The essence of MRI diagnostics
The essence of magnetic resonance imaging is the effect of energy production by the hydrogen nucleus when exposed to a high-power magnetic field.
Hydrogen is a constituent unit of a water molecule, so working with “dry” stones (stones, sand) in the case of MRI is ineffective. The excitation of the nuclei is displayed and recorded on the computer in the form of a three-dimensional image, which is the result of the examination.
Preparing for the study
Taking medications, eating, drinking - everything is done in the usual way for a person, if contrast is not used during the study. It is only recommended to limit yourself to fatty foods and exclude alcoholic drinks. On the day the procedure is scheduled, it is recommended to wear underwear made from natural material.
Magnetic fields will attract metal towards them. You should remove keys, phones from your pockets, watches, jewelry, and things with metal zippers or rivets.
The procedure does not create difficulties and does not cause harm to the body. The patient is placed on a special table, which slides into the equipment tunnel. During the scanning process, you should remain calm and still. If a person does not tolerate confined spaces well, the doctor may prescribe a sedative.
What the study shows
As a result of magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys, the specialist operates with the following data:
- dimensional characteristics of organs, changes in the structure of local tissues;
- kidney condition (whether pathologies develop or the organs do not have structural abnormalities);
- the presence of new formations, prerequisites for the growth of tumor neoplasms;
- the state of the vascular system, the presence of congestion and other pathological processes in structural elements;
- degree of kidney functionality (whether there is renal failure, inflammation).
What is MSCT?
Multislice computed tomography of the kidneys is the gold standard examination. The MSCT technique involves constant translational movements of the table and the patient during the examination, as well as the simultaneous rotation of a tube with several detectors around it. It is no coincidence that this particular method is indicated for seriously ill and bedridden patients. In addition, such a procedure allows one to examine the internal state of tissues and organs in a three-dimensional image and carry out examinations much faster and more accurately.
When is an MRI scan prescribed?
MRI diagnostics of the kidneys and adrenal glands is prescribed in the following cases:
- with alarming symptoms of unknown origin: swelling of the face, arms, legs, colic, pain in the lower back, intoxication of the body in combination with an increase in body temperature;
- after injury to the abdominal organs, kidneys and adrenal glands;
- to monitor the condition of organs in the postoperative period;
- in case of hormonal imbalances (the adrenal glands are a component of the corresponding system that produces adrenaline, androgens, etc.);
- if ultrasound of the kidneys is unsuccessful due to poor blood and urine tests;
- during abnormal pressure surges;
- when there is a contraindication to urography with contrast;
- in case of suspected development of tumor processes.
Among the popular indications for undergoing MRI diagnostics of the kidneys is the development of cancer in the patient’s body.
Indications and contraindications for MRI
MRI is done to assess the extent of kidney damage before surgery or to select an effective treatment regimen. Also, indications for kidney examination are many diseases or some symptoms:
- swelling of the legs and arms;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- endocrine diseases;
- difficulty urinating;
- fast fatiguability;
- high blood pressure;
- poor urine tests;
- lower back pain with simultaneous fever, dizziness and chills;
- renal colic;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- inability to send the patient to an alternative research method or contraindications to them.
Contraindications include pregnancy, the presence of metal implants, or a pacemaker. The examination is not given to people prone to seizures or claustrophobia.
If a contrast method is used, the patient must first be checked for allergies to solutions or drugs. MRI also has technical limitations, so it is not done for people with a high degree of obesity - 120-150 kg and above. When breastfeeding, scanning is permitted only if the child is transferred to artificial nutrition for a couple of days.
Are there any contraindications?
We are talking about a safe diagnostic procedure that does not harm the health of the subject. However, there are a number of limitations to diagnostics:
- implanted metal implants, pacemakers, pins, etc.;
- the patient’s weight is more than 120 kg (specialized equipment may be used);
- claustrophobia (open type devices are used as an alternative);
- epileptic syndrome;
- pregnancy by week (up to 14 weeks).
If we are talking about MRI using a contrast agent, a number of additional restrictions are added:
- renal failure;
- gestation period;
- breastfeeding (subject to the procedure, the child must be weaned for 2 days).
Contraindications
MRI does not harm the patient’s body and does not create side complications. There are not many restrictions on such a procedure, however, they exist. MRI is not prescribed in certain situations:
- there is renal failure;
- allergic reactions occur to drugs administered to the patient to provide contrast;
- the presence of a pacemaker, metal implant, or fragments in the body;
- if the patient has claustrophobia or suffers from mental disorders;
- pregnant women, when the period does not exceed three months;
- the patient’s body weight exceeds one hundred and twenty kilograms;
- If a procedure using contrast is prescribed to a nursing mother, then she should not feed the baby for one or two days.
Preparatory stage
No preparation is required for MRI diagnostics of the kidneys. Preparatory activities are most likely carried out by a specialist. For an accurate examination, the doctor interviews the patient, takes care of the patient’s medical history, and analyzes the results of preliminary examinations.
On the eve of the procedure, the doctor should be informed of the following facts:
- Concerns regarding prolonged stay in the CT scanner. In such cases, specialists resort to the use of sedatives.
- During the onset of menstruation: diagnosing during menstruation is not recommended.
- Pregnancy, lactation period.
Immediately before the scan, the patient will have to remove metal objects (jewelry, glasses, belts, etc.). Women should come for examination without makeup: it may contain metal particles. Preference should be given to comfortable clothing so that you can quickly change into a special robe.
It is not recommended to take gadgets or media with you to the procedure. The mobile phone must be left outside the diagnostic room. There are no special instructions regarding medication or nutrition. The exception is the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
You will have to be in a stationary position in the tomograph, which is practically impossible when performing an MRI of the kidneys in children. To ensure the child’s peace of mind during the examination, the patient is given sedatives or light anesthesia before the scan.
How is a kidney MRI done?
The scan takes on average from 15 minutes to half an hour. No special preparation required. Before the examination, it is recommended to remove all metal objects and hearing aids, if any. If the scan is performed with contrast, it is injected into a vein before the procedure begins.
Order of conduct
During the procedure, I suggest the patient take a special table, which will subsequently be placed in the device. It is recommended to relax and calm down as much as possible so that the pictures are as clear as possible.
If the patient suffers from claustrophobia or begins to experience any discomfort during the procedure, he can report it to the doctor using the microphone built into the device. In most cases, the doctor will try to calm the patient, but sometimes the study may need to be interrupted (for example, if the patient has a severe panic attack).
If the study was interrupted, it will have to be done again, since the quality of the images will already be spoiled.
This article contains general information only, is not scientific material and should not be construed as a substitute for medical advice.
Survey process
Depending on the severity of the disease and other factors, MRI diagnostics of the paired organ lasts from 15 to 45 minutes. The patient enters the office, changes clothes and lies down on a movable table, where the body is secured with special belts. Then the table moves inside the tomograph and scanning begins. During operation of the equipment, the patient may hear crackling and other sounds.
If the general condition worsens, the patient needs to inform the doctor, who can be contacted using a microphone inside the magnetic cylinder.
Once the scan is complete, the patient can get up from the table, get dressed and leave the room.
Magnetic resonance semiotics of major diseases
Tumors
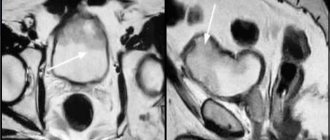
MRI is intended, first of all, to identify structural organic lesions of internal tissues. Tumor diseases are accompanied by changes in both structure and qualitative cellular composition, primarily in the renal parenchyma. Even low-field magnetic resonance imaging scanners are capable of detecting a tumor at an early stage, however, high-field machines with a power of 3 Tesla can visualize a lesion up to 1 mm. Thus, the problem of identifying tumors at an early stage is the absence of clinical symptoms. Most often, the first thing that forces a person to see a doctor is visually detected blood in the urine. Back pain directly depends on the size of the lesion, and does not bother you right away. Often this turns out to be renal cell carcinoma, which originates from the tubular epithelium.
The tumor can reach large sizes, especially Wilms tumor. The magnetic resonance structure is heterogeneous and differs from the tissue of the kidney itself. There is no typical structure of the parenchyma of the medulla and cortex. However, despite the heterogeneity of the lesion, it is impossible to say solely from the MRI picture whether the tumor is malignant or benign (such as angiomyolipoma) - the diagnosis is established only morphologically after a biopsy.
If it comes from the epithelium of the pyelocaliceal system, then the main clinical and instrumental sign will be symptoms of obstruction: deformation and hydronephrosis according to the MR picture, but if the growth does not occur by infiltration of the wall, but into the lumen. The tumor itself is a focus with altered density.
Metastatic damage to the kidneys is associated with their abundant blood supply and structure, which causes frequent damage. Metastases look the same as tumors originally from the organ parenchyma, but, as a rule, they are multiple and most often injure both kidneys.
To clarify the location of the tumor, determine its boundaries or detect very small sizes, contrast enhancement is used, for which preliminary preparation is necessary. The cost of carrying out also changes if the passing is not included in the insurance. In this case, it is necessary to clarify in advance how much this procedure will cost. The difference in price can vary significantly depending on the locality, or even different clinics in the same city.
Kidneys on a tomograph
Cavity formations
Cystic lesions of the organ are often primary and multiple. It originates from the tubular epithelium and produces urine. The cyst looks like a focus with reduced density and a regular round shape.
Polycystic disease manifests itself as multiple cysts in both kidneys. Being of different sizes, they affect all segments of a given organ. Visually, they are severely deformed, enlarged, lumpy, the division of the parenchyma into the cortex and medulla is disrupted, and CRF (chronic renal failure) develops. All this is demonstrated by the MRI picture.
Fibrosis
The kidneys are very sensitive to hypoxia. One of the most common causes of chronic ischemia of this organ is atherosclerosis of the arteries, arterial hypertension. In this case, a primary wrinkled kidney develops. In chronic diffuse inflammatory diseases of the organ parenchyma, secondary wrinkles are formed. This is essentially referred to as cirrhosis. Over time, structure disappears due to the fact that the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue. It has a higher density, therefore the MRI picture will reveal a higher concentration, a change in the bean-shaped shape, impaired division of the parenchyma into the cortex and medulla, and a general decrease in size. A primary wrinkled kidney has a “broken branch” pattern on MR angiography of the renal arteries (typical of atherosclerosis). Secondary wrinkle develops against the background of diseases such as glomerulonephritis, nephritis, chronic pyelonephritis and systemic ailments, such as diabetes mellitus.
Heart attack
A heart attack develops as a result of acute tissue ischemia, caused by thrombosis or embolism of the renal artery or its branch. As a result, a wedge-shaped zone of necrosis is formed, with its base facing the pyelocaliceal system. This area is swollen and gives a darker appearance. When using contrast enhancement, there is no distribution of the contrast agent in the area of ischemia and infarction.
Pyelonephritis
With this disease, the presence of high-intensity foci on MRI in the affected area is noted. When using contrast enhancement, you can see that the area in question is less well filled with the substance used for diagnosis. When the inflammatory process becomes chronic, atrophy of the kidney parenchyma occurs, especially the cortical layer with the development of secondary wrinkling. As for the pyelocaliceal system, it undergoes cicatricial deformation and re-expansion.
Urolithiasis disease
Stones in the urinary tract and bladder are formed for various reasons, but often one complements the other, which again stimulates the first, forming a vicious circle. Among such disorders are metabolic changes, errors in diet (excessive consumption of meat products (in particular, red meat), sorrel), long-term inflammation of the urinary tract and pyelonephritis, an enlarged pyelocaliceal system, and disturbances in the outflow of urine (for example, with nephroptosis). However, MRI tracks the signal from protons, so the stones are not visualized. Computed tomography and ultrasound diagnostics are used to recognize this disease.
Nephroptosis
Using the described method, it is possible to quite clearly determine the degree of organ prolapse; however, in this regard, MRI has no advantages over ultrasound, which requires much less cost to demonstrate changes in the position of organs over time.
Developmental defects
MRI is good at recording such unusual variants of the structure of the excretory system as changes in the number of kidneys, location, shape, size, and structural relationships. Clinically, this can be manifested by impaired urine outflow, insufficiency, and frequent infectious diseases. Failure of vascular supply may be of important clinical significance: arterial aneurysms, disturbances of venous outflow (more typical for the left renal vein), stenosis, etc.
Magnetic tomography with contrast: indications
MRI diagnostics of the kidneys with contrast significantly increases the diagnostic efficiency of the method. This fact is explained by the ability of the drug to concentrate in organ tissues, providing a better magnetic signal.
More often, the study is resorted to in case of suspicion of the development of tumor pathology. This approach helps to detect tumors even at an early stage of development: tumor cells actively accumulate substances and are clearly visualized in the image.
MRI diagnostics of the kidneys with contrast is also applicable if it is necessary to evaluate the therapeutic course. During the process of introducing the component, the specialist can clearly visualize the vascular network of organs, assess the level of functionality and involvement in the pathological process.
Indications for scanning
An inexpensive MRI of the adrenal glands is recommended if you have the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations localized in the lower back segment;
- Swelling not associated with increased fluid intake;
- A history of renal failure;
- Unexplained surges in blood pressure;
- Deviations in laboratory test results;
- Disturbances in the process of urination.
MRI of the urinary system with the introduction of a contrast agent is indicated for suspected cancer. This method allows you to determine with maximum accuracy the location of the tumor, determine its structure, exact size and blood supply.
Scan results
After the magnetic tomography is completed, the specialist studies the resulting images. In the case when a change in the size of the kidneys or an uneven contour is detected, we can talk about the development of a pathological process in the paired organ. The process of decrypting images takes no more than 2 hours.
In the images obtained as a result of a contrast study, the doctor visualizes new formations, determines their location and degree of prevalence.
If kidney pathologies are detected, the doctor prescribes a series of additional tests and only after this determines the diagnosis and therapeutic course.
How does the procedure work?
Kidney MRI is performed by appointment. Conventionally, the procedure is divided into three stages: organizing the examination, scanning itself and issuing results.
At the organization stage, the patient will have to perform the following actions:
- Provide documents for verification and register, draw up an agreement for the provision of paid medical services.
- Fill out the questionnaire to determine contraindications and restrictions.
- An MRI with contrast may require the results of blood tests to determine the degree of kidney function. This question should be clarified with the administrator when registering for the procedure.
- To accurately calculate the dosage of the contrast agent, you must be weighed.
- For a comfortable scanning, it is better for the patient to arrive in loose-fitting clothes without fasteners or decorative metal fittings. Some MRI centers provide a disposable changing kit.
- Listen to the nurse's instructions about the rules for performing an MRI, ask the necessary questions to clarify any unclear points.
Kidney MRI scan procedure:
- Once the patient is comfortable on the sliding platform, the nurse will secure the patient's body with soft straps to prevent unwanted movement during the examination.
- The table slides into the tomograph, and the diagnosis begins.
- The study with contrast takes place in two stages: a basic scan and a repeat tomography after the solution is administered.
Output of results:
- If the radiologist at the MRI center is not overloaded with work on transcripts, the results will be ready within 60 minutes.
The patient can receive images printed on film and/or recorded on electronic media, as well as a specialist’s report for the attending physician.
- If there is a large flow of clients, the delivery of results may be scheduled for the next day. Some clinics upload materials to the patient’s personal account on the website or send them by email to save the patient from having to return to the medical facility.
Pros and cons of MRI diagnostics of the kidneys
The basic advantage of the described type of technique is obtaining high-quality images of organs, the analysis of which determines the condition of the tissues and the area of location of formations or damage.
The safety of the procedure is another significant advantage of MRI. The patient is not exposed to radiation. The examination is relatively comfortable for the patient and is prescribed even for small children.
The disadvantages of the technique include its duration. This is relevant in severe clinical cases, when diagnosis takes about an hour. The patient will have to lie motionless on the table and maintain even, calm breathing.
The disadvantage of magnetic tomography is also considered the fact that it is impossible to conduct an examination for people with a pacemaker, implants and implanted metal elements.
The cost of the study will also not please the patient. This is an expensive procedure, the price is several times higher than the amount of money that will have to be paid for alternative diagnostics - CT or ultrasound.
The process of carrying out MRI - examination of the kidneys and urinary tract
MRI of the kidneys and adrenal glands is carried out in a room specially designated for this procedure, with an MR tomograph installed in it. The specialist explains to the patient the norms of behavior, according to the rules of the procedure itself. Takes written consent to perform an MRI procedure using contrast.
The procedure, which lasts about half an hour, has the following steps:
- The patient being examined lies down on a table and is placed in an MRI chamber. In this case, the patient’s main task is to lie still, breathe evenly, so as not to distort the image sent to the monitor;
- To absorb noise emitted by the MRI machine, the patient is recommended to wear special headphones;
- In case of discomfort, the patient can notify the doctor about the unpleasant sensations through a special microphone installed in the chamber;
- During the diagnosis, the presence of relatives and friends is acceptable.
Magnetic tomography or computed tomography - which is better?
As a result of magnetic and computer diagnostics, three-dimensional images of organs are obtained, but the operating principles of the two methods are different, and their sensitivity is different.
With CT, a person uses X-rays and an installation that, while rotating, transmits a series of images to the computer.
In the case of MRI, everything is different: the magnetic field is taken as the basis for the functioning of the method. This implies the advantageous characteristic of magnetic resonance imaging - the procedure does not have an adverse effect on the body of the subject.
The harmfulness of CT does not allow one to make a choice in favor of computed tomography, for example, when it comes to the upcoming diagnosis of a small child or a pregnant woman.
The key point when choosing a specific diagnostic method is the object and purpose of the study. MRI is powerful in examining renal vessels and nearby soft tissue.
If you have to deal with solid elements (stones, sand), you can’t do without computed tomography. When diagnosing an adrenal tumor, CT demonstrates the physiological data of the formation, and magnetic tomography helps to classify the tumor in detail.
Thus, there is no specific answer to the question of the best choice of diagnosis: you should be guided by the situation.
The most harmful diagnostic method
Indications for the procedure
Magnetic resonance therapy is performed to identify and study the following data:
- parameters of organs, information about departments with determination of their exact boundaries;
- anatomical structure of kidney tissue, its structure;
- dynamics of development of cysts, tumors, stones;
- stages of cancer, its spread;
- level of renal vascular damage;
- organ performance.
Indications for this type of study are:
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- colic;
- pain in the lower back, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, dizziness, chills;
- deviations from normal urine analysis parameters.
MRI or ultrasound - what to choose
In the case of ultrasound, we are talking about a basic method for diagnosing local pathologies. This technique helps to identify the pathological process or its absence, as well as the structure of the kidneys and their location. Ultrasound helps to identify stones and tumor processes in organs, but this method is ineffective if you need to know the nature of the phenomenon or the features of the development of pathology.
MRI diagnostics of the kidneys and urinary tract is more informative in this regard, since it will demonstrate a decrease in kidney functionality and determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Magnetic tomography is often prescribed to a patient “following up” an ultrasound - when the result of the study did not provide a clear picture of the condition of the organs, and more data is required to make an accurate diagnosis.
Despite the high level of information content of MRI, ultrasound examination is prescribed to patients much more often. It is simple to explain this phenomenon: the procedure is accessible, equipment for its implementation is available in every medical center, and the cost of the study for the patient is relatively low.
Magnetic resonance imaging is an innovative diagnostic method that detects pathological processes in the kidneys even at an early stage of development.
MRI is safe for the health of the subject; it helps to obtain an informative picture, which is detailed through the use of a contrast agent.
The latter measure is relevant when diagnosing the smallest tumor processes in the kidneys. Among the disadvantages of the procedure, it is worth highlighting its duration, high cost and a voluminous list of restrictions.
The question of whether MRI is done as part of diagnosis instead of kidney CT and ultrasound cannot be answered in the affirmative. Despite a number of advantages of the method, the purpose of the study is in any case preceded by determining the purpose of the diagnosis and assessing third-party factors. The decision to conduct a specific type of examination remains with the specialist. We recommend reading: “Radiography of the kidneys.”
What can you see
So, what does this diagnosis show? The kidneys are parenchymal organs located outside the abdominal cavity and have a bean-shaped shape. The left one is located slightly higher than the right one: at the level of the eleventh rib (the right one is at the eleventh intercostal space). The adrenal glands are located on top.
The structure of these organs consists of nephrons with glomeruli and collecting ducts, which make up the parenchyma and are located on the periphery, and the pyelocaliceal system, located in the center. The latter has a sign that is displayed in a paler color with lumens of the organ cavities that do not give off a signal and are revealed as black areas. The parenchyma is represented by a lighter medulla in the form of pyramids, with their apex facing the pyelocaliceal system, and the cortex, which has a relatively darker appearance.
Around the kidneys there is a fatty capsule and fascia that separates them from other organs of the retroperitoneal space.
The pyelocaliceal system ends and exits the so-called renal pedicle, which includes the ureter, renal vein and artery, nerve plexuses and lymphatic vessels. Failure of work in this part is the cause of many structural violations.
Tomography of the kidney allows one to differentiate various macrostructures directly in the location of the organ.
When tomography with contrast is performed, preparation for the study includes a test with a small dose of it.
It is important to keep in mind that diseases associated with renal failure require care when prescribing medications, as well as the contrast agent used in contrast-enhanced MRI.
How is the examination done?
During scanning, the most important thing is immobility, so in some cases general anesthesia is allowed for children. The patient removes all jewelry, metal objects, and electronic devices and lies down on a special pull-out couch. The doctor secures it with straps, after which the table slides into the machine and scanning begins.
If an MRI is performed using contrast, it is administered intravenously 15 minutes before the examination. The procedure is painless and does not cause discomfort to the patient, with the exception of the noisy apparatus. Most clinics use headphones or earplugs for this. The examination time is half an hour, if contrast is used - 1.5 hours.
What patients say
Larisa, 42 years old: “It all started with the fact that my lower back hurt wildly. And the temperature suddenly rose. Let me surf the Internet and look for a diagnosis. What haven’t I found in myself! And cancer, and a cyst, and chronic kidney disease... I decided to consult a doctor. Pleasant, smart man. He sent me to do a urine test. The difference between my results and the norm was huge. I went for an ultrasound. The doctor still had questions about my diagnosis. Therefore, I decided to have an MRI. The result is a timely detected angiomyolipoma!”
Andrey, 31 years old: “My review will be brief: MRI is a good thing. My bladder was bothering me and I had pain in my sides. I won’t tell you about my misadventures, but only thanks to this examination was the correct diagnosis established. There are also photos from the procedure as a souvenir. And how much it costs, believe me, is not so important when it comes to saving your health.”
X-ray or MRI, which is better?
MRI and X-ray of the kidneys rely on different technological processes and have different diagnostic capabilities. Their comparison will be correct if the following indicators are taken into account:
Imaging technology.
MRI is a magnetic resonance imaging study that relies on the ability of hydrogen atoms to vibrate at different frequencies, depending on the tissue structure. X-ray is a radiation diagnostics based on the ability of ionizing radiation to penetrate organic tissues of different densities, leaving a mark on the film.
Device capabilities.
MRI visualizes soft tissues best, so for examining the kidneys, the procedure is more informative than x-rays, which display dense bone structures. In some clinics, the material and technical base allows only plain radiography of the kidneys. This method involves the use of x-ray contrast solutions.
Image quality.
X-ray images have poor resolution and allow the recognition of progressive kidney pathologies. The high resolution of magnetic resonance imaging projections makes it possible to examine the early stages of the formation of pathologies, including oncological ones.
| X-ray | Kidney MRI |
Availability and cost of research.
A plain radiography of the kidneys can be performed in a city clinic. The compulsory medical insurance policy provides patients with the opportunity to undergo examinations free of charge. You can get a kidney MRI for free only in large inpatient departments. On an outpatient basis, the procedure is carried out for a fee in specialized commercial MRI centers or regional medical institutions. And the prices for it exceed the cost of an x-ray on average up to 3 times.
Safety.
MRI can be performed as many times as necessary for high-quality monitoring of pathology. Radiography was limited to 1-2 procedures per year due to the danger of ionizing radiation.
How much does the research cost?
Diagnostics are carried out in many diagnostic centers in Moscow. To register, all you need is access to the Internet and a couple of free minutes. The price of an MRI of the kidneys and urinary tract may vary depending on many factors. This is, first of all, the type and power of the equipment, as well as the qualifications of the doctor and the specialization of the clinic. On average, the cost without the introduction of contrast is 6,000 rubles. Minimum cost – 3500 rubles.
With the use of contrast, the cost increases. The average price in Moscow is from 15,000 to 16,000 rubles. The maximum cost with gadolinium is 19,000 rubles.
Decoding the results
After the study is completed, the images are first decrypted. A radiologist performs an MRI and interprets the data obtained, which is then assessed by the attending physician and compared with normal values.
In the image, the specialist analyzes the size and shape of the entire organ, as well as the structure of adjacent tissues. The condition of the vessels, the lumen in them and the speed of blood flow are also assessed. The description indicates the degree of functioning of the pyelocaliceal region.
Based on the interpretation of the scan results, the attending physician has the opportunity to make a diagnosis or draw conclusions regarding surgical intervention. A treatment regimen is also prescribed depending on the study indicators. When a tumor is detected, the oncologist analyzes its location, possible metastases and the degree of damage to the organ.
MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast
Such a study is prescribed if there is a suspicion of the existence of a tumor. In this case, a special substance is injected intravenously, which, passing through the vessels, begins to color them, accumulating in organs and tissues. The quality of the images depends on how active the blood flow is in the desired area. The amount of contrast is prescribed based on the patient’s weight. This substance is removed from the body along with urine within 24 hours.
Thanks to this study, hollow cysts and dense space-occupying formations can be seen. In addition, the images are used to evaluate the fluid in the cyst and diagnose inflammation and bleeding. This procedure is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Many people are interested in the question of if they have prescribed an MRI of the kidneys, where to do such a study. You can undergo the examination in diagnostic MRI centers, which are becoming more and more numerous due to the popularity and high accuracy of the procedure.
What are the possible contraindications?
The examination method using magnetic resonance imaging is considered safe. However, it has a number of contraindications:
- Body weight over 150 kg. This is justified by the fact that excess adipose tissue interferes with a high-quality examination. Sometimes there may be situations in which the patient cannot be positioned correctly on the tomograph bed.
- The presence of a pacemaker, prosthesis, implant containing metal parts. If the warning is ignored, the implants may shift and internal bleeding may occur.
- Severe anomalies of the kidneys and adrenal glands. The factor refers to relative contraindications, since it is valid only if it is necessary to use a contrast agent. The possibility of conducting this type of examination depends on the overall clinical picture of the disease, and the decision is made directly by the attending physician.
- First trimester of pregnancy. In general, MRI is not contraindicated later in the gestational period.
- The presence of epilepsy, claustrophobia and mental illness. If absolutely necessary, it is possible to use anesthesia while you are in the tomograph.
If any contraindication is detected, the specialist decides to conduct the examination using another method.