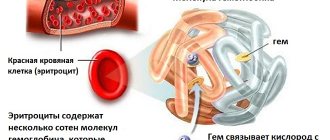
What is the coagulation system
The hemostasis system is very complex, involving many tissue and serum factors. Its launch is really similar to a cascade: it is a chain of reactions, each subsequent link of which is accelerated by additional enzymes.
A simplified blood coagulation scheme looks like this: thromboplastin is released from the damaged endothelium, with the participation of calcium ions and vitamin K, it activates prothrombin. Prothrombin is converted to active thrombin, which in turn triggers the formation of insoluble fibrin from soluble fibrinogen. This process is completed by the stage of retraction of the blood clot, that is, its compaction and the actual blockage of the damage.
At each stage, many more factors are involved in this scheme. In total, there are 13 plasma and 22 platelet types.
Norms
Analysis is performed in one laboratory
Standard values are 90 - 110%, but may vary depending on the laboratory. It is necessary to compare your result with the reference indicators on the analysis form. Therefore, it is not recommended to compare the value of the same patient obtained in different laboratories.
Normally, the hemostasis mechanism reliably protects the circulatory system from hemorrhages and increased thrombus formation, that is, it prevents blood loss during vascular damage by creating obstacles - blood clots, and then dissolves them so that the blood always remains in a liquid state. A decrease or increase in the natural time of clot creation indicates the presence of certain negative factors in the body that require mandatory identification.
What is prothrombin
This is a glycoprotein produced in liver cells, plasma coagulation factor II.
The synthesis of prothrombin requires vitamin K, so one of the reasons for its decrease is insufficient intake of this vitamin from food or a low level of its synthesis in the intestines.
Prothrombin is an inert protein, its activation occurs under the influence of coagulation factor XII (internal system) or when the endothelium is damaged (external mechanism of hemostasis).
The normal level of prothrombin in the blood is 0.1-0.15 g/l. However, its quantitative determination is not used in routine diagnostics. This is a rather unstable protein, easily destroyed and difficult to separate into a separate fraction and count.
In practice, qualitative tests for prothrombin are used, which reflect its content in the blood only indirectly. They are based on calculating the period of time during which the blood clots when thrombokinase activators are added to it (which in turn activates prothrombin, converting it into thrombin, and thrombin catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin).
Therefore, when we say “test for prothrombin”, “blood for prothrombin”, this does not mean determining its concentration in the blood, as, for example, glucose, hemoglobin or bilirubin are examined. And the result is given not in quantitative units, but as a percentage. This concept characterizes the external mechanism of hemocoagulation as a whole and reflects the activity of the entire prothrombin complex (factors II, V, VII, X).
The quantitative content of PTI is “95” in the blood: is this the norm?
Test for PTI blood
So that the blood can thicken and clot at the right time, a chemical agent acts in it - prothrombin. In case of injury, thrombin is formed from this substance, which serves for aggregation of a blood clot. Briefly about this process:
- Such a formation clogs the injured vessel.
- A natural mechanism is activated to prevent excess blood loss.
- If the quantitative content of PTI goes beyond the normal limits, then there is a danger of a blood clot appearing not at the site of the accident, but at any part of the vascular bed.
People suffering from high blood pressure and heart disease often take blood thinners. With such therapy, it is necessary to keep PTI under control. As mentioned above, the normal PTI level is limited to the range of 70-140. The quantitative content of PTI in the blood - “95” falls within normal limits. This means that you don’t have to worry about vascular pathologies and this is the norm.
How are prothrombin tests performed?
The essence of almost all methods for studying the activity of the prothrombin complex is to calculate the time of formation of a fibrin clot immediately after adding activators to the blood, as well as comparing this time with normal values.
Blood is drawn into a test tube with an anticoagulant (sodium citrate). The test tube with citrated blood is slightly heated in a water bath. A reagent consisting of thromboplastin and calcium chloride is added to it. The time of loss of fibrin fibers is measured using a stopwatch. This is prothrombin time (PT). Its normal value is 11-15 seconds.
Having determined the patient's PT, it is compared with the normal prothrombin time (PT). It is usually indicated on the reagent bottle and depends on the activity of the thromboplastin used. Usually this figure is from 12 to 18 seconds (it may be different in each new reagent sample). The ratio of PVN to PT of the subject, expressed as a percentage, is the prothrombin index (PI). Its normal value is 80-105%. The longer the blood clotting time (PT), the lower the PI, which will indicate hypocoagulation.
Pre-preparation and progress of the study
Blood diagnostics for coagulogram (PTI and other indicators of the coagulation system) are carried out in all laboratories of public or private clinics. The collection is always carried out from a vein. To ensure the reliability of the data, proper pre-preparation for analysis is necessary:
- blood is donated on an empty stomach, in the morning;
- on the eve of the study, refuse to drink alcohol or cigarettes;
- the use of medicinal herbs is excluded;
- coordinate with the doctor the intake of medications;
- warn about the use of hormonal contraceptives, the presence of allergies;
The time it takes to analyze and decrypt data does not exceed a day. The method of analysis for PTI is optical and chromogenic coagulometry. The bottom line is that a synthetic peptide (chromogenic compound) is added to a test tube with test blood, a reaction occurs with the coagulation factor, as a result of which the dye is released, and its amount can be measured photometrically, visually.
Prothrombin according to Quick
The test is also based on the ratio of the patient's normal prothrombin time to the patient's PT, expressed as a percentage. But the method is considered more accurate. For the study, several dilutions of plasma are used (1:2, 1:3,1:4) and the construction of a calibration graph. For each dilution, the PT is determined and marked on the graph.
Prothrombin rates according to Quick are from 75% to 140%.
Within the normal protein content, the Kwik and PTI results may be identical. At low contents, these indicators sometimes diverge.
Another indicator is the INR (international normalized ratio). It is mainly used to assess the effectiveness of anticoagulants. This indicator is calculated using the formula:
INR = (patient's PT/normal PT)*value of the international thromboplastin sensitivity index (ISI).
This index is indicated on each package of the reagent. INR allows standardization of the results of PT and IPT performed in different laboratories. The INR value in healthy individuals is 0.8-1.2.
The numbers of prothrombin according to Quick and INR are inversely proportional to each other: if prothrombin according to Quick is increased, then the INR is reduced and vice versa.
Changes in coagulogram parameters by trimester
Normal hemostasis is the key to successful pregnancy and easy childbirth. Therefore, special attention is paid to the quality of blood clotting. During this period, the amount of blood in a woman’s body increases, and any clotting failures are fraught with complications.
If you are taking any medications, tell your doctor about it.
A planned coagulogram is performed for pregnant women every trimester. If the doctor has doubts about the health of the expectant mother, blood should be donated more often. As pregnancy progresses, the normal coagulogram parameters change, which is why the study is carried out at least 3 times during pregnancy. Changes in parameters in a pregnant woman’s body are normal. This is how he prepares for the large blood loss that is inevitable during childbirth. It is important that hemostasis at this stage is high, and any bleeding stops quickly so that it does not threaten the mother and child.
- In the early stages, platelets fibrinogen in the blood of a pregnant woman increase. Shorter clotting periods appear;
- during pregnancy, fibrinogen is increased, and in the third trimester it increases to a level of 6 g/ml;
- D-dimer also increases. If in a healthy woman the level does not exceed 250 ng/ml, then by the 3rd trimester of pregnancy it reaches 1500 ng/ml;
- One coagulogram indicator that should not change throughout 9 months is the prothrombin index. Its increase indicates a developing process of detachment and a serious danger for the child.
When is prothrombin tested?
A coagulation test (coagulogram) is not a routine examination; it is not prescribed to all patients in a row. The test is carried out in the following situations:
- The presence of symptoms indicating problems with clotting: frequent nosebleeds and other bleeding, bruising for no apparent reason, bleeding gums when brushing teeth, hemorrhagic rash on the skin.
- Thrombophlebitis of the veins of the lower extremities.
- Examination of the patient before any surgical interventions.
- Pregnant women must be examined.
- Control during treatment with anticoagulants. They are prescribed to patients with arrhythmias, after valve replacement, and for thrombophlebitis. The purpose of these drugs is to increase blood clotting time, but keep it within a safe range. In this case, PT will be increased by 1.5-2 times, PTI and prothrombin according to Quick will be reduced, INR will be increased (safely up to 2-3).
- For liver diseases to clarify its functional insufficiency.
- Before prescribing estrogen-containing hormones, as well as during their use.
In what cases does it need to be tested regularly?
Particular attention is paid to IPT during pregnancy
An analysis for the PTI indicator must be taken regularly in cases where it is necessary to monitor the blood clotting mechanism.
- After a stroke, heart attack, or with vascular diseases.
- When taking hormonal contraceptives.
- During long-term therapy with anticoagulants.
- During the period of bearing a child.
- For liver pathologies.
Prothrombin norms in different groups of patients
The levels of this glycoprotein in the blood vary somewhat among different age groups. In children under 18 years of age, its normal content ranges from 80 to 110%, in adults – from 78 to 145%.
The norms for adult men and women are no different. A moderate increase in prothrombin may occur in women before childbirth.
Prothrombin index
This indicator is determined in all coagulograms. What does prothrombin index mean?
The normal prothrombin index is 80-105%. The greater the patient’s PV compared to normal, the lower his PI will be and vice versa. Accordingly, a low index indicates poor coagulability, and a high index indicates hypercoagulation (propensity for thrombosis).
The prothrombin index test is prescribed in the same situations as the Quick prothrombin test. Basically, both of these values are in direct correlation and in the range of normal content can be the same.
The norm of the prothrombin index during pregnancy differs slightly by trimester:
- I trimester – 80-119%
- II – 85-120%
- III – 90-130%.
Norms of prothrombin index by age
PTI norms have no gender differences and are correlated only by age and gestational age.
| Age | Norm in % |
| Newborns on the first day | 60-142 |
| 1 month | 60-120,5 |
| Up to 1 year | 55,5-100 |
| Up to 6 years | 69,9-150,5 |
| Up to 15 years | 50,5-145,5 |
| Under 18 years old | 55,5-150 |
| After 18 until the end of life | 70-140 |
How to decipher a coagulogram
This analysis is carried out in order to obtain answers to the questions:
- does the blood clot normally?
- is there a risk of postoperative or postpartum hemorrhage;
- what is the cause of frequent bleeding and bruising;
- what dose of anticoagulants is safe if their use is necessary.
Blood hypocoagulation and tendency to bleeding will be indicated by:
- reduced prothrombin according to Quick (less than 75);
- decreased prothrombin index (less than 80);
- increased prothrombin time (more than 18 seconds);
- increased INR (more than 1.3).
Hypercoagulability and tendency to form blood clots is characterized by:
- increased prothrombin index (more than 110);
- increased prothrombin (above 145);
- shortening of PT (less than 10 s);
- decrease in INR value less than 0.8.
Rules for taking a blood test for IPT
- The last meal should be taken no later than 12 hours before the planned analysis.
- Attention is paid to the quality of food: fewer fat-containing foods, preference for durum wheat, light drinks.
- Patients taking Warfarin should keep their own dietary recommendations in mind to ensure that the INR is not too high or too low.
- All medications that the patient takes must be prescribed separately, indicating the dose, number of tablets, frequency and time of administration, as well as the approximate duration of their use.
- Most laboratories collect blood in the early morning hours; collection at a later time may distort the results for physiological reasons.
- It is not recommended to smoke before the procedure, and at least a week before the tests you should completely abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages.
Following these rules and recommendations will allow you to most accurately determine the necessary indicators of the blood coagulation system.
The main reasons for the decrease in prothrombin
We remember that prothrombin is a protein that is formed in liver cells with the participation of vitamin K. It becomes active with the help of several tissue and plasma clotting factors. The gene responsible for normal prothrombin synthesis is recessive and is located on chromosome 11.
In addition, there are also anticoagulant factors in the blood, the increased activity of which can inhibit the components of the prothrombin complex.
The main causes of low prothrombin and IPT (PT and INR are increased) follow from this physiological mechanism:
- Congenital pathology - changes in the genes responsible for the synthesis of prothrombin (quite rare).
- Liver diseases accompanied by decreased function or death of hepatocytes: chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis. The insufficiency of structural units for synthesis leads to the fact that prothrombin in the blood is reduced.
- Vitamin K deficiency. This happens both when there is insufficient intake from food, and when its absorption and synthesis in the intestines is impaired. Therefore, gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by dysbiosis and impaired fat absorption can also lead to its deficiency.
- Reduced levels of blood clotting factors V, VIII, X.
- Autoimmune diseases, including the production of antibodies to prothrombin (more precisely, to the phosphatidylserine-prothrombin complex).
- Low fibrinogen levels.
- 2nd phase of DIC syndrome (exhaustion phase).
- Increased activity of the anticoagulant factor antithrombin III.
- Treatment with anticoagulants (heparin, fraxiparin, warfarin, neodicoumarin).
What is a coagulogram and why take it during pregnancy?
Coagulogram is a blood test showing the level of its coagulation in the body (hemostasis). In medicine, a coagulogram analysis is also called a hemostasiogram. The study is complex, as it requires studying the coagulation and anticoagulation systems.
Why is a coagulogram needed? The condition of the circulatory system is an important indicator of health. During gestation, many changes occur and the functions of the circulatory system are no exception. Hemostasis indicators increase as the human and female body adds an additional circle of blood circulation, and it prepares for blood loss during childbirth.
Any changes in coagulogram parameters should alert the expectant mother. If the level of hemostasis is reduced, then placental abruption and severe blood loss are possible. If elevated, there is a risk of thrombosis and fetal hypoxia during pregnancy. Of course, all this is bad for the child.
Insufficient or excessive blood clotting can lead to death
The formation of blood clots threatens blockage of the pulmonary artery vessels and vein thrombosis. A bleeding disorder can lead to spontaneous abortion.
First of all, it would be better to do a coagulogram for women with risk factors for pregnancy failure:
- hereditary poor blood clotting;
- a history of miscarriages and intrauterine fetal death, with gestosis;
- tendency to thromboembolism, heart attack, stroke.
Reasons for increased prothrombin and PTI
An increase in PTI indicates hypercoagulation and is dangerous for the development of thrombosis (heart attacks, strokes, thrombosis of the veins in the legs, pulmonary embolism). This condition is especially unfavorable after operations and after childbirth.
- Last weeks of pregnancy.
- DIC – syndrome (1st stage).
- The use of estrogen-containing hormones by women (and sometimes men).
- Congenital thrombophilia.
- Excess vitamin K.
- Mutation of the prothrombin gene G20210A (carriers of the defective gene are 2-3% of the population).
- The period after severe operations, burn disease.
- Postpartum stage.
- Malignant tumors.
- Antithrombin III deficiency.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome.
List of possible pathologies
If the results of a coagulogram during pregnancy are deviated upward or downward, this indicates the development of pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus in pregnancy;
- kidney or liver disease.
The first results are noticeable immediately after sampling. Usually the tests are ready in about a day
If blood clotting is absent, this leads to uterine bleeding and miscarriage. When blood clotting increases, there is a risk of blood clots forming, which cause oxygen deficiency in the fetus, that is, its hypoxia.
Changes in hemostasis values are possible with late toxicosis of pregnant women, which is fraught with serious consequences:
- premature birth;
- intrauterine developmental delay;
- renal and heart failure;
- placental abruption.
When checking the indicators, the doctor looks at the lupus coagulant. During the normal course of pregnancy it should not be present. If it is present, this indicates autoimmune pathologies and the development of diseases such as:
- rheumatoid joint damage (arthritis);
- Libman-Sachs disease (lupus);
- ischemic stroke (cerebrovascular accident);
- spontaneous abortion;
- intrauterine death of a child;
- placental infarction (abrupt cessation of blood supply to the placenta);
- thrombosis of blood vessels.
During pregnancy, the likelihood of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation increases. It is caused by a violation of the blood coagulation system due to the following situations:
- premature placental abruption;
- gestosis;
- entry of amniotic fluid into the woman’s bloodstream;
- placenta previa;
- liver pathologies;
- high blood pressure;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- Rhesus conflict;
- infections, hormonal imbalances that threaten pregnancy;
- hemorrhagic shock;
- chronic maternal pathologies (diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, systemic pathologies).
You should not look for transcripts of analyzes on the Internet. Only the attending physician can correctly interpret test results.
If you decipher in time what kind of analysis it is, you can promptly identify the pathology and increase the chances of preventing its further development.
What to do with indicators that do not fit into the norm?
Prothrombin is increased or decreased, what to do?
First, you need to see a doctor. Many people think that the answers to all questions can now be found on the Internet. In fact, this is far from the case. This is especially true for the coagulation system. The information presented on the Internet about this matter is very confusing and 50% of it is completely wrong. This indicates the high complexity of this issue.
Which doctor should I contact?
To the one who ordered the analysis. If you took a coagulogram on your own, first we go to a therapist.
What should you definitely tell your doctor?
- You must list all medications that you are taking or have taken recently, including dietary supplements. Many medications tend to affect coagulogram parameters, and this applies not only to anticoagulants. Thus, Nevigramon, Streptomycin, Tetracycline, Levomycetin, L-thyroxine, vitamin A, and Aspirin in high doses can reduce prothrombin.
The following can increase PTI: contraceptive hormonal drugs, caffeine, antihistamines, high doses of vitamins C, K, corticosteroid hormones.
- Long-term alcohol abuse can also reduce PTI.
- An excess of foods rich in vitamin K in the diet can lead to an increase in prothrombin, and insufficient consumption of them can, on the contrary, lead to a decrease. These are foods such as greens, green vegetables and fruits, liver.
- Women must be informed about their pregnancy.
What additional examinations can be prescribed?
- Liver function test (advanced biochemical analysis with determination of bilirubin, liver transaminases, total protein, albumin).
- Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tract.
- Fibroelastography of the liver for suspected cirrhosis.
- Determination of antibodies to viral hepatitis.
- Extended examination of the coagulation system (APTT, fibrinogen, thrombin time, D-dimers, plasminogen, antithrombin III, plasma fibrinolytic activity, lupus anticoagulant, etc.)
- Intestinal examination (stool analysis for dysbacteriosis, colonoscopy).
How to lower or increase the prothrombin index?
If the readings are only slightly outside the normal range, there is no need to panic. It is possible that some time after stopping some medications, a repeat analysis will not reveal any abnormalities. Many women are concerned about the question - what to do with taking contraceptives? If cardiovascular diseases are diagnosed, definitely stop taking it, but if the woman is generally healthy, the pills can be taken, but the analysis should be periodically monitored.
You can also try to correct PTI with a diet if you are sure that your diet is clearly lacking foods such as greens (parsley, dill, spinach), vegetables (cabbage, broccoli), beef or pork liver. Green tea improves PTI quite well.
If prothrombin levels are elevated and there is a risk of thrombosis, doctors usually prescribe anticoagulants. At the same time, only warfarin will clearly reduce this indicator. New generation anticoagulants (Pradaxa, Xarelto, Eliquis and others) act on other coagulation factors, but the level of prothrombin may not change.
Aspirin also does not change this indicator, but taking it in small doses makes sense to reduce the risk of blood clots.
In what cases should you not waste time on a diet?
- If the coagulogram values are significantly higher or lower than normal.
- There are symptoms of impaired homeostasis: recurrent bleeding or thrombosis.
- Presence of pregnancy.
- Abnormal coagulogram in a child.
- There are other symptoms (yellow skin, dark urine, swelling, rash, itchy skin, etc.)
In these cases, you need to undergo a full examination and find out the cause of the pathology of the coagulation system.
Author:
Akimova Valentina Konstantinova general practitioner
Decoding the coagulogram of pregnant women (normal values in the table)
Interpretation of blood results in pregnant women is carried out by a doctor in the antenatal clinic, as they may have errors associated with a lack of vitamins, lack of nutrition, or if you take certain medications. The specialist takes into account all these factors when deciphering the study.
If the coagulogram parameters are normal, a conclusion is made about isocoagulation or something else. If there are deviations, the doctor tells you what treatment during pregnancy and what is possible, what pills to take. See the norms during pregnancy in the table.
Coagulogram during pregnancy: detailed breakdown of indicators:
| Index | Norm |
| Fibrinogen | 1st trimester – 2-4 g/l; 2nd trimester – 4-5; 3 trimester – 6. |
| APTT | 17-20 sec. |
| Thrombin time | 18-25 sec. |
| Platelets | 150-400 thousand/µl. |
| D-dimer | 1st trimester – 750 ng/ml; 2nd trimester – 1000; 3rd trimester – 1500. |
| Lupus anticoagulant | 0 |
| Antithrombin III | 74-115% |
| Prothrombin | 78-142% |
Causes of deviations from the norm and methods of correction
When testing PTI blood, the norm in women may fluctuate. If PTI is increased, more than 150%, this indicates the following reasons:
- Diseases that are manifested by a lack of vitamin K.
- DIC syndrome,
- Pathologies in which fibrin is poorly produced.
- Hereditary diseases characterized by decreased blood clotting.
PTI increases if a woman has been taking medications for a long time, such as Aspirin, antibiotics, anabolic steroids, Heparin, laxatives, nicotinic acid, Methotrexate. PTI in women increases at 45-50 years of age. In women, the index may increase due to the use of hormonal drugs. If the patient has heart disease, then the use of hormonal contraceptives should be discontinued.
Deviations
In a healthy person, the prothrombin index should always be normal - from 78 to 140%. This is a relatively constant indicator, so if there is a deviation from the norm, diagnostics and identification of the causes are required.
After studying the results, a number of conclusions can be drawn:
- Assess the risk of heart attack, stroke and vein thrombosis due to varicose veins;
- Assess the functioning of the digestive system;
- Assume the presence of a tumor in the pancreas, liver and other organs;
- Determine the effectiveness of medications;
- Determine vitamin K deficiency or deficiency.
A deviation from the norm must be treated or further examination must be carried out to determine the cause.