5268
Author of the article
Evgeniy Nikolaevich Konoplev
Reading time: 6 minutes
AA
TRUS of the prostate gland or special transrectal ultrasound is a special diagnostic option for examining the male body and examining the general condition and functioning of the prostate. According to professionals, TRUS is considered today the safest and at the same time informative option for medical examination. With its help, you can adequately assess the general condition of the tissues and the level of blood supply to the prostate, its dimensions and the possible presence of various pathological formations.
Why is it carried out?
This type of diagnostic study has a number of advantages, which are as follows:
- TRUS can give reliable results.
- Such a procedure can detect pathology at the initial stage of its development.
- This study does not require x-rays, making this method safe for the body.
- TRUS can detect the infectious process of inflammation.
- The procedure is painless. However, the patient may feel slight discomfort only during insertion of the sensor into the rectum.
- Thanks to TRUS, it is possible to examine in detail all the soft tissues of the prostate gland.
As for the frequency of TRUS, such a procedure is allowed to be performed as often as required. Healthy men over 45 years of age should undergo such an examination at least once a year, and if they have prostatitis, then once every six months.
What is it: objectives of the study and its benefits
The main task of TRUS, like other ultrasound diagnostic methods, is to visualize the tissues of the organ under study in order to assess their echogenicity, homogeneity, structure, shape and size. The introduction of an ultrasound probe directly into the anus allows you to accurately assess the volume of the gland, the integrity of the capsular membrane, the consistency and structure of parenchymal and glandular tissue. If possible signs of cancer are detected (the most clinically significant is a decrease in the echogenicity of the prostate, which is characteristic of most tumors), during the procedure the doctor may take biological material (biopsy) for further histological examination.
Advantages of TRUS
Unlike conventional ultrasound, which is performed transabdominally (through the skin of the abdomen), TRUS has a higher information content. The accuracy of diagnostics performed using a transrectal sensor is about 98.4% (with conventional ultrasound diagnostics - just under 93%). The advantages of transrectal diagnostics also include:
- obtaining a clearer image with the possibility of using high-frequency sensors (due to a tight fit to the organ being examined);
- the ability to assess the condition of the blood vessels of the prostate in order to diagnose cognitive prostatitis or identify the prerequisites for its occurrence;
- identification of tumor foci and accurate assessment of their size, location and structure.
TRUS is more informative than ultrasound
An important advantage of such diagnostics is the possibility of repeated use , which may be required to monitor therapeutic dynamics and correct treatment regimens used.
Performing TRUS of the prostate
Important! The use of TRUS for prophylactic purposes in men over 40 years of age allows for timely detection of changes in the tissues of the prostate gland and the necessary treatment before the development of serious complications, the most common of which are inflammatory diseases of the prostate and seminal vesicles (prostatitis and vesiculitis), as well as various tumors, including including malignant etiology.
Vesiculitis
What can be seen with transrectal ultrasound?
TRUS is included in the list of research methods recommended by experts to exclude or confirm prostatitis in a man, as well as prostate cancer or adenoma. In addition to these diagnoses, such an examination also detects the presence of fibrosis, stones in the gland, as well as various anomalies in the structure of the organ.
TRUS can show the following parameters of the prostate:
- top-bottom size;
- anterior-posterior size;
- transverse size of the prostate gland;
- prostate shape;
- vas deferens;
- contours of the prostate gland;
- echogenicity;
- presence of a median lobe;
- total volume of the prostate gland;
- volumetric formations;
- structure of the central and peripheral zones;
- symmetry;
- structure and size of seminal vesicles;
- paraurethral fibrosis;
- amount of residual urine.
To determine the amount of residual urine, TRUS must be performed twice: the first time the procedure is performed on a full bladder, and the second time it must be done after urination.
Differences between TRUS and ultrasound
TRUS (preparation for the examination begins 2-3 days before it) is a type of ultrasound examination. But due to the introduction of the device’s sensor into the rectum, this method has a higher level of information content, since it allows you to accurately determine the structure and size of the prostate. Also, thanks to better visualization, the doctor can see tumors and other pathologies.
A regular ultrasound cannot give a complete picture of the organ, since the prostate is located behind the bladder and rectum. Therefore, in the absence of contraindications, transrectal examination is recommended.
Indications
TRUS is prescribed if any pathology arising in the prostate gland is suspected. As a rule, a specialist prescribes this diagnosis for certain patient complaints, as well as after a digital examination if there is a suspicion of a disease. Transrectal ultrasound examination is recommended in the following cases:
- The patient has chronic prostatitis. In this case, using TRUS it will be possible to track the dynamics, as well as determine the effectiveness of the selected treatment therapy.
- TRUS may be prescribed if the prostate antigen test is higher than normal.
- The patient has tumors in the prostate gland, which requires a biopsy. In this case, TRUS shows from which area of the prostate gland it is necessary to take biological material for research.
- The procedure may be prescribed if the patient experiences pain during a digital rectal examination of the prostate.
- With planned brachytherapy. In this case, TRUS determines the volume of the prostate.
- The patient's age is more than 45 years. In such a situation, TRUS is a preventive standard for examining the organ.
- It is necessary to exclude cystic neoplasms in the seminal vesicles.
- When planning elastography.
When is a prostate examination necessary?
The prostate gland performs the most important functions in the male body, so any disturbance in its activity can cause serious problems. If you suspect the development of any prostatic pathology, you should immediately contact a specialist. But how can a man understand that something wrong is going on with the gland? Experts identify several specific pathological signs, the occurrence of which should be a reason to contact a urologist.
- Painful sensations. They occur in the perineum and abdomen and can be aching, dull or acute. In the initial stages of inflammation of the prostate, the pain syndrome will be mild, but as the pathology develops, this symptom becomes stronger and becomes permanent. The pain becomes especially obvious during urination and sexual intercourse.
- One of the first signs of inflammatory damage to the prostate is a violation of urination, which is manifested by frequent urges, but final emptying does not occur, and the process itself is accompanied by very unpleasant sensations and an intermittent stream.
- Sexual dysfunction is also a sign of prostatic inflammation. A man's libido noticeably decreases, his erection weakens, and early or late ejaculation is observed. And with advanced prostatic inflammation, sperm lose their viability, which reduces a man’s fertility.
- Inflammation of the prostate is often characterized by the presence of concomitant infectious processes.
- If the inflammation has a chronic, advanced form, then purulent masses may be released along with urine.
If such symptoms occur, urgent medical attention and additional examination, for example, transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland, are necessary.
Indirect testimony
In addition, ultrasound examination is recommended for the following patient complaints:
- Weak stream during urination.
- Discomfort occurring in the perineal area.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Discharge from the urethra during urination.
- Pain and stinging sensation when emptying the bladder.
- Presence of blood in the seminal fluid.
- Enuresis.
- Weakened potency.
- Erased orgasm.
Interpretation of analysis results: norm of pancreas size and deviations
When the sensor is inserted into the anus, you can see:
- structure and shape of the organ. It is a symmetrical organ. The shape can be either oval or rectangular;
- contours. In normal condition they are even. In the absence of pronounced pathologies, the contours are clear;
- organ size. Normally, the length of the prostate ranges from 26 to 40 mm. The width of the organ is approximately 24 mm;
- volume. It is in the range of 210-280 mm3.
We advise you to read: Localization and treatment of pain in prostatitis with reviews
When carrying out the study, you can obtain reliable information about the condition of the seminal tubercle. Its normal dimensions are no more than 3 mm. When performing the study, the condition of the paraprostatic tissue, the duct intended for the release of seminal fluid, and the neck of the bladder are also assessed.
Blurred contours of the organ in combination with high echogenicity may indicate the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the organ. With this form of the disease, the following symptoms are observed:
- pain in the head;
- decreased performance;
- pain localized in the groin area;
- problems with bowel movements;
- excessive nervous excitability;
- presence of urinary retention.
In some cases, the chronic form of the disease is asymptomatic: latent. When the clinical picture of the disease is blurred, patients may ignore minor symptoms of illness. If the disease is detected early using TRUS, the disease can be successfully treated.
For complex therapy of the chronic form, the following are used:
- drugs with antibacterial properties;
- drugs belonging to the group of antibiotics;
- painkillers;
- alpha-blockers;
- medications intended to eliminate stagnant processes in the organ area;
- medications that help normalize blood circulation;
- various folk remedies. Products made from pumpkin seeds are effective. They help eliminate the inflammatory process. Products containing pumpkin seeds help improve metabolic processes in the body. They help increase the elasticity of the tissues of the pelvic organs and help with sexual impotence.
Low echogenicity may indicate the presence of acute prostatitis in a representative of the stronger sex. The likelihood of this pathology occurring is increased by the following factors:
- the appearance of stones;
- urethritis, accompanied by an inflammatory process in the urethra;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle;
- presence of bad habits;
- hormonal imbalance;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic area;
- surgical intervention in the area of the urinary canal;
- presence of proctological diseases;
- hypothermia;
- promiscuous sex life.
Antibacterial tablets are used for treatment. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are also effective. In acute prostatitis, medications are also used to relieve pain. To relieve pain, medications belonging to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They help eliminate swelling and help reduce pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include Diclofenac.
The most complex form of the disease is parenchymal. With this course of acute inflammation, the pain becomes unbearable. The following symptoms occur:
- sharp pain in the perineum area that radiates to the head of the penis;
- increase in body temperature to 40 degrees;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- chills;
- high fever;
- the appearance of mucus clots in the stool;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the rectum;
- the appearance of cutting pain in the urethral area;
- flatulence;
- frequent constipation.
In the absence of proper treatment, the parenchymal form of the disease passes into the chronic stage or becomes the cause of an abscess in the gland area.
Preparation for TRUS of the prostate in men
The procedure is carried out in a clinical setting. However, the patient is required to prepare for TRUS of the prostate. In this case, the study will not need to be repeated.
Preparatory measures should include bowel movement a couple of hours before the start of this procedure. But what does such preparation for TRUS of the prostate mean? The study can be carried out after bowel movement, which can be done in several ways:
- Method No. 1. If a man does not have the desire to empty his bowels on his own, then he will need to drink a laxative or give an enema. This will require about one and a half liters of warm water. If for some reason an enema is not given, then you can use a microenema, for example Microlax.
- Method No. 2. You can also empty your intestines using a glycerin suppository, which is placed into the anus. Before inserting it, the patient should lie on his side so that it does not leak out during dissolution. When the urge to defecate appears, you must immediately go to the toilet, because it will be very difficult for a man to endure in such a situation. To prevent defecation from happening in a specialist’s office, it is best to carry out a similar procedure at home.
Sometimes patients have some difficulties with bowel movements, so do not be shy in such cases. It is better to immediately tell your doctor about the problem, who should take appropriate measures. This is due to the fact that the bowel cleansing procedure itself is a very important part of the preparation for TRUS of the prostate. The examination should also be carried out after the bladder has been prepared. More on this below.
Common Questions
TRUS of the prostate is not a very psychologically comfortable procedure, so it is important to understand its significance, purposes of use and capabilities. It has been proven that patients feel more confident and calm during the examination if they have complete and truthful information regarding the features of the procedure and the technique of its implementation, so below are answers to the most frequently asked questions regarding TRUS of the prostate gland.
Transrectal ultrasound examination of the prostate is one of the most effective research methods
How often do you need to undergo transrectal ultrasound diagnostics of the prostate?
TRUS of the prostate gland is prescribed when clinical symptoms are detected that may indicate the presence of inflammatory, purulent-infectious and congestive changes in the glandular epithelium of the prostate. In most cases, TRUS is included in the complex of primary hardware diagnostics after a visual examination, collection of a medical history and physical examination (palpation of the gland through the anus).
Stages of prostate cancer
For preventive purposes, TRUS is recommended to be performed at least once a year for men who are at high risk for the development of prostatitis and prostate adenoma. This category includes men over 40-45 years of age, patients with obesity and endocrine pathologies, as well as persons with severe hypodynamic disorders and disorders.
TRUS of the prostate – does it hurt?
About 33% of men refuse transrectal examination of the prostate gland not only because of psychological discomfort, but also because of the fear of pain during the insertion of the ultrasound probe and throughout the entire procedure. The reason for such fears, according to practicing urologists, is the lack of awareness of patients about the purpose of the procedure, its features and the possible consequences of refusal.
TRUS does not cause pain or discomfort
If a man does not suffer from hemorrhoids and does not have other pathologies of the rectum (anal fissures, fistulas, etc.), TRUS does not cause painful or unpleasant sensations. With proper preparation and following the instructions of specialists, the procedure causes only moderate discomfort, which in most cases occurs only during insertion of the sensor and its movement.
Advice! To minimize possible discomfort during TRUS, it is necessary to relax the muscles of the anus and perineum and avoid deep breaths. Breathing should be smooth, calm, without delays or chaotic movements of the diaphragm.
About discomfort during TRUS
Can I take sedatives before the procedure?
The use of any medications with a sedative effect before conducting transrectal diagnostics is possible only after consultation with a doctor. In some cases, such measures may be justified, since psychological discomfort associated with the presence of a foreign body in the rectum is the second most common reason for patients refusing to undergo the necessary examination. Without consulting a doctor at home, it is permissible to use herbal sedatives and tinctures based on motherwort, valerian, hawthorn, but strictly in the specified dosage and taking into account possible contraindications (indicated in the instructions for the drug).
"Valerian"
If there is strong emotional stress, you can take 25-30 drops of Valocordin or Corvalol the morning before the procedure and the evening before.
"Corvalol"
Are there any restrictions or contraindications for performing TRUS of the prostate?
Like any medical procedure, the TRUS procedure has its contraindications. These include:
- cracks, ulcerations, erosive defects of the mucous membranes of the anus;
- infectious-inflammatory and purulent pathologies of the rectum (proctitis, paraproctitis);
- acute and subacute hemorrhoids (including chronic hemorrhoids outside periods of remission);
- active bleeding from the anus of unspecified or unclear etiology.
Stages of hemorrhoids
The procedure also cannot be performed if the man has previously undergone rectal resection (removal). In the presence of these contraindications and the need for urgent examination of the prostate, ultrasound is performed using the traditional transabdominal method.
Is it possible for the rectum to become infected during the procedure?
The likelihood of infection in the rectum during TRUS is extremely low, since disposable condoms are used to insert the sensor, which must be removed from the package in the presence of the patient.
Disposable condoms are used to insert the sensor.
Is it possible to injure the rectum with the sensor?
It is impossible to completely eliminate the possibility of microtrauma during transrectal diagnosis of the prostate, but this risk is minimal, since the diameter of the device does not exceed 1.5-2 cm. If the patient does not strain the muscles of the anus and perineum, does not move during the procedure and follows other doctor’s recommendations, the likelihood of microtrauma is very low.
The sensor diameter does not exceed 1.5-2 cm
After TRUS there was bleeding from the anus - what is it?
The appearance of blood after TRUS may indicate damage to the mucous membranes of the rectum or internal hemorrhoids, which the patient might not know anything about if the lumps are small. To exclude possible pathologies, you should make a second appointment with the doctor who conducted the study, or with a proctologist - a specialist involved in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases of the rectum.
TRUSI
Video – Preparation for TRUS
TRUS is a modern, highly effective and safe (with proper preparation and technique) method for diagnosing prostate diseases. Preparation for the examination and the emotional comfort of the patient during the procedure are of great importance for obtaining a reliable and complete clinical picture . One of the tasks of diagnostic urology is to timely and sufficiently inform men about the purposes and possibilities of transrectal ultrasound diagnostics, which after 40 years of age is recommended to be performed at least once a year.
Bladder preparation
An equally important step in preparing for such a procedure is preparing your bladder. But how to prepare for TRUS of the prostate gland in this case? To perform this procedure, you need to completely fill your bladder. This can be done in several ways, and the choice will depend on what type of research needs to be performed.
When answering the question of how to prepare for TRUS of the prostate, it should be noted that filling the bladder can be done independently, although most specialists perform this procedure themselves. Typically this is done using a catheter. Here, too, there are two methods for preparing TRUS. Let's look at them separately:
- Method No. 1. If the patient has reduced potency, has infertility, or has an increased level of PSA in the blood, then 1 hour before the test, you need to drink one liter of plain water. Thanks to this, the bladder will fill very quickly, and it cannot be emptied until the TRUS examination is completely completed. Preparation for the study can also be done in another way.
- Method No. 2. If it is necessary to identify the cause of existing difficulties with urination, then a completely different preparation method is used. Such preparation for TRUS of the prostate in men involves taking one and a half liters of still water. After this, it is also forbidden to visit the toilet, as in the previous case. If the patient drinks carbonated water, the specialist will not be able to conduct the study, since such a procedure will have to be postponed for several hours. When the first urge to urinate appears, you must immediately tell a specialist about it, who should begin the TRUS procedure of the prostate.
When the study is completed, the patient can go to the toilet, since urine should not be stored in a bladder under any circumstances. Otherwise, an infection may begin to develop in urine. This is especially true in situations where patients have a severely weakened immune system. Then the bacteria penetrate the human body very quickly, because stagnant urine is an excellent place for the proliferation of various pathogenic microflora.
Those patients who do not know how to prepare for TRUS of the prostate gland will be consulted by a specialist.
Indications and contraindications for analysis
TRUS is prescribed in the following cases:
- Elevated PSA level (this may be a sign of hyperplasia, prostatitis, tumor);
- The need to assess the volume and direction of radiation therapy before starting a course of treatment (study of the volume and localization of formations);
- Clarification of the nature of the neoplasm detected during palpation;
- The appearance of blood in semen or urine, difficulty urinating;
- Prostatitis, including complicated by an abscess;
- Infertility, checking the patency of the spermatic cord.
The color of urine, depending on the volume of blood in it,
TRUS is also prescribed to assess the dynamics of the results of therapy for various prostate pathologies. This method is also used to take a biopsy. Under the control of the sensor, you can precisely take the desired areas of tissue using the puncture method.
The cause of difficulty urinating is often an adenoma. In such cases, ultrasound voiding cystourethroscopy (UMCUS) is performed simultaneously with TRUS. This type of study is performed during urination and allows you to assess the degree of narrowing and deformation of the urethra.
TRUS is a safe procedure in terms of negative effects on the body. Since the study is carried out through the rectum, any damage to its walls (cracks, hemorrhoids) are direct contraindications to manipulation.
The cost of the procedure ranges from 1 to 3 thousand rubles. For example, in “Invitro” and “Hemotest” (Moscow) TRUS costs 1,500 rubles.
Features of nutrition before TRUS
In addition to the procedures described above, it is also necessary to follow some dietary rules before conducting the study. Preparing for TRUS of the prostate gland involves eliminating gas-forming foods from your diet. These products include:
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- fresh baked goods;
- pasta;
- some fruits, such as green apples, grapes, plums;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks.
It is best for the patient to switch to boiled fish and meat, light soups and cereals before the procedure. In addition, preparation for the TRUS procedure of the prostate gland involves refusing to eat approximately seventeen hours before the start of the study.
Contraindications
There are few contraindications for TRUS of the prostate. The ban applies to patients who have had rectal surgery. The study is contraindicated for pathologies:
- exacerbation of hemorrhoids;
- rectal fissures;
- intestinal obstruction;
- inflammation around the anus;
- patients with a removed rectum.
The ban on manipulation must be approved by a specialist after examination and study of the medical history.
Carrying out TRUS
When the patient has prepared for this procedure, the main part should begin. To do this, the man lies on his side on the couch, with his back to the specialist, with his legs tucked to his chest.
After this, the doctor places a condom on the smart sensor, lubricating it with lubricant to facilitate insertion into the rectum. The device is inserted into the anus to a depth of approximately six centimeters. This is quite enough to assess the size and shape of the prostate gland. If it is necessary to check the condition of the bladder neck and seminal vesicles, then the device is inserted to a depth of ten centimeters.
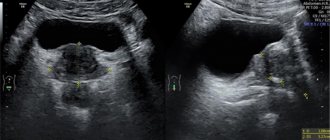
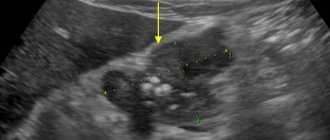
After this, all information about the prostate gland appears on the monitor in the form of an image. When the prostate is examined, the specialist removes the sensor. At this point the procedure is completed.
All results are given to the patient in the form of a protocol, where the parameters of the organ are described in detail, and a presumptive diagnosis is made.
How is the reception going?
The duration of the examination in most cases is about 10-15 minutes, but if there are any complications or poor tissue visualization, this figure can reach up to 30 minutes. In the ultrasound room, the patient needs to undress to the waist, lie down on the couch, bend his knees and pull them towards his stomach. This position is determined by the anatomical location of the prostate and the features of its structure and allows you to obtain an image not only of the gland itself, but also to carefully examine the prostatic urethra, as well as the neck of the bladder.
TRUS of the prostate in men
Further actions of the doctor are carried out in accordance with a certain algorithm: first, a special latex condom is put on the sensor, which is used specifically for ultrasound, after which the device is carefully inserted into the anus through the anus. The insertion depth sufficient to obtain a high-quality image is usually 5.5-6 cm. To facilitate insertion, the sensor is lubricated with a special medical gel (for example, “Mediagel”).
"Mediagel"
Reviews and advice
Most men who have resorted to the TRUS procedure speak positively about this method. Patients note the absolute painlessness of this procedure, as well as the reliability of the results.
In addition, patients claim that TRUS is a very inexpensive and informative method for detecting prostate disease.
The only advice is to follow all the doctor’s recommendations regarding preparation for a prostate examination. They have been described in this article.
The essence of the method
Modern diagnostics uses 2 types of examination of the prostate gland, based on the ultrasound effect:
- TRUSY.
- Abdominal ultrasound.
TRUS of the prostate has a number of advantages due to the proximity of the ultrasound source to the gland, which results in a clearer image and increases the information content and reliability of the results obtained. Examination of the prostate gland is done using an ultrasound machine and a special rectal sensor. Preparing for the tests is simple. Preparing the patient for the procedure consists of:
- The patient is dressed in a sterile hospital gown.
- They are placed on the couch with their back to the doctor.
- They ask you to lie in the “fetal position” with your knees pulled up to your chest.
The ultrasonic sensor is a cylinder 2 cm in diameter. To facilitate its insertion into the rectum, a special condom is put on, and the preparation of the insertion area consists of treating it with Vaseline or gel. The sensor, under the control of tracking equipment, is inserted into the rectal cavity to a depth of 5-6 cm. The examination lasts from 20 to 40 minutes. Video in real time and high resolution is displayed on the device’s monitor.
The doctor can visually assess the structure and volume of the prostate gland. If there is a suspicion of impaired blood supply to the prostate and pathology of the vessels of the prostate gland, TRUS is done together with color dopplerography, which in color allows you to assess the strength, direction, speed of blood flow in the organ to be examined, as well as the condition of the vessels and the presence of blood clots in them.
TRUS is also done to assess the degree of bladder emptying. Preparing for a bladder examination involves emptying it. To do this, the patient is asked to go to the toilet, after which the ultrasound probe is reinserted. By the presence or absence of residual urine in the bladder cavity, the presence of problems with urination and the degree of pathology are judged. After the diagnostician has examined the prostate gland, the seminal vesicles are examined.
A comprehensive examination of the pelvic organs allows you to obtain an accurate picture of the causes of the pathology and make a reasonable diagnosis. According to indications, during TRUS, material can be selected for histological and cytological examination. No special preparation is required for the biopsy. The biopsy procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
As evidenced by patient reviews, the entire TRUS procedure of the prostate causes minimal discomfort. However, some reviews indicate that the procedure is painful. Pain may occur with inflammation. After the diagnosis, the doctor deciphers the information, draws up a conclusion and passes it on to the patient or the attending physician. Modern ultrasound machines make it possible to obtain not only high-quality images, but also video on digital media. The transcript is attached to the photo and video materials.
Service cost
TRUS of the prostate gland can be done in a public health facility or in a private clinic. The cost of the service will depend on this. The average price usually does not exceed 1000–1200 rubles.
In the Moscow region, the price ranges from 650–2200 rubles. In St. Petersburg from 500 to 1900 rubles. In other regions 600–1800 rubles.
Are you familiar with TRUS of the prostate? How informative was it for you? Did it hurt? Share your comments. Repost on social networks. Be healthy. All the best.
What medications can you take?
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the male prostate gland if a person takes medications? This is also a very important question.
Preparation for transrectal ultrasound of the prostate does not involve stopping absolutely all medications a few days before diagnosis. Only drugs that thin the blood are subject to a general ban. These medications include aspirin and its analogues.
But still, if there is an urgent need to take any medications before the examination, it is best to consult a doctor with this issue and resolve it individually.
Results of transrectal ultrasound of the prostate
At the time of the diagnostic action, the doctor describes the prostate gland itself - its symmetry, shape and size, irregularities in the contours, echo density of the organ. The following describes the organ structures detected by ultrasound. These are the periurethral glands and the spermatic tubercle with the spermatic cord.
The doctor must report not only about pathological disorders in the organ, but also about the complete condition of the organ at the time of the study. Detected anomalies in the conclusion are listed separately.
If the conclusion states that no echo signs of pathology were found during the examination, then the patient can be congratulated, everything is in order with his prostate gland.
Types of prostate diagnostics
Modern medicine is represented by four methods of ultrasound diagnostics of the prostate:
- Transabdominal echography. It is performed externally in men through the abdominal cavity using a special sensor. This method is used in rare cases, since it does not make it possible to calculate the exact size of existing formations and the location of their concentration. In some advanced forms of the disease, the use of other methods is prohibited, which makes the transabdominal method the only acceptable one. Transabdominal echography is used not only for ultrasound of the prostate and bladder, but also for ultrasound of the kidneys.
- Transrectal scanning. The most reliable method of diagnosis, performed rectally by inserting a sensor. It will allow you to qualitatively assess the condition of the rectum, the size and lesions of the organ under study and find out the causes of problems with potency.
- Transurethral scanning. It is considered the most traumatic ultrasonography, since for a thorough examination of the gland, a sensor is inserted into the urethra. Used only with anesthesia.
- Transperineal scanning. It is practiced extremely rarely due to the presence of a blurred image when examining the prostate. It is carried out in men through the perineum.
How to decipher TRUS indicators
The person being examined does not need to decipher the transrectal examination himself. The doctor speaks all the necessary information during the examination in the most accessible style. The patient may find out:
- Is the prostate enlarged?
- Are there any tumors?
- Are there stones?
However, men do not always trust the diagnostic specialist, suspecting him of hiding information. In this case, you can try to decipher the result yourself, but to do this you need to know the terminology and indicators in the absence of pathology.
Practical advice: if the results indicate that no echogenicity was detected, there is nothing to worry about. It is this parameter that indicates pathology in the prostate.
All parameters that will be recorded based on the results of the transrectal study can be found in the table.
| Index | Fine | For pathology |
| Form | Symmetrical | Asymmetrical |
| Prostate contours | Smooth, clearly visible | Poorly visible, uneven |
| Gland volume | 200-280 mm3 | More or less |
| Seminal tubercle size | 2-3 mm | 4 mm or more |
In conclusion, there may be other indicators, but those listed in the table are the main ones. It should be borne in mind that the results of TRUS alone do not make a diagnosis - the doctor takes into account blood and urine tests, patient complaints, uroflowmetry and other values.