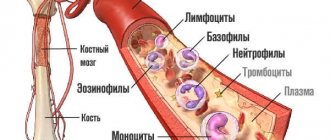
Blood is divided into a liquid part (plasma) and a cellular part (formed elements). The main representatives of the cellular part are erythrocytes (red cells). In clinical hematology, their quantity, designated RBC, sedimentation rate (ESR or ESR), and hematocrit number (HCT) are studied.
Hematocrit or HCT in a blood test is the percentage of red blood cells relative to the total volume of body fluid. GCA (general clinical analysis) is a method for studying the physical properties and chemical composition of blood, used in laboratory diagnostics. The study is prescribed to determine possible violations of microbiological processes in the body. Deviations identified during the analysis indicate the development of certain diseases.
Main indicators of OKA
| HB – hemoglobin | Leukocyte formula: NEU - neutrophils, LYM - lymphocytes, MID: (BAS - basophils, EOS - eosinophils, MON - monocytes) |
| RBC - red blood cells | |
| RET – reticulocytes | |
| HCT – hematocrit | |
| ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate | |
| WBC - white blood cells | |
| PLT - platelets |
The interpretation of the analysis is carried out by comparing the results obtained and the reference values accepted in clinical hematology for all blood parameters studied.
Hematocrit number
The hemorrhage value reflects the degree of saturation of the blood with red blood cells and their performance. Red blood cells act as a conductor of oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. This is their main function. In addition, red blood cells are responsible for the delivery of vitamins, amino acids, cholesterol and glucose from the digestive system to cells.
Take part in:
- in maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body (homeostasis) and the processes of adaptation to biological changes;
- in nutrient metabolic processes;
- in protecting blood vessels from the negative effects of free radicals.
The hematocrit level shows how much the blood is filled with red cells to ensure the full functioning of the body.
Laboratory microscopy
Calculation of the hematocrit number is included in the general clinical blood test. A separate study of this indicator may be prescribed in case of unsatisfactory results of OKA: anemia (anemia) and high concentration of red blood cells, as well as in case of bleeding of various etiologies (origins), in case of dehydration (dehydration) of the body. HCT is an important indicator of chronic hematological diseases.
To obtain objective final data, on the eve of the study, the patient is recommended to eliminate heavy foods (fatty and fried foods) from the diet, eliminate alcohol-containing drinks, and limit sports and other physical activities. The blood sampling procedure is carried out in laboratory conditions, in the morning.
Before the analysis, it is advisable to give up breakfast and smoking. The hematocrit value is determined using a laboratory device into which a glass graduated tube containing the blood sample being tested is placed. An anti-clotting agent is first added to the biofluid.
Under the influence of centrifugal forces (centrifugation), the blood is stratified. Red blood cells precipitate, clearly demonstrating their volume, and the plasma rises to the top. The remaining formed elements (leukocytes and platelets) are concentrated between them.
Brief scheme for hematocrit allocation
In modern laboratories, the process of measuring red blood cell volume is fully automated. The measurement value of hematocrit in clinical microscopy is taken as percentages or units (% multiplied by a factor of 0.01).
Decoding the hct indicator in a clinical blood test
A clinical blood test is a basic study that allows you to obtain a lot of information about the state of the body at the moment.
We are not yet quite accustomed to the fact that now such research has become automated and instead of the familiar names “erythrocytes”, “leukocytes”, etc. we are given the result with English abbreviations.
You have to gradually get acquainted with new abbreviations and understand what they mean. Let's look at the decoding of the HCT indicator in a general blood test. What does it mean? In what cases does it deviate from the norm? How can I fix it?
Reference values
The volume of red blood cells in the body is not a constant value, so the hematocrit depends on the following conditions:
- patient's gender;
- age category;
- chronic pathologies.
Temporary conditions of the body (pregnancy, infectious viral diseases, physical overload) are of no small importance. A change in the hematocrit number indicates the density (level of concentration) of the blood. In women, the standard values are lower than in men, since due to physiological characteristics the blood is renewed more often. In addition, the total amount of fluid in the body decreases with age, so children's HCT changes as they get older.
HCT reference values for adults
| Floor | Men | Women | ||
| Age | 18–45 | 45+ | 18–45 | 45+ |
| Norm (%) | 39–49 | 40–50 | 35–45 | 35–47 |
Reference! The average hematocrit for a healthy adult is 40–45% of the total volume of biological fluid.
The maximum permissible upper limit is 50%, the lower limit is 35%. The liquid part of the blood, accordingly, should not occupy less than 50% and more than 65%. When hematocrit values are less than 35%, as a rule, diet correction and systematic monitoring of TCA indicators are prescribed. A decrease in HCT by up to 25% is compensated not only by diet therapy, but also by taking medications. The patient's condition requiring hospital treatment is determined by a hematocrit value of less than 20%.
Normal children's indicators
Children's HCT norm is determined according to age category. Indicators approach adult values at puberty. Standard indicators for children and adolescents:
| Age | Newborn | Infants up to one year old | 1–5 years | 6–11 years | Puberty | |
| Boys | Girls | |||||
| Norm (%) | 33–65 | 33–44 | 32–41 | 33–41 | 35–45 | 34–44 |
Depending on the laboratory conducting the research, standards for children may have a more detailed gradation by age.
The high level of hematocrit in a newborn baby is explained by the transition from the intrauterine state, when the baby is in the amniotic fluid, to a full life (outside the liquid environment).
Decoding
After taking a blood test and receiving the result, you need to compare the red blood cell readings with the norm. An increased or decreased content of a substance in the human body can indicate the presence of a pathology and require immediate treatment. This means that the patient must undergo additional procedures to obtain an accurate diagnosis.
The interpretation of the analysis is carried out taking into account the age and gender of the patient. There are different standards for the content of red blood cells in the blood of men, women, pregnant women and children (childhood is divided into the category “newborn”, etc.).
Important information: What are platelets in a blood test (the norm and what they are responsible for)
Physiological reasons for changes in hematocrit levels
A natural change in hematocrit level, which is not a consequence of the disease, occurs in the following cases:
- Pregnancy. In women in the second and third trimester of the perinatal period, plasma volume increases significantly, while the number of red blood cells does not change. The blood becomes more dilute, so the hematocrit number drops to 35–40%. In addition, during delivery, heavy blood loss is often observed. In the postpartum period, the ratio of the liquid part of the blood and the formed elements should return to its original values.
- The first 6–7 days of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. During the period of natural blood loss by the female body, the composition of the blood changes. The hematocrit percentage decreases. The maximum permissible difference is 5%.
- Conditions associated with oxygen deficiency in body tissues. To compensate for the lack of oxygen, the body strives to produce more red blood cells, and accordingly, the hematocrit increases. An increased need for oxygen occurs during intense sports training (other physical overload), nicotine addiction, and in high mountain climates. And this condition is also observed in newborns, especially with complicated delivery, accompanied by fetal hypoxia.
In the absence of chronic diseases, a slightly reduced HCT is not considered a pathology in people over 65 years of age.
Pathological deviations
A change in hematocrit number not related to physiological characteristics means thickening or thinning of the blood. The abnormal composition of the biofluid indicates acute conditions or the presence of chronic pathological processes.
Increase and decrease in the percentage of hematocrit and plasma
Increased hematocrit
Hemoconcentration - an increase in the percentage of blood cells relative to plasma, is associated with hyperactive production of red blood cells or exceeding their natural size. If the hematocrit is elevated, the blood becomes thicker, circulation is impaired, and there is a risk of blood clots (thrombi) forming, risking heart attack and stroke.
A high level of red blood cells and hemoglobin is called erythrocytosis. This is not an independent disease, but a clinical sign of dysfunction of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, renal apparatus, hematological diseases, and oncology. Blood thickening is characteristic of the following chronic pathologies and temporary disorders:
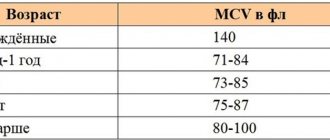
MCV in a blood test - what is it?
- erythremia (oncohematological disease, a type of leukemia);
- gas exchange disorders in the respiratory system (pulmonary failure);
- decompensation of the renal apparatus, as a complication of diseases of the urinary, endocrine system, etc.
- kidney cancer;
- dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces (hydronephrosis);
- dysfunction of the myocardium (coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy, cardiac asthma and other types of chronic heart failure);
- chronic inflammation of the airways (bronchial asthma) and diffuse inflammation of the bronchi (obstructive bronchitis);
- dehydration of the body caused by severe intoxication, intestinal obstruction, extensive burn damage;
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis), occurs as a concomitant symptom of menopause, diabetes, obesity, neuropsychological disorder, etc.;
- incorrect therapy with hormone-containing medications.
An increase in the synthesis of the renal hormone erythropoietin accompanies gestosis (late toxicosis during pregnancy), as a result of which the hematocrit level increases. In most cases, a woman needs inpatient treatment.
Decrease in hematocrit number
The reasons for a decrease in hematocrit are associated with insufficient production of red blood cells in the bone marrow or blood thinning due to hyperhydration of the body (excess fluid content). Since hematocrit and hemoglobin are closely correlated, the development of anemia (anemia) of various types is primarily expected:
- hemolytic anemia, caused by the destruction of red blood cells (the cause may be incorrect blood transfusion, heavy metal poisoning);
- pernicious anemia, otherwise Addison-Biermer disease, is characterized by impaired hematopoiesis due to a deficiency of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) in the body;
- iron deficiency anemia, caused by a lack of iron or the body’s inability to absorb it rationally;
- aplastic anemia associated with impaired bone marrow function.
The stage of anemia, in this case, is determined by the ratio of red blood cells and hemoglobin:
| Stage | Original | Moderate | Heavy |
| HCT indicator | 32–33% | 25–30% | less than 20% |
| HB indicator | 89–110 | 50–89 | up to 50 |
Reference! HB (hemoglobin) is a complex blood protein contained in red blood cells, without which it is impossible to supply the body’s tissues with oxygen.
Other reasons why HCT in a blood test is lowered are:
- excessive blood loss due to injury, surgery, internal bleeding (stomach, pulmonary, etc.);
- bone marrow diseases, most often of oncological etiology;
- high level of protein fractions in the blood (hyperproteinemia), caused by chronic liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatosis), oncology of lymphoid tissue and other pathologies;
- drinking large amounts of fluid that the organs of the urinary system are unable to fully process;
- postoperative period;
- diabetic glomerulosclerosis (transformation of living kidney tissue into connective tissue) and diabetic nephropathy (damage to the vessels of the renal apparatus);
- uncontrolled treatment with blood thinning medications (antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants).
An imbalance of water-salt balance, in which hyperhydration develops, can be caused by a decrease in the production of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) by the pituitary gland. If the stability of the hematocrit number is caused by pathological reasons, then it is necessary to reconsider the therapy of the underlying disease.
Correction of physiological deviations of HCT towards a decrease is carried out using a diet high in protein foods, with the parallel use of iron-containing medications and dietary supplements. If the etiology of the hematocrit abnormality is unclear, the patient is prescribed additional examination.
Results
The hematocrit value (HCT) is a reflection of the red blood cells (RBCs) in the blood relative to the plasma. The hematocrit level is determined as part of a general clinical blood test. HCT laboratory standards are developed taking into account the age and gender of the individual.
Women's normative values are lower than men's, which is associated with monthly blood loss. The upper limit of HCT for women of reproductive age is 45%. With the onset of the premenopausal period and during menopause, the norm increases to 47%. During the perinatal period, the hematocrit number decreases due to thinning of the pregnant woman's blood. For men under 45 years of age, the reference value is 39–49%, for men over 45 years of age, 49–50%.
The reasons for the increase in the indicator are:
- chronic pathologies of the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs;
- dehydration of the body;
- oxygen deficiency due to smoking or intense sports training.
A decrease in hematocrit number, first of all, indicates anemia (anemia). Children's values increase as they grow older. In newborns, the level is elevated due to changes in living conditions. A pathologically high rate is recorded during oxygen starvation (hypoxia) of the baby during birth. If there are systematic deviations of hematocrit, hemoglobin and red blood cells from the reference values, the patient needs advanced laboratory and hardware diagnostics.
What is hct in blood test
Blood is divided into a liquid part (plasma) and a cellular part (formed elements). The main representatives of the cellular part are erythrocytes (red cells). In clinical hematology, their quantity, designated RBC, sedimentation rate (ESR or ESR), and hematocrit number (HCT) are studied.
Hematocrit or HCT in a blood test is the percentage of red blood cells relative to the total volume of body fluid.
GCA (general clinical analysis) is a method for studying the physical properties and chemical composition of blood, used in laboratory diagnostics.
The study is prescribed to determine possible violations of microbiological processes in the body. Deviations identified during the analysis indicate the development of certain diseases.
Main indicators of OKA
| HB – hemoglobin | Leukocyte formula: NEU - neutrophils, LYM - lymphocytes, MID: (BAS - basophils, EOS - eosinophils, MON - monocytes) |
| RBC - red blood cells | |
| RET – reticulocytes | |
| HCT – hematocrit | |
| ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate | |
| WBC - white blood cells | |
| PLT - platelets |
The interpretation of the analysis is carried out by comparing the results obtained and the reference values accepted in clinical hematology for all blood parameters studied.