Red blood cell distribution index (RDW) is a very important factor during a complete blood count. This indicator shows the size and shape of red blood cells.
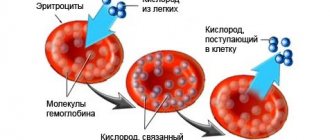
Red blood cells perform the transport function, thereby assisting in the penetration of oxygen into all tissues and organs and at the same time taking away toxins and carbon dioxide accumulated in the cells. In their normal state, red blood cells are approximately the same size, which allows them to quickly stick together, forming blood clots.
The indicator of red blood cells in the blood may reflect the presence of pathological processes in the body, especially if the sizes of these cells vary significantly. Next, we will talk about in what situations the erythrocyte distribution index decreases, how this manifests itself and what it indicates.
Reduced RDW: norm and pathology
A person in good health has red blood cells of the same shape, density and color. In case of deviation, especially in the presence of autoimmune diseases or oncology, the failure occurs at the level of microcells, when young cells do not receive a certain number of components, which, in fact, inhibits their performance. Thus, anemia occurs - a pathology during which the body does not receive the required amount of oxygen, in other words, the metabolic function in red blood cells is disrupted.
High RDW
The coefficient is considered increased when the indicator is more than 15%. This means that red blood cells vary greatly in size.
There are many possible causes for this condition. To determine the most likely diagnosis, RDW is compared with MCV.
High MCV
If we consider that MCV is the average volume of space that each blood cell occupies, then an increased level of both indicators may indicate several possible deviations in the condition of the body.
Liver diseases
The liver is the largest internal organ in the human body, which produces substances necessary for the body, filters blood, and removes harmful chemicals. Liver health worsens with alcoholism, as may be indicated by elevated RDW levels.
Hemolytic anemia
A disease in which red blood cells die or are destroyed earlier than their healthy life cycle would suggest.
Megaloblastic anemia
Large oval red blood cells with an underdeveloped nucleus and a short life cycle appear in the blood. This condition usually occurs due to a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12 in a person's diet or due to impaired absorption of these substances.
Vitamin A deficiency
A minimum amount of vitamin A must be present in the body for cell synthesis in interaction with vitamin B12.
Low MCV
In other cases, the average volume of red blood cells is reduced, while the width of the distribution is still higher than normal. This may be a sign of some less common anemias or iron deficiency conditions.
Decreased hemoglobin level
Hemoglobin is present in red blood cells. It helps deliver oxygen to the cells of the body. Iron is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin, so a deficiency of this trace element leads to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
Iron deficiency anemia is usually caused by insufficient iron in the diet or poor absorption of iron from food or dietary supplements.
Thalassemia intermedia
Thalassemia intermedia is a blood disease in which the synthesis of one or more components of hemoglobin is impaired. As a result, the blood cells are fragmented (broken into smaller particles).
If the red blood cell fragments are noticeably different in size but do not take up more space, this may appear in the analysis as a low MCV with a high RDW.
Normal MCV
An increased RDW value with a normal MCV level can be caused by:
- the initial stage of iron deficiency anemia, leading to a decrease in hemoglobin;
- a decrease in the level of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body, which is a prerequisite for macrocytosis anemia.
What does RDW mean in a blood test?
During a general blood test, the erythrocyte distribution index is determined. If the presence of a specific disease is suspected, a blood test is prescribed to determine only this indicator.
Most often, the width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume is determined together with the MCV indicator. This is the average volume of red blood cells. This happens because these indices (in quantity and volume) are closely related to each other and help in determining the type of anemia.
It happens that the erythrocyte distribution index is reduced. What does it mean? The thing is that for a qualitative judgment about the state of red blood cells, not only their concentration in the blood is important, but also their shape. An increased distribution of red blood cells is observed in 1 out of 10,000 cases, but if the RDW index is reduced, which is much less common, we are talking about the presence of serious problems in the human body.
A blood test to determine the erythrocyte distribution index can be carried out both during medical examinations (routinely) and as prescribed, if there are suspicions of any abnormalities in the hematopoietic function. The analysis is required before surgery, during pregnancy and in childhood.
Red blood cells, their functions in the body, main indicators
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBC, red blood cells), are red blood cells, biconcave disc-shaped blood cells, lacking a nucleus. The shape of a red blood cell allows the cell to deform as it moves through small blood vessels. The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs, and from them - carbon dioxide to the lungs. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow and destroyed in the spleen; the average lifespan of cells is 120 days. Newborns have larger red blood cells than adults.
The condition in which red blood cells of abnormal sizes are detected in the blood is called anisocytosis.
A physiological increase in the number of red blood cells is observed in children in the first days of life, with frequent stress, intense physical activity, malnutrition or fasting, and with prolonged clamping of a limb with a tourniquet during blood collection for a blood test. A physiological decrease in the number of red blood cells occurs immediately after eating, between 17:00 and 07:00 and when blood is drawn from the patient in the supine position.
In the blood, in addition to normal red blood cells, there may be cells that differ in size - larger (macrocytes) or small (microcytes) red blood cells. The condition in which there are more than 50% macrocytes in the blood is called macrocytosis. If 30–50% of microcytes are present, microcytosis is diagnosed. The appearance of red blood cells of different volumes in the blood is called anisocytosis, the degree of which allows one to determine the RDW index.
In addition to RDW, erythrocyte indices in a general blood test include MCV (mean erythrocyte volume), MCH (mean hemoglobin content in erythrocytes), MCHC (mean hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes).
Erythrocyte indices are determined during a general (clinical) blood test. The count is carried out using an automatic hematological analyzer, according to the appropriate formulas and/or in a stained blood smear under a microscope when calculating the leukocyte formula. In addition to RDW, erythrocyte indices in a general blood test include MCV (mean erythrocyte volume), MCH (mean hemoglobin content in erythrocytes), MCHC (mean hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes).
Why is it necessary to do an RDW analysis?
It was already mentioned above that the index of distribution of red blood cells in the blood makes it possible to conduct a qualitative assessment of the composition of red blood cells, taking into account their size.
But why is this necessary? The thing is that these cells are very similar to each other, which gives them the opportunity to replace each other or form blastulas. An increase in cell size entails an increased need for nutrition and, in addition, this means that their life expectancy is reduced. All this directly affects the overall indicator of red blood cells in the blood and the human condition.
When a large number of red blood cells die, iron is released and more bilirubin becomes available, which puts increased stress on the liver, and as a result, it cannot process these substances.
The RDW index is directly related to the pathological process, during which the dimensions of erythrocytes change (anisocytosis). This condition is a complex chemical process that causes all blood cells to suffer.
general characteristics
RDW in a blood test allows you to estimate the ratio of red blood cells by volume. This is a very important indicator, since all red blood cells should have approximately the same size. Only then will they be able to transport hemoglobin normally and provide tissues with oxygen and nutrients. Identical red blood cells can replace each other if necessary, which prevents a decrease in hemoglobin. But human blood often contains red blood cells that are larger or smaller than normal.
It is the RDW indicator that allows you to evaluate the difference between such red blood cells. This is the percentage ratio between large and small size cells. If there are many red blood cells of different sizes in the blood, this condition is called anisocytosis. It can be dangerous to health, as it leads to the fact that the blood does not perform all its functions. It is to assess the severity of this condition that a similar indicator is used.
Important: RDW allows you to assess the width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume and the degree of anisocytosis.
For these purposes, two options for this parameter are used. The RDW SD is used to estimate the difference between the smallest red blood cell and the largest in a blood sample. The result of this study is expressed as a percentage.
It is also necessary to examine the RDW CV indicator in a blood test. It is needed to determine the degree of anisocytosis, as it reveals the number of altered cells that differ in volume from normal red blood cells.
How is it calculated?
The RDW indicator is calculated as a percentage, the norm of which is considered to be the limit from 11.5 to 14.8. The red blood cell distribution index is determined using a mathematical equation that represents the ratio of modified red blood cells to their total mass.
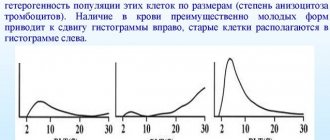
Nowadays, laboratories use computer technologies that make it possible to calculate the percentage of deviation from the established norm. The calculation results are presented in the form of a histogram depicting a curve that indicates probable changes in the dimensions of red blood cells.
RDW reduced
A low RDW value indicates that your red blood cells are uniform in size, which is desirable for health. [] However, it is worth remembering that there is still a possibility of having some kind of disease. []
For example, with reduced RDW values, one may suspect disturbances in the functioning of the spleen, where damaged red blood cells are recycled. In addition, if RDW is low, it is worth thinking about the following possible reasons:
- Recent surgery
- Blood donation
- Severe blood loss (including hidden in the stomach and intestines)
- Hormonal disorders during pregnancy, puberty, and when taking contraceptives
Normal indicators
The norms of the erythrocyte distribution index depend on gender, age and the presence of certain conditions that occur in the human body. For children under one year of age, the normal rate is 11.5-18.7%. At one year of age and older, the values tend to the generally accepted norm of 11.5-14.5%.
For the female half of humanity, the upper limit shifts to 15.5%, since their hormonal levels change too often: during pregnancy, lactation, taking oral contraceptives, menopause.
For analysis, blood is taken on an empty stomach in the morning (before 9 am). It is very important that before this procedure the person does not take any medications and is in a balanced internal state.
Decoding the result
Decoding RDW in a blood test consists of comparing the result obtained with normal values. It is also necessary to evaluate the relationship between RDW and other red blood cell characteristics.
Norms by age
The average RDW rate in a blood test is 10.5-14.5%. In adult men and women it is almost the same, and varies slightly with age. The greatest fluctuations are observed in newborns and the elderly. The tables below show age-related changes in RDW.
RDW in blood tests in women
| Age | Norm for women, % |
| 14-18 | 10,5 |
| 19-25 | 11-12 |
| 25-45 | 11-13 |
| Over 45 | 10-14 |
RDW in blood tests in men
| Age | Norm for men, % |
| 14-18 | 11 |
| 19-25 | 11-12 |
| 25-45 | 12-13 |
| Over 45 | 10-14,5 |
RDW in blood tests in children
| Age | Norm in children, % |
| Children under one year old | 17-18 |
| 1-5 years | 15-17 |
| 6-10 years | 13-14 |
| 11-14 years old | 11-12 |
Raising RDW
The RDW level can be elevated in some situations. The most common cause of this pathology is iron deficiency anemia. The indicator can change at different stages of pathology development, which is clearly reflected in the histogram of red blood cells:
- The initial stage of anemia development is characterized by normal indices, but hemoglobin will be greatly reduced. This is the result of healthy functioning of the spinal cord.
- The next stage of development in the histogram will show an increase in RDW. When there are problems with hemoglobin, indicators such as the average concentration and content of hemoglobin in a blood cell and the average volume of red cells decrease.
When treating IDA, it is necessary to normalize the level of concentration of iron-containing protein and its characteristics in the human blood.
Indications for RDW analysis
The RDW study is not prescribed separately. The indicator is part of the general blood test. It is examined if the following diseases are suspected:
- chronic inflammation of an infectious or autoimmune nature;
- acute and chronic liver diseases - hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- renal failure;
- heart diseases;
- oncological diseases;
- dysfunction of the brain.
RDW is a nonspecific indicator; it changes in various diseases.
What do the reduced numbers mean?
Patients often ask what this means: “red blood cell distribution index is reduced.” Since the erythrocyte distribution index cannot be assessed without a volume indicator, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with all the options for underestimated indicators and their relationship:
- RDW is low and MCV is below average - indicating problems with the spleen and liver.
- RDW is lowered, and MCV is higher than the normal level - indicates the presence of oncological pathologies, mainly the development of metastases in the bone marrow.
The fact that the erythrocyte distribution index RDW sd is reduced, from a biological point of view, cannot, in principle, be observed. For this reason, most often the patient is offered to donate blood again, observing the following conditions:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol for 24 hours before blood sampling;
- do not take any medications before the analysis;
- Avoid eating smoked and salty foods the day before.
In the case when the erythrocyte distribution index RDW sd is indeed reduced, which is necessarily confirmed by deviations from the norm in the MCV indicator, then this indicates the occurrence of certain pathologies. These include:
- Hypochromic microcytic anemia - sometimes also called anemia. A condition in which irregularly shaped red blood cells die because they have no biological value in the body.
- Malignant tumors - usually in this case we are talking about mastopathy, bone marrow and lung cancer.
- Hemolysis of red blood cells is a process during which red blood cells die without reaching their target. As a result, active hemoglobin is released.
Detailed Definition
Red blood cells are disc-shaped, biconcave red cells that color the blood accordingly. In addition, they are its basis and transport oxygen to organs and tissues. In a healthy person, red blood cells do not differ in shape, color or volume. The proper functioning of red blood cells is determined not by their diameter, but directly by their volume. Its average is designated as MCV.
The coefficient is significant only when the RDW CV readings are fully identified. This value in a healthy person can fluctuate only slightly. This range in medicine is called the heterogeneity of erythrocytes, or the width of their distribution over the total volume. Most often, red cells decrease in volume as a person ages, that is, differences appear between them. This may also be caused by malignant tumors or anemia. If red blood cells of different volumes appear in the blood, this is called anisocytosis. To detect changes, the specialist must refer the patient to determine the RDW. It is often elevated in blood tests.
Causes
So, the erythrocyte distribution index is reduced - what does this mean? There are several reasons that can reduce the RDW indicator:
- Acute blood loss due to injuries and pathological bleeding.
- Frequent operations.
- A metabolic disorder during which the food consumed is not completely digested.
- Hormonal imbalance, which most often occurs in women.
- Deficiency of B vitamins and iron in the body.
- Blood diseases characterized by rapid destructive processes.
Circumstances of reduced RDW
A low red cell distribution may occur for the following reasons:
- Large blood loss due to injuries and other circumstances.
- Surgery when an organ is removed.
- Disruption of the metabolic process, the remains of undigested food ferment in the digestive organ, which causes rotting.
- Failure of hormonal levels most often occurs in females.
- Lack of iron, vitamins.
- Blood pathologies when red cells lose their biological function.
Characteristic signs of anemia:
- dizziness;
- weakness, fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- increased blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- increased heart rate.
Such negative symptoms occur due to a failure of the biological process. Blood cells become small and poorly oxygenate the body. Initially, the nervous system responsible for impulses begins to suffer.
At the first signs, you should consult your doctor. The doctor will order a blood test, prescribe additional diagnostic methods and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What measures to take?
What to do when the red blood cell distribution index is low?
A highly qualified doctor during a consultation will most likely ask the patient to take the test again, because the RDW indicator is almost never underestimated. Because this suggests that all cells are ideal in their parameters, but this cannot happen in principle. If the indicator is confirmed by repeated analysis, then a full examination of the body’s condition is carried out, paying special attention to oncological examinations.
Interpretation of the values of RDW-SD and RDW-CV indicators in the diagnosis of anisocytosis
Very often, clients of those laboratories where blood tests are carried out using automatic hematology analyzers ask for an explanation of the results of all parameters of a general blood test. The question is logical, since instead of the usual five indicators, patients receive a statement containing from 18 to 22 indicators. Product Manager Svyatoslav Polovkovich has prepared an article that will help doctors and laboratory specialists explain this issue to patients.
Blood, its functions and what are “red blood cells”
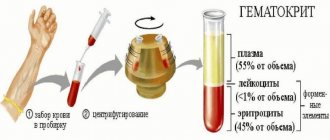
Blood is one of the important components of a living organism. It is a liquid tissue consisting of plasma and formed elements. Formed elements include platelets, erythrocytes and leukocytes.
Erythrocytes or “red blood cells” (Red Blood Cells, RBC) are non-nuclear cells that have the shape of a concave disk. The anucleate nature of red blood cells and their shape provide them with the most optimal properties in the process of gas exchange and maintaining osmotic resistance. The normal size of a red blood cell is 7.5-8.3 microns; life expectancy is 90-120 days. Red blood cells have antigenic properties, on the basis of which four main blood groups are distinguished. The cytoplasm of an erythrocyte is 96% filled with hemoglobin. In addition to mature erythrocytes, young erythrocytes—reticulocytes—can normally be found in peripheral blood. These are anucleate cells with a large amount of RNA and ribosomes that have membrane receptors for transferrin. In the reticulocyte stage, up to 30% of the total amount of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte can be produced. The other 70-80% of hemoglobin is synthesized earlier, in the pre-reticular stages of cell differentiation. The reticulocyte loses RNA and the ability to produce hemoglobin when it becomes a mature red blood cell. In the reticulocyte stage, the red blood cell resides for one day in the bone marrow and another day in the peripheral blood.
The circulatory system connects and nourishes all organs, so it is very important to monitor its condition and regularly conduct a general blood test. When performing a general blood test, you should pay attention to the size, color and shape of blood cells. By the deviation of the shape and size of cells from normal, one can judge poikilocytosis and anisocytosis.
Signal message from the hematology analyzer “Anisocytosis”: what indicators to pay attention to
Laboratory specialists often have to answer questions about interpreting hematology analyzer readings. The automatic hematology analyzer itself informs about the patient’s clinical picture. However, at meetings of laboratory technicians, the most asked questions are questions about what indicators are used to make these conclusions, and questions about the interpretation of hematology analyzer indicators. Let's try to explain these aspects using the example of interpreting the values of the RDW-SD and RDW-CV indicators in the diagnosis of anisocytosis.
Blood anisocytosis is an excess of the number of cells of non-standard size. Depending on which blood cells have changed their size, anisocytosis of erythrocytes and anisocytosis of platelets are distinguished.
Anisocytosis of red blood cells in a general blood test indicates that the size of blood particles differs from the standard. The normal size of red blood cells is 7.5-8.3 microns. The presence in the blood of a small number of red blood cells of non-standard size (compared to the total number) is allowed. On average this value is 30%. It is considered normal if 15% of blood cells have a size smaller than the standard one, and 15% of cells have a larger diameter than theirs. Red blood cells with a smaller diameter (<6.9 µm) are called microcytes. Large diameter red blood cells are divided into two groups:
- macrocytes 8 µm
- megalocytes: d>12 µm.
If the blood cells differ significantly in size from the acceptable value, a diagnosis of “Increased anisocytosis of red blood cells” will be made.
Based on the size of cells that predominate in the blood, microcytosis, mixed type and macrocytosis are distinguished. Mixed type anisocytosis occupies an intermediate position between microcytosis and macrocytosis; This type is characterized by the presence of both small and large blood cells in the blood. For example, mixed type anisocytosis with a predominance of microcytes means that the particle sizes in the blood are heterogeneous, but the majority are small in diameter particles.
To indicate the degree of heterogeneity, there is a special index - RDW (“red cell distribution width”) or erythrocyte anisocytosis index. That is, RDW demonstrates heterogeneity in the size of the red blood cell population in the sample being studied.
There are two types of indicators - RDW-CV and RDW-SD. The first, RDW-CV, shows the percentage distribution of cells by size. The second, RDW-SD, is their standard deviation, which is the difference in size between the smallest and largest red blood cells in a blood sample.
The determination of the RDW-CV index is carried out automatically by a hematology analyzer using a special formula, which takes into account the average volume of erythrocytes MCV of blood and the standard deviation from MCV. The indicator calculated in this way is usually expressed as a percentage. The RDW-CV norm is 11-15%. RDW-CV is directly related to the mean red cell volume MCV, so if most of the cells in the population are small (as in microcytosis), the RDW-CV will remain within the normal range. RDW-CV is less sensitive to the presence of small populations of microcytes, macrocytes, or reticulocytes, but better reflects overall changes in red blood cell size in macrocytic or microcytic anemia.
You can also find the RDW-SD indicator in the blood test results. This indicator is determined using a different method and does not depend on the average volume of red blood cells. The RDW-SD definition is a direct measurement of the width of the red blood cell histogram at 20% of the height of the curve; the height of the RBC histogram is taken as 100%. RDW-SD is measured in fl (femtoliters) and reflects the difference between the maximum and minimum volume of red blood cells in the test sample. Normal RDW-SD is 35-60 fl. RDW-SD is a more sensitive indicator when small numbers of macrocytes and microcytes appear in the red blood cell population, as it measures the lower part of the red blood cell volume distribution curve. Also, this indicator will change more quickly with reticulocytosis, since a broadening of the base of the erythrocyte histogram will be observed.
Clinical value of RDW value in making a diagnosis
Interpretation of the RDW value in test results is always carried out in parallel with the assessment of the mean erythrocyte volume (MCV), since quite often the width of the distribution of erythrocytes remains normal in the presence of a homogeneous cell population with microcytosis or macrocytosis.
If RDW in a blood test is elevated, the following pathological conditions can be assumed in the patient:
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Immune hemolytic anemia
- Megaloblastic anemia (with a lack of vitamins B9 and B12)
- Hemoglobinopathy
Elevated RDW values are also common in patients with liver disease and patients who have undergone blood transfusion. In addition, the anisocytosis index may be erroneously overestimated if cold agglutinins are present in the test sample. It is also worth noting pathologies in which RDW does not change. These include: beta thalassemia, anemia in severe chronic diseases, sickle cell anemia, acute hemorrhagic and aplastic anemia, spherocytosis.
It is important that conducting research on an automatic hematology analyzer is more accurate, since the width of the distribution of red blood cells can increase even before changes in red blood cells appear, and the value of hemoglobin, that is, an increase in the anisocytosis index, can be called an early marker of anemia. It is worth noting that during the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, the RDW indicator not only does not decrease, but also increases, while the histogram changes noticeably (two peaks appear on the distribution curve). This is due to the fact that young cells appear that differ in size from mature red blood cells. If drug therapy is effective, the anisocytosis index normalizes, but it is the most recent of all erythrocyte indices to normalize.
offers automatic hematology analyzers from the European manufacturer DIATRON. These analyzers measure, in addition to other standard indicators, the distribution width of red blood cells (RDW) in two versions: RDW-CV and RDW-SD, which fully shows the heterogeneity of the size of the red blood cell population in the test sample. A wide range of DIATRON analyzers is represented by analyzers of various capacities (from 30 to 80 tests per hour), with various technical characteristics (small sample module, auto-puncture function, auto-loading, etc.). This allows us to fully meet the needs of laboratories of various sizes and specializations (primary medical care centers, family doctors, pediatrics, oncology, etc.). The company offers an individual approach to each client in terms of payment, delivery and service. We provide warranty and post-warranty service.
Preventive measures
You can prevent a reduced RDW by following these simple rules:
- The diet should be balanced, which includes plenty of fresh fruits, lean meats and vegetables.
- It is recommended to breathe fresh air as often as possible.
- An active lifestyle will help prevent a decrease in the RDW index.
- It is very important not to skip routine medical examinations, during which most often serious deviations from the norm are detected that do not have external symptoms.
As a result, we learned that the red blood cell distribution index reflects their dimensions relative to each other and makes it possible to learn about their biological value. A decrease in RDW is very rare, but if the erythrocyte distribution index is decreased, this means that various pathologies may be present.
The index is calculated based on the results of a general blood test, but can only be fully valid in conjunction with the MCV indicator, since they are closely interrelated.
What is this
The main composition of the blood contains cells that are produced by the bone marrow. There are three types of cells - blood, red, white. Red cells themselves are red blood cells. Their norm is determined by a blood test.
In healthy individuals, cells have the same volume, color, and shape. The result of the study may vary slightly; this indicator in medicine is called the width of the distribution of red cells by volume.
There are two types of this coefficient:
- RDW-CV, reflects the distribution of cells in percentage proportionality;
- RDW-CD – makes it possible to assess the level of deviation.
The discrepancy between the norm of red cells in the blood is called anisocytosis. A blood test is carried out using a special apparatus, the indicator is set as a percentage. RDW in an adult varies from 11 to 15 percent; any discrepancy indicates pathological trends in the body. An increased coefficient indicates that the red cells differ in parameters, and the vital activity of the cells decreases. If the level of distribution of red blood cells in volume is reduced, then most often this indicates some degree of anemia.
Only an experienced specialist can correctly analyze the composition of the blood and find out the root of the pathology. If there are deviations from the norm, the patient is prescribed an additional examination to determine the source of the disease.
Before donating blood, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of doctors so that the result is as reliable as possible. There are certain factors that go into establishing the RDW.
The analysis is taken in the morning; before the procedure, it is forbidden to eat, drink tea, coffee, or smoke cigarettes. After the last meal, at least 10 hours must pass before donating blood.
If the result is positive, then the procedure is repeated to exclude an incorrect result.
Decoding
Anisocytosis of red blood cells is determined by a hematology analyzer, which produces a histogram plotting the number of RBCs of different volumes in the sample.
Important information: What is PDW or platelet population distribution width and deciphering the norm in a general blood test
If the analysis is carried out manually, the value of the red blood cell coefficients of variation is calculated from the histogram curve and formula. Manual calculation of parameters is rarely used, because does not provide the necessary accuracy of the result.
A positive test result is when the rate of erythrocyte anisocytosis exceeds the norm. If the result is within the normal range, the test will be negative.
The RDW designation characterizes the heterogeneity of red blood cells:
- RDW-CV in a blood test is a relative value measured as a percentage (%);
- RDW-SD is an absolute parameter measured in volume units of femtoliters (fl) or µm3.
Comparison of the scatter of RBC volumes in the sample is carried out with normal values of 80-100 fl.
Relative index is a value that reflects the distribution of red blood cells, showing by what percentage the red blood cell volumes differ from the average volume.
The value of the absolute indicator indicates how many femtoliters the volumes of red blood cells differ. The calculation is done according to the histogram graph.
The level of relative anisocytosis depends on the value of the MCV parameter (mean blood cell volume). The calculated value of the relative indicator of erythrocyte anisocytosis is obtained by multiplying 100% by the ratio of the standard coefficient to MCV.
The RDW-SD parameter in a blood test allows you to determine how many femtoliters the smallest and largest red blood cells differ from medium-sized red cells.
Normal values
The values of the distribution width of erythrocytes according to norms do not depend on gender. They are the same for an adult of any gender. With age, normal coefficient values do not change.
If heterogeneity does not exceed the norm, it means that the red blood cells are approximately the same size. The norm for absolute anisocytosis in adults is 37-47 fl.
Normal RDW levels for women and men are 11.5%-14.5%.
In women during pregnancy, the normal value of the parameter changes by trimester (%):
- first trimester - 11.7-14.9;
- second trimester - 12.3-14.7;
- third trimester - 11.4-16.6.
In children, the normal level varies. The first 6 months after birth, RDW values are higher than the adult norm. Gradually they decrease.
RDW standards for children (%):
- up to 6 months - 14.9-18.7;
- after six months - 11.6-14.8.
The result of the calculation of relative anisocytosis, which the patient receives in the analysis, is often elevated or normal. A decreased RDW-CV most likely indicates an error.
If the anisocytosis of red blood cells is slightly higher than normal, most often the deviation is random. This value becomes clinically significant for diagnosis when it exceeds 60 fl.
Important information: How are red blood cells designated in a general blood test?
A decrease in the absolute coefficient of anisocytosis has no significance for diagnosis.
Increased level
Red blood cells are heterogeneous in size and hemoglobin saturation. If anisocytosis is higher than normal, it means that there are blood cells in the bloodstream that are different in volume from the normal range.
Normally, each cell goes through a life course, during which its volume changes. Cells of different sizes are simultaneously present in the blood:
- microcytes, characterized by their small sizes, not exceeding 6 microns;
- normocytes corresponding to normal sizes, in the range of 6-8 microns;
- macrocytes, characterized by large sizes exceeding 8 microns;
- megalocytes, with a diameter > 12 microns.
Normal human RBCs fall within the normocyte range on average. An increased value of heterogeneity is possible with the appearance of microcytes and megalocytes.
The heterogeneity of erythrocytes is characterized by the degree of anisocytosis:
- The first degree corresponds to 27-50% of defective cells.
- Anisocytosis of the second degree is characterized by 55-70% of modified blood cells.
- The third degree of anisocytosis is characterized by the presence of more than 75% of such cells. Their sizes deviate from the norm.
- With the fourth degree of anisocytosis, all 100% of the cells are defective.
If the relative width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume is increased, it means that more than 50% of the cells deviate from the norm.
Relative coefficients of erythrocyte heterogeneity may increase when:
- leukocytosis with a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes;
- lack of nutrients necessary for hematopoietic processes (iron, B vitamins);
- microcytic anemia;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- hemolytic crisis;
- malignant tumors that metastasize to the bone marrow;
- RBC agglutination;
- poisoning with heavy metals (lead);
- Alzheimer's disease.
The anisotropy coefficient of erythrocytes increases in vascular diseases. Increased RDW in intoxication caused by alcohol abuse.
If the blood was tested after surgery, severe bleeding, heterogeneity above normal may also be noted. In such a situation, the result exceeds the acceptable standard deviations as a result of the increased production of juvenile cell species.
RDW is elevated in iron deficiency anemia, which is common in pregnant women. The RDW indicator for this disease exceeds 14%.
With vitamin B12 deficiency, macrocytes and megalocytes are found in the bloodstream.
If the anisocytosis index reaches 27%, this means that RDW in a blood test may suggest B12 deficiency anemia.
Important information: What does a platelet distribution width below normal mean in a blood test?
The width of the distribution of red blood cells is increased during processes accompanied by increased destruction of red blood cells. The death of blood cells is caused by:
- increased bilirubin levels;
- an increase in the size of the liver and spleen;
- accumulation of iron ions in the body.
An increase of up to 40% is possible with thalassemia or Cooley's anemia. This disease is hereditary. Cooley's anemia is most widespread in areas affected by malaria.
Increased values correspond to changes in other erythrocyte parameters. It is necessary to take into account the MCV parameter when interpreting analyses. Simultaneous changes in parameters are observed in cases where:
- the RDW indicator is exceeded, the MCV is reduced (with iron deficiency anemia);
- above normal MCV and RWD (may mean liver pathologies, megaloblastic, hemolytic anemia, cold agglutination);
- there is an excess of the RDW norm in combination with the MCV norm (indicates the likelihood of myelofibrosis).
Reduced index
A reduced RDW in the analysis means that in the sample taken for the study, the cells have practically no difference in volume. Cases where the analysis reveals that all RBCs are the same size are most likely in error.
Red blood cells may be of equal size in anemia, leading to an increased number of defective forms in the bloodstream.
The values of erythrocyte distribution indices decrease with:
- anemia (iron deficiency, folate deficiency, B12 deficiency);
- pregnancy (with the appearance of fetal hemoglobin);
- extensive blood loss (trauma, internal bleeding, childbirth).