The adrenal glands are part of the endocrine system of the human body. They are paired endocrine glands, and are responsible for the production of a number of hormones: adrenaline, norepinephrine, corticosteroids, mineralocorticoids. These substances - adrenal hormones - are responsible for regulating various processes in the human body, therefore both their excess and deficiency have a certain impact on health.
The adrenal glands regulate water and electrolyte metabolism and participate in the process of protein metabolism in the body. As soon as even a slight deviation in the functioning of the glands appears, the body immediately reacts with atypical conditions and processes - metabolic disorders, reproductive function disorders, changes in body weight and a general deterioration in well-being, the appearance of diseases. In order to identify such deviations and select the correct therapy aimed at eliminating them, doctors prescribe various examinations, including computed tomography of the adrenal glands.
What does a CT scan of the adrenal glands show?
This examination method is recognized as the “gold standard” for detecting a tumor process in the adrenal glands. This is due to the fact that the adrenal glands are adjacent to fatty tissue, and the right one is adjacent to a dense organ - the liver. This anatomical location allows the glands to have a natural distinction from surrounding tissues and makes it easier to recognize their size and structural features.
CT scan can detect a volumetric neoplasm with a size of 0.5 cm or more. Spiral tomography helps not only to identify tissue proliferation (hyperplasia), but also its shape - nodular or diffuse. For even greater accuracy of the study, a contrast agent is injected intravenously.
As a result of the diagnosis, you can evaluate:
- size, shape of the gland;
- contours, structure, density of the volumetric process (tumors, cysts);
- degree of hyperplasia;
- the presence of calcium salt deposits, focal destruction (necrosis), hemorrhage;
- enlarged lymph nodes, which helps in the differential diagnosis of malignant tumors.
We recommend reading the article about diagnosing adrenal adenoma. From it you will learn about the primary diagnosis of adrenal adenoma, what tests are taken, and detailed examination methods.
And here is more information about MRI of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure, possible complications
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Doctors generally respond positively to this diagnostic method. It is non-invasive, so the risk of complications is minimal. The scanning process itself usually does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient. The subject can contact the doctor at any time.
The most significant advantage of this procedure is the high accuracy of its results - provided that all preparation and implementation requirements are met, the images provide the most objective visualization of organs. The adrenal glands are visible from all sides, and it is possible to construct a three-dimensional model of them. The scales of organs are conveyed as close to real as possible.
However, there are some risks of tomography. First of all, they are associated with the radiation that the patient receives during the process. Of course, the level of radiation exposure from the tomograph is very small, but if the procedure is performed too often, it can become a catalyst for the growth of cancerous tumors.
Another danger is the possibility of allergic reactions to iodine. For emergency assistance to the patient, antihistamines are available in the CT room.
It is imperative to notify the doctor about all medications taken by the test subject, since the contrast agent may react with them, which is not always safe for humans.
Which is better - CT or MRI
Imaging performed using X-ray scanning (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect diseases with the same degree of probability. Their sensitivity for tumors approaches 100%. At the same time, “silent, asymptomatic space-occupying processes—incidentalomas”—are also found.
Due to lower cost, CT is more often used, and MRI is recommended if there are contraindications to X-ray diagnostics. Both of these types of tomography are combined with contrast enhancement in order to specifically examine the tumor.
Although there are criteria by which the likelihood of a malignant process can be determined, in practice there are often cases when the type of tumor is confirmed only during surgery after histological analysis of the tissue.
Watch the video about which is better than CT or MRI when diagnosing the adrenal glands:
What can a CT scan detect?
Based on the scan results, the doctor determines the size and location of organs, tissue density, their structure and integrity, as well as whether all indicators are normal. The images visualize signs of the presence of neoplasms and pathological inclusions:
- adenoma;
- cysts and lipomas;
- cancerous tumors;
- other types of neoplasms.
CT scan of the adrenal glands is considered especially effective for identifying a cancerous tumor and the degree of development of metastases. In this way, even the smallest tumors can be detected, which is especially important for cancer. The doctor is able to determine the nature of the formation, the dynamics of its development and growth, and develop treatment tactics.
Tomography also displays the size and location of hematomas in organs - they are distinguished by torn edges and tissue heterogeneity.
Indications for tomography
Computed tomography of the adrenal glands is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- arterial hypertension resistant to traditional therapy;
- crisis increases in blood pressure with a feeling of fear, increased heartbeat, sweating, trembling of hands, having a sudden beginning and end;
- signs of hyperandrogenism (excess of male sex hormones in women) - increased hair growth on the limbs and face, acne, lack of menstruation, infertility, rough voice;
- early puberty in children;
- premature loss of testicular or ovarian function;
- enlargement of the mammary glands in men, sexual weakness, decrease in the size of the testicles;
- symptoms of excess cortisol - obesity, purple stretch marks, moon face, hypertension, diabetes, fatigue, osteoporosis;
- detection of increased levels of steroid hormones in the blood (cortisol, testosterone, estrogens), high or low levels of corticotropin;
- hypertension, muscle weakness, decreased potassium in the blood, changes in the fundus, thirst, excessive urine output;
- preoperative examination if it is necessary to remove the tumor (to determine the method of surgical intervention and its volume);
- guiding the needle during fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the adrenal gland to enter the tumor tissue.
Alternatives
When during the course of treatment it has been determined that the patient has certain contraindications to computed tomography, the specialist must select a different diagnostic option that can provide the most accurate data about the person’s condition.
To begin with, the patient may be referred for an ultrasound examination. The result of the examination is displayed on the monitor in real time, the doctor has the opportunity to visually assess the condition of organs, the correctness of their placement, pathological deviations, and new formations.
The second option is MSCT, which is also based on the use of radiation exposure. Diagnosis allows you to identify malignant and benign tumors; if necessary, contrast fluid is used.
If beam exposure is contraindicated, MRI will help save the situation. When it is performed, the patient is exposed to a magnetic field that does not create danger or negative consequences, as happens with CT.
Contraindications
The study is not carried out if:
- pregnancy;
- recent diagnosis of the digestive organs with barium contrast or the use of medications with bismuth (they may interfere with the visibility of tissues);
- high motor activity, mental agitation, inability to maintain a stationary body position (as an exception, sedatives and muscle relaxants that relax muscles can be administered);
- intolerance to contrast, allergy to iodine, decompensation of diabetes mellitus, reduced filtration capacity of the kidneys.
Features of the method
The adrenal gland is a small organ, but it is responsible for producing many hormones in our body. It is not easy to accurately diagnose problems with its functioning, but computed tomography is quite capable of doing this.
The method was invented and refined in the 1970s. The point is:
- That the area of the adrenal glands is irradiated with cross-rays of X-rays.
- Next, all information is processed by computer into a single slice.
- During the examination, the X-ray tube rotates around the lying person continuously and at high speed.
- When the rays pass through the area of the adrenal glands, they are absorbed by different tissues of this organ: the rate of absorption and other features depend on the density of the tissue.
When the rays hit special matrices with high sensitivity and are read from there by a computer that reconstructs the organ. Using this method, you can obtain an image of the adrenal gland in any plane and it will be three-dimensional, which greatly facilitates the diagnosis of diseases of this gland. CT has other advantages:
- non-invasive;
- the ability to clearly see the size of the organ;
- painlessness;
- the adrenal gland can be viewed from all sides and even from the inside;
- possibility of early diagnosis of cancer.
Many people are interested in the question of what is the difference between MRI and CT:
- MRI uses magnetic field forces to obtain information about organs.
- For CT - x-ray.
Both methods are non-invasive and maximally informative, but it is worth understanding that the X-ray radiation from a CT scan, although negligible, is there, which means there is a risk to health. That is why MRI will be more preferable for regular diagnostics.
CT scan is prescribed only after ultrasound and laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis.
As for prices, it all depends on the city, and on the medical center, and on whether the diagnosis is carried out with a contrast agent or not. On average, these are the numbers:
- Moscow - on average 4500 rubles;
- St. Petersburg - from 2600 rubles;
- Novosibirsk - from 2600 rubles;
- Ekaterinburg - from 4300 rubles;
- Samara - from 3000 rub.
Preparing for the examination
If it is necessary to undergo a procedure with the introduction of a contrast agent, you must refrain from eating for 4 hours. To eliminate the risk of developing an allergic reaction, patients are prescribed a trial administration of the drug that will be used in the study of the adrenal glands,
It is recommended to warn the doctor performing the CT scan about iodine intolerance, medications, and the presence of food allergies. If you have previously had blood tests for hormones or an ultrasound scan of the adrenal glands, you should take the results with you.
The risks of the diagnosis are insignificant, however, patients may experience hot flashes, burning or itching of the skin, and a metallic taste in the mouth after receiving intravenous contrast. These phenomena are temporary and usually do not require additional treatment.
How to prepare for research
The accuracy of the results obtained directly depends on how carefully the patient treats the issue of preparation. The doctor informs you about all special requirements in advance. If a CT scan without contrast is planned, no preliminary dietary restrictions are introduced, but it should be taken into account that the tomography is performed on an empty stomach. When a CT scan with contrast is scheduled, you should not eat or drink 3-4 hours before the start of the study.
For those who suffer from increased gas formation in the intestines, it is recommended to take activated carbon in advance, as well as follow a diet that excludes foods that cause flatulence 5-6 days before the procedure. If constipation occurs shortly before the day of the CT scan, a cleansing enema is prescribed.
All metal devices, devices, jewelry and removable dentures must be removed and left outside the office along with the mobile phone, as they can distort the results.
How is a CT scan done with and without contrast?
Before the examination, the patient must remove all metal objects; there should also be no metal elements on clothing in the scanning area.
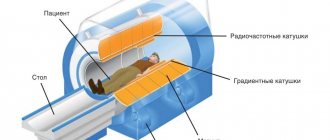
The essence of tomography is to pass X-rays through the body and process the resulting data using special equipment. The patient is placed on a couch that is connected to a scanning device.
When contrast enhancement is used, the patient is given intravenous Omnipaque or Ultravist before scanning. Otherwise, all stages of the procedure are similar to native CT (without contrast). During the diagnostic period, it is important to remain motionless.
When the beam tube of the tomograph moves, a layer-by-layer examination of tissue occurs in the form of images - tomograms. They are processed by a computer program and produces the final image. The result can be printed or recorded on media.
The entire procedure usually takes about half an hour. Upon completion, the patient needs to drink as much plain water as possible, avoid eating salty and spicy foods, so as not to create additional stress on the kidneys and remove the contrast agent from the body as soon as possible
Computed tomography - how it works
Content:
- Computed tomography - how it works
- Indications for CT scanning of the adrenal glands
- Contraindications for computed tomography
- How to prepare for research
- The process of performing a CT scan of the adrenal glands
- What can a CT scan detect?
- Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure, possible complications
- Alternative methods for examining the adrenal glands
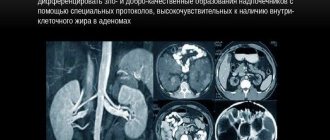
The diagnostic method of computed tomography, or CT, is based on the principle of the difference in the degree of absorption of X-rays by tissues of different densities. To carry it out, special devices are used - tomographs. A computed tomography study is a radiation study, and allows the doctor to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the structure of the organ. The data recorded during tomography is subjected to computer processing, thanks to which it is possible to visualize the organ on the monitor. The displayed image is the result of layer-by-layer images superimposed on each other with a cutting step of 3 to 10 millimeters. This way, the doctor has the opportunity to see even the deep tissues of an organ and create a three-dimensional model of it on the screen.
CT scanning of the adrenal glands is most often part of a comprehensive examination of the abdominal organs, but can also be prescribed as an independent examination. In some cases, when it is necessary to achieve maximum clarity of contours, or when the doctor is going to study the condition of blood and lymphatic vessels, the contrast method is used. For this purpose, a special contrast agent containing iodine is used. The drug is administered intravenously, after which scanning is performed several times in a row.
Norm and formations of the adrenal glands, kidneys, which reveal
Depending on the detected abnormalities, the doctor can presumably make a conclusion about the existing pathology.
Norm
When describing a tomogram of a healthy person, the adrenal glands have the following characteristics:
- shape - the left one looks like the letter V, the right one is usually linear;
- size – not increased;
- structure – homogeneous;
- outlines – smooth and clear;
- perinephric tissue (perinephric) – no changes;
- lymph nodes are of normal size and structure;
- contrast accumulation is uniform.
Kidney tumor
When examining the adrenal gland, neoplasms of the adjacent renal tissue may also be detected.
Their distinctive features:
- boundaries are unclear;
- density is reduced;
- the structure is heterogeneous;
- there are areas of calcium deposition, hemorrhage, and decay (necrosis).
- When contrast is administered, a local enhancement of the vascular pattern is noted.
Adrenal tumor
Using tomography, you can also detect a cavity (kidney cyst), a stone, an abnormal structure of organs, an abscess.
Adenoma, cyst, hematoma of the adrenal gland
The formation has the shape of an oval or circle, the contour is clear and even, the structure is either homogeneous or moderately heterogeneous. The cyst is characterized by a clearly visible thin capsule and the same (low) density of the contents. There may be pockets of calcium deposits in the walls. After the administration of contrast, the adenoma becomes clearly visible, and the cysts do not change their symptoms.
A hematoma, like a cyst, has a capsule, but its contents look heterogeneous, since there are areas of coagulated blood in the cavity. The boundaries of the hemorrhage are clear, but uneven.
Adrenal hematoma (white arrow)
Lipoma
A hormonally inactive tumor has the shape of a ball with a smooth structure. There is also slight heterogeneity due to fat inclusions. There is complete delineation of the neoplasm from the adrenal tissue; the glands are not deformed.
Pheochromocytoma
The medulla on the tomogram is indistinguishable from the cortex. The tumors found have a heterogeneous structure, smooth outlines, and a clearly visible capsule that separates the pheochromocytoma from the unchanged adrenal gland tissue. After contrast administration, intensive absorption is observed due to the developed vascular network.
Phochromocytoma of the adrenal gland
Findings on CT
First of all, the position of the adrenal glands and gross anomalies of their structure are assessed.
Aplasia is a complete absence of one or both adrenal glands of a congenital nature. The absence of an organ may be a consequence of surgery.
Hypoplasia is a congenital reduction in size. Hyperplasia is an increase in the size of an organ on one or both sides. Hyperplasia can be:
- nodular (nodal);
- diffuse (uniform).
In the first case, the edges of the organ become lumpy, in the second they remain smooth. Normally, the transverse dimensions of the adrenal gland are: 4-5 mm (body) and 2-3 mm (legs). The right adrenal gland is slightly thicker than the left.
Then the volumetric formations are assessed.
- Most often, adenomas (90%), pheochromocytomas (3-4%), primary cancer, and metastases are found in this area.
- Cysts, lymphangiomas, and vascular malformations are rare.
To differentiate between benign and malignant processes on CT scans of the adrenal glands with contrast, washout coefficients are used.
Adenoma is a benign tumor; however, a big problem is small foci of cancer that are not visible on tomography. They can only be detected by biopsy with microscopy.
On MSCT of the adrenal glands, the adenoma looks like an oval or round space-occupying formation with smooth edges.
Adenomas are divided by density into:
- tumors with a predominant fatty component;
- solid;
- mixed.
A tumor with a diffuse fatty structure is most likely an adenoma. Solid tumors belong to a more uncertain group.
Pheochromocytoma is less common. More often:
- pheochromocytomas appear solid;
- may contain a fatty component, calcifications;
- their structure is more heterogeneous;
- a focus of lower density may be detected in the center.
Pheochromocytoma can be distinguished from adenoma by the nature of contrast washout.
Rarely occurs malignant pheochromocytoma with the following symptoms:
- invasive growth;
- fuzzy edges;
- lymphadenopathy;
- secondary foci.
Adrenal cancer and metastases differ in appearance from adenomas.
- The edges of the tumor are uneven and lumpy, the solid component is pronounced, areas of necrosis and calcifications are possible.
- For cancer with metastases, invasive growth with damage to surrounding fatty plates, neighboring organs, and lymph nodes is typical.
Contrasting
The contrast is administered in three phases. First, a precontrast study is performed:
- for overview assessment of anatomy;
- search for gross pathology.
An iodine-based contrast agent, such as Omnipaque, is then injected into the vein.
- 10-15 seconds after the start of administration, the scan starts and the arterial phase is obtained.
- The venous phase begins with a delay of 10-20 seconds.
- The delayed phase is performed after 8-15 minutes.
The contrast agent first accumulates in the tumor, then is washed out of it. Based on the difference in density, washout coefficients are calculated. The coefficient shows the probable nature of the tumor.
Benefits of diagnosis
This diagnostic method is non-invasive, so a person has no reason to worry that there will be complications or serious consequences. During the scanning process, the patient does not feel pain, discomfort or other unpleasant feelings. The patient can contact the doctor at any time, so if things get worse, the doctor will provide timely assistance. Despite the fact that a person is exposed to radioactive rays, their dose is insignificant and generally does not affect the well-being and functioning of the body. The results of the images and three-dimensional images allow the doctor to assess the situation as accurately as possible, so the method is often used to clarify and finalize the diagnosis.
Examination of the adrenal glands and what is the essence of diagnosis
The adrenal glands are paired endocrine glands that are located above the upper pole of the kidneys. Their size is small, but their functional role is significant, because they synthesize a number of important biological substances - hormones. The cortex produces steroid hormones (corticosterone, aldosterone, cortisol). They regulate water-salt and carbohydrate metabolism. The medulla is a source of adrenaline and norepinephrine, which increase blood pressure and bronchial lumen, determine the body's adaptive capabilities, and also increase blood sugar levels. But even with all their proximity to the kidneys, they are not urinary organs, but perform only an endocrine function.
If there is a suspicion of problems, a CT scan of the adrenal glands may be prescribed, because this examination is almost 100% likely to determine any changes, the presence of adenoma and neoplasms (cysts, lipomas, malignant tumors), and also visualizes various types of hematomas, characterized by torn tissues and heterogeneity structures. During the procedure, the radiologist looks at the localization of the glands, their tissue density, integrity and compliance of size and shape with the norm.
What can be seen in the picture:
- benign neoplasms (adenomas);
- malignant tumors;
- adrenal glands, lymph nodes, kidneys and other soft tissues of the examined area;
- lipoma, hematoma, cyst;
- existing dead foci of tumor tissue with areas of calcification;
- lymph nodes involved in the pathological process.
Beam scanning produces the most accurate 3D image possible. For the most accurate result, a study can be performed with iodine-containing contrast.
Who treats adrenal glands
Treatment of the adrenal glands can be carried out by an endocrinologist, nephrologist, or urologist. Moreover, during the treatment process, the patient may be prescribed to visit each of these specialists, since the influence of the gland on the urinary and endocrine systems is too great. You need to understand that the body works in strict balance. It doesn’t matter what the balance concerns: metabolic processes are complete only if they are in full compliance with the necessary standards. Any deviation in the production of hormones is the road to serious illness.
Do not be upset if CT is not available according to indications, when it can be replaced by other methods. Today, medicine has enough instrumental diagnostic methods to establish the clinical picture of almost any disease. Even when there are autoimmune processes that no one has yet been able to explain. In any case, the first step to recovery is a complete diagnosis.
Some will say that medicine is not particularly accessible now, because many procedures are simply unaffordable for half of the patients. However, in every city there are social programs, preferential categories, in which everything can be completed free of charge or with serious reductions. After all, health is always worth much more than money.
Where to go with the results
After receiving the CT scan report, you need to go to the doctor who referred you for this study. He will be able to evaluate the images obtained and prescribe the necessary therapy or, if necessary, refer you for consultation to another specialist.
In the case where this diagnosis was carried out on the person’s personal initiative, one should go to a specialist, starting from the violations that were obtained in the process. If the patient does not know where to go, he can consult with the doctor who was involved in describing the results of the CT scan.