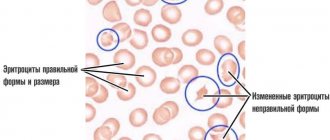
Lymphocytes are cells of the immune system from the group of leukocytes.
A large amount is called lymphocytosis, and a reduced amount is called lymphocytopenia (or lymphopenia). The level of lymphocytes is indicated in a general blood test. The exact number and proportion among all protective bodies is reflected in the leukocyte formula. Lymphocytes are synthesized in the bone marrow, mature and differentiate in the lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen. Little bodies live from several hours to several decades. Their role is to recognize foreign material that has entered the body and produce antibodies to it. Deviations in lymphocyte counts from the norm may indicate disease.
The essence and types of cells
When assessing the results of a clinical blood test, special attention is paid to leukocyte parameters. These cells reflect the presence of pathological processes in the body, and the relationship between the bodies demonstrates the nature of the changes. According to the leukocyte formula, allergic reactions, autoimmune, infectious, inflammatory, and tumor processes can be detected. The intensity of unfavorable changes is determined by the degree of deviations. Lymphocytes reflect the immune response to what is happening.
The tasks of these cells are different. They carry out humoral immunity by triggering the synthesis of antibodies. The role in cellular immunity is to destroy target cells. Lymphocytes are recognized as “warlords” among all protective bodies. They recognize foreign genetic material, analyze it and, if necessary, send leukocytes with special functions (eosinophils, basophils, monocytes) to them. To stop the “enemy” as quickly as possible, the cells send neutrophils (cells that respond to inflammation immediately) to them.
With increased viability, lymphocytes can function for years. These are memory immune bodies. If necessary, and if they encounter infection again, they resume the production of specific antibodies. Lymphocytes perform various functions. There are 3 different groups:
- T cells. They differentiate in the thymus (thymus gland), make up 70% of the total number, and are found in maximum numbers in children. They are divided into highly specialized cells. Receptor T lymphocytes recognize foreign genetic material and make it visible to the immune system. Helper T cells introduce protective bodies to potentially dangerous antigens. Killer T cells can destroy the pathogen itself and tissues damaged by it, and suppressor T cells control the intensity of immune reactions and, if necessary, restrain them.
- B cells. Lymphocytes of this type are concentrated in the lymph nodes, where they first encounter pathogens. These are “memory cells” that store information about infections and activate the production of antibodies.
- NK cells. This smallest group (5‒10%) is called natural killers. Cells have cytotoxic properties - they can produce substances that destroy or suppress the activity of pathological structures. Most often, such lymphocytes “work” against mutated or degenerated cells in the human body.
The number of lymphocytes in the blood determines the activity of the immune system. At the end of the life cycle, the bodies enter the spleen, where they are destroyed.
Lymphocytes are below normal: what does this mean and what diagnostic methods are used?
Blood donation is the most effective and common way to diagnose lymphopenia
Absolute or relative lymphopenia can be detected using a blood test. However, due to the lack of specific symptoms, examination is usually not prescribed. Lymphopenia is often discovered by chance, only during an examination for other reasons. The situation does not change until the patient complains of recurring infections. If immunodeficiency is suspected, the doctor may initiate examinations. In these cases, a blood test can provide information about the absolute numbers and relative distribution of various white blood cells as well as lymphocytes.
To find out if an adult has low lymphocytes in the blood, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following tests.
A complete blood count measures different components: it analyzes the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets and can thus determine whether there is a deficiency of white blood cells.
Lymphocytes represent only a small percentage (20-40%) of white blood cells. A complete blood count can determine the total number of leukocytes, but is not able to detect lymphopenia. Also, a blood test cannot indicate signs or symptoms of lymphopenia.
Flow cytometry examines the different types of white blood cells in more detail than blood counts using a white blood cell count. Flow cytometry can measure the concentrations of different types of lymphocytes: T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes and NK lymphocytes.
Testing can help diagnose lymphocytopenia. The absence of T cells can be caused by various autoimmune diseases. Infectious pathologies can lead to a decrease in B or NK lymphocytes.
Lymph nodes are part of the immune system and are found in different areas of the body. During a physical examination, your doctor can find out if your lymph nodes are enlarged. If lymphocytopenia occurs, they will likely be slightly enlarged and reddened. The lymph node in question must be removed and sent for histological examination.
Norms for the content of lymphocytes in the blood
To determine the number of immune cells, a clinical blood test is prescribed; in some laboratories it is positioned as a detailed one, with a leukocyte formula or leukogram. In the results, cells are designated LYMPH, LY, or LYM. Not only quantitative indicators per unit volume of biomaterial are important, but also the proportion of lymphocytes among other bodies, reflected in %.
Table - Normal leukogram values
| Leukocyte type | Share, in % | Absolute indicator, 10⁹/l |
| Band neutrophils | 1‒6 | 0,04‒0,3 |
| Segmented neutrophils | 46‒72 | 2,0‒5,5 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5‒5 | 0,02‒0,3 |
| Basophils | 0‒1 | 0,0‒0,065 |
| Monocytes | 19‒37 | 0,09‒0,6 |
| Lymphocytes | 3‒11 | 1,2‒3,0 |
White blood cell levels are the same for men and women. The level of lymphocytes changes as a person grows older and the immune system improves. In adults, slightly reduced corpuscle counts are observed, which is associated with the natural decline of the bone marrow and thymus gland.
Table - Lymphocyte norms by age
| Population category | Proportion among leukocytes, % | Absolute quantity, *10⁹/l |
| Up to a year | 45‒70 | 2‒11 |
| Up to 2 years | 39‒60 | 3‒9 |
| 2‒4 | 33‒50 | 2‒8 |
| 4‒10 | 30‒50 | 1,5‒6,8 |
| 10‒18 | 30‒44 | 1,2‒5,2 |
| Adults | 19‒40 | 1‒4,8 |
Deviations from the norm of up to 10% are not considered a cause for concern. The minimum acceptable values are 19% or 1*10⁹/l. If the level is lower, lymphocytopenia is stated. The condition is considered relative if there is an increase in other types of leukocytes, or absolute if the concentrations of all cells are reduced at the same time.
An increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood of an adult of more than 5*10⁹/l when their share among other protective cells is more than 41% is called lymphocytosis - read more about this condition in the article “Increased lymphocytes in the blood.”
Decoding the results
Abs lymphocytes are the main component of the leukocyte group. Their purpose is to penetrate the center of the lesion and fight the slightest infection. Standard indicators may differ depending on the gender and age of a person.
There are three groups of lymphocytes:
- Group B. Formed in lymph nodes. Responsible for identifying foreign proteins and producing antibodies for protection.
- Group T. The most numerous group of cells, divided into three subgroups. Produced by the lymph nodes and thymus gland. The action of this group is aimed at destroying cells affected by pathogenic organisms. They regulate the activity of the immune reaction, accelerating it or stopping it.
- NK Group. Destroys cells that have changed their structure due to damage by infectious agents.
Important information: What does it mean to have an increased average platelet volume in a blood test in an adult?
A blood test for lymphocytes allows you to determine their relative and absolute quantity in the blood. The number of lymphocytes in an adult is 18-40 percent of the total number of leukocytes. In children, this indicator depends on age; by the age of 17 it reaches the level of an adult. Only 2% of the total number of lymphocytes moves with the bloodstream throughout the body. The rest are in bone tissue.
If lymphocytes are below normal and the levels reach a critically low point of 13% or less, you should immediately take a blood test to find out why the levels are low. Reduced LYM values may indicate the development of acute infections or purulent processes.
The level of lymphocytes is affected by taking certain types of medications. Drugs used in the treatment of cancer during chemotherapy are particularly toxic.
A rapid change in white blood cell levels occurs in a person in shock.
What does lymphopenia mean?
Lymphocytopenia is a laboratory term that means there is a problem in the body. After discovering the fact, it is necessary to figure out why there are not enough cells. There are several mechanisms by which a deficiency of immune cells is formed:
- lymphocytes are produced in small quantities by the bone marrow;
- enough precursor cells are produced, but the process of their maturation and differentiation is disrupted, then few full-fledged and functionally active bodies enter the blood;
- synthesis and maturation proceed normally, but lymphocytes are actively consumed (they die prematurely in the spleen or are destroyed by foreign agents);
- the balance is disturbed due to other white blood cells (too many cells of a certain type are produced).
According to the etiology, lymphocytopenia can be congenital or acquired. With the first, a person is born. They are caused by pathologies that are transmitted along with genes or accompany developmental abnormalities. For example, in severe combined immunodeficiency, there is a lack of bone marrow function. In Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, lymphocytes are intensively destroyed.
Acquired lymphocytopenias appear during a person’s life. Most often they are provoked by somatic pathologies, protein-energy deficiency, lack of enzymes, infectious diseases (viruses, AIDS).
Iatrogenic lymphopenia is a result of the use of certain medications. Cell deficiency can be caused by chemotherapy drugs, glucocorticosteroids, and antilymphocyte immunoglobulin. Acquired lymphopenia can be the result of the development of autopathologies (rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism of the joints and heart, systemic lupus erythematosus).
What are lymphocytes, their functions
Lymphocytes are one of the types of leukocytes, they account for about 40% of their total number in adults, 50-75% in children. This is necessary to strengthen the protective function of the child’s body until the immune system is fully strengthened.
Lymphocytes are able to directly interact with the pathogen, destroying it. They activate the process of synthesis of protein antibodies, which neutralize toxins and stop the proliferation of infectious agents. According to the modern classification, there are 3 types of lymphocytes with characteristic functional features:
- B cells are responsible for the humoral type of immunity. They turn into plasma cells that secrete antibodies, or into memory cells, which allows for a rapid immune response upon repeated contact with the antigen;
- T cells – destroy infected and cancer cells of the human body;
- NK cells - destroy those infected or mutant cells that do not recognize T lymphocytes. Play an important role in the antiviral response to HIV.
Main article: Meet our bodyguards - lymphocytes!
Causes of low lymphocyte count
Acute and chronic purulent-inflammatory processes in the body can provoke relative lymphocytopenia. With them, all the forces of the immune system are directed towards the production of neutrophils (cells that regulate inflammatory reactions), while the reserves for other leukocytes are reduced. This situation occurs when:
- pneumonia;
- abscesses;
- phlegmon;
- osteomyelitis;
- tuberculosis.
In autoimmune diseases, active production of protective bodies is observed only at first. As the pathology worsens, the body's reserves are depleted. In addition, during autoimmune reactions, one’s own cells are attacked by one’s own immunity, which can also be reflected in the leukogram. This is observed in scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and dermatomyositis.
The most common cause of lymphopenia is viral diseases. The most dangerous for the immune system is HIV. When infected, T lymphocytes are affected. At first, this manifests itself as leukocytosis (with the active production of other protective bodies), later the body’s strength is depleted and the level of all cells rapidly drops. Lymphopenia can be caused by measles, chickenpox, herpes, and yellow fever.
Lymphopenia due to adverse effects on the body from the outside is quite common. These include radiation, contact with chemicals, radiation therapy, medication, acute and chronic poisoning. With all of them, the work of the bone marrow is suppressed, which leads to a decrease in the level of all blood elements, but lymphocytes are the first to suffer.
A significant decrease in the number of cells is observed in bone marrow pathologies (Fanconi anemia, aplastic processes in stem cells). In this case, the tissues that should synthesize the bodies stop performing their functions or produce inferior, useless cells. In diseases of the lymphatic system (lymphogranulomatosis, lymphosarcoma, etc.), the process of differentiation of protective bodies is disrupted, resulting in a decrease in the level of lymphocytes.
Useful information: Bilirubin in urine is increased: more than 3 reasons, what does this mean, normal, treatment in adults and children. What diseases can it talk about?
Deficiency of white blood cells develops against the background of a long course of somatic diseases:
- liver pathologies (cirrhosis, viral hepatitis);
- splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- heart failure;
- renal dysfunction;
- multiple sclerosis, etc.
Abnormalities in clinical blood tests in women can be caused by hormonal changes. In the pre- and menopause, during pregnancy, as well as when the balance of hormones changes during the menstrual cycle, the activity of the immune system also changes. As a rule, the decrease in lymphocyte counts does not go beyond normal limits, however, in the presence of predisposing diseases, deviations can be more significant. During pregnancy, a reduced number of lymphocytes may be due to natural immunodeficiency, which is provoked by hormones and aimed at maintaining pregnancy.
In men, fluctuations in the leukogram are caused by bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse), excessive physical activity, severe stress and psycho-emotional shocks.
With relative lymphopenia in children, chronic and acute infectious diseases are suspected. If the assumptions are not confirmed, a comprehensive examination is necessary to exclude pathologies of the hematopoietic system, leukemia and other life-threatening conditions.
Analysis procedure
It is performed in the morning on an empty stomach, the material is taken from the toe or heel of one year old children. Upon delivery, the puncture site is wiped with alcohol, a puncture is made and the sample is collected in a flask, which is signed and sent for analysis.
Taking blood from the baby's heel
General rules
A number of rules will need to be followed:
- The last meal should be taken in the evening; you cannot include foods containing a lot of spices or fat, otherwise this will affect the material sent for analysis.
- In the morning, you should awaken your body with a glass of water on an empty stomach.
- Morning brushing will need to be canceled due to the possibility of toothpaste getting into the mouth and subsequently into the blood.
- The day before the test, stop taking medications and notify your doctor about the course of treatment.
In infants:
- In infants, material is collected on a full stomach.
- The procedure is carried out at the right time of day; feeding is allowed 2 hours before blood sampling.
If you need to track the dynamics of changes, a clinical study is carried out a certain number of times, at the same time.
Could there be symptoms?
In most cases, lymphopenia is discovered incidentally during a preventive or diagnostic examination. A blood test is considered the main way to assess the general condition of the body, and therefore it is prescribed to almost all patients, regardless of complaints and the reason for going to the hospital.
Minor deviations in the blood formula rarely show any symptoms. Clinical signs occur in the later stages of disease development, when irreversible changes occur in the body. Lymphocytopenia has no specific symptoms. The condition can be suspected by the manifestations of the provoking pathology. Often this is:
- weakness, fatigue, decreased ability to work;
- irritability, sleep disturbances, psycho-emotional lability;
- changes in the size and sensitivity of lymph nodes, tonsils;
- enlarged spleen (noticeable by asymmetry of the abdomen, pressing pain on the left);
- hair loss;
- dryness, peeling, pale skin, pustular rash;
- tendency to colds and ARVI;
- change in body temperature (usually evening low-grade fever).
The disease may not manifest itself at all. Some pathogens are capable of latent persistence in the body. You should contact a general practitioner and undergo basic tests in case of any health problems, without waiting for the situation to worsen.
Norm of lymphocytes
To make a preliminary diagnosis and determine possible deviations, it is necessary to correctly pass the test.
Rules for donating blood during examination:
- On an empty stomach.
- No physical activity before the procedure.
- Without taking medications that could affect the results.
When checking blood, two indicators of lymphocyte levels are distinguished:
- Absolute.
- Relative.
Absolute is the number of cells per 1 liter of blood multiplied by ten to the ninth power. Relative – shows the percentage relation to other types of leukocytes.
If everything is done correctly, the norm of lymphocytes should be as follows:
Category of the subject; results
| Adults | 1 – 4, 5 |
| Up to 21 years old | 1 – 4, 8 |
| Up to 10 years | 1, 5 – 6, 5 |
| Up to 6 years | 1, 5 – 9 |
| Newborns | 2 – 11 |
In pregnant women, lymphocytes may be lower than normal, which is natural . To exclude pathological processes in the body, monitoring by a specialist is necessary. If a woman follows all the recommendations of her attending physician, such a decrease will not cause any consequences.
If in infants lymphocytes remain at a high level, then in adults the absolute number is reduced to 4.8 . Even if the indicators are reduced to 1, there will be no cause for alarm. When the absolute number of lymphocytes is less than 1, they speak of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems.
Diagnosis of diseases
Determining the causes of lymphopenia is the main task when detecting abnormalities. Only by correctly establishing the diagnosis can you choose therapy. Flow cytometry (an in-depth blood test) may be ordered to determine which cells are missing.
Lymphocyte activity is determined using immunoglobulin analysis. To detect infectious diseases, PCR diagnostics are prescribed (for HIV, cytomegalovirus, tuberculosis, etc.). To find somatic pathologies, a biochemical blood test, ultrasound of internal organs, MRI or CT are prescribed. To determine functional activity or malignant processes in the bone marrow, a biopsy is performed.
Diagnostics
It is possible to determine whether lymphocytes are low or not only by conducting a laboratory blood test. In order for the result to be reliable, you should adhere to some rules for the procedure of collecting biomaterial:
- You need to donate blood in the morning, on an empty stomach - at least 8 hours must pass between the procedure and the last meal;
- one day before the procedure, you should stop drinking alcohol, heavy food, and medications - the latter must be agreed with your doctor;
- You need to take the test in a calm emotional state.
If the research results show that the number of immune cells in the blood is significantly lower than it should be based on age, the doctor will order a repeat test in order to eliminate the possibility of error. If the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed, a comprehensive examination is prescribed.
Treatment of lymphopenia
The level of lymphocytes will return to normal on its own if the provoking disease is identified and treated in time. Viral infections are treated with antiviral drugs; for HIV, antiretroviral therapy is used.
Malignant lesions of the bone marrow and lymphatic system are eliminated with the help of cytostatics, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. In severe cases, bone marrow transplantation is used.
For anemia and nutritional depletion, vitamin preparations and a balanced diet are prescribed. In severe inflammatory processes, the administration of class G immunoglobulins (0.4 g/kg, once a week) is indicated. In case of persistent changes, stem cell transplantation is performed.
The causes of lymphocytopenia should be looked for by a doctor. Only a specialist can treat abnormalities. Without specific knowledge, it is impossible to correct the condition, and delay in proper therapy can aggravate the disease and lead to irreversible consequences.
Prognosis of lymphopenia
The prognosis of lymphopenia directly depends on the underlying disease. If lymphopenia occurs without other associated disorders, it may be asymptomatic and without serious complications.
The duration of the course depends on the causative disease. Treatment also depends on the cause and severity of the underlying disease. Most cases of lymphocytopenia do not require therapy. If lymphocytopenia causes severe infections, antibiotics or other treatments may need to be used.
FAQ
Question: How to prepare for a study to exclude false results?
Answer: Before a general blood test, you should not take medications, expose yourself to heavy physical activity or stress, and it is undesirable to consume alcohol and heavy foods (fatty, fried, flour, smoked, canned food). One hour before the test you should not smoke. Before donating blood, you should sit quietly for at least 10 minutes. Women should not take the test during their period. The period after a cold or flu (2 weeks) is unfavorable for preventive examination. At this time, OAC is given to monitor the healing process, on the recommendation of a doctor.
Question: How can I normalize the level of lymphocytes using nutrition?
Answer: You need to eat a balanced diet. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of healthy proteins (turkey, chicken, fish, cottage cheese, seafood), fats (vegetable oils, nuts, dairy fats), carbohydrates (whole grain cereals, vegetables and fruits). You need to saturate your menu with vitamin foods (greens, berries, fresh vegetables). Taking multivitamin complexes (Vitacap, Supradin, Multi-Tabs) will not hurt, but it is better to select them with a doctor, based on the results of a biochemical blood test.
Question: Can the level of lymphocytes decrease due to painkillers?
Answer: Yes, this is indeed possible. Moreover, the indicators of all leukocytes usually decrease simultaneously. Contrary to popular belief, the blood picture can be negatively affected not only by regular use of NSAIDs, but also by occasional treatment with Analgin or Indomethacin. These drugs tend to inhibit the synthesis of blood cells, including protective ones.
Question: Is it possible to improve performance using folk remedies? If yes, which ones to choose?
Answer: It is permissible to use alternative medicine recipes for minor deviations in the blood picture that are not associated with serious pathologies. If there are suspicions of dangerous causes of disorders, it is better to abandon traditional methods in favor of drug therapy, because treatment with untested methods is fraught with serious consequences. To increase the level of lymphocytes, take pine decoction and pollen. As sources of vitamins, it is recommended to consume 100 ml of freshly squeezed pomegranate, beetroot, blackberry, cranberry, pumpkin or carrot juice daily, three times a day.
Question: If the total level of leukocytes is elevated and lymphocytes are decreased, what does this mean?
Answer: Most likely, an infectious-inflammatory process is developing in the body. This may be a viral or bacterial infection of the respiratory, digestive, or urinary system. A thorough examination of the patient, collection of complaints and medical history will help determine the problem.
Treatment
Lymphocytopenia is not an independent disease, so there is no special treatment. To correct its manifestations as much as possible, you need to identify the true cause of this condition and fight it.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, if lymphocytes are low, drugs that stimulate the immune system can be prescribed. Treatment with antiviral or anti-inflammatory drugs may be recommended, since a decrease in lymphocytes may be caused by the development of an inflammatory process.
The list of necessary medications and other treatment methods depends on what disorders have been recorded in the body. Self-treatment can cause complications.
Important information: Norm of lymphocytes in the blood of children (table by age)
In most cases, a full examination is prescribed to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment for the underlying disease.
In some cases, a low blood cell count is a congenital condition indicating an immunodeficiency that appears in the first days of a child's life. Medicine knows methods to combat this problem. The patient surgically receives stem cells from a healthy donor. In most cases, operations end favorably.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a blood test reveals low lymphocytes, adult patients should consult a physician. For children, visit a pediatrician.
ethnoscience
If lymphocytes in the blood are slightly reduced, most often this situation occurs during the period of colds. In this case, you need to improve your immunity.
Traditional medicine recipes will help strengthen your immune system:
- Flower pollen and honey should be mixed in a 2:1 ratio. Eat 1 tsp daily on an empty stomach. mixture with 150 ml of milk.
- At least 3 times a day, drink ½ glass of any fresh juice: pomegranate, beets, blackberries, cranberries, apples, carrots.
- Finely chop fresh pine needles. 5 tbsp. pour 1 liter of hot water. Cook over low heat for 15 minutes. Leave for 2 hours, strain. Add 2 tbsp. honey Take a glass of the product 2 times a day.
Regular consumption of vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins, incl. citrus fruits. It is useful to drink herbal teas and consume natural honey. Rosehip decoction helps not only improve immunity, but also reduce the risk of developing anemia.
The patient's diet should be supplemented with:
- greens, berries;
- beef, poultry, fatty fish;
- cheese, milk;
- legumes;
- nuts.
It is necessary to increase the consumption of clean water to 2 liters per day.
Taking tinctures and decoctions of medicinal plants will help adjust the composition of the blood, but this is not enough. Traditional medicine recipes can only be considered as an addition to the main therapy. In addition, before taking folk remedies, you should consult your doctor.
conclusions
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. These cells participate in the functioning of the immune system and reflect its state. A decrease in the level of corpuscles is observed when:
- dysfunctions and malignant lesions of the bone marrow;
- diseases of the lymphatic system;
- chronic intoxication;
- the presence of foci of inflammation in the body;
- infectious diseases.
The cell level will return to normal after the provoking factor is eliminated. Progressive lymphopenia provokes a decrease in the body's resistance to infections and can end in disaster.
A number of autoimmune and infectious diseases at the beginning of their development may be accompanied by an increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood. Read about this in the article “Elevated lymphocytes in blood tests in adults and children: what does lymphocytosis mean. Symptoms and treatment of the condition."
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of lymphocytopenia is aimed primarily at treating the disease that caused it. For example, if a decrease in the level of lymphocytes occurred due to taking medications, then the only possible treatment would be to replace the medication. If the lack of cells is a congenital condition, then the patient is prescribed intravenous administration of gamma globulins. Although this method will not eliminate lymphocytopenia, it will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing infectious diseases. If the patient’s diet was low in protein, then he is prescribed a high-protein diet.
Causes
The risk group for lymphopenia includes patients with congenital autoimmune pathologies, chronic viral or infectious diseases, as well as those who expose their body to radiation or chemotherapy.
A serious factor that increases the likelihood of developing the disease is poor nutrition combined with the abuse of bad habits .
Exposure to constant stressful situations, taking potent medications and lack of timely treatment for chronic diseases increase the risk of lymphopenia.
The causes of lymphopenia are the following factors:
- congenital pathologies of the immune system;
- insufficient protein nutrition;
- infectious diseases (including AIDS);
- damage to the structure of the lymph nodes or thymus gland;
- purulent-inflammatory diseases of the acute period;
- long-term or uncontrolled use of drugs from the psoralen group;
- development of cancer;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- diseases associated with changes in blood composition;
- long-term therapy with potent drugs;
- development of intestinal obstruction;
- progression of rheumatic diseases;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome;
- consequences of viral diseases.
Prevention and care
Parents may not be able to completely prevent lymphocytopenia, but there are ways to help strengthen their child's immune system and protect them from infections. Healthy eating, rest, and reducing the likelihood of contact with germs are necessary as the baby's body restores the level of lymphocytes.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
just today
( 39 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)
Increased lymphocytes in the child’s blood: causes of deviations
Increased hemoglobin in men: what does it mean and what to do
Related Posts
How are lymphocytes formed?
The term B lymphocytopoiesis describes the steps in the formation and differentiation of new B cells from their precursors. During intrauterine development, B lymphocytes in the fetus are formed in the bone marrow and liver, and after birth this function is performed only by the bone marrow.
T lymphocytes are produced in the thymus, followed by the destruction of cells with insufficient protective activity. Complete cells enter the systemic circulation and lymphatic vessels.
Natural killer cells are formed from lymphoblasts. There are no cellular receptors or protein antibodies on the surface of mature cells.
Of particular importance is the stage of differentiation, during which cells change in size and shape, and metabolic activity is also transformed due to genetic rearrangements. This is a complex multi-stage process, the correct implementation of which determines the further functioning of all components of the immune system.
Symptoms of lymphopenia in children
Parents may not notice any symptoms of lymphocytopenia in their child. In some cases, children may exhibit symptoms of an underlying disease or condition, such as:
- fever;
- cough;
- runny nose;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- inflamed tonsils;
- joint pain;
- skin rash;
- night sweats;
- weight loss.
Important
If there are any alarming signs, you need to contact a pediatrician and undergo an examination.
Lymphocytes in children: norms, functions
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. They are part of the child's immune system. These important white blood cells circulate in the blood and as part of the lymph fluid. They protect the baby's body by attacking harmful organisms at the first sign of invasion. Lymphocytes also play a key role in initiating other immune actions and help strengthen the child's body's immunity after infections and as a result of vaccinations.
There are three main types of lymphocytes that work together to help identify and eliminate infections and other diseases:
- B cells produce antibodies and signaling proteins that help block or attack bacteria, viruses and toxins.
- T cells seek out and destroy cells that have become infected or cancerous, plus they also communicate with B cells.
- Natural killer (NK) cells contain compounds that can kill cancerous tumor cells and cells infected by a virus.
Low levels of T cells or a deficiency of NK cells can lead to the development of uncontrolled viral or fungal parasitic infections. If lymphopenia predominantly affects B cells, this may lead to an increased risk of various types of infections, including microbial ones.