The advent of X-rays was a real revolution in diagnostics: doctors were able to see images of internal organs and assess their condition. However, this method has a number of disadvantages: in particular, two-dimensional x-rays lead to the fact that images of some organs can “overlap” on images of others, and as a result, the correctness of the diagnosis depends only on the experience and skill of the doctor interpreting the x-ray. In addition, due to the nature of the examination, a number of formations, such as hernias or inflammation, cannot be seen on an x-ray. All this prompted researchers to develop new types of diagnostics, among which CT and MRI occupy a special place.
What is the MRI method?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive method for studying body tissue and does not require surgical intervention. The operating principle of MRI is based on the ability of magnetic field rays to penetrate tissue and act on cells, causing a reaction on their part.
The device records this “response” and converts it into a three-dimensional image, which is displayed on the monitor screen. The diagnostician deciphers the received signal, obtaining information about the condition of the organ being examined.
Information! Read what is the difference between the lungs of a healthy person and a smoker
The procedure is carried out using a device - a tomograph. They come in closed types (which is more common) and open ones. The types of magnetic resonance imaging depend on the object of study and the characteristics of its implementation.
Does the quality of the result depend on the power of the device?
If it is necessary to prescribe an MRI procedure, the doctor proceeds from the expected diagnosis: the higher the power of electromagnetic radiation, the smaller the defects and pathological foci the tomograph can detect. Therefore, in case of cancer, specialists prefer diagnostics using a tunnel scanner. It concentrates the field around the patient, which allows you to obtain three-dimensional images with unique detail.
Open MRI is suitable for diagnosing chronic diseases of internal organs and assessing the patient’s condition after surgery. But if it is necessary to clarify the type of tumor, it is recommended to use a device with a power of 1.5 Tesla. This is important when detailing blood flow, searching for the smallest punctures, cracks or deformations.
It should be noted that, regardless of the power of the tomograph, there is no dangerous effect on the human body. This makes magnetic resonance examination practically safe.
Advantages and disadvantages of MRI
Like any technique, MRI has pros and cons. Advantages:
- Safety (absence of ionizing radiation and other harmful effects)
- Penetrating into the body of the subject, electromagnetic rays easily reach the deepest biological tissues. This is possible due to the fact that bones do not pose an obstacle to them.
This feature can be considered both a plus and a minus of MRI diagnostics.
On the one hand, the method makes it possible to thoroughly study soft tissues, but on the other hand, if bone research is necessary, it cannot be called optimal. Among the disadvantages of the method, its cost is noted. For example, ultrasound or x-rays are cheaper, but their effectiveness in complex cases is lower. Only MRI can answer many problematic questions.
How to Apply for an MRI Procedure
To undergo the procedure in government agencies and at the expense of the insurance company, a referral from a specialist , which makes preventive research impossible. However, if desired, any person can undergo examination for a fee . In this case, concluding a written agreement with a medical institution and the fact of payment for services is sufficient to undergo the MRI diagnostic procedure. In this case, the complicating factor may be the price, since tomography is an expensive procedure and significantly impacts the wallet of a patient with an average level of income, and even more so for socially vulnerable segments of the population.
Types of MRI
There are types of MRI, depending on the design of the tomograph, which can be open or closed. The procedure is also divided into types depending on the specifics of the procedure. There are:
- Conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which uses only magnetic radiation.
- MRI with contrast, when a special coloring agent is injected into the blood of the subject. When it enters the organ under study, it colors the cells in one color or another (healthy and sick people give different reactions). The result is a clear and eloquent image. It is possible to see what would be “behind the scenes” using conventional research.
- Recently, methods based on the principles of MRI, but which are mixed, have begun to appear. These include magnetic resonance angiography, which examines blood vessels.
- Functional MRI is also rapidly developing, with which it is possible to thoroughly examine the state of nerve cells in the brain.
There is also a classification of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which takes into account the specific object of examination - the part of the body that is being studied.
Information! Read what MRI is
There are different types of MRI:
- spine;
- brain;
- joints;
- abdominal organs (intestines, kidneys, bladder, uterus in women, etc.).
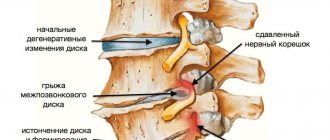
Magnetic resonance imaging of the intestine is the least effective. This is explained by the specific structure of this organ. Intestinal loops, overlapping each other, prevent the rays from providing a clear image.
The picture turns out blurry and uninformative. Therefore, in this area, more conservative and less safe colposcopy is often used. Although, if we are talking about areas of the intestine where the probe is not able to reach, then MRI is used.
Features of MKST
Multislice computed tomography is an advanced type of CT scan that was originally used as a way to diagnose diseases of the brain only, but over time has found wider use. The multislice method differs from standard computed tomography in the equipment design:
- During scanning, the device moves in a special way: the ring rotates and the table moves along a horizontal path. Thus, the emitter moves in the form of a spiral.
- The tomograph is equipped with several detectors. This allows you to obtain images with the thinnest sections up to 0.5 mm.
- For one revolution of the ring, the device takes up to 300 pictures.
- Pictures can be reproduced in several planes.
What can the technique reveal?
The range of capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is extremely wide. The study reveals the following dysfunctions:
- inflammatory diseases;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the brain and spinal cord, as well as their causes;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- damage due to trauma;
- infectious lesions.
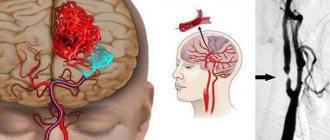
MRI is indispensable in neurosurgery. Although, if we are talking about cerebral strokes, then CT scans are often done here. The greatest merit of magnetic resonance imaging is its ability to detect benign and malignant neoplasms in the initial stages.
A huge number of cancer patients can be saved only thanks to timely diagnosis using MRI, when the tumor is still in its embryonic state and can actually be removed.
Main advantages of an open tomograph
Open type tomographs have appeared on the medical services market relatively recently. The high price limits their purchase for small diagnostic centers. But they have a number of advantages over standard models:
- allow scanning of a patient weighing up to 180 kg;
- the doctor can be next to the patient, monitor his condition and well-being;
- During the scan, drugs can be administered, and a person can be examined under a drip;
- do not provoke panic attacks in people suffering from claustrophobia or other nervous disorders;
- the structure of the open apparatus makes it easy to examine a victim with severe ruptures and fractures;
- noise and light effects during sensor operation are minimized;
- Open MRI allows you to obtain high-quality images if the patient moves slightly;
- recommended for examining children without the use of anesthesia;
- facilitates scanning the body of an immobilized patient after a stroke.
With the development of open MRI, doctors have a unique opportunity to perform complex operations under the control of the device. It can be used to install a cardiac bypass, remove a blood clot from an artery, or replace coronary arteries. In real time, the surgeon monitors the conductivity of the veins and aorta and cleaves the brain aneurysm. This significantly reduced the number of complications and deaths, and reduced the time of surgical intervention for stenting.
When is an MRI prescribed?
All dysfunctions listed in the previous section or suspicions of them can be considered indications for MRI. The list of symptoms for which patients are referred for this type of examination is long:
- headaches of unknown origin;
- dizziness;
- unexplained increase in temperature, which is regular;
- painful sensations in the abdomen, back, side;
- severe disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Not all symptoms are listed. If the doctor is unable to make a diagnosis based on test results, as well as ultrasound, x-rays and other available methods, he will refer the patient for an MRI.
Which method to choose
If it is necessary to choose between MSCT or MRI of the brain, the attending physician decides which is best for the patient. He is guided by the danger of the procedure in the presence of contraindications, evaluates the risks and the informativeness of the result. For tumors and disorders of the structure of the brain or nervous tissue, preference is given to electromagnetic resonance. For injuries to the vertebrae or skull bones, it is better to use x-rays when searching for calcifications.
What is better than MRI or MSCT for emergency diagnosis? In cases of acute stroke or severe trauma, it is rarely possible to obtain information from the patient about embedded prostheses, foreign bodies, or metal fragments in the body. In addition, multispiral scanning takes several minutes, which is important when providing resuscitation measures.
Contraindications
The list of contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging is much shorter. It includes:
- metal objects in the patient’s body (shards, prostheses, etc.);
- implanted stimulators of the heart muscle and brain activity;
- Hearing Aids.
Obesity is considered a relative contraindication. The point here is not the condition of the patient’s body, but the fact that most tomographs cannot withstand a weight of 120-130 kilograms. Exceptions are rare. Therefore, patients with large body weight are prescribed other research methods.
Another relative “taboo” is claustrophobia. A person suffering from this deviation is nervous in the first minutes of being in a closed tomograph, and open installations are not available in every hospital. There are other dysfunctions of the nervous system or psyche for which magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is difficult to implement.
These are deviations when a person is unable to remain motionless for a long time, which is important for this type of examination. For this reason, MRI is not performed on young children. In extreme cases, they, as well as patients at psychoneurological dispensaries, are given anesthesia, and the procedure takes place under general anesthesia.
Pregnancy is not a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging. However, in the early stages, it is better for women to avoid such examination. In the first trimester, the child’s vital organs are formed, but scientists have not yet given clear answers about the effect of magnetic radiation on the fetus. Although they are inclined to believe that, most likely, there will be no harm.
Features of diagnosing asymptomatic diseases
Many of the diseases that can be seen using CT scans do not show visible signs and symptoms until they reach a stage that is difficult to treat. This is especially true for various types of tumors, including cancer . It is also important to monitor the condition of cerebral vessels to prevent aneurysms and strokes, especially in old age. Vascular conduction disorders may be asymptomatic or characterized by mild and irregular headaches. In this case, only MRI diagnostics can give an accurate answer about the patient’s health condition.
That is why tomography is a safe way to preventively study the state of the body in cases where the patient is worried about his health, but there are no pronounced symptoms of any disease.
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
There is no need to prepare for an MRI in any special way, and this is one of the advantages of the method. Those who experience anxiety are advised to take a sedative the day before the procedure. Be sure to ask your doctor any concerns you may have in advance. Before entering the diagnostic room, metal objects are removed from the body (metal objects, jewelry, bank cards). That's all the preparation.
An exception is MRI of the intestine, which requires preliminary cleaning of the organ being examined. For two or three days, patients refuse food and drink that can cause flatulence, take carminatives and laxatives, and do enemas. The procedure in such cases is carried out on an empty stomach.
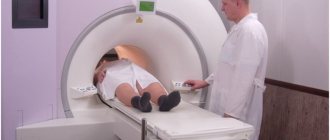
When the patient is ready, he is dressed in loose clothing and placed face up on a mobile table, which is then rolled into a CT scanner shaped like a pencil case. The doctor is in the next room, and the patient communicates with him using a special headset. The table with the patient moves under the device using a remote control. The patient's arms, legs and head are fastened to the table surface. It is imperative to remain still.
There is no pain or other unpleasant sensations during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The only thing is that someone may not like the noise made by the tomograph. To protect yourself, use provided headphones or earplugs.
The procedure lasts 30 - 60 depending on the complexity and type (with or without contrast). The results are ready after a short time (an hour or two). Decoding is the task of the attending physician.