
After the study, results are given on the percentage and quantitative content of salts, on the basis of which the doctor makes a conclusion.
Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine are a clear sign of impaired metabolism.
The accumulation of calcium oxalates in the urine, forming insoluble particles in the form of sediment, is called oxaluria.
When carbohydrates are incompletely oxidized, oxalic acid accumulates, which tends to interact with calcium, iron, and magnesium. When metabolism is disrupted, these compounds form oxalates, which are retained by the body. Calcium oxalate particles form kidney stones. This state of the body is dangerous because urolithiasis develops, which leads to unpleasant consequences.
The primary disease occurs due to hereditary oxalosis (hyperoxaluria). Secondary oxaluria is a condition of the body caused by reasons that arose during life, such as:
- insufficient activity of small intestinal enzymes;
- diabetes;
- hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, blockage of the urinary tract;
- unbalanced diet;
- nervous shock, stress, shock;
- excess bile production;
- ethylene glycol poisoning;
- intestinal neoplasms, operations on it, peptic ulcer;
- insufficient intake of magnesium and B vitamins;
- indiscriminate use of medications.
One of the main reasons for the occurrence of excess oxalates in the urine is dehydration, which can occur for various reasons. The insidiousness of oxaluria lies in the fact that it begins asymptomatically. With an increase in the amount of oxalates, the following appear:
- pain when changing position;
- disorders of the central nervous system in the form of headaches, neuroses;
- nagging pain in the lower back, abdominal cavity;
- weakness, general malaise;
- bright color of urine;
- often increased, less often limited urination;
- attacks of renal colic.
The peculiarity of dehydration in men is that they experience a large amount of physical activity and sweating increases. Another reason for the development of oxaluria is inflammatory processes caused by infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
On a note! Men more often deal with car fluids containing ethylene glycol, which cause intoxication of the body. This is due to the fact that they develop urolithiasis more often than women.
Female dehydration is often associated with vegetarian diets and fasting.
In pregnant women, the reason for this is toxicosis, the fight against swelling. They also often take excessive amounts of vitamin C and consume more fruits and vegetables containing oxalic acid. As the size of the uterus increases, pressure on the bladder increases, which leads to congestion. Toxicosis in late pregnancy indicates the accumulation of calcium oxalates.
The presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, allergies, and low blood pressure in a child are symptoms of exceeding the norm of oxalates.
The causes of the disease in newborns are often congenital abnormalities of the intestines and the metabolism of oxalic acid salts. In the future, this can lead to severe kidney damage.
It is important to know! Children under 5 years of age acquire oxaluria due to a lack of vitamin D. In older children, the causes are the same as in adults
Whether the norm of oxalates is exceeded or not will be determined by a biochemical analysis of urine. It is almost impossible to identify this visually.
And if you neglect periodic examination, the crystalline structure of oxalates can lead to the formation of blood in the urine, and later, to urolithiasis.
To understand whether renal pathology is developing, you need to know the normal content of oxalate salts in the urine.
Causes
The etiology of the appearance of salts is most often based on metabolic disorders. And all other factors only create the preconditions for microlithiasis and further stone formation. Experts identify the following reasons for the appearance of sand:
- Tendency to urolithiasis, which is inherited. Genetic predisposition occurs in idiopathic familial hyperuricemia, cystinuria, and oxalatosis.
- Nutritional features. An important role is played by an insufficient amount of fluid in the diet, a lack or excess of certain vitamins, and the predominant consumption of protein foods or water with a high content of microelements (phosphorus, magnesium or calcium).
- Urinary tract diseases. Inflammation, stagnation of urine, and the presence of pathogenic flora change the acidity of urine. Such phenomena are observed with pyelo- and glomerulonephritis, drug-induced kidney damage, and structural anomalies.
- An increase in microcalcifications in the urine causes an increase in parathyroid hormone with excessive function of the parathyroid glands. It promotes calcium retention due to its reabsorption in the renal tubules.
Provoking factors are also a sedentary lifestyle, diseases of the digestive organs, long-term use of diuretics, steroids, and sulfonamides. Most often, salts are detected in the urine when living in a hot climate or increased sweating with insufficient water intake, vomiting and dehydration.
Treatment
For any inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, antibacterial drugs with urological action are prescribed. These include: Norfloxacin, Furamag, Furagin, etc. All of them require prescription by a specialist because they have side effects, as well as the necessary dosages, frequency and course of administration.
Diuretics are prescribed to avoid stagnation of urine and unnecessary growth of microorganisms. With prolonged accumulation of urine, it thickens, creating a breeding ground for bacteria, and there is also a risk of stone formation.
As a preventive measure and to provide an auxiliary effect, it is necessary to:
- normalize your lifestyle, avoid stress and physical strain;
- be sure to follow the rules of personal hygiene;
- resort to contraception during sexual intercourse, in the acute phase of the disease - maintain sexual rest;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- If the pathological process worsens, consult a doctor in a timely manner.
It is important for a man to adhere to a balanced and rational diet. It is necessary to avoid foods rich in spices, spicy and fatty foods.
At the beginning of treatment, it is better not to eat meat, alternatives to which can be poultry and fish.
Treatment of urolithiasis, which is a consequence of crystalluria, is carried out depending on the composition of the stones, their size and location. This is determined by several methods:
- X-ray diffraction analysis to reveal the molecular structure of crystals;
- spectroscopy using infrared rays;
- determination of urine pH (uric acid stones - at low pH);
- urine culture for bacterial culture;
- analysis of urinary sediment under a microscope;
- cystine tests (Brand or others);
- determination of the amount of urate in blood serum.
Conservative treatment includes the following methods:
- Drug therapy: drugs for the passage of stones - thiazides (Cystenal, Marelin, Uroflux and others);
- orthophosphates used for intolerance to thiazides (neutral potassium orthophosphate);
- stone-dissolving agents for loosening stones made from uric acid, cystine, citrate, oxalate, urates (Blemaren, Uralit, Magurlit);
- magnesium preparations that prevent crystallization and adhesion of oxalate crystals (Panangin, Asparkam);
- vitamin B6, which reduces the synthesis of oxalic acid (Pyridoxine);
- antispasmodics (Platifillin, Drotaverine, Atropine and others);
- painkillers for acute renal colic (Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Tramadol and others).
- hardware physiotherapy to stimulate urodynamics of the urinary tract (exposure to sinusoidal electric currents, ultrasound, pulsed low-frequency magnetic field);
Open abdominal surgical operations are performed in the following cases:
for large stone sizes (
Additional symptoms of diseases causing high salt levels
Changing the pH of urine does not affect a person’s general well-being. But imbalance is provoked by inflammatory, infectious or endocrine pathologies. Therefore, clinical manifestations largely depend on the cause of the formation of salts in urine.
Impaired urine outflow, accompanied by crystalluria, is dangerous due to stone formation in the organs of the urinary system.
Possible pathologies and clinical picture
| Types of diseases | Characteristic manifestations |
| urolithiasis disease | renal colic pain in the perineum burning sensation when urinating elevated temperature cloudy urine nausea passage of stones |
| hyperthyroidism | feeling hot increased fatigue heartbeat excitability goggle-eyed hand tremors |
| diabetes | constant thirst weight loss bed-wetting acetone in urine muscle weakness dry mouth |
| gout | joint pain elevated temperature swelling of the joints urinary disorders (dysuria) |
| pyelonephritis | flakes in urine lower back pain frequent urge to urinate hematuria (blood in urine) increased sweating pastiness (mild swelling) of the eyelids |
| cystitis | burning sensation when emptying the bladder lower abdominal pain cloudy urine frequent urge to go to the toilet jet interruption elevated temperature feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder |
The appearance of additional symptoms - dysuria, joint pain, fever - is a reason to make an appointment with a doctor. Timely treatment of diseases reduces the likelihood of complications - hydronephrosis, renal failure, thyrotoxic crisis.
How to get rid of salts in urine
Special treatment for salt in the urine may not be required if, after following a diet excluding the richest foods, a control test shows the norm. If there are bacteria in the urine, in addition to salts, leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, casts, mucus, bacteria, it is still better to undergo an examination. After all, salt deposition is possible against the background of sluggish inflammation.
A diet for salts in the urine must include a sufficient amount of fluid to drink. It is necessary to limit or completely eliminate the products listed above. And in the diet, products that have a binding effect and maintain energy balance are recommended.
If urates are present, it is recommended to use purine-free products and fortify food:
- dairy products;
- poultry meat;
- eggs;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- cereals;
- nuts.
For oxalaturia, the daily menu should include:
- beans;
- liver meat;
- sprouted wheat or bran;
- seaweed;
- pumpkin seeds;
- potato.
The products will provide the necessary salts of oxalic acid:
- magnesium;
- vitamin B6, E, A.
Recommended fruit drinks and compote from:
- cranberries;
- cherries;
- lingonberries;
- flax seed decoction;
- pear leaves.
For phosphaturia the following are indicated:
- brown rice products;
- meat soups and broths;
- drinks made from berries and fruits;
- boiled vegetables.
The effectiveness of the diet can be assessed by a control urine test after 2-3 weeks of dietary restrictions. Lack of results will indicate the need to prescribe medications. The dietary approach should be maintained throughout life.
In addition, each person should carefully understand their habits and proper nutrition. An indicator such as salts in the urine can be a warning of more significant disorders in the form of urolithiasis.
Correction and treatment methods
If it turns out that the presence of crystals in the urine is increased, you first need to determine the reason that led to this change. If stones are found in the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract, then a method for removing them is chosen.
This can be ultrasonic crushing so that the stones become smaller in size and it becomes possible to remove them from the body in a painless and non-traumatic way. Currently, such procedures are successfully carried out not only in Moscow, but also in smaller cities, and they allow people to get rid of the problem in a fairly quick time. Or surgery may be required if the stone cannot be crushed or has a shape that makes other treatments impossible.
If the appearance of amorphous crystals is associated with diseases (gout, pyelonephritis, diabetes mellitus), a therapeutic strategy is developed aimed at the underlying pathology. If an attack of renal colic occurs, the complex of emergency measures includes the prescription of painkillers, such as No-shpa, Drotaverine, as well as uroseptics.
In situations where no serious pathological causes of crystalluria were found during the examination, in order to prevent the possible development of diseases, it is enough to change the diet. A diet for salts in the urine implies a refusal or a reduction in the amount of foods consumed, depending on the characteristics of the identified crystals, namely:
- If you have urates, you will need to limit the consumption of meat, cocoa, legumes, salt, coffee, and you will have to completely abandon fatty and spicy foods, offal, meat broths, and alcohol. They need to be replaced with plant foods and dairy products.
- If oxalates have been detected, then you should exclude spinach, sorrel, baked goods, strong coffee, tea and limit the consumption of dairy foods, as well as those rich in ascorbic acid. It is allowed to eat dishes made from plant and meat products.
- If phosphates are detected, the patient should exclude hot and spicy foods, dairy products, cocoa, alcohol, most vegetables and herbs from the diet. His menu should be dominated by meat and flour foods (preferably not baked goods).
At the same time, it is very important to maintain a drinking regime, which involves taking a large amount of liquid - at least 3 liters of clean filtered water and drinks made on its basis.
Causes of salt in urine
Today, there are a significant number of reasons why excess salt deposits may appear in urine. All of them can be divided into several groups. It is necessary to understand that the causes are not the symptoms; accordingly, it is very difficult for a person to determine the presence of oxalates, phosphates, urates and other salt compounds in his body - this is done on the basis of appropriate diagnostic measures and tests.
Why is there a lot of salt in urine:
A person is not eating properly
Perhaps the most common and main cause of pathology. If there is an increase in the concentration of salts in urine, first of all, it is imperative to exclude from the diet all foods that contain oxalic acid - the main “culprit” of acid-base imbalance. Such food includes the sorrel itself, as well as tomatoes, any sour berries and chocolate. Instead of the above products, you can start eating prunes, watermelons, cauliflower, as well as any fresh fruit.
It is not recommended to eat monotonous food for a long time. This very often leads to the fact that the level of salts in the body begins to gradually increase. Over time, they will enter the urinary system, with all that ensues. This is especially true for products such as cheese, smoked meats, canned food, meat broths, mushrooms and, not surprisingly, alcohol.
It is strictly not recommended to abuse diets and, especially, fasting. This generally has an extremely negative impact on human health, and in the case of the urinary system, it can lead to the fact that the body will try to replace the lack of useful compounds and biologically active substances with salts.
Infections of the genitourinary system
Infections refer to the penetration of third-party pathogenic microorganisms, such as a virus, bacteria or fungus, into the urinary tract or genitals. Starting to actively multiply, they provoke the occurrence of an inflammatory process. If there is a lot of salt in your urine, it is likely that you have some kind of infection. The pathogen disrupts many physiological processes in the genitourinary system, one of which may be the regulation of acid-base balance.
At the moment, the greatest threat is posed by infections such as chlamydia, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis and common thrush. Contrary to popular belief, candidiasis can affect both female and male bodies; accordingly, representatives of the stronger sex are not protected from problems of this nature.
Blood supply disorders
The kidneys are a very sensitive paired organ. It is especially dependent on an adequate blood supply. A minimal lack of useful microelements or oxygen, which are transported in the blood, leads to significant impairments in their functionality, and this is a direct path to the appearance of an impressive amount of salts in urine.
Problems with blood supply traditionally arise against the background of vascular pathologies. The kidneys may not receive enough blood if there is a narrowing or, even worse, blockage of the feeding artery, prolapse of one or two kidneys at once, the development of nephrosis, pyelonephritis and many other common diseases of the urinary system.
Lack of fluid
A urine salt test may be needed if the body is dehydrated. The less water in it, the higher the chance of the formation of additional salt deposits, which can be localized not only in urine, but also in tissues.
The reasons for the lack of water in the body are associated with increased physical activity, which leads to increased sweating, overheating in the sun, vomiting and diarrhea, high body temperature, etc.
It is very important to drink plenty of fluids immediately after all of the above cases - this will help restore water balance in the body and avoid the formation of salt compounds
Drug therapy
Some types of medications have not only positive, but also negative effects on the body. Many of them are excreted through the kidneys. Strong drugs such as antibiotics, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc., can provoke the formation of urates in this paired organ.
Treatment and prevention of crystalluria
Repeated detection of salts in urine cannot be ignored. Over time, this disorder can transform into urolithiasis (UKD), which creates the preconditions for frequent inflammatory diseases, provokes the appearance of severe symptoms and ultimately requires traumatic and expensive surgical interventions.
If asymptomatic crystalluria is detected, you must:
- thorough comprehensive examination;
- determine the type of salts;
- correction of the diet taking into account the type of salts and stone-forming components in each specific case.
To find out the reason for the increase in the level of salts in urine, you need to take a general and biochemical blood and urine test, undergo an ultrasound examination of the liver and kidneys, and take a general stool test.
The diet includes the following recommendations:
- If the level of uric acid and urate is high, limit the amount of meat (up to 100-150 g per week), increase the consumption of fruits, vegetables, milk and dairy products, flour products, eggs, nuts and cereals. Poultry is allowed to eat meat. Products containing vitamins A and B and microelements (zinc, calcium, magnesium) are also added.
- For oxalaturia, avoid foods rich in oxalic acid. The diet should consist of meat, fish, potatoes, cabbage (white or cauliflower), lentils, peas, cucumbers, asparagus, turnips. You can eat white bread, lard, cottage cheese and fermented milk products, cheese.
- For phosphaturia, limit the consumption of cheese, cottage cheese, sour cream, fish liver, eggs, fried fish and caviar. They contain a lot of calcium, which precipitates in urine in the form of phosphates.
Normalization of the water and drinking regime is of key importance. To prevent crystals from depositing in the urinary tract, they need to be “washed off” in time, and for this the patient must increase fluid intake taking into account body weight, but not less than 2 liters per day.
If other clinical manifestations do not occur during these activities, then it is enough that the doctor simply observes such patients; treatment is not always required. If additional symptoms appear, the patient should be referred for consultation to a specialized specialist.
Drugs for the treatment of crystalluria
Normalization of the level of salts in the urine occurs after elimination of the underlying disease, for example, treatment of inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract, liver, diabetes mellitus and other pathologies. But when crystalluria persists constantly, doctors consider this as the onset of urolithiasis and direct their actions to reduce the excretion of salts in the urine.
Doctors may prescribe the following medications:
- Blemaren. Studies have revealed that crystalluria occurs when there is a deficiency of citrates, which are normally also excreted in the urine. It regulates the pH of urine, reduces the secretion of substances from which sediment is formed, and increases the content of crystallization inhibitors in the urine. Therefore, one of the ways to reduce salt levels is citrate therapy with Blemaren. It increases the ability of urine to suppress the growth of urinary stones, reduces the excretion of calcium (an activator of crystallization) by the kidneys, reduces its concentration in the urine and thereby prevents stone formation. The drug is prescribed for almost all types of urinary stones, as well as for gout as an adjuvant.
- Allopurinol. For gout, it is the main drug that helps reduce the concentration of uric acid in the urine and blood. Under the influence of Allopurinol, already deposited crystals gradually dissolve, and the synthesis of uric acid is inhibited (urostatic effect), which leads to a decrease in its level in the body, and hence excretion in the urine.
- Canephron H. Is a herbal preparation. Can also be used in pregnant women. Its components are centaury herb, lovage root and rosemary leaves. They relieve spasms of the walls of the urinary tract, normalize the pH of urine, have an antimicrobial effect and reduce the loss of protein in the urine. Canephron N has a diuretic effect by increasing blood flow in the kidneys.
Additionally, taking vitamins (pyridoxine, folic acid) is indicated if the imbalance is caused by their deficiency.
The specific method of treatment is always selected individually. The treatment of diseases that cause an increase in salts in the urine is carried out by therapists, urologists, nephrologists, and less often by gynecologists.
What affects the formation of phosphates
The phosphate group includes salts and esters of phosphoric acid. Phosphorus is very necessary for children to build bones, ensure safety and mobility in adulthood, and support tooth enamel. It is constantly associated with calcium.
Both elements are necessary in the processes of excitation of muscle tissue, for the cells to obtain energy. Phosphate stones have a porous structure and are susceptible to destruction. They do not cause traumatic injuries like oxalates and are much easier to treat.
Amorphous phosphates in urine are detected against the background of:
- predominantly dairy food;
- using oatmeal, buckwheat and pearl barley porridge too often to feed a child or adult;
- hobbies for pasta;
- uncontrolled consumption of baked goods, chips, sweet soda.
Phosphaturia is one of the symptoms:
- inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system;
- increasing the functioning of the parathyroid glands;
- Fanconi syndrome.
More about crystalluria
In the process of life, the human body synthesizes many different substances necessary for its existence. As a result of multiple reactions, decomposition products remain, and some of them are capable of subsequently forming unique strong formations - calculi (stones).
As a rule, such compounds are amorphous crystals of various salts, such as phosphates, urates, oxalates, etc. In urine they can be seen with the naked eye - these substances, which do not have a specific form, are presented in the form of unorganized urinary sediment.
Reference! Normally, a small amount of amorphous crystals may be present in the fluid secreted by the kidneys, but with increasing concentration they can combine with each other into stones, leading to urolithiasis (KD).
Such formations have different sizes - from fairly small (sand) to large ones, reaching or even exceeding 5 cm in diameter. Moreover, the increase in one or another type of amorphous crystals in urine is determined by the influence of various factors.
Reasons for the appearance of salts
There are several factors that regulate the amount of salts in urine. The first of them is not associated with diseases, but the rest are direct activators of pathological processes, as a result of which the concentration of salt compounds increases.
Unbalanced diet. Monotonous food, frequent diets and fasting lead to an increase in the level of salt deposits. Meat, canned food, smoked meats, mushrooms, tomatoes in the daily diet are products that negatively affect the acid-base balance in the human body. This list includes alcoholic drinks and soda.
Impaired blood supply. For the kidneys to function properly, they must be constantly supplied with blood. If, for various reasons, blood flow is disrupted, the kidneys experience a deficiency of oxygen, which they receive from the blood. This will lead to unstable functioning of this organ, and, as a result, to an increase in the concentration of urates in the urine.
Dehydration. With a decrease in fluid in the body, the amount of salt deposits increases. Moreover, they are now localized not only in urine, but also in soft tissues. Lack of water can be associated with prolonged physical activity, overheating, diarrhea, high fever, and the like.
Drug therapy. Some drugs from the group of anti-inflammatory and painkillers, when entering the body, are not completely dissolved in it. Their remains are excreted by the kidneys, often causing the accumulation of urates in this organ.
Analysis transcript
To determine the salt level, inorganic urine sediment is specially isolated. For this purpose, physical and biochemical research is used. Normally, in a healthy person, crystalluria is absent or detected in very small quantities. The detection level of urates, phosphates and oxalates is indicated by a + sign. Where one plus indicates the minimum level of salts, two – moderate, three – high, and four – significant. When receiving a result of ++ or higher, prevention should begin, and from +++, treatment of microurolithiasis, since this indicator indicates the presence of pathological processes in the body.
Teas to eliminate oxalates
Herbal teas will help reduce the level of salts in urine. Moreover, in folk medicine there are a huge number of recipes to eliminate this problem.
A collection of pear and black currant leaves has proven itself to be excellent in the treatment of oxaluria. The former will need 100 grams, and the latter – 300. These ingredients should be mixed and placed in a glass container. To prepare healthy tea, you need to pour boiling water over one spoon of dried leaves and leave to infuse. It is advisable to take the resulting drink an hour after a meal.
There is another no less effective tea recipe, to create which you will need pear and apple leaves, as well as its dried fruits. You should brew them in a thermos and leave them to brew overnight. This decoction can be consumed as regular tea during the day.
In most cases, such a diet is prescribed for 2 weeks, and then the patient must re-test his urine to monitor the dynamics of treatment.
Prevention
Considering that crystalluria is practically not accompanied by severe symptoms, for prevention purposes you should periodically take urine tests. In addition, it is necessary to eat a balanced diet, avoiding the predominance of one or another food in the diet, as this can cause disruptions in mineral metabolism and lead to the appearance of salts in the urine.
It is strictly not recommended to drink unfiltered water, as it contains many foreign substances that can cause various disorders in the body. If you have the slightest ailment, you must always seek qualified help. All these recommendations are quite simple to follow, but with their help you can prevent the development of serious diseases.
Reasons for the appearance of salt in urine
An unhealthy diet is a direct path to excess salt in urine.
Crystals in the urine settle when its pH changes. Urates and oxalates are formed by salts of acids, and phosphates by alkalis. Most often, the cause of pH imbalance is errors in the diet. An increased content of protein products in food, which contain purine, causes the formation of urate stones. The appearance of salts in urine is associated with hormonal imbalance, severe physical activity or fever. Low or excessive fluid intake also leads to the formation of kidney and bladder stones. The appearance of oxalates is associated with the consumption of foods rich in vitamin C. Thus, the reasons for the appearance of salts in the urine are varied and indicate metabolic disorders, which are most often reversible. In addition, men are more susceptible to the disease, since their white blood cell count is slightly lower.
Drugs
Oxalate or urate crystals in the urine appear when taking the following medications:
- antibiotics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
Pharmaceutical products change the acid-base balance of urine and also increase the content of microelements in the body. Antibacterial drugs inhibit kidney function and, as a result, the organs cannot remove excess salts and reduce salt concentrations. An increase in their number in urine leads to the formation of stones.
Patient nutrition
An increase in the salt level in a general urine test indicates errors in the diet. This is facilitated by salty foods, an increased concentration of food of animal origin in the menu, or a lack thereof. If urate or oxalate levels are found in urine in large quantities, then the food consumed shifts the urine pH to the acidic side. It is caused by eating chocolate, cheese, alcoholic drinks and mushrooms. Increased phosphate levels mean an advantage in eating vegetables and fruits.
Circulation problems
A lot of salt in the urine appears in people with infectious and other kidney diseases, which cause disruption of normal blood flow in them. As a result, the process of urine filtration in the glomeruli is disrupted. This contributes to a violation of the pH of urine in the acidic or alkaline direction, which means an increased risk of stone formation. Also, disruption of local blood flow may be associated with kidney injury, atherosclerosis of the great vessels, or prolapse of organs due to weakness of the ligamentous apparatus. Therefore, salts that appear in urine can be treated only after the underlying disease has been eliminated.
Dehydration
Water imbalance is one of the factors in the formation of salts in urine.
Increased levels of salts in the urine develop with a lack of water in the body and indicate the influence of such factors:
- vomit;
- overheating in the sun;
- heatstroke;
- high body temperature;
- intense physical activity;
- increased sweating;
- diarrhea;
- insufficient fluid intake.
What contributes to the formation of crystalline substances in urine?
Excess salts in urine are the result of exposure to various unfavorable factors on the patient’s body. Such a condition can be diagnosed only after conducting an appropriate study. The main causes of salt in urine are the following disorders:
- Dehydration – when a person does not drink enough fluid per day, his secretions become more concentrated. A large amount of crystalline substances are formed in them, because in such a situation they simply do not have time to evacuate from the patient’s body in a timely manner. Fluid loss increases and accelerates during active physical activity. If timely excretion of urine does not occur, metabolic products crystallize, settling in the secretions and on the tissues of the body.
- Wrong diet - a balanced diet is of great importance for maintaining normal urine. It is unacceptable to include in your menu too many products containing excess oxalic acid (dark chocolate, tomatoes, sorrel, sweet and sour berries). In this case, cauliflower, dried apricots, watermelon, prunes, and currants will help neutralize the increased salt in the urine. The likelihood of salt crystals appearing in the discharge increases significantly after prolonged consumption of monotonous food (improper diets), consumption of alcoholic beverages, canned food, feta cheese and cheese, and smoked meats.
- Use of medications - many medications have a rather complex chemical structure, so some of their components are not completely eliminated from the body. Some substances do not dissolve in water and form salts in the urine of men and women.
- Infections of the genitourinary tract - the penetration of harmful pathogens of a bacterial or viral nature into the human body disrupts all its activities. In this case, the acid-base balance changes dramatically - as a result, the salt content in the urine increases, and insoluble crystals form a characteristic precipitate. Such diseases include urethritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis.
- Impaired tissue circulation - due to insufficient supply of cells and organs with nutrients, a functional failure occurs in the patient’s body. At the same time, the performance of the kidneys decreases, and inorganic compounds begin to be washed out of the patient’s body. They collect in urine, where they subsequently form salt crystals.
Tips for cooking with oxalates
For patients suffering from this disease, it is better to bake or steam food. It is advisable to avoid raw smoked and fried foods. In order not to harm the functioning of the kidneys, it is not recommended to eat salty and spicy foods, as well as spices.
A diet with an increase in oxalic acid crystals in urine suggests including in the menu a huge amount of foods rich in B vitamins. Therefore, it is worth introducing bananas, millet, pearl barley, barley and buckwheat, chicken meat, peas and rye flour into the diet. If there is a lack of such vitamins, the patient must take courses of medications containing them.
It is advisable to include seaweed in your daily menu. This food additive is useful, and it can also be added to various dishes during cooking, especially if oxalates are detected in the urine. The diet, one might say, with such seasoning becomes more effective.
Types and norms
Urine consists of 95% water and only 5% protein, salt and acid. In laboratory studies, attention is paid to the deposited sediment. An increased concentration of urates or oxalates is formed due to a lack of fluid or taking specific medications. If salt deposits are detected systematically, this is a reason to undergo a thorough examination to identify the disease.
Based on their acid composition, there are 3 types:
- calcium and ammonium salts of oxalic acid – oxalates;
- uric acid salts - urates;
- salts of phosphoric acid - phosphates.
A special scale allows you to determine the rate of crystals in the urine. A laboratory report can have a value from 1 to 4. A value of 1–2 pluses is considered optimal, if there are more of them, this indicates pathology.
Urine testing also involves determining its pH level. Usually urine is neutral, but under the influence of a number of reasons it can change, and accordingly, salts characteristic of a particular environment will precipitate.
The following salts are found in acidic urine at a pH below 5.5:
- Uric acid, which gives a brown-yellow precipitate.
- Hippuric acid.
- Urates form a red-brown precipitate.
- Calcium acid phosphate.
- Calcium sulfate.
Calcium oxalate is detected in urine at a pH of 5.5 to 6.
In alkaline urine at a pH above 7, the following salts are formed:
- Amorphous phosphates.
- Tripelphosphates.
- Calcium carbonate.
- Ammonium urate.
In pathological processes in urine the following is detected:
- cystine;
- leucine;
- tyrosine;
- cholesterol;
- bilirubin;
- fatty acid crystals;
- hematoidin;
- hemosiderin.
The number of leukocytes in the urine is determined to identify inflammatory processes that could lead to sedimentation.
Interpretation of research
When studying a urine salt test, pay attention to such indicators as:
- color;
- transparency;
- density;
- pH level;
- amount of sediment;
- norm of protein, glucose.
The color of urine varies from light yellow to straw depending on the concentration, and it should be clear. Density varies from 1012 g/l to 1022 g/l. A pH of 4 to 7 is considered optimal.
Protein occurs in small quantities up to 0.033 g/l, glucose levels are allowed up to 0.8 mmol/l. There should be no sediment.
For men and women of each age group, there are different standards for compounds in the urine. Based on the degree of deviation from them, a preliminary diagnosis can be made.
Increase in children
When conducting tests in children, the presence of urates is most often detected. Oxalates are characterized by formation not only in alkaline, but also in acidic environments, while phosphates are more often formed in alkaline environments.
It is necessary to take into account that the appearance of crystals in urine in childhood and adolescence may be associated with the consumption of a special group of foods with a high content of purine bases.
Such dishes include meat broths and meat, offal and legumes.
It is necessary to use smoked foods, mushrooms and chocolate in a child’s diet in minimal quantities. The presence of crystals is often caused by all sorts of congenital disorders in metabolic processes. Against the background of their occurrence, in this case, diseases such as kidney inflammation and urolithiasis develop. In addition, children may experience increased oxalate levels due to the following diseases:
- Pyelonephritis;
- Diabetes;
- Ulcerative colitis;
- Intestinal lesions.
Phosphate levels may increase in completely healthy children. This process is associated with overeating, as a result of which the level of uric acidity is significantly reduced.
In addition, sedimentation is observed in childhood during the gastric lavage procedure.
Salt crystals in pregnant women
During the period of bearing a baby, expectant mothers may experience urine stagnation and untimely outflow, and toxicosis and frequent vomiting dehydrate the body. Taste preferences also change, a woman consumes what she can eat at the moment, and other necessary foods drop out of her diet. Hormonal changes affect the entire body, as a result of which metabolic processes slow down and often too many salts are formed.
Some diseases worsen during this wonderful period, so pregnant women are prescribed a large number of tests every 2-3 weeks. Such careful monitoring allows you to avoid negative consequences arising from excess crystals.
Choice of treatment depending on results
When removing excess salts from the body, an integrated approach is required. Conservative treatment will not bring results if you do not start leading a healthy lifestyle and eating rationally. To eliminate crystals, you can also use alternative medicine, but only as part of the main therapy and after the recommendation of your doctor.
Nutrition
To remove excess salt from the body, you need to change your usual diet.
- Drink at least 1.5-3 liters of fluid per day (its volume depends on gender, weight category and physical activity).
- Reduce salt intake (it is advisable to eliminate it completely for the first days, after 2-3 days, consume no more than 1-2 g per day).
- Eat sea salt, as it is healthier than table salt.
You need to eat regularly. Portions should be small. Excluded from the diet:
- fatty and fried, with a high content of spices and seasonings;
- fast food;
- canned and pickled;
- semi-finished products;
- carbonated drinks;
- coffee Tea.
Products with a diuretic effect also help eliminate salts. These include any green vegetables, citrus fruits, beets, and onions. It is best to consume them without heat treatment. You can make juices, salads, or eat them raw from fruits and vegetables.
Folk remedies
To remove salts using folk remedies, you can use regular rice:
- 3 tbsp. l. rice pour 1 liter of cool water. Let it sit overnight. In the morning, drain off the excess liquid and add new liquid. Cook over low heat for 5 minutes. After this, rinse the cereal and put it on the stove for another 5 minutes. Repeat these steps 4 times. The resulting porridge is consumed warm. Approximately 3 hours after preparation.
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. rice with cold water. Let it brew overnight. After this, cook over low heat without adding salt. Eat the resulting porridge on an empty stomach. After this, you can have breakfast only after 4 hours.
This treatment lasts 10 days. During this period, it is necessary to include fruits, dried fruits, and vegetables in the diet.
Symptoms and signs of occurrence
All types of crystalluria have similar symptoms. Clinical manifestations of the pathological process can be divided into 2 phases. What does it mean? At the beginning, a person may not notice any changes in the body. Crystals gradually accumulate and as soon as there are enough of them to disrupt the functioning of the urinary system, the second phase of the process begins. It is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Reducing the amount of fluid consumed. As a result, water-electrolyte imbalance occurs with a decrease in the amount of urine excreted. Insufficient fluid levels contribute to the deposition of salts in the kidneys;
- Impaired normal functioning of the kidneys. This condition is characterized by the accumulation of toxic metabolic products that cause poisoning of the body. A person may feel a headache and other unpleasant sensations, such as itching;
- Periodic nagging pain in the lower part of the sleep.
- Urinary dysfunction. Characterized by pain, stinging, unpleasant sensations;
- Changes in the color and smell of urine. The urine becomes cloudy and has an unpleasant odor.
How does the presence of salts manifest?
Crystals may not reveal themselves for a long time. The absence of obvious discomfort leads to the fact that the concentration gradually increases, resulting in the formation of kidney or bladder stones.
Symptoms of acute disease:
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the lumbar region, gradually spreading to the entire pelvis;
- difficult and painful urination;
- change in urine color, cloudy sediment;
- general weakness, body aches.
If you have at least two symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. High salt concentrations can be very dangerous.
Types of salts
Crystalluria involves the presence of various types of salts in urine. There are three of them in total. It is from these that kidney stones are formed. In some cases, stones may combine several types of crystals.
The first category is urate salts. Such salts appear against the background of acid-type reactions. The cause of the appearance can be fever, excessive zeal in the gym, dehydration and even leukemia. Diseases of the kidney tissue cannot be ruled out. Speaking of non-pathological reasons, consumption of smoked meats, meat, and strong tea can trigger an increase in urate levels. The detection of such precipitation indicates that the diet needs to be varied with foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and zinc. It is important to take vitamins A and B.
Calcium oxalate in urine can be detected against the background of diabetes mellitus, ulcerative colitis, pyelonephritis, intestinal lesions and poisoning. In this case, treatment consists of taking large amounts of fluid. It is recommended to switch to oats, millet and seaweed. You can replace ordinary water with a decoction of birch, strawberries, and spur.
The formation of phosphates most often occurs against the background of an alkaline reaction; it appears against the background of cystitis, vomiting, fever or during overeating. An increased amount of parathyroid hormone cannot be ruled out.
In the analysis, the presence of such crystals is indicated by a plus sign, and their number can range from one to four. If the analysis has no more than two pluses, then this is a normal indicator. Exceeding is already a deviation. It is important to note the presence of some crystalline species, which always indicate the presence of pathology in the body. We are talking about salts of hypuric acid, accumulation of cholesterol, bilirubin, leucine, hematoidin and irosine. Normally, the kidneys should not produce such substances.
How to withdraw?
You can remove excess salt with the help of special medical diets, normalizing water balance and eliminating bad habits.
Having found out which salts are in excess, the doctor prescribes drug therapy:
- Pyridoxine and magnesium oxide are used to remove oxalates.
- To get rid of excess phosphates, drugs are used that slow down the secretion of gastric juice.
- With an increased amount of urate, Asparkam and Blemaren are prescribed.
Important! You cannot use medications on your own without consulting a doctor. Without accurate knowledge of the type of salt found in the urine, this is fraught with additional complications and the exact opposite effect.
Nutrition and diet
Each type of salt has its own diet.
If there is an excess of urates, foods with increased amounts of vitamins A, B, potassium, magnesium, and zinc are introduced into the menu. The emphasis is on dairy foods and vegetables. Alkaline mineral water is also indicated.
If there are oxalates in urine, it is recommended to introduce more grains (oats, wheat), seaweed, citrus fruits and other foods containing vitamin B6 into the diet.
To get rid of phosphates, it is recommended, firstly, to reduce the amount of salt consumed, or better yet, completely eliminate it from the diet, and secondly, to increase the intake of foods rich in vitamin D and calcium: eggs, liver, fish, milk.
Attention! You need to gradually increase the amount of recommended products.
Folk remedies
This is not a panacea, but they help remove large amounts of salt from the urine, which means they can be used within reasonable limits.
To get rid of urates, decoctions of birch buds, strawberry leaves, dill seeds and corn silk are used.
Freshly squeezed juices of carrots, parsley and rowan berries work well with other types of crystals.
Normal indicators
The generally accepted scale of permissible uric acid content in urine:
- Infants and children of the first year of life – 0.35–2 µmol/day.
- From 1 year to 4 years – 0.5–2.5 µmol/day.
- Children from 4 to 8 years old – 0.6–3 µmol/day.
- From 8 to 14 years – 1.2–6 µmol/day.
- Adults and adolescents over 14 years of age – 1.5–4.4 µmol/day.
There should be no deviations either up or down, otherwise this is regarded as a possible development of pathology.
What will it reveal?
Daily urine analysis reveals the presence of the same salts as in OAM.
Urats
These are sodium and uric acid salts that have precipitated. Their occurrence in urine is not dangerous. Most often, this occurs when drinking alcohol or eating a poor diet. Urates can also form as a result of heavy physical exertion and systematic fasting.
To bring this indicator back to normal, you need to reduce your alcohol consumption (or better yet, give it up completely) and start eating rationally. Carefully ensure that the body receives all the nutrients it needs.
Phosphates
If there are phosphates in urine, the collected material has a cloudy tint. A burning sensation occurs during urination. This pathological condition indicates the development of cystitis, alkaline diathesis (uraturia).
Oxalates
Elevated levels of oxalates indicate the occurrence of urolithiasis. Sometimes such deposits can be manifestations of infectious pathologies, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
If oxalates are detected in the urine, a repeat test is prescribed. If it gives the same results, the doctor conducts a full diagnostic examination and makes an accurate diagnosis. Only after this the necessary therapy is prescribed.