Most of us are accustomed to considering cholesterol as a harmful substance that must be gotten rid of by any means.
In fact, this component can bring not only harm to the body, but also benefit, and also act as a marker of health.
For example, by the volume of this substance in the blood, one can determine the presence, as well as the degree of development of such dangerous diseases as atherosclerosis, abnormalities in the heart, and hepatitis. Also among the diseases that cholesterol levels can detect is diabetes.
Therefore, quite often doctors, having a suspicion of diabetic processes in the patient’s body, prescribe tests for sugar and cholesterol for patients.
Types of cholesterol and indications for testing
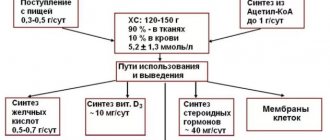
Cholesterol is a natural fatty alcohol that is generated eighty percent by the liver, and the remaining twenty percent is obtained by the body from food. This is a very important component for the whole body.
This:
- Formation of cells, because cholesterol is their building material;
- Production of important sex hormones such as estrogen, cortisone and testosterone;
- Normal digestion, since cholesterol is involved in the process of fat metabolism.
The so-called total cholesterol consists of two components:
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is the fraction of cholesterol that is called “good cholesterol.” It is involved in the creation of hormones, the formation of new cells, and the metabolism of vitamin D. This type of cholesterol acts as a kind of transport, delivering oxygen to the brain. It also collects “bad cholesterol” throughout the body and delivers it to liver cells for elimination.
- Low density lipoproteins (LDL). This species is considered "bad". It is involved in the process of formation of sclerotic plaques. But normally it also performs positive functions - it disarms toxins in the body.
The test results include a result for triglycerides. It is a component of very low density lipoproteins.
Triglycerides are the “creators” of cholesterol plaques.
Chol is involved in lipid metabolism, and its content is of great importance for the whole organism.
Therefore, from time to time, even absolutely healthy people, for the purpose of a preventive medical examination, must take a cholesterol test.
The recommended frequency of testing for healthy people is once every five years for the age group under thirty, and once every three years for people over thirty. Those who already have high cholesterol should be monitored much more often, as prescribed by the doctor, since everything is individual.
Also, this analysis is indicated for people with a potential risk of developing many diseases, such as:
- Diabetes mellitus or prediabetes;
- Overweight or obesity;
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Heart attack;
- Stroke;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
- Hypertension;
- Kidney and liver pathologies.
This analysis can also be prescribed to track the dynamics of treatment with statins or other lipid-lowering medications.
In order to see the overall picture of the patient’s condition, one cholesterol test will not be enough. In such cases, a lipid profile is performed, which contains not only the content of the total level of Chol, but also the ratio of HDL and LDL.
Vitamins A, C, E are powerful antioxidants. Cholesterol penetrates into the blood vessels due to the oxidation process. Antioxidants interfere with this process. Therefore, for prevention purposes, it is recommended to consume these vitamins.
It is important to prepare properly for a cholesterol test.
More information about blood sugar testing
When you are advised to test your blood for sugar, they mean determining the glucose in your blood. Glucose is the main source of nutrition for the cells of our body and provides energy to all organ systems.
The glucose level in the blood is constant and does not go beyond normal limits in the normal state. With some diseases and conditions of the body, it can increase and decrease, even threatening life and health.
Who needs to check blood sugar
Blood sugar is checked:
- if you suspect diabetes mellitus;
- before surgery and invasive procedures performed under anesthesia;
- in patients with coronary heart disease and systemic atherosclerosis;
- routinely, during a medical examination, as part of a biochemical analysis;
- in patients with diabetes mellitus to monitor treatment;
- in patients at risk (obesity, heredity, pancreatic diseases).
Getting ready for analysis
Preparing for analysis involves following some rules:
- take the test strictly on an empty stomach, and at least 10 hours must pass since the evening meal;
- avoid stress and excessive physical activity the day before;
- do not smoke before taking the test;
- If you have a cold, be sure to tell your doctor.
The blood test itself is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach.
It is possible to take blood from a vein in a complex biochemical analysis; to determine only glucose, taking blood from a vein is inappropriate.
Analysis results
The normal level of glucose in the blood of an adult does not depend on gender and is from 3.3 to 5.7 mmol per liter on an empty stomach. If blood was taken from a vein on an empty stomach, the norm is from 4 to 6.1 mmol/l.
There is another unit of measurement - milligram per deciliter. In this case, the norm will be 70-105 mg/dl when collecting capillary blood.
It is possible to convert an indicator from one unit of measurement to another by multiplying the result in mmol/liter by 18.
In children, the norm differs depending on age. At the age of up to one year it will be 2.8-4.4 mmol/liter. In children under five years of age - from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol per liter. Well, with age it comes to the adult norm.
During pregnancy, blood sugar is 3.8-5.8 mmol/liter on an empty stomach. Deviation from the norm may be a consequence of gestational diabetes or the onset of a serious disease. It is necessary to repeat the analysis and if the sugar rises above 6.0 mmol/liter, carry out load tests and perform a number of necessary studies.
Glucose tolerance
Please note that we were talking specifically about a fasting blood sugar test. After eating, your blood sugar level will be elevated for some time. And it will be physiological. To confirm or deny diabetes, a stress blood sugar test is used.
First, blood is taken from a finger to test for sugar on an empty stomach. Then the person being examined is given a glucose solution to drink, and the analysis is repeated an hour and two hours later. This method is called a glucose tolerance test or glucose loading test. It allows you to identify a hidden form of diabetes. Also used when the results of other tests are questionable. It is important not to eat or drink anything during this period, not to be physically active and not to be nervous, so as not to distort the result.
Glucose tolerance test results:
- after an hour – no more than 8.8 mmol/liter;
- after 2 hours – no more than 7.8 mmol/liter.
Based on blood sugar levels on an empty stomach and after a glucose load, hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic indices are calculated.
The hyperglycemic index should be no more than 1.7, the hypoglycemic index should be no more than 1.3. When sugar on an empty stomach and after exercise is normal, and the indices are elevated, there is a high risk of developing diabetes in the future.
Deviations from the norm
When blood sugar is high:
- after eating;
- after significant physical or mental stress;
- when taking certain medications (hormones, adrenaline, thyroxine);
- for diseases of the pancreas;
- for diseases of the thyroid gland;
- in patients with diabetes mellitus and in patients with impaired glucose tolerance.
When blood sugar is low:
- in diabetics with a high dose of glucose-lowering drugs and skipping meals;
- with an overdose of insulin;
- with prolonged fasting;
- with alcoholic delirium;
- in the presence of a pancreatic tumor;
- in case of poisoning with certain poisons (arsenic, chloroform);
- for pancreatitis, gastroenteritis;
- after gastric surgery.
Suspicious symptoms
Signs of high sugar:
- dry mouth;
- increased appetite and constant feeling of hunger;
- increased urination;
- itching of the skin;
- trophic changes in the skin of the lower extremities.
Signs of low glucose levels:
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- headache and nausea;
- fainting;
- impaired consciousness up to coma (hypoglycemic);
- cold and damp skin.
In diabetics, when taking glucose-lowering drugs, glucose levels are very labile. Both high and low blood glucose are unfavorable and sometimes even dangerous. Therefore, constant monitoring is necessary, especially for patients injecting insulin. For these purposes, there is a portable device for measuring blood sugar - a glucometer. Anyone can use it at home to control their glycemic profile.
Procedure for measuring sugar
- We treat the puncture site, from where blood will be taken for analysis, with an antiseptic.
- Using a scarifier, we make a puncture in the area of the fingertip.
- Remove the first drop with sterile cotton wool or a bandage.
- Apply the second drop to the test strip previously installed in the glucometer.
- The next stage is to evaluate the results obtained.
In the modern world, unfortunately, diabetes is a common disease. A blood sugar test allows you to identify pathology in the early stages of the disease, preventing the development of complications. In order for the analysis to be reliable, it is necessary to prepare for the test. The results of the analysis are interpreted by the doctor, as is the treatment, and only the doctor prescribes further examination.
Interpretation of a blood test for INR
Ways to check cholesterol
To explain how cholesterol testing is done, it is necessary to know what kind of testing will be performed, since it can be examined using the following tests:
- Express test;
- Determination of total cholesterol level;
- Detection of high density lipoproteins;
- Detection of low density lipoproteins;
- Lipidogram;
- Triglycerides.
The first item on the list is carried out at home using a special express analyzer. The material for this analysis is capillary blood taken from a finger.
Other types of research require laboratory conditions, and most often, the material for them is venous blood.
All for the war on cholesterol
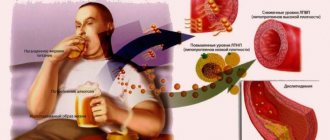
So, we are all afraid of high cholesterol levels. Vessels affected by atherosclerosis can no longer function fully. The functions of the cells and organs to which they supply blood are disrupted. If atherosclerotic plaques have formed in the coronary vessels, the functioning of the heart muscle worsens. If in the vessels of the body, the delivery of nutrients to muscles and organs suffers, and blood pressure begins to rise. If it is in the vessels of the head, then brain function weakens, the speed of decision-making and memory deteriorate.
But before you go on the warpath, don’t forget: you don’t need to completely “harass” cholesterol as a class, you need to learn how to manage your lipid profile and make certain efforts so that the negative side effects of atherosclerosis either do not develop or develop as slowly as possible.
The new drug “Vascular” from the Lekolaik company will help normalize the lipid profile and prevent the formation and calcification of atherosclerotic plaques. The drug contains: natural statin - policosanol, vitamin K2 and selenium. Regular use of Vascular will help prolong and significantly improve a person’s quality of life.
Preparation and execution
There are two ways to carry out the analysis: by collecting capillary blood and venous blood.
The first method is carried out by carrying out analysis with a portable express analyzer. To carry out the procedure you need:
- Turn on the device. (Some express analyzers, when inserting a test strip, have an automatic switching function).
- The fingertip must be wiped with a disinfectant.
- Perform a puncture using a disposable lancet. Sometimes a portable analyzer is used by several family members. If the puncture is performed with a special device, then you need to change the needle in it.
- Apply a drop of blood to the specially marked area of the test strip.
- Wait and evaluate the results.
- Remove the test strip from the device and discard.
When taking an analysis in a laboratory, the procedure proceeds differently. Blood is taken from a vein. And after collection it is analyzed using a special apparatus.
There are rules that must be followed, regardless of whether you do a rapid test at home or go to a laboratory.
These rules are:
- If the patient is taking certain types of medications, then with the agreement of the doctor, they are canceled at the required time interval before the tests are taken;
- You should not drink alcohol a few days before the test;
- On the eve of the analysis, you should not eat fatty, spicy, sweet or flour products;
- On the eve of the study, dinner should be light and taken no later than 18:00.
The analysis itself is carried out on an empty stomach.
Preparation for laboratory tests
If blood tests are prescribed, there are general rules on how to prepare for donating blood for both sugar and cholesterol.
A biochemical blood test must be taken from a vein on an empty stomach. This means that you can eat your last meal 12 hours before the test. You should not drink tea, juice or coffee - this can also distort the results. On the day when blood is drawn, only drinking water in normal quantities is allowed.
The day before the examination, preparation for the test involves eliminating alcohol. You cannot eat fatty meat and fish, fried foods. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of eggs, fatty cottage cheese, fatty and hot sauces. After a heavy meal during a feast, at least two days should pass. Even a light breakfast eaten on the day of the test can completely distort the result.
Before donating blood, please note that you should not smoke for an hour.
If drug therapy has been prescribed or the patient is taking any medications on his own, then the date of the test must be agreed upon with the attending physician. You cannot donate blood while taking diuretics, hormones, or antibiotics.
After diagnostic examinations - radiography, sigmoidoscopy or physiotherapy procedures, at least 24 hours should pass.
On the day of the test, as a rule, intense physical activity is not recommended; the day before you should not go to the sauna.
The question of how to correctly take a blood test for cholesterol or test blood for sugar in various phases of the menstrual cycle in women is not relevant for these types of tests. It is permissible to carry out diagnostics on any day.
To correctly evaluate the results of repeated studies, it is advisable to carry them out in the same laboratory.
Decoding the results
It has already been noted that one cannot say affirmatively that cholesterol is evil, and there is no need to strive to reduce its level for preventive purposes if there is no reason for this. Decreased results are also a deviation from the norm.
Moreover, doctors confirm the information that too low cholesterol levels are an even bigger problem than too high ones, and also lead to a number of diseases. Therefore, you need to stay within normal limits.
In healthy people, it does not exceed 5.2 mmol/l, but does not fall below 3.1 mmol/l. Triglycerides should be in the compartment from 0.14 to 1.82 mmol/L.
The norms for lipoprotein levels are different for men and women. More information about this is provided below.
If the indicators are too high, this may indicate the possible presence of diseases such as:
- Hypothyroidism;
- Congenital hyperlipidemia;
- Pancreas cancer;
- Kidney diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Pathologies of the hepatobiliary system.
Elevated levels may be the result of an unhealthy lifestyle. This is drinking strong alcoholic drinks, excessively eating fatty, fried foods, and eating fast food. Ultimately, these factors lead to obesity. And obesity is one of the first causes of increased cholesterol.
Sometimes pregnant women experience increased levels. In this case, the expectant mother needs to listen to the doctor’s advice and, together with him, adjust the diet.
If cholesterol levels are low, this may indicate the following pathologies:
- Chronic anemia;
- Liver cancer;
- Hypolipoproteinemia;
- Bone marrow pathologies;
- Hypothyroidism;
- Chronic pulmonary pathology;
- Cirrhosis.
In addition to the listed diseases, low levels may be the result of burns, sepsis or acute infections. This condition is also typical for people who are overly addicted to diets based on fasting. Excessive consumption of omega fatty acids also leads to low cholesterol levels.
Whatever the indicators, adjustment of cholesterol levels must be carried out under the guidance of a doctor. You cannot self-medicate. Deviations from the norm are a signal of the presence of serious diseases in the body.
How to get tested?
To determine the level of sugar and cholesterol in the blood, two types of laboratory tests are used: biochemical and detailed analysis. The first of them shows a general deviation from the norm, and the second is more detailed and describes these changes in detail. It is prescribed if the indicator is elevated and a more detailed diagnosis of the condition is required. Blood for biochemical analysis is taken from the ulnar vein into a special sterile tube. Sufficient volume for research is 5-10 ml. Afterwards, the container is placed in a centrifuge, where the material is separated into plasma and dense elements. You can also do a sugar test at home using special monitoring systems (glucometers).
Designations in biochemical and detailed analysis
A detailed analysis is otherwise called a lipid profile. The lipidogram reflects the ratio of all cholesterol indicators: high and low density lipoproteins, as well as readings of triglycerides and atherogenicity coefficient.
Having received the results of the analysis, the patient can see the following designations in the biochemistry results:
- TC or Chol is the designation for total cholesterol. When its values are elevated, atherosclerosis begins to develop. The norm does not exceed 5.2 mmol/l.
- TG or TRIG – triglycerides. Due to the resynthesis of lipid breakdown products, triglycerides are formed. Further, entering into an integral part of transport connections, triglycerides enter the general bloodstream. Standard values should not exceed 1.77 mmol/l.
- HDL or the Russian abbreviation HDL - high density lipoproteins. This is an integral part of total cholesterol, which performs positive functions - it participates in the structure of cells, the production of sex hormones, supplying the brain with oxygen, and the breakdown of fats. HDL also collects excess cholesterol throughout the body and, like a transport structure, delivers it to the liver, where the “bad” cholesterol is subsequently processed and utilized. Thus, this form of lipoproteins prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Normally, levels should not exceed 1.20 mmol/l.
- VLDL or Russian abbreviation VLDL - very low density lipoproteins. Their positive function is that they transport cholesterol and fatty acids to body tissues, as building material. This form of lipoprotein is generated by the liver and then released into the bloodstream. In this process, very low-density lipoproteins are converted to low-density lipoproteins. Normally, VLDL should be no higher than 1.04 mmol/l.
- LDL or LDL in Russian – low density lipoproteins. Their main function is the same as that of other species - the release of cholesterol to tissues. But if this form of lipoproteins is outside the normal range, then many diseases develop, from atherosclerosis to stroke or heart attack.
- IA or KA – atherogenicity coefficient. This is an indicator of the ratio of atherogenic and non-atherogenic forms of lipoproteins. Its normal level is 3.5 mmol/l. An increase in indicators threatens the development of atherosclerosis.
Modern gradations of standards can be viewed in the table:
Determination of the concentration of free and esterified cholesterol in blood serum
Free cholesterol is capable of forming sparingly soluble compounds with digitonin, tomatine, and pyridine sulfate. Most often, an aqueous-alcoholic or isopropanol solution of digitonin is used.
Principle
Cholesterol is extracted from whey using isopropyl alcohol, the extract is divided into two parts, and the content of total cholesterol is determined in one. In another portion of the extract, free cholesterol is precipitated with digitonin, the supernatant is discarded, and the precipitate is dissolved and the content of free cholesterol is determined by any method. The content of esterified cholesterol is calculated as the difference between total and free.
Normal values
| Serum | the fraction of esterified cholesterol makes up 60‑80% of the total |
Clinical and diagnostic value
The cholesterol esterification coefficient is an important functional test of the liver. The decrease in the coefficient is proportional to the decrease in liver function: acute and exacerbation of chronic hepatitis, obstructive jaundice, cirrhosis of the liver. The degree of esterification also depends on the activity of the serum enzyme lecithin-cholesterol acyl-transferase, so storing the sample at room temperature may change the ratio between the free and esterified cholesterol fraction.
Factors on which cholesterol levels depend
When assessing the results, the doctor relies on many factors. It is impossible for one indicator to determine the norm for people of different ages or gender. It is necessary to look at the individual characteristics of each organism. Concomitant diseases are also important to consider.
Normal indicators vary depending on:
- Patient's age;
- Gender;
- Concomitant diseases;
- Individual characteristics (in the case of women, pregnancy).
For each of the presented categories there is a certain norm.
Norms for men
Long-term observations of medical researchers lead to a conclusion. Cholesterol in men rises throughout life. Therefore, for each temporary compartment of a man’s life there is its own norm. This can be clearly seen in the table below.
An adult man needs to keep it normal.
The indicators should be like this:
- Total cholesterol (Chol) – from 3.6 to 5.2 mmol/l;
- HDL – from 0.7 to 1.7 mmol/l;
- LDL – from 2.25 to 4.82 mmol/l.
Table of cholesterol norms for men:
How to prepare to donate blood
Preparation for routine venous blood donation for cholesterol analysis includes several limitations.
- 2-3 days before the examination: limit physical activity, switch to a diet without fatty animal foods, give up alcoholic beverages, do not visit the solarium, gym, do not undergo X-ray or ultrasound examination.
- Before taking the lipid profile: you can’t eat for half a day, you can drink clean still water. Since blood is taken to test cholesterol levels on a hungry and empty stomach, it is better to choose the morning hours to go to the laboratory. In essence, this is how government agencies work: after lunch they no longer take material. Private laboratories are ready to accept a patient at any time convenient for him, but not everyone can endure a 12-hour fast during the day.
- You must refrain from smoking within half an hour to an hour.