- June 11, 2019
- Prostatitis
- Yulia Kazakova
One of the most effective methods for examining the prostate is transrectal ultrasound. The doctor can detect or exclude pathology by obtaining an accurate and detailed image of the shape of the prostate gland structure using a penetrating ultrasonic wave. An endoscope is inserted into the body through the rectum, that is, rectally, during transrectal ultrasound. Preparation for prostate examination must be thorough. Frequent omission of this stage by doctors leads to distortion of results and repeated diagnosis.
What is TRUS
TRUS has the same principle of operation as conventional ultrasound - external. It is carried out like this: an endoscope with a sensor is inserted into the patient’s anus. Ultrasound waves travel into tissue from the transducer and create echo waves when reflected. These waves are captured by an endoscope with a sensor, analyzed and displayed on the screen.
The nature of the image will depend on the difference between the ultrasound waves and those reflected from the tissues. Based on these data, the device determines the distance between different parts of the organ, its structure and size, and the density of some areas. Under ultrasound guidance, a biopsy may be performed during the procedure to diagnose conditions in questionable areas.
Purpose of the event
Transrectal ultrasound examination of the prostate in medical practice is one of the most informative ways to diagnose pathologies in this organ. It allows you to accurately exclude or identify problems arising in the bladder or prostate gland.
TRUS helps identify such disorders in the genitourinary system:
- Malignant and benign tumor processes in the prostate.
- Prostatitis, the presence of stones, cysts, hyperplasia and prostate adenoma.
- Bladder pathologies.
- Problems with the blood vessels of the pelvis.
How does the prostate gland work?
The shape of the gland resembles a chestnut; it can be conditionally divided into two lobes along the groove on the posterior surface of the prostate. The body of the organ contains up to 50 small glands, each of which has a duct. Merging, the ducts form an outlet into the urethra. In addition, in medical practice it is customary to distinguish zones in the gland, each of which has its own characteristic features.
The location of the prostate gland is the pelvis, below the bladder. The prostate covers the urethra (urethra), its back part is adjacent to the rectum, and the top is connected to the pelvic floor muscles (diaphragm).
There are inferolateral, upper and lower surfaces. In the posterior surface of the prostatic urethra there is a seminal tubercle, which has a prostatic utricle in its upper part, through the openings of which seminal fluid enters the urethra. The ejaculatory ducts connect to it, passing through the body of the prostate from behind.
In addition to the glandular layers, the prostate gland also has fibromuscular tissue. When performing an ultrasound, it becomes possible to study the condition of the tissues and ducts of the gland, which makes it possible to accurately determine the location of the inflammatory or other pathological process.
Indications for the study
This diagnostic method is carried out not only when problems arise with the functioning of the bladder or prostate, but also during a routine preventive examination.
The risk of developing pathologies in the genitourinary system increases at the age of 40-50 years. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that men regularly undergo ultrasound of the prostate gland and take a test that determines the level of PSA in the blood - a tumor marker of the prostate.
In some cases, indications for TRUS are the following symptoms:
- The patient complains of discomfort during urination or pain.
- Pain periodically occurs in the perineal area.
- At night, frequent urination is observed, accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
- The stream of urine became thinner and the pressure weakened.
- An elevated PSA protein level in a patient. Often, TRUS is prescribed even when the PSA tumor marker is within the normal range, but its level has sharply increased compared to previous results.
- Signs of prostate adenoma.
- Rectal examination revealed problems.
- Spermogram and urine indicators are abnormal.
What is prostate ultrasound
Ultrasound (sonography) of the prostate is a diagnostic study performed using ultrasound in a hospital stay or during a routine examination. The procedure is included in the list of differentiated diagnostics, since it allows you to obtain a lot of useful information and correctly diagnose the patient. Modern medicine does not stand still and offers patients 2 main ways to study the prostate gland and its tissues.
Doctors offer patients to undergo examination using two methods:
- Transabdominal (abdominal) ultrasound examination (TAUS).
- Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate (TRUS).
Methods are selected on an individual basis; TRUS is considered the most accurate and informative.
But if its implementation is impossible (there are contraindications), preference is given to another method. It is not so informative and accurate, especially if the disease is at the initial stage of development.
Advantages of TRUS
The main advantages of TRUS are:
- The most detailed assessment of the condition of soft tissues is provided.
- Allows you to reliably determine the size of the prostate and its individual sections.
- Unlike external, transrectal examination allows the doctor to examine the seminal vesicles in detail.
- The procedure does not cause harm to the body.
- It has no quantitative or time restrictions due to its safety.
The disadvantages of this study include an unpleasant physical sensation during the procedure and the patient’s emotional discomfort.
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland. How to prepare for research
Unlike conventional ultrasound, this type of examination requires preliminary preparation. However, doctors do not always warn about this in advance, which can lead to incorrect results and forced repeat ultrasound of the prostate gland.
Preparation for the study includes adjusting the diet a few days before the test date. It is best to avoid eating foods that cause gas in the intestines. These products include: baked goods made from yeast dough, white cabbage and dishes made from it, pasta, fresh fruit. You should also avoid carbonated drinks and alcohol. Also, preparation for the examination (ultrasound of the prostate gland using the transrectal method) implies the abandonment of Aspirin and the medications that contain it, since this drug thins the blood and can distort the results of the examination. It is imperative to discuss with your doctor the impossibility of refusing to take such medications.
TRUS is usually done early in the morning on an empty stomach. The last meal must be taken twelve hours before. If the study is scheduled for the morning, then no later than nineteen hours there should be dinner the day before, which includes only light dishes.
How else can you prepare for a prostate ultrasound in men? Basic preparation involves two steps: filling the bladder and emptying the bowel.
Transrectal ultrasound
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed using a thin oblong probe, which is inserted through the anus. Many men are categorically against such a diagnostic procedure, explaining this by psychological discomfort.
However, this type of study has the highest diagnostic value and is painless, without the risk of infection by pathogenic microflora. The patient may feel mild pain impulses during acute prostatitis, prostate adenoma, or when it is necessary to examine the seminal vesicles in case of infertility.
An informative examination of the prostate through the rectum is possible only with high-quality cleansing of the rectum. Preparation for a rectal ultrasound of the prostate includes a mandatory enema.
How to give an enema before a prostate ultrasound
A man is given an enema 2–3 hours before the start of the diagnostic procedure. It is better to seek professional help from a healthcare professional, especially if there are hemorrhoids, inflammation and neoplasms in the peri-anal area. Then preparation for the study will not only be of high quality, but also painless.
An Esmarch mug will help thoroughly cleanse the intestines. It is suspended to a height of up to 1.8 m, filled with cool water, air is released from the siphon, and the tip is thickly lubricated with rich baby cream or Vaseline.
The man lies in the “fetal position,” the tip is carefully inserted into his anus, and the clamp on the siphon is opened. Water fills the lower gastrointestinal tract. During this period, it is important to relax the abdominal and buttock muscles.
To better dilute stool, water should be retained in the body for as long as possible, then visit the toilet several times. Enema is an unpleasant procedure that is increasingly being replaced by microenemas.
Microenemas are sold in every pharmacy, are inexpensive, and easy to use. Defecation appears just 15 minutes after the medication is administered through the anus. The special tube has an elongated front part, which allows you to perform an enema hygienically and independently.
Patients do not report colic, spasms or other side effects from the use of the medication. Using a microenema, you can prepare for an ultrasound of the prostate gland 50–60 minutes before the expected diagnostic examination of the prostate. The drug of choice is Microlax, Normacol, Norgalax.
Laxative: necessary or not?
Preparing a patient for a prostate ultrasound should not be accompanied by uncontrolled use of laxatives. If there are medical contraindications to an enema or the patient wants to avoid an unpleasant procedure, the doctor prescribes Fortrans.
This is a modern laxative that can cleanse all parts of the gastrointestinal tract from gases and food debris. The powder is taken at the rate of 1 packet per 15–20 kilograms of weight. The required amount of medication, following the instructions, is dissolved in water, then the resulting solution is drunk.
Before an ultrasound, it is important to correctly follow the preparation recommendations, and this process will require time and care. But the diagnostic capabilities of this study allow us to accurately verify dozens of diagnoses. This is important for timely initiation of treatment and achieving stable remission. If necessary, you should definitely use ultrasound diagnostics - a simple, reliable, cheap way to visualize the prostate gland.
Source potenon.com
6 minutes Author: Irina Bredikhina 39131
The prostate gland (prostate) is one of the important organs of the male reproductive system, and at the same time one of the most frequently affected by various diseases. As a rule, pathologies develop in men over 30–40 years of age, and timely diagnosis helps prevent serious complications.
The ultrasound method has long been recognized as the leader in identifying structural disorders that lead to a decrease in the quality of organ functioning. The combination of its characteristics and advantages makes it possible to quickly and painlessly identify even minor pathologies in the early stages for patients.
Like most diagnostic methods, ultrasound (ultrasound) requires the patient to perform a series of sequential actions to facilitate the procedure without any obstacles. The most important thing for the patient is not to forget that preparation for a prostate ultrasound is an integral part of the diagnostic process.
How to empty your bowels before the test
Preparation for a prostate ultrasound includes two main methods of bowel cleansing.
- A few hours before the examination, you need to drink a laxative and do an enema. For an enema, cool or warm water is used, the volume should be one and a half liters. If there are certain physical reasons that do not allow you to give an enema, you can use a microenema. It is a tube with a small amount of laxative (25-100 ml). At the end of such an enema there is a flexible tip that is inserted into the rectum. It is necessary to position yourself on the right side when introducing a substance into the body, this will greatly simplify and speed up the process. After some time, the urge to defecate will arise.
- The second method is to cleanse the intestines immediately before the procedure. A special fast-acting glycerin suppository must be inserted into the anus, after which the patient should lie on his back or right side. After some time, the urge to defecate will also appear. A couple of hours before visiting the ultrasound room, this procedure can be performed at home.
If a man encounters difficulties during preparation for a prostate ultrasound, the doctor should be notified about this. Indeed, if it was not possible to empty the intestines, TRUS will not give the desired result.
What patients can and cannot do before the procedure
Since the diagnosis of the prostate gland involves certain restrictions on the time of preparation for the procedure, during this period patients are allowed to:
- when correcting nutrition, include in the daily diet well-boiled mucous porridge without sugar, low-fat protein products, low-fat varieties of cheese, 1 egg per day, still water;
- light dinner on the eve of the study;
- crackers with half a glass of tea for patients with diabetes;
- minor physical activity;
- have an intimate relationship.
During the same period of preparation for prostate ultrasound, the following is prohibited:
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- drinking strong tea and coffee;
- any fried food;
- on the day of breakfast diagnostics.
Proper preparation for an ultrasound examination of the prostate is a reliable result in assessing the function of the gland. Early diagnosis will allow timely treatment to be prescribed in the presence of a pathological process, and to avoid various complications.
According to reviews of men who have undergone prostate ultrasound, the discomfort during diagnostics through the rectum is more psychological than physical.
An ultrasound can be performed free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy in a functional diagnostics office at your place of residence upon referral from a doctor. You can independently check the condition of the prostate gland in paid clinics or offices. The price of the service can range from 300-400 rubles in the regions and up to 2000-2500 rubles in Moscow.
Bladder filling
This step can be carried out in different ways, it all depends on what the purpose of the prostate examination is. If we are talking about decreased potency, increased PSA levels or infertility, it is enough to drink about four glasses of water an hour before TRUS. You are not allowed to go to the toilet until the examination is completed.
If you have difficulty urinating, the preparation will be slightly different. The patient must have a container (1.5 liters) with clean water without gas. You should start drinking water 30-40 minutes before the procedure. The first urge to urinate should be reported to your doctor. After completing the examination, you should immediately visit the toilet, since in such cases long urinary retention is prohibited. In all other cases, the procedure must be discussed with your doctor.
Carbonated water is not suitable for preparing for a prostate ultrasound in this way, as this can lead to distorted results and the need for repeat TRUS. Some cases require examination while the bladder is empty. To do this, the patient needs to urinate after the procedure and undergo TRUS again. Based on the amount of urine remaining in the bladder, the doctor will make a conclusion.
Preparation for ultrasound examination
The positive features of examination using TRUS and transabdominal examination include minimal preparation. So, for ultrasound performed on the surface of the abdominal wall, it is necessary to have a slightly full bladder (about 150 ml of urine). This effect can be achieved by drinking 1.5 liters of liquid an hour before the procedure.
Some features of preparation for TRUS
Transrectal ultrasound examinations should be approached with clean bowel to avoid surprises during transducer insertion. For effective emptying, you can use a ready-made microenema or carry out the traditional procedure yourself.
TRUS is preceded by sigmoidoscopy or sigmoidoscopy if rectal disease is suspected to prevent bleeding and mechanical damage.
How does the procedure work?
Just above it was described how to prepare for an ultrasound of the prostate gland. Only after these procedures is it possible to conduct research.
Description of the procedure. The patient needs to lie on the couch on his left side and tuck his bent legs towards his stomach. In this position, small access to the prostate will be open, this will allow for a maximum assessment of its condition. The doctor inserts an endoscope with a sensor into the anus, which allows you to take all the necessary parameters. 5-6 cm is the approximate depth of insertion of the device into the rectum. The endoscope head is pre-lubricated with gel or a sterile film with a special coating is used - this will eliminate the discomfort as much as possible when inserting the device.
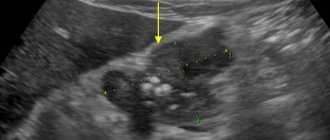
The prostate is assessed from different angles during the examination. To do this, the doctor records images of transverse and longitudinal sections of the gland, which are indicators of its size, integrity of the capsule and structure. The examination also allows you to exclude or detect focal formations. If questionable areas are identified during TRUS, a biopsy is performed. The procedure is performed without interrupting the ultrasound by inserting a needle. TRUS is a painless procedure that lasts 20-30 minutes.
Options
Ultrasound of the prostate can be performed using two methods:
- Transrectal. The patient lies down on the couch and bends his knees. Through the anal canal, the organ is examined with a thin endorectal sensor. The doctor does not inject it deeply, so there is no discomfort. The intestines must first be emptied.
- Transabdominal. The man frees his stomach from clothes and lies down on the couch. The bladder should be full. Transabdominal access is a painless procedure during which the abdominal cavity is examined with a special sensor through a gel guide.
The first method is considered more informative than the second; it gives more accurate results and better image quality.
Decoding
The advantage of this diagnostic method is the ability to obtain almost all the results of the study before it is stopped. The sensor that is built into the TRUS equipment allows you to evaluate the following data:
- A complete description of the structure and shape of the prostate. The organ is usually characterized as symmetrical; its shape varies from oval to triangular.
- Contours of the gland. They are displayed clearly and are even in normal condition. Fine grain outlines may resemble in some places. Visually, they are quite easily separated from the prostate tissue.
- Dimensions of the prostate gland. In a healthy man, the prostate is 25-40 mm long, 23 mm wide, and 43 mm thick. The volume of the organ varies between 200-280 cubic millimeters. With other indicators, this is a sign of pathology. The normal size of the seminal tubercle is 2-3 mm, it has a triangular shape.
- The condition of the rectum, paraprostatic tissue, and bladder neck can be assessed by the study, as well as the condition of the ducts through which seminal fluid is released.
Contraindications to the procedure
This procedure is contraindicated only in rare cases. TRUS is not performed if the following pathologies are present:
- aggravated hemorrhoids;
- paraproctitis and proctitis;
- fissures in the anus;
- surgical removal of the rectum.
Only in case of a critical condition of the patient, even if there are contraindications, can a urologist perform an ultrasound procedure of the prostate and prescribe a specific preparation for it.
Prostatitis
The most common male disease in the world is prostatitis. Statistics show that seven out of ten men who suffer from prostatitis die from prostate cancer. What makes the situation worse is that many men completely ignore all the symptoms of prostatitis; seeing a doctor may already be at the last stage of the disease.
The main symptoms of prostatitis include:
- cutting and pulling pain in the scrotum, lower abdomen or perineum;
- burning in the urethra, frequent urination;
- feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- weak stream;
- the quality of erection has deteriorated;
- premature ejaculation;
- irritability and increased fatigue of the body.