There are features of computed tomography of the chest in children due to the child’s inability to maintain a still position during the scan. Any activity during tomography is unacceptable, as signal distortion occurs. The information content of a conventional CT scan of the lungs in children under 6 years of age is close to zero due to multiple errors from moving objects. For this reason, children's scans are performed under general anesthesia or after taking sedatives.
Is it possible to have a CT scan for a child? This is a common question from readers. The research is indeed harmful to health, as tissue is exposed to radiation. However, the danger from an undetected disease can be much greater. Before issuing a referral, doctors evaluate the harm-benefit index of a computed tomography scan. There is no doubt about the need for timely detection of a number of dangerous diseases:
- Lungs' cancer;
- Lobar, lobar pneumonia;
- Tuberculosis.
If these nosological forms are suspected and there is a lack of information from alternative diagnostic methods, X-ray examinations are prescribed.
Indications for CT
Computed tomography is based on exposure to x-rays. Therefore, it cannot be considered an absolutely safe method. The examination can be prescribed only from a certain age - sensitivity to radiation exposure is five times higher in comparison with adults.
Due to radiation exposure in children under one year of age, computed tomography will be replaced by safer diagnostic methods (for example, MRI). Read about the features of MRI diagnostics in childhood in the article “Indications and features of MRI of the brain in childhood.” CT is prescribed in extreme cases and only for strict indications:
- bruises, diseases, injuries;
- developmental disabilities;
- tumors;
- depressed fractures of the skull;
- premature birth;
- suspected juvenile stroke;
- hemorrhages inside the skull;
- traumatic brain injuries and hematomas;
- cystic formations;
- fractures of the bones of the vault and base of the skull;
- vascular abnormalities;
- intracranial pressure;
- symptoms of mental disorders;
- aneurysms;
- abnormal development of the respiratory system;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- chronic otitis;
- temporal bone fractures;
- mastoiditis;
- examination of the maxillary sinuses;
- abnormal structure of the inner ear;
- preparation for cochlear implantation.
The radiation dose a child receives does not exceed the permissible minimum norm, so examinations can be scheduled several times a year, but at certain intervals. However, computed tomography of the chest is prescribed extremely rarely, only if there is no other way to examine the child’s condition, since radiation can provoke the development of oncology.
If it is necessary to examine the brain, then after 2-3 years, ultrasound will no longer be effective, since the fontanelles are already hardening and closing. In this case, a computed tomography scan is performed.
head tomography of a child
Natalya Kazhaeva (Volkova) is Anyuta’s adoptive mother. Writes: Finally got to my computer! There are so many things I want to tell here, but I’ll start with the main thing... Anyutka is a practically healthy child))))) Yes, yes... Everything that has happened to her in recent months is caused by psychological reasons. As I had previously assumed - stress, fear, not being needed by anyone, loneliness... This is what it’s all about... Not the care and not the evil employees of the institution.. Anyuta was born almost healthy as her mother’s daughter... her mother took her home, but a few months later it turned out that it was difficult for the mother to cope with the baby and she took her to the hospital for several months.. Then she took her home.. And then she decided that it would be easier for her to live without her daughter and she abandoned her completely... According to my feelings, it was then that the girl stopped in intellectual development….After all, awareness of what was happening would bring her pain…. Well, then they began to examine her and discovered a congenital heart defect, about which the head physician of the nursing home said - yes, everything there has long been compensated for... You can ignore it... And there is another terrible diagnosis in her chart - agenesis of the corpus callosum... in other words, part of the brain is missing ... It sounds scary at first glance... But I opened a forum for mothers of such children and read the following.” When I researched this topic, I realized one thing: if we all regularly had CT and MRI scans, the statistics on diseases would be terrifying. I read stories of those who discovered the absence of a corpus callosum. One is just awesome. Written by a special forces officer. Due to the nature of my service, I undergo such and such training, participate in special operations, and do so many parachute jumps. I have combat wounds here, there and there, including a shrapnel wound to the head. By the age of 50, my head began to hurt, I had a tomography done. They made a diagnosis: agenesis of the corpus callosum. “When I asked the head doctor whether this diagnosis was accompanied by mental retardation, he answered - of course not, she has a delay in intellectual development, but with training with specialists everything can be corrected... Then I asked where this terrible thing came from. diagnosis? So they placed the child in the home to transfer her to us…..Well, the last reason for her current condition is constant vomiting…. Having analyzed the stories of doctors and the director of the children's hospital, it is quite obvious that it intensifies after each change of place of residence, as well as in moments of strong excitement...pure psychosomatics... But in the summer, severe pneumonia was superimposed on attacks of unmotivated vomiting... It was during the acute period of the disease that that photograph was taken , which shocked everyone so much.. What follows from all this?? And the fact that I brought a very malnourished, very neglected, but almost healthy child.. Now Anyutka eats well, though only pureed food, she has started to sit up on her own, and can stand for several minutes with support. sleeps great all night. She laughs often and has begun to show interest in what is happening around her. Of course, there is regurgitation, but we have already noticed that if immediately after eating she is distracted, interested in something, then she calms down and everything stops.. Thank you very much everyone for your kind words, for your wishes, for your financial support)))) Without your help I couldn’t this miracle would happen! —————————————————————— Anyuta is now almost 5 years old. This is the state they brought her to in the special orphanage. But Natasha has already accepted 4 children with disabilities into her family and raised them to their feet, Anyuta is the 5th adopted child. Natasha is an adoptive mother from Samara. This is the hero of our time!!!
photo is still under the cut...
Features of preparation for scanning
Computed tomography does not require special preparation (if the abdominal organs are not checked). However, regardless of age, a full preliminary examination is carried out. Blood and urine are given for analysis and a cardiogram is done. However, in emergency cases, when there is no time for a preliminary examination, CT scanning for children is performed immediately.
But scanning is often done with contrast injection. After it, short-term side effects may occur. To avoid them, you need to not let your child eat for several hours before the examination. This will help prevent possible nausea, dizziness and itching.
Contrast agents can also cause allergic reactions. Sometimes, against this background, swelling develops, even threatening life. To avoid such a situation, the child is given special tests before the scan to check for allergies. Before the examination, parents should warn the doctor about the medications they are taking (especially if they cannot be stopped even temporarily), previous diseases, the presence of diabetes, asthma, pathologies of the thyroid gland, and kidneys.
When examining the abdominal organs, it is necessary to exclude all foods and drinks that cause gas formation from the child’s diet 3-5 days before the procedure, and give him laxatives. In the evening before the study, you need to do a cleansing enema (for constipation, it is repeated in the morning).
During a CT scan, you must remain still while the machine is operating. For this, infants are tightly secured with diapers; older children may be prescribed anesthesia. It is short-term and can be used up to 7 years of age. Older children need to be prepared psychologically, since during the procedure the person is placed in a confined space.
Immediately before entering the office, all metal objects and jewelry must be removed from the child. The procedure is painless, so no painkillers are required, but if the baby is afraid, sedatives may be given.
How to prepare a child for a CT scan
To get the clearest pictures possible, you must remain motionless until the end of the procedure. A child under six years old will not fulfill this requirement. This is why CT scans are often performed on children using short-term anesthesia.
Leading preparation for tomography is directly related to the use of general anesthesia. Food should be taken no later than four hours before the start of the study. Anesthesia should not be used when the stomach is full, as vomiting may occur with the risk of aspiration of these masses.
When a newborn is being prepared for examinations, he is fed for the last time three hours before the examination; before anesthesia, the child cannot even drink.
If this is a fairly mature child, then he does not need anesthesia; it is simply necessary to prepare him for the fact that he will lie inside a closed “pipe” for a certain time. The baby needs to know that this will not hurt him.
The child should breathe through his nose. If problems arise, it is better to use vasoconstrictor drops, dripping them into the nose in advance.
The doctor may order some tests . The clinic itself selects the list of tests.
When a contrast agent is required, the child should be tested for an allergic reaction when the child being tested is at risk for allergies.
Carrying out the procedure
The procedure is carried out according to a certain scheme. The patient is placed in the tomograph tunnel and secured with soft straps. The doctor supervises the scanning process from an adjacent room. He turns on the machine, the couch slides into the tunnel and the examination begins. Once completed, the table is pulled out and the patient is released.
However, when examining children, there are some nuances. He must be accompanied by his parents, who are with the doctor during the procedure. An anesthesiologist is required to be on duty, since in some cases the child is given anesthesia to prevent movement. Children under 7 years of age are usually scanned this way. If a newborn is examined, he is swaddled tightly. To keep children warm, they are covered with a light blanket.
When scanning a child, the tomograph settings change. The intensity of irradiation is reduced to reduce radiation exposure. However, it is impossible to change the tinctures much. Children have more water in their tissues than adults. Therefore, it is impossible to greatly reduce the dosage.
Some devices are equipped with a monitor so that children can be distracted by cartoons. This reduces the risk of stress and anxiety. Now new tomographs have appeared - open type. They help to avoid anxiety and panic in the child, since he does not completely close himself in the capsule and behaves calmly. The duration of the examination is approximately 20 minutes.
What is computed tomography and how does the tomograph work?
CT is a type of conventional x-ray examination, carried out using a special device (tomograph) that produces x-ray radiation and detectors that are connected to a computer.
Passing through a child’s body, X-rays are blocked by body structures to varying degrees. Thanks to this effect, bone formations appear lighter in the pictures, and soft tissues, for example, are almost invisible. Special programs installed on the computer process the received data and form a series of images from them: in the form of layer-by-layer sections and in the form of a three-dimensional structure of organs.
A CT scanner consists of two parts: a table for the patient and a housing that contains the emitter and radiation detectors. During the procedure, the child is placed on a table that is rolled through an opening in the body, which allows X-ray images to be obtained.
Possible consequences of CT
Possible consequences of a CT scan include short-term nausea, slight dizziness, and weakness. However, these manifestations go away on their own and are only a consequence of anesthesia or the introduction of contrast agents. More serious consequences include Quincke's edema. This is a consequence of an allergic reaction.
With a high dose of radiation (or if CT scans are performed frequently), the child receives a large dose of radiation, which can trigger the development of cancer. However, serious complications are practically excluded, since even a single dosage does not exceed the maximum permissible.
Severe consequences no longer arise. In the 90s Old tomographs were used, on which radiation doses were much higher. Accordingly, the risks increased. Now tomographs have already been modernized several times, and the level of radiation has been reduced to a safe level. Therefore, the dose of radiation does not cause harm and does not cause cancer.
Every day a child receives a radiation dose of 3 m3v - from earth rocks, sunlight, isotopes, etc. On tomographs it is no more. However, according to the recommendation of the Health Service, computed tomography can be performed for children no more than once every six months. After each examination, the child should be given plenty of water to drink and spend as much time outdoors as possible (but in the shade, avoiding sunlight). This will help remove radiation from the body faster.
Methodology: what is specific in CT scans of children?
Scanning a child's body differs from scanning an adult in that anesthesia is administered before the procedure itself. Often the anesthesiologist uses inhalation with light anesthesia, so there is no need to artificially ventilate the lungs. After mask anesthesia, the baby awakens easily and quickly.
Newborns must be swaddled before the procedure. Children from the age of one are dressed in clothes that do not hinder the child’s movements; You can use a light blanket. When placing the child on the couch, he is fixed in a lying position.
Then the doctor sets the position of the X-ray tube and its stroke as accurately as possible, so as not to scan an unnecessary area, and calculates the required radiation dose.
- The child receives anesthesia.
- The couch is placed in the tomograph and scanning begins. The baby’s reaction and condition are constantly monitored by a doctor and an anesthesiologist.
- When the operation of the device is completed, the child must be taken out of anesthesia.
- The results are carefully analyzed by specialists, and the doctor monitors the little patient until the anesthesia wears off completely.
- After the study, a conclusion is drawn up and given to parents.
CT scanning is not considered completely safe; the child’s body is under the influence of radiation exposure. But we cannot refuse computer research, because without modern diagnostics, significant harm can be caused.
Decoding the results
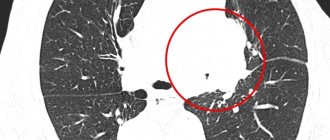
The results after computed tomography are always highly informative and reveal even the smallest changes. The advantages of the method include obtaining many high-resolution images and three-dimensional images (necessary in complex cases). Computed tomography can reveal:
- appendicitis;
- tachycardia;
- inflammation of the bronchi;
- acute and chronic intestinal diseases;
- stones in the kidneys or urinary tract;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- cystic formations;
- tumors;
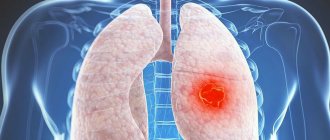
- lung tissue defects;
- vascular injuries;
- various neoplasms;
- diseases of the hip joints;
- complications after lung infection;
- bladder dysfunction;
- birth defects in the abdominal cavity.
After scanning, parents are given the pictures. If desired, you can write data to disk, which allows you to instantly transfer it over long distances if necessary.
Computed tomography is an expensive procedure, the price depends on the area of study and region. For example, in Moscow its cost varies from 3,000 to 32,000 rubles. Computed tomography is performed if other diagnostic methods are uninformative. In such cases, the use of CT scans for children is a justified examination, the harm from which is much less than the danger of tumors, injuries, and diseases.
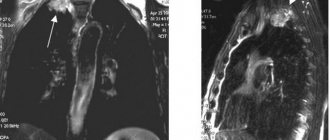
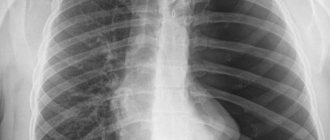
- CT chest
- CT scan of the sinuses
- Types of brain ultrasound for children and adults
- The test is positive, but the ultrasound does not show pregnancy
- CT lungs
How to prepare your child for an MRI
To perform an MRI, no specific preparation is needed. The only thing you need to do is remove items that have metal parts: jewelry, straps or glasses.
It is strictly prohibited to bring any objects or electronic devices into the office.
When it is necessary to achieve good clarity in the pictures, the small patient must lie still. To achieve this, infants and children up to 6-7 years old are given a sedative.
The child is not given anything to eat or drink for several hours before the procedure.
Effect of braces on MRI
Many children have their bite corrected by wearing dental appliances. Is it possible to use a tomograph for scanning in this case?
The doctor will talk to the mother before the test to check with her whether there are metal staples or other objects in the child’s body.
The dental plates will need to be removed. What to do with braces? This will depend on the area of the body being examined.
If you need to scan the brain or head, then you need to ask the orthodontist in advance what material is used to make the braces. There are alloys that do not interfere with the procedure. But there are metals that are incompatible with the magnetic field emitted by the tomograph, and then the doctor will carry out the diagnosis in a different way.
If very complex cases arise, then in order to carry out diagnostics it will be necessary to remove metal structures from the teeth. But this is done quite rarely.
How to help your child prepare for a tomography?
Before an MRI, parents should tell the child about the expected procedure, that there will be no pain, try to calm him down and tell him that the machine will buzz and knock - there is no need to be afraid of this.
If a contrast agent needs to be administered, the child should not be afraid of the injection - everything will happen quickly.
It is necessary to remind the baby once again that you cannot move during the examination.
At what age can children have a CT scan?
This is the most common and frequently asked question from parents. It is not surprising, since the examination is based on ionizing radiation, and not every parent is fully aware of what dose the tomograph produces and what standards are generally acceptable. Yes, we can say with confidence that if there is an alternative to x-ray examination, then it is better to use it, but this is not always possible. For example, MRI has a number of contraindications, although it is based on a harmless magnetic effect. CT examinations are performed from birth. But there must be a good reason for the doctor to order a CT scan for the baby. Such examinations are carried out only by children's hospitals. And one more nuance - the examination process requires the patient to remain motionless. Try to put the children to bed calmly! Yes, older children can lie down quietly during the procedure, especially if one of their relatives is nearby (this is allowed, there are restrictions for pregnant mothers). But very young children cannot lie without moving for even a couple of minutes. In this case, the examination is performed under anesthesia.
They've been through it
I recently had an SCT of the brain done in one of the clinics in St. Petersburg, everything went quite quickly, under the supervision of specialists and generally at a high level, the price is acceptable, especially when you realize the importance of this study.
Marina, July 2020
Lately I have been tormented by constant headaches and often had high blood pressure. My doctor advised me to do an MSCT of the brain, thanks to which he was able to see the problems that had arisen and prescribe an effective comprehensive treatment.
I am absolutely satisfied with the examination, I am very glad that I carried it out in a timely manner and eliminated the ailments at their early stages of development.
Mikhail, Nizhny Novgorod, September 2016
Indications for lung tomography
The main indication is the presence of respiratory symptoms (cough, shortness of breath) against a background of elevated body temperature, detection of wheezing when listening to the lungs and changes in blood tests indicating inflammation.
Other main indications:
- injuries;
- injuries;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- contact with people sick with tuberculosis against the background of specific skin tests;
- previously identified anomalies in the development of the skeleton and soft tissues;
- enlargement of the thymus.
For the purpose of early detection of diseases in healthy children, tomographic methods are not used in Russia.
Lung CT is much more informative than radiography, but is not used for screening in children.