When calcitonin is elevated
Any even slight increase in calcitonin levels is a serious reason for an in-depth examination of the patient by specialists experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of C-cell carcinoma.
It is believed that the probability of medullary cancer with calcitonin concentrations above 100 pg/ml is close to 100%. There is a direct connection between the degree of increase in this hormone and the stage of cancer, as well as the presence or absence of distant metastases.
If, according to the results of a fine-needle biopsy, the nodes in the thyroid gland are benign, but the level of the hormone is elevated, the second analysis has an advantage, since the likelihood that the results of the study are erroneous is very small. If the upper limit of normal is significantly exceeded (more than 100 pg/ml), the patient’s thyroid gland and all nearby lymph nodes are completely removed to exclude the presence of regional metastases. Therefore, the determination of calcitonin is a very serious analysis, and its results must be as accurate as possible.
It should be noted that hereditary predisposition contributes to the occurrence of medullary cancer. In nearly 50% of cases of people who have C-cell carcinoma, their children also get the disease. Sometimes the thyroid gland has to be removed in children aged 5-7 years or even younger to prevent the growth of malignant cells. In such cases, even the slightest increase in calcitonin indicates that the doctor is doing everything correctly.
There are difficult situations when the hormone level exceeds the norm slightly, i.e. below 100 pg/ml, but above the upper limit of normal values. This result can indicate either a very small tumor or its absence. In any case of elevated hormone levels, you must contact a specialized endocrinology center for additional research.
These may include:
- Fine-needle puncture of the node with histological analysis of the tumor and determination of calcitonin in the washout from the needle;
- Stimulated test with the study of calcitonin in the blood after the administration of calcium gluconate.
The information described above allows us to derive the following points:
- Calcitonin is a tumor marker used to diagnose medullary cancer;
- A blood test for the hormone calcitonin must be taken in all patients with nodules in the thyroid gland;
- The analysis should be taken in a specialized laboratory that conducts research on a third-generation chemiluminescent analyzer;
- Any increase in the level of calcitonin in the blood should be a reason to contact a specialized endocrinology center.
Author of the article:
Education: Diploma from Russian State Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov, specialty “General Medicine” (2004). Residency at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University, diploma in Endocrinology (2006).
‹
Regimen for taking medicinal herbs for any female diseases (basics of herbal medicine)
7 mistakes that cause the tonometer to overestimate blood pressure readings
›
High calcitonin levels
A blood test for calcitonin determines the function of the thyroid gland. The growth of the hormone is associated with increased C-cell function. This occurs due to their malignant degeneration.
What does an increase in calcitonin levels indicate?
An increase in calcitonin levels of more than 100 pg/ml is an almost 100% probability of thyroid cancer. The higher the hormone level, the more advanced the disease. An increase in the indicator also indicates the appearance of metastases. With this indicator, as well as confirmation of the malignant nature of the tumor by biopsy, radical removal of the thyroid gland with adjacent tissue and lymph nodes is indicated.
A value of less than 100 pg/ml may be a sign of both a malignant thyroid tumor and other diseases. When making a diagnosis, they are guided by the existing symptoms and data from other examination methods.
Causes of increased calcitonin
A high level of calcitonin in a blood test is observed in the following diseases:
- thyroid cancer;
- benign proliferation of C cells;
- lung, breast and pancreas cancer;
- adrenal tumor;
- pernicious anemia;
- renal failure;
- liver cirrhosis due to alcohol abuse;
- pancreatitis;
- leukemia;
- adrenal tumor;
- chronic inflammation.
A physiological increase is observed during pregnancy and in young children. Calcitonin is elevated during recovery from severe injury.
Symptoms of increased calcitonin in the blood
Symptoms with a high rate depend on the disease. In the early stages of thyroid cancer, the following symptoms are observed:
- soreness in the front of the neck;
- difficulty swallowing;
- attacks of suffocation;
- change in voice timbre;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
Lung cancer does not manifest itself for a long time. Symptoms become noticeable only at stages 3-4. A lung tumor is characterized by a prolonged cough, heaviness in the chest, hemoptysis, and attacks of suffocation.
A malignant breast tumor is initially felt as a small lump. Gradually it becomes painful. In later stages, discharge from the nipple appears.
Liver cirrhosis develops due to cell damage from alcohol. In place of properly functioning tissue, scar tissue appears. Liver cirrhosis is manifested by yellowing of the skin, enlargement of the abdomen due to fluid accumulation, and dilation of the saphenous veins.
An increase in the indicator does not have independent symptoms. All manifestations are associated with the underlying disease.
The course of the calcitonin test and the rules for preparing for it
In order to determine the concentration of calcitonin in the blood, blood is drawn. The process looks like this and includes the following steps:
- After venipuncture has been performed, the material is placed in a sterile empty tube. It is also possible that a specialized gel is present in the test tube.
- The sample is sent into the cold, but the material must not be allowed to freeze. While in a portable thermal container, the blood is transferred to the laboratory.
- In the laboratory, whole blood is placed in a centrifuge and the serum is separated.
- The resulting material is analyzed using specific equipment and reagents. The results of the reaction are noted down and transferred to the patient for further review and transfer to the attending physician.
The need to take a hormonal test means strict adherence to medical recommendations for preparing for it.
The main points of preparation that will allow you to obtain true indicators of blood enzyme concentration are the following:
- A calcitonin sample is taken on an empty stomach. The last meal can be taken the night before, but no less than 8 hours before the actual test. An interval of 8-12 hours is considered ideal. Fasting time should not exceed 14 hours.
- If it is necessary to take a calcitonin test, the patient must refrain from consuming alcoholic beverages - the interval between the last alcohol consumption and the test is at least 24 hours.
- One hour before the event you are required to stop smoking.
- It is advisable to refrain from sexual contact and active physical activity 2 days before the test.
- On the eve of taking the sample, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations and nervous tension.
As for the medical worker, the doctor is obliged to conduct an explanatory conversation with the patient, which consists of the following points:
- The physician needs to explain the need to take a certain test, describe the risks if it is refused, and also explain the difference between the methods used in laboratories and what their impact on the final result of the analysis is.
- The doctor informs the patient about some of the main points of the procedure, such as the collection of material from the vein, who should carry out the collection procedure and at what time the procedure should take place.
- The specialist informs the patient about what venipuncture is, and also describes its main stages - applying a tourniquet, puncture, sensations from the tourniquet and puncture of the vein.
- Inform that the test results will not be ready immediately, but only after 1-7 days from the moment the material was taken for analysis. The average cost of a study in Moscow is about 1000 rubles.
After the patient receives the answer, he must visit the attending physician, who will review the obtained values and, based on their results, will be able to assume, establish or confirm the diagnosis.
How to get tested
In order for the data obtained to be reliable, preparation is required:
- 10 days before the examination, you need to agree with the doctor who is sending you for a blood test about the possibility of using medications.
- Some medications can change the level of calcitonin in the blood; it is especially important to consider the use of calcium (available in dietary supplements and vitamin-mineral complexes) and hormones. In a situation where a drug is vitally necessary, it must be included in the referral form.
- During the day, you should exclude sweets, fatty and fried foods, and drinks with alcohol from your diet. Before the analysis, the last meal is allowed no later than 10 hours, then you can drink only clean water.
- On the previous day, it is not recommended to engage in sports or work that requires significant physical effort.
- If the patient is prescribed X-ray examinations, ultrasound, endoscopy or physiotherapeutic procedures, then they can only be completed after diagnosis
- You should not smoke in three hours, and in half an hour you should maintain physical and emotional peace.
The biomaterial for analysis is venous blood. Serum is isolated from it and the level of calcitonin is determined by immunometry, the results are given to the patient the next day.
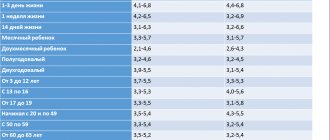
Hormone norm
The level of calcitonin in adults in the blood depends on gender, age, and laboratory techniques. There are 2 types of determining the level of thyrocalcitonin: ELISA and ELISA (enzyme-immunoenzyme and immunochemiluminescent). Their research indicators are different.
ELISA is more common. For example, the calcitonin norm for ELISA is as follows:
- in adult women of fertile age – 0.07-12.97 pg/ml (picogram – trillionth of a gram);
- adult men – 0.68-32.26 pg/ml;
- children – up to 79 pg/ml.
With ICHLA - calcitonin hormone (thyroid hormone) in women and girls - does not exceed 0-1.46 pmol/l; for adult men and boys – no more than 2.46 pmol/l. All this data is collected for the work of laboratory technicians in special tables.
Calcitonin for women: the norm is different in that it has no lower limit. Even if the blood serum contains zero levels of the hormone, this will be considered normal. An increase is a rise in numbers above the upper limit of normal.
The table of norms shows that there is no difference between girls and boys. The highest level of calcitonin (physiological) was observed in infants in the first 7 days of their life: 70-348 pg/ml; this comes from feeding on breast milk, when Ca is transmitted from the mother.
Calcitonin levels decrease with age, especially during menopause in women. Calcitonin may temporarily increase during pregnancy. Why? Because during gestation the background of hormones completely changes in the body and general standards are invalid here. Calcitonin in the blood becomes especially high before childbirth. The numbers also remain high during breastfeeding.
Calcitonin increases with hormone replacement therapy containing estrogen. After treatment, calcitonin levels in the blood return to normal on their own. Another reason for the increase is the consumption of alcohol and intravenous administration of calcium. Calcitonin levels are tested separately from other thyroid hormones in specialized diagnostic centers.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
The main reasons why the concentration of a hormone such as calcitonin in the blood of women may change:
- osteoporosis, if the norm is low;
- the occurrence of an oncological disease - thyroid cancer, including its relapse can be detected;
- consequences of injuries in the form of cracks in the bones, severe bruises and fractures.
If we talk specifically about those cases when calcitonin is low, the reasons may be the following:
- excessive physical stress for a long time;
- decreased hormonal levels;
- severe fatigue, which occurs very often;
- cretinism, mental retardation;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- lack of calcitriol, one of the active forms of vitamin D, which is responsible for the absorption and assimilation of calcium and phosphorus.
Sometimes a reduced level of calcitonin is a consequence of removal of the thyroid gland, and therefore cannot be considered as an indicator of a serious disorder in the body. When this hormone in the blood is low, the situation is usually more positive than when it is high.
If a decrease in the normal level occurred after treatment of cancer, the indicator may even be a positive factor. Often in such cases this means that the disease is receding.
Structure and functions of the hormone
Calcitonin (hormone calcitonin) - what is it? This is a peptide hormone consisting of 32 amino acid units. 8 sources (from animals) of calcitonin have been identified, but 3 have received medical significance and are used: thyrocalcitonin thyroid gland from salmon, pigs and humans.
The functions of calcitonin are such that, in addition to its main control over the levels of Ca and P, the hormone performs:
- regulation of calcium absorption in the intestine, and therefore reduces it in the blood serum;
- participates in the production of vitamin D;
- increases daily urination due to the excretion of sodium ions and uric acid;
- has a slight anti-inflammatory effect;
- reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach;
- the level of phosphorus in the blood decreases slightly.
The mechanism of the hormone:
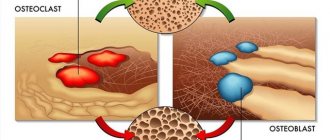
- Stimulates the functional activity of osteoblasts, helping to form bone tissue;
- Calcitonin blocks the absorption of Ca in the intestine;
- Inhibits Ca reabsorption (reabsorption of calcium from primary urine) in the kidney tubules and removes it with urine.
- Thyroid calcitonin inhibits the functioning of osteoclasts; Unlike osteoblasts, they can resorb the mineral component of bone tissue.
What to do to normalize the indicators?
In order to reduce the amount of calcitonin, the exact reason for the increase in its parameters should be established. First of all, the patient needs:
- review your daily routine;
- avoid excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- sleep at least 8 hours;
- include foods rich in calcium in your diet.
If there are significant deviations of the indicators from the reference values, a course of drug therapy is prescribed aimed at eliminating the source of the inflammatory process or surgery to remove the tumor formation
It is important to remember that even a slight change in the amount of biologically active substance of C-cells leads to increased fatigue, the development of oncological processes in the human body, premature termination of pregnancy, fragility and brittleness of bones, secondary fibrocystic osteitis, endemic cretinism. In conclusion of the above information, I would like to emphasize once again that a blood test, which allows you to determine the level of calcitonin, must be performed regularly.
Of course, one analysis is not enough to diagnose malignant neoplasms. For this purpose, qualified specialists (endocrinologists, oncologists, surgeons) prescribe the patient ultrasonography, positron emission tomography, genetic analysis to identify point mutations in the RET proto-oncogene (the initiator of the formation of tumor formations), determination of the concentration in the blood of iodine-containing hormones produced by the thyroid gland - T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine).
Indications for use
Application:
Systemic diseases with skeletal restructuring (Paget's disease, osteogenesis imperfecta, spontaneous bone resorption, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head); osteoporosis (postmenopausal, senile, steroid, parathyroid, etc.), fibrous dysplasia, traumatic bone damage with a complicated course of the repair process (slow healing of fractures); osteomyelitis (traumatic, radiation), zonal pathological reorganization of bones in athletes, periodontal disease, Sudeck syndrome, familial hyperphosphatemia, hypercalcemia of various origins (including idiopathic hypercalcemia of newborns), thyrotoxicosis, myeloma, bone metastases, hypervitaminosis D, prevention of bone disorders in as a result of prolonged immobilization; bone pain associated with osteolysis and/or osteopenia; acute pancreatitis (as part of combination therapy).
Calcitonin is normal
When testing blood for calcitonin and assessing the results of this analysis, it should be remembered that there is no lower limit of normal for this hormone
. If its level in the blood is zero, this is also normal. It is important that it does not rise above those limits that are designated as the upper limit of normal for this particular analyzer and this particular set of reagents.
It doesn’t make much sense to indicate any specific norm for calcitonin here, since laboratories now use very diverse models of analyzers - this leads to the fact that the concept of norm in this case should not even be discussed. When you take a calcitonin test in a high-quality modern laboratory, the norm will be indicated on the same form - this rule is followed very strictly by good laboratories.
The norm and its excess
The norm of calcitonin in men and women is different; in women it should be within 5.0 ng/l, and in men – up to 8.4 ng/l. It is also important to remember that each laboratory equipment may determine the results differently, so the standards may have different indicators.
In medical practice, a calcitonin test is carried out to diagnose a medullary malignant tumor of the thyroid gland. This rather serious disease is hereditary in nature and is very often diagnosed in very young children. With this disease, this indicator increases sharply. Moreover, if after surgery the CT scan is higher than normal or even increases, then the treatment is ineffective and the disease progresses.
In addition to the fact that a CT scan is necessary to detect medullary cancer of the gland, it is also carried out to determine calcium metabolism along with a test for parathyroid hormone.
Calcitonin may also be higher than normal for the following indications:
- Various lung tumors, non-malignant.
- Kidney failure.
- Acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Increased function of the parathyroid glands, which are located on the posterior wall of the thyroid gland.
- Anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12.
- Certain chronic bone diseases involving bone tissue.
- Malignant formations of internal organs.
There are situations when an increase in this standard is associated with the following conditions:
- Pregnancy in women.
- Children at birth.
- Sex hormone therapy.
- Intravenous calcium administration.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages.
You should know that when calcitonin increases, the remaining thyroid hormones remain normal and perform their function.
In order to obtain correct analysis results during the examination, you must adhere to certain rules. Before taking tests, both women and representatives of the stronger sex need to exclude physical overload, stressful situations, and it is advisable not to overeat or drink alcoholic beverages. Women are also advised to take contraceptives. The most suitable time for examination is the morning.
Reasons for the increase
The following factors of pathological changes are encountered:
Kidney damage
Inflammatory, degenerative, other organic and functional disorders. There can be many options.
In any case, the pathological process leads to disturbances in the removal of harmful products and traces of mineral compounds. All this artificially stimulates the production of calcitonin in order to speed up natural recycling processes.
Among the most common pathologies:
- Pyelonephritis. Infectious inflammations.
- Glomerulonephritis. Autoimmune lesion.
- Degenerative disorders.
- Anatomical changes. Wrinkling, prolapse of the kidney and other disorders of the same kind.
- Cancer or benign oncology.
The process is complex, including a decrease in the production of specific kidney substances. This is a complex cycle that ends with biochemical deviations.
Treatment is carried out by a nephrologist (not to be confused with a neurologist). The technique must correspond to the primary pathology.
- For infectious diseases, antibiotics and antivirals are prescribed.
- If an autoimmune process occurs, glucocorticoids and anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
- In case of organic disorders, surgical correction cannot be avoided.
- The same applies to cancer and oncology.
The process is more than creative. Requires an accurate assessment of the situation and sufficient qualifications of a specialist.
Thyroid disorders
Various diseases. An entire subsection of the ICD classifier is dedicated to them.
Among the possible pathological processes, the most common ones are:
- Nodular growths. The so-called goiter.
- Diffuse changes. When the tissue increases in volume evenly. In many ways, the violation is similar to the previous one.
- Cancer. We will talk about it further.
- Inflammatory processes of autoimmune and infectious types.
The hormone calcitonin increases because the thyroid gland is disrupted and its secretory function falls into chaos.
Restoring the normal state is the task of the endocrinologist. Iodine group drugs are prescribed and a diet is indicated. If the changes are advanced, surgery will be required. Resection of an organ (removal of part of it). The question is complex.
As soon as the functionality of the structure is restored, calcitonin itself will return to normal. This is not the fastest process; up to several months of constant correction are required.
Thyroid cancer
A common cause of excess levels of the substance. The fact is that the altered cells grow through healthy tissue, thereby stimulating increased production of calcitonin.
This phenomenon will only intensify over time, since the pathological process will not go away on its own.
Attention:
Thyroid cancer is very mild. Even in advanced stages, symptoms are minimal. Clinical signs similar to those of hyperthyroidism may occur.
Among the manifestations:
- Loss of body weight.
- Rising temperature.
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- Dyspnea.
- Exercise intolerance.
- Pressure surges.
- Tachycardia, heart rhythm disturbances.
Oncologists are involved in treatment. There is time, because, among other things, thyroid cancer develops very slowly and almost does not metastasize. An operation is scheduled. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are carried out.
The prognosis is relatively favorable even at the 3rd stage of the pathological process. But there is no need to delay.
Then comes the turn of rehabilitation. Recovery from cancer takes up to a year and only then does the level of the thyroid hormone calcitonin return to normal.
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas. The increase in calcitonin concentration is associated with the biochemical characteristics of the endocrine system. Therefore, a change in level is observed immediately. Especially in the acute course of the disorder.
Chronic pancreatitis does not manifest itself so harshly and aggressively. But the numbers are also growing.
Specific symptoms of the disorder:
- Pain in the left side of the abdomen. Surrounding, sharp.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Inability to digest food.
- Increased body temperature. As a rule, in an acute condition.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Dyspnea.
- Heart disorders.
Therapy falls on the shoulders of an abdominal surgeon and gastroenterologist. The issue is resolved in the hospital; it is too dangerous to leave the patient alone with the disorder.
Acute forms are treated promptly. Part of the gland needs to be removed. Because necrosis begins very quickly, that is, the death of the tissues of the structure.
Chronic forms can be corrected conservatively. Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed and a gentle diet is prescribed. Antibiotics are used to quickly cope with the situation.
To facilitate the functioning of the organ, enzymes are indicated: Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon. Dosage is strictly individual.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Acute or chronic disorder of the structure of an organ. There is death of tissues and hepatocyte cells.
With rapid currents, the chances of survival are negligible. The process is aggressive and develops in a matter of days. Then it gets late.
Chronic cirrhosis goes through three stages:
- Compensation. When the disorder is just beginning and there are no symptoms yet. Everything is relatively normal.
- Subcompensations. The body is coping so far, but is already starting to get tired. Clinical signs are pronounced.
- Decompensation. Complete frustration. Increasing disturbances in the functioning of the liver and all body systems.
Treatment is possible in the first two stages. Then it will make little sense. The level of calcitonin increases intermittently as cirrhosis moves to a new stage.
Correction is carried out by hepatologists and gastroenterologists. Hepatoprotectors are prescribed and a diet is prescribed. If possible, a liver transplant is performed. At the first two stages this is still permissible. In addition, it gives good results.
The only problem is the number of donors and the lack of organs for transplantation.
Some natural factors
Calcitonin in a blood test increases as a result of the influence of normal factors not associated with diseases. The following reasons especially often affect the results of research:
- Pregnancy. During gestation, indicators grow very quickly. This is acceptable because the child's skeleton is being formed. Without calcitonin, it is impossible to achieve body growth and normal development.
- Breast-feeding. Levels of the substance remain at high levels due to inertia, so there is no danger of illness. Gradually the condition will become normal.
- Puberty. There are surges in hormone levels. This is the result of a real biochemical storm. The body is growing, anything is possible.
No special treatment is required, but the patient's health condition must be carefully monitored.
A high level of physical activity, stress, and a change in geographic location have an effect. These are short-term influencing factors. But they need to be taken into account at the time of taking the analysis.
This also includes bad habits: drug addiction, alcoholism, cigarette addiction.
What is calcitonin?
Calcitonin is a thyroid hormone that is produced by special C cells. These cells are often located near the follicles, which is why they were previously called parafollicular cells. C-cells are of neuroendocrine origin and are formed in the pancreas during the intrauterine development of the human body. Calcitonin synthesis is the main function of C cells.
The functions of calcitonin are not yet fully understood; this distinguishes it from other thyroid hormones. The number of C-cells that secrete calcitonin is significantly less than the B- and C-cells included in the follicles of the gland. While the T3 and T4 hormones are tested to determine organ function, the blood calcitonin value is used for other purposes.
In various textbooks and manuals, the hormone calcitonin is considered an antagonist of parathyroid hormone, a product of the parathyroid (or parathyroid) glands. The importance of parathyroid hormone lies in the activation of special cells - osteoclasts. The latter, under the influence of this hormone, destroy bone tissue, as a result of which calcium is released from it and enters the blood. Another function of the parathyroid hormone is to enhance the reabsorption of calcium ions in the kidney tubules from primary urine. Parathyroid hormone also stimulates the conversion of vitamin D into its active form, calcitriol, which ensures the transport of calcium ions from the small intestine to the blood. Thus, the end result of the activity of parathyroid hormone is an increase in the level of calcium in the plasma, and calcitonin has the opposite effect.
In terms of its activity, calcitonin is much weaker than parathyroid hormone; therefore, it cannot be argued that calcium metabolism in the body is regulated only by these two hormones. In this complex process, in addition to parathyroid hormone and calcitonin, vitamin D and many other compounds take part.
C-cells of the thyroid gland synthesize calcitonin in very small quantities, so its concentration in the blood is normally very low. This hormone can also be produced in small amounts in the intestines. In this article we will consider calcitonin as a tumor marker, which is used in the diagnosis of a dangerous tumor from the thyroid tissue - medullary cancer.
Low levels of calcitonin in the blood
The blood test for calcitonin has no lower limit of normal. Low numbers do not indicate the presence of diseases or other abnormalities. A decrease in hormone levels can indirectly indicate a lack of calcium.
Reasons for decreased calcitonin
A low rate always has a physiological origin. In women, especially at the beginning of menopause, it drops to zero. This is due to hormonal changes in the body and a decrease in estrogen production.
The decrease in the indicator determines the effectiveness of treatment for thyroid cancer. Patients treated for cancer are prescribed quarterly tests for five years. The growth of the hormone after its normalization indicates a relapse of the disease and the appearance of metastases.
How to increase calcitonin in the blood
There is no need to increase calcitonin without strict indications. A reduced rate in itself does not mean the presence of diseases. It should be assessed only in conjunction with other tests and symptoms. Low levels of the hormone are often accompanied by a decrease in bone strength due to lack of calcium. This is manifested by pathological fractures, which occur even with a small load on the bone.
You can increase your calcium levels with proper nutrition. The diet should include fermented milk products - cottage cheese, kefir, whey. Regular physical activity and taking vitamin D will help strengthen bone tissue. Calcitonin is a protein substance produced by C-cells of the thyroid gland. Its main function is to lower calcium levels in the blood, retaining it in bone tissue. A thyroid tumor causes increased C-cell function, so calcitonin increases. The test is used to confirm thyroid cancer. The test can be done by referral from a doctor in any private laboratory or clinic near your place of residence. It is done in 1-2 days.
Blood test for calcitonin
The concentration of calcitonin can now be determined in many laboratories, which use various equipment for this purpose. The most reliable information about the content of this hormone can be obtained using 3rd generation analyzers based on the immunochemiluminescent method. More common 2nd generation analyzers using enzyme immunoassay methods are cheaper, but have a serious drawback - a significant error in the result. Their use may lead to inaccuracies in the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of patients.
A very dangerous malignant tumor, C-cell carcinoma, or medullary cancer, can develop from the C-cells of thyroid follicles. A feature of this tumor is its relatively slow but steady growth. Over time, medullary cancer metastasizes to the lymph nodes located in the neck and mediastinum; through the bloodstream, metastases can also reach the lungs, liver, bones and even the brain. Treatment of C-cell carcinoma presents significant difficulties, since the tumor does not respond to antitumor chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy. Only antitumor agents based on kinase inhibitors can have a minor effect on C-cell carcinoma. The only effective treatment for this type of cancer is surgery in the early stages of the process. This is the only way that gives a chance for recovery if cancer is diagnosed early.
Since C-cell carcinoma grows from cells that secrete calcitonin, its content in the blood increases sharply already in the early stages of cancer. This is why the content of this hormone is of such interest to endocrinologists and surgeons. Calcitonin concentration testing is the most reliable and early method for determining medullary cancer, which allows saving more than one thousand human lives.
Every year, approximately 100-150 new cases of C-cell thyroid carcinoma are registered throughout Russia. Statistical studies have shown that in 16 densely populated regions of the European part of Russia, about 40 diagnoses of medullary cancer are made per year.
Among all cases of thyroid tumors, the most dangerous are the anaplastic and medullary forms. While effective treatment methods have not yet been developed for anaplastic cancer, C-cell carcinoma is completely curable if diagnosed early. And only a blood test for calcitonin can help with this.
In 2012, the European Thyroid Association added to its recommendations an indication of the need for a single determination of calcitonin in all patients with nodules in the thyroid gland. This analysis does not have to be performed every year; a repeat study in the case of the first normal result is prescribed only if new nodes have been registered.
This fact has led the European endocrine community to believe that the financial costs of conducting 300 studies will be justified if at least one of them reveals the presence of medullary cancer. At the same time, the American Thyroid Association still believes that such a massive scale of calcitonin research is not economically justified. This concerns only the financial part of the issue; no one doubts the clinical value of this method.
What is the essence of the analysis?
Calcitonin blood test, what does its result show? The main purpose of the procedure is to detect medullary cancer that affects the thyroid gland. You can also determine the size of the tumor and the presence of metastases.
In a healthy body, the hormone is produced in small volumes, although it is present even in the intestines.
A high concentration of calcitonin is a tumor marker, which in almost 100% of cases indicates damage to the thyroid tissue by malignant neoplasms.
If after resection of the tumor, thyrocalcitonin levels remain elevated, this indicates that:
- the tumor was not completely removed;
- metastases appeared;
- there was a relapse of the disease.
About the hormone
In most medical textbooks, it is considered to be a kind of antagonist of parathyroid hormone, which is synthesized by the cells of the parathyroid glands. Parathyroid hormone triggers the action of special cells - osteclasts, which cause the destruction of bones and remove calcium from them into the blood. Other properties of the hormone are reduced to increased absorption of calcium from urine and to the formation of calcirol, which helps better absorption of the element from the gastrointestinal tract. That is, the functions of parathyroid hormone are reduced to increasing the level of calcium in the blood. The hormone calcitonin, in a certain way, “counteracts” parathyroid hormone, helping to deposit the element in the bones, and therefore reducing its concentration in the blood.
Nevertheless, in its effects it is weaker than parathyroid hormone. In addition, once in the blood fluid, it disintegrates quickly (half-life ranges from 2 to 15 minutes). That is why it is not correct to say that calcium balance is ensured purely by the balance of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. It should be noted: parathyroid hormone, if introduced into the body in small dosages at intervals, will also enhance the deposition of the element in the bones. Therefore, it is more correct to think that calcium metabolism is a complex process in which calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, vitamin D and other substances are involved.
If there is an imbalance in this balance, in particular when doctors suspect primary osteoporosis, the person is asked to undergo a test to measure hormone levels, as well as to study other markers of bone remodeling. As a rule, primary osteoporosis is associated with a decrease in normal calcitonin levels. However, if a person has secondary osteoporosis, in this case the level of calcitonin does not decrease.
However, the test indicators are especially important for detecting thyroid cancer and identifying multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome, which manifests itself as medullary cancer, pheochromocytoma, parathyroid hyperplasia, and hyperparathyroidism. It should be noted that the thyroid gland produces small amounts of calcitonin, so there cannot be a lot of it. Of course, it is produced in the intestines, but these quantities are completely miniscule.
How and under what conditions is it produced?
The mechanism of calcitonin production is triggered by an increase in the level of calcium in the blood.
Simplified, its action can be described as follows:
- If the concentration of calcium increases (for example, after eating a meal containing this mineral), C-cells, under the influence of gastrin produced in the stomach (a hormone that regulates the digestion process), begin to work intensively, synthesizing calcitonin.
- Calcitonin, acting on bone tissue receptors (osteocytes), initiates the process of calcium absorption by it, activates osteoblasts and blocks osteoclasts.
- As a result, bone mineral density increases and the amount of calcium in the blood decreases to safe levels.
If necessary, under the influence of calcitonin, the kidneys join the process of calcium removal, absorbing more calcium from the blood, and the intestines temporarily stop absorbing this mineral.
This mechanism for regulating calcium levels protects the body from hypercalcemia - excess calcium:
- leading to disruptions in the functioning of internal organs;
- negatively affecting the functioning of the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract;
- provoking the development of cardiovascular diseases.
After the calcium level drops to normal values, within a few minutes calcitonin breaks down into its components and is removed from the body. Normally, the more calcium enters the body, the more calcitonin is produced, and vice versa.
Symptoms of increased calcitonin
First signs:
- the timbre of the voice changes;
- dysphagia;
- breathing becomes difficult at times;
- pain at the site of the tumor and visual changes in the neck;
- enlarged lymph nodes, the appearance of metastases.
A calcitonin level above 100 pg/ml indicates the need for surgical treatment. Most often, total excision of the entire gland with lymph nodes is performed. What does elevated thyrocalcitonin indicate? If the excess does not go beyond the upper limit of the norm, you often just need to reconsider your work and rest schedule, establish proper sleep and a balanced diet.
Sometimes tests show a calcitonin value of 2.00. This indicator is not considered high, since the normal level of a hormone such as calcitonin in women, 2.00 pg/ml, fits into the existing specified range in the table.
With an age-related decrease in calcitonin, if there are no contraindications, its level can be supported by taking medications and increased, but treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Myxedema. Cretinism. Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone.
Myxedema. Cretinism. Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone.
Proper preparation for research
To obtain correct final analysis data on the eve of taking biological material, the patient must fulfill certain requirements. Women should stop taking oral contraceptives 30 days before laboratory testing. For three days you should limit physical activity, including going to the gym. During the day you must refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages and eating too much food.
You need to donate blood after a 12-hour fast. Do not smoke 2 hours before the diagnosis. A sample of biomaterial (venous blood) is collected in the manipulation room of the clinical diagnostic center in the morning - from 8.00 to 10.30. The patient should come to the laboratory half an hour before the procedure to have the opportunity to sit down, relax and unwind.
To determine the level of calcitonin, enzyme-linked immunosorbent or chemiluminescent immunoassay methods are used.
Laboratory diagnostics
A calcitonin test is performed to identify tumor markers. High levels of this hormone in the blood, as a rule, indicate tumor growth in the thyroid gland (sometimes in other organs). Therefore, thyrocalcitonin level testing is mainly used to determine medullary cancer (C-cell carcinoma).
To test for calcitonin, a blood test is prescribed. There are two research methods:
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This method is cheaper and more common, but less accurate. A high error can lead to an erroneous diagnosis and, accordingly, incorrect treatment. It is carried out using second generation analyzers.
- Immunochemiluminescent (ICHLA). This technique is characterized by increased accuracy, but also a higher price.
In addition, not every laboratory uses third-generation analyzers required for CLIA. However, ICHLA increases the likelihood that the diagnosis will be made correctly.
Additionally, blood biochemistry is also carried out to clarify the calcium content. Venous blood serum is used as a biomaterial for studying calcitonin parameters.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
A test for thyrocalcitonin levels is carried out in cases where there is a suspicion of cancer. The hormone content in the blood also changes in the following disorders:
- primary osteoporosis,
- hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands,
- multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome,
- hyperparathyroidism,
- hypoparathyroidism,
- pheochromcytoma,
- disruption of the body's calcium supply.
If you have symptoms of any of the above diseases, your doctor may order a blood test to determine your hormone levels. The study is also sometimes used during the rehabilitation period after injury to monitor the process of bone healing. After removal of part of the thyroid gland or the entire organ, monitoring of the patient's condition during the recovery period is required. To do this, they resort to calcitonin analysis. Its concentration in the blood will indicate to the doctor whether additional therapy is required to restore normal levels of the hormone.
Preparing for the study
To ensure that the analysis results are as accurate as possible, the patient should prepare:
- You must stop taking hormonal medications for two weeks before the test. If it is impossible to refuse them, their list is recorded and taken into account when deciphering the results.
- The day before the procedure, you must give up fatty foods, alcohol and cigarettes.
- The day before the analysis, it is recommended to suspend sports training. Heavy exercise can have a significant impact on results because physical activity releases hormones into the blood.
- You should not do x-rays or ultrasound examinations. If the patient is prescribed an x-ray or ultrasound, it is necessary to reschedule them for the period after the blood test for calcitonin.
- Blood from a vein is donated for the hormone calcitonin on an empty stomach.
Calcitonin: how it is formed, what it is responsible for in the body
Thyroid calcitonin, or calcitonin, is a hormone produced primarily by the thyroid gland, as well as other organs, of which its production is most noticeable in the lungs. Unlike thyroxine and triiodothyronine, which are also produced by the thyroid gland, the production of calcitonin does not depend on iodine in any way.
Calcitonin has not yet been fully studied, and information about it is not comprehensive, but it is known that its functions in the body are important, since it takes an active part in metabolism, namely in the balance of calcium and phosphorus in the body. In this sense, calcitonin can be considered an antagonist of parathyroid hormone, which also regulates the exchange between these substances.
The fact is that calcitonin and parathyroid hormone act on a feedback principle in maintaining this balance: parathyroid hormone stimulates an increase in calcium in the blood by leaching it from bone tissue, and calcitonin, on the contrary, retains calcium in the bone. The same is with phosphorus: parathyroid hormone ensures its increase in the blood, and calcitonin has the opposite effect, improving the excretion of this element from the renal tubules in the urine.
In the struggle of these two opposites, the balance of calcium-phosphorus metabolism is achieved. Thus, without calcitonin, proper regeneration of bone tissue and maintenance of the musculoskeletal system in a healthy state is impossible.
So, calcitonin prevents the destruction of bone tissue, strengthens the structure of bones during periods of increased stress on the musculoskeletal system and on the body as a whole (for example, during pregnancy and lactation); in diseases that arise from disorders of mineral metabolism (for example, osteoporosis), it reduces bone fragility.
But in diagnostic procedures, another ability of calcitonin is especially important: it is an oncological marker - a calcitonin test can detect thyroid cancer. This is why calcitonin testing is so important. To summarize, let us outline the main reasons why the concentration of calcitonin in the blood may change:
- Thyroid cancer - at the initial stage of the disease or during its relapse;
- Osteoporosis is a systemic disorder of the structure of bone tissue, characterized by increased fragility of bones (can occur with too intense production of parathyroid hormone;
- Severe bruises, fractures, cracks in bones resulting from injury.
Women are more susceptible to thyroid diseases than men. The bone tissue of women experiences serious stress during pregnancy and breastfeeding, because both of these conditions are accompanied by the provision of calcium not only to the female body itself, but also to the body of the child - the fetus or infant. That is why women are recommended to periodically donate blood for calcitonin.
Calcitonin hormone: general information
The concentration of a specific substance depends on the levels of parathyroid hormone (a regulator produced by the parathyroid gland) and free calcium. An important component affects the exchange of Ca and phosphate ions, which are responsible for the constancy of the membrane potential. For this reason, even small fluctuations in thioreocalcitonin are dangerous. The production of the hormone maintains optimal concentrations of potassium (K) and calcium (Ca). A long peptide of 32 amino acids provides counteraction to the influence of parathyroid hormone.
The main share of the thyroid hormone calcitonin is produced by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland; thyrocalcitonin is also produced in small quantities by the structural elements of the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. To reduce Ca levels, the body uses several mechanisms.
In newborns, levels of an important regulator are increased in the first days of life. During pregnancy and in nursing mothers, the level of thyrocalcitonin is higher: it is important to protect the woman’s body from increased loss of Ca, to ensure optimal supply of the microelement to the fetus, for the formation of a complete musculoskeletal system.
Calcitonin is a specific indicator indicating a pathological process in the body. The hormone is a tumor marker for medullary thyroid cancer, but high values do not always indicate the development of a malignant process. If the levels are elevated, additional examination is required: ultrasound of the thyroid gland and tissue biopsy of the affected organ, a provocative test using pentagastrin or calcium gluconate. Excessive concentration of thyrocalcitonin may indicate active inflammation of the thyroid gland, lungs, and severe dysfunction of the excretory system.
Learn about nutritional features and rules for following the 5P diet for pancreatitis.
Instructions for using the drug Endorm to restore the functioning of the thyroid gland are described on this page.