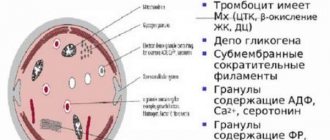
Blood biochemistry
07/13/201801/24/2019 Chernenko A. L. 1909 Views creatinine
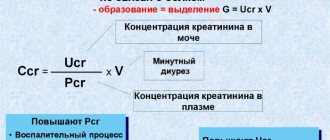
Creatinine is the end product of protein metabolism involved in energy metabolism in muscle cells. The formation of creatinine occurs in the liver tissue, then this substance enters the blood.
Disposal of this substance from the body is carried out by the kidneys. When the kidneys are fully functioning, creatinine is completely filtered without subsequent reabsorption of this substance. In this regard, creatinine level is a highly accurate marker reflecting kidney function.
The levels of this substance in the blood are relatively stable and are determined primarily by muscle volume.
An analysis of creatinine levels is carried out when:
- study of kidney function;
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy for acute renal failure and chronic renal failure (acute and chronic forms of renal failure);
- taking medications that may have a negative effect on kidney function (nephrotoxic drugs);
- bleeding;
- dehydration (due to vomiting, intestinal infection, etc.);
- damage to muscle structures;
- hyperthyroidism;
- acromegaly, gigantism, etc.
Read further: Table with creatinine levels in the blood of women and men
- 1 What can elevated creatinine levels indicate?
- 2 What do the reduced values indicate?
- 3 What does it mean if both creatinine and urea in the blood are elevated?
- 4 How to reduce creatinine and urea in the blood using folk remedies
- 5 How to lower creatinine in the blood at home
- 6 How to reduce creatinine in the blood in case of renal failure 6.1 How are patients with acute renal failure treated?
- 6.2 How is chronic renal failure treated?
What can elevated creatinine levels indicate?
Increased creatinine levels may occur in individuals with:
- acute renal failure and chronic renal failure;
- unbalanced diet and consumption of a significant amount of foods that increase creatinine;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- severe internal bleeding;
- large volume of muscle tissue;
- radiation sickness;
- diseases of endocrine origin (gigantism, acromegaly, hyperthyroidism);
- severe injuries or inflammatory damage to muscle tissue.
Also, treatment with nephrotoxic drugs (sulfonamides, thiazide diuretics, aminoglycosides, tetracycline agents, barbiturates, salicylates, androgenic hormones, etc.) can lead to an increase in the level of creatinine in the blood.
A false-positive increase in cratinin levels in the blood can be observed in individuals with high levels of glucose, fructose, ketone bodies, urea, as well as during treatment with ascorbic acid, levodopa, cefazolin, cefaclor, reserpine, nitrofurazone, ibuprofen, etc.
Renin: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
The components of our body - renin, angiotensin, aldosterone system - play the role of a valve that regulates blood volume and blood pressure levels. The way renin works looks the same as how a stream of water from a watering hose behaves when we water the beds. If we squeeze the tip of the hose with our fingers, the stream of water becomes thinner, but hits with greater pressure.
The hormones renin-angiotensin, or more precisely, the aldosterone-renin ratio of these hormones, also act on our blood system: as soon as the pressure of our blood in the body decreases, the components of the aldosterone system, through complex biochemical reactions, cause the blood vessels to contract and thereby increase blood pressure.
The group of hormones renin-angiotensin is synthesized by the adrenal cortex, therefore all major disturbances in the concentration of this hormone are often associated with pathologies of the adrenal cortex or directly by the kidneys. And high or low levels of these hormones can cause a number of diseases, usually related to abnormal blood pressure levels.
A referral for analysis of the hormone renin is most often caused by the detection of hypertensive diseases, tumor diseases of the adrenal cortex, and renal failure.
- High renin levels
- Low hormone levels
Low hormone levels
Primary hyperaldosteronism. The disease is based on increased production of the hormone aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, caused by a decreased level of the renin-angiotensin hormone group.
It is quite rare to diagnose the disease at the initial stage due to the absence of symptoms, with the exception of mild hypertension. The cause of primary hyperaldosteronism may be adrenal cancer and other tumor diseases of the kidneys.
Under the influence of decreased renin, excessive amounts of sodium begin to be retained and excessive amounts of potassium are excreted. This leads to the accumulation of large amounts of water in the body, without the ability to exit through the urinary canals.
The huge amount of fluid that accumulates in the body immediately causes severe swelling of many parts of the body, increased fatigue and high blood pressure.
Source: https://ogormonah.ru/endokrinologiya/gormon-renin.html
What does it mean if both creatinine and urea in the blood are elevated?
Urea is a name given to nitrogen-containing products formed as a result of protein breakdown. The production of urea is carried out by the liver tissues due to the processing of ammonia, and the utilization of urea is carried out by the kidneys. In this regard, urea levels can be used to determine the rate of protein catabolism and kidney function.
Elevated readings may indicate:
- development of azotemia against the background of glomerulonephritis, acute renal failure and chronic renal failure, renal amyloidosis, pyelonephritis, use of nephrotoxic drugs, etc.;
- the patient has heart failure;
- severe burn damage to the skin;
- bladder tumors;
- severe blood loss;
- intestinal obstruction;
- the patient has a prostate tumor;
- leukemia;
- excessive consumption of protein foods;
- treatment with androgen drugs, etc.
Low values may be detected in patients with:
- liver diseases accompanied by a violation of its protein synthetic function;
- hepatic coma;
- acromegaly;
- malabsorption, etc.
Also, a decrease in urea levels can be diagnosed in pregnant women, vegans and people on a low-protein diet.
The most common cause of a significant increase in creatinine and urea in the blood is acute renal failure or chronic renal failure. In this regard, a blood test for creatinine and urea is used both to diagnose this disease and to monitor the quality of treatment.
Treatment for high creatinine and urea in the blood should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable and can cause irreparable harm to the patient’s health.
Read further: Norms of creatinine in urine and causes of deviations
What is the hormone responsible for?
Renin in the blood is broken down by a protein structure that is synthesized in the liver - angiotensinogen.
As a result of chemical processes, a substance is formed that controls the process of contraction of the muscular apparatus of the vascular network.
Due to this, blood pressure increases and the adrenal glands are stimulated to release the appropriate hormones.
Renin activity is extremely important for maintaining normal functioning of the human body. The substance, in addition to regulating blood pressure, controls and maintains the normal volume of circulating blood.
The need for this substance arises when there is a deficiency, which may occur due to physiological reactions to external and internal processes.
Due to the synthesis of renin in the blood plasma, blood pressure begins to increase. At the same time, the blood vessels narrow and the pressure in them increases. At the same moment, aldosterone is released.
Factors influencing hormone secretion
The release of the hormone begins in the following conditions:
- decrease in blood pressure,
- stress and worries,
- insufficient amount of potassium and sodium in the blood,
- insufficient blood circulation in the renal segments,
- decrease in overall blood count.
Changes in indicators occur with neoplasms of benign and malignant origin, as well as as a result of taking certain types of medications.
Values may vary depending on the time of day, the psycho-emotional state of a person and physical activity.
How to lower creatinine in the blood at home
A diet with elevated creatinine should be low in protein. This is explained by the fact that these substances appear as a result of protein metabolism.
A diet to reduce creatinine in the blood involves:
- limiting the consumption of meat products;
- refusal to eat sausages, sausages, smoked meats, canned food, red and black caviar, mushroom dishes;
- limiting the consumption of chocolate;
- limiting the consumption of spices, garlic, onions, coffee, strong tea and cocoa.
It is recommended to eat fruit and vegetable dishes, lean meats and fish, and cereals.
The specified diet for elevated creatinine in the blood in women and men can be used provided that the patient does not have pathologies of the kidneys, liver, endocrine glands, etc., and the increase in urea and creatinine levels is caused only by poor nutrition.
The diet for kidney failure and elevated creatinine includes strict restrictions on the amount of fluid, salt and protein consumed. The menu for this disease is compiled strictly individually and depends on the form of the pathology and its stage. The amount of fluid and protein consumed is calculated based on the stage of the disease and the patient’s body weight.
How to reduce creatinine in the blood with kidney failure
Many patients are interested in what drugs are used to reduce creatinine in the blood. It should be understood that with chronic renal failure or acute renal failure, high creatinine in the blood is a reflection of impaired renal function. In this regard, treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of acute renal failure or chronic renal failure and correcting impaired renal function.
How are patients with acute renal failure treated?
In the acute course of the disease, the most important role in treatment is played by the elimination of the pathological condition that caused renal failure (sepsis, infectious-toxic shock, CRASH syndrome, peritonitis, acute blood loss, etc.)
Plasmapheresis is also performed. The volume of plasmapheresis performed depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and the severity of intoxication symptoms.
Plasma removed during plasmapheresis is replaced with fresh frozen solutions of plasma, albumin, etc.
According to indications, blood transfusions or blood substitute solutions may be performed. Intravenous drips of prednisolone are also used. Exchange transfusions are performed in patients with severe intravascular hemolysis and a hematocrit below twenty.
Additionally, anti-shock therapy and detoxification are carried out. For bacterial infections, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Antibiotic dosages are reduced according to the severity of renal failure.
According to indications, in the early stages of development of acute renal failure, it is advisable to use mannitol® or furosemide® to eliminate anuria.
Under the control of creatinine levels, Adsorbix® is prescribed.
In addition to drug therapy, a low-protein diet is prescribed (the caloric content of the diet is provided by fats and carbohydrates), and the intake of salt and liquid is limited. The volume of orally consumed fluid depends on the patient's urine output and the volume of intravenous infusions.
Salt intake should be limited to 0.2-0.3 grams per day, and protein to 0.5-0.6 grams per kilogram of body weight. The volume of fluid consumed = the volume of the patient’s urine output over the past day + three hundred milliliters.
Additionally, homeostasis disturbances are corrected.
Patients with urea levels above two grams per liter, as well as decompensated forms of metabolic acidosis or acute uremia, are prescribed hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Dialysis is contraindicated in patients with hemorrhages in brain tissue, gastric and intestinal bleeding, or arterial collapse.
Peritoneal dialysis is contraindicated in patients with adhesions in the abdominal cavity, as well as in cases where the patient has recently undergone abdominal surgery.
Preparation for analysis and collection of biomaterial
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
Plasma isolated from blood is used for research. The biomaterial is taken on an empty stomach (you are allowed to drink only still water). You should stop taking ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II antagonists, diuretics 3 weeks before, and spironolactone 5-7 weeks before (after consultation with your doctor). 3 weeks before the analysis, a diet is recommended: the patient should reduce salt intake to 3 g/day, without limiting potassium intake. The day before the test you need to stop drinking alcohol. 1-2 hours before the analysis, it is important to avoid severe stress and physical activity. Before blood collection, the patient should rest in a sitting or lying position for at least 20 minutes.
Blood is taken at about 8.00 after a night's sleep (staying in a horizontal position). After this, after 3-4 hours, the material is taken again, during which the patient is in a sitting position. The biomaterial for research is collected in a test tube with the addition of EDTA. Freezing of plasma is allowed at a temperature of -20°C. The study of intact renin is carried out using a chemiluminescent immunoassay. The technique is based on an immunological reaction, during which phosphors (substances that convert energy into light radiation) are added to renin. The level of luminescence is determined using luminometers, thereby assessing the activity of the enzyme. The analysis period usually does not exceed 1 business day.