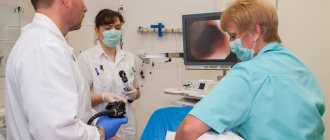
FCS (fibrocolonoscopy) is a common and multifunctional method for diagnosing various disorders in the intestine.
With the help of a colonoscope, not only the condition of the mucous membrane is examined, but also many other manipulations that are not available in most modern devices.
If necessary, the area of interest is photographed, and the doctor has the opportunity to point the lens as accurately as possible.
Also of interest to patients is taking a biopsy and removing tumors as they are detected. All these functions are available and actively used by professional specialists.
What it is?
FCS is one of the most modern and constantly improving methods for examining the condition of the intestinal mucosa. Visually, the procedure looks like an examination of the inner surface of the rectum using the insertion of a special tourniquet, equipped on all sides with light devices and additional instruments.
The tourniquet is very flexible, so it easily passes even into distant parts of the intestine. The fibers of the device contain conductive particles that serve to transmit the resulting image, which can be recognized and evaluated by a doctor. He must constantly monitor the process through a special eyepiece.
FCS allows the doctor to become familiar with the condition of all parts of the colon, as well as check the distal part of the intestine, located in the ileal region. Thanks to this, with due care, it is possible not only to make a diagnosis, but also to be absolutely sure of its correctness, which provides the maximum guarantee of prescribing meaningful and confident treatment.
If polyps or small tumors are detected, their resection is performed almost instantly and with excellent accuracy, which allows the patient not only to protect himself from surgery, but also to avoid all the processes associated with preparation and rehabilitation after surgery.
The FCC has the ability to grant the doctor the right to take pictures as the tube passes through the intestines, and to carry out associated therapeutic measures of a local nature.
This examination is safe and painless if the patient is under general anesthesia. Often this diagnostic measure shows some similarity with other diagnostic tests, but its capabilities cannot be overestimated.
Colonoscopy - what is it?
The procedure involves inserting a probe into the anus to examine the lining of the large intestine. This type of diagnosis is carried out using fiber colonoscopes, invented in the second half of the 20th century.
The device is a long, thin and flexible tube, at one end of which there is an eyepiece with a light bulb and special levers for controlling the device, and at the other end there is an optic for examining the colon (camera). The structure of the tube is fiber, which ensures complete internal reflection of the light beam and prevents its scattering. And the location of the ends of the fibers at the input and output is similar, which avoids distortions in the results. The fiber colonoscope is connected to a monitor, to which the received information is transmitted with sufficient magnification to see all the details.
It is important to note that modern devices use only cold light, so there can be no burns.
Indications and contraindications
Indications:
- IBS. It is expressed in constant diarrhea or periodic constipation, sometimes these phenomena alternate with each other. Additionally, the patient experiences a set of symptoms indicating incomplete bowel emptying with the subsequent occurrence of flatulence. The patient may be constantly plagued by abdominal pain or heaviness in the intestines.
- The presence of blood in the stool structure or its separate release during bowel movements.
- Anemia when it is impossible to quickly find its provocateur.
- Dramatic weight loss without a reasonable justification.
- Appetite disturbances associated with severe and persistent weakness.
Contraindications:
- Failure of the heart or lungs.
- Hypertension 3 degrees.
- Having had a stroke in the past.
- Crohn's disease, which manifests itself in a chronic and quite severe form.
- Peritonitis.
- Adhesions in the intestines.
- Hemorrhoids, vascular thrombosis in acute form.
- Postoperative period.
Chewable tablets Maalox: instructions for use and patient reviews.
How to use sea buckthorn oil to treat gastritis? Find out in this article.
Indications
The technique of visual inspection of the lumen of the large intestine in real time is a mandatory diagnostic measure in the following cases:
- Early diagnosis of polyps and benign neoplasms in the intestines identified by sigmoidoscopy.
- Chronic pain in the right or left iliac region, as well as in the umbilical area.
- Unreasonable sharp decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood.
- Rapid decrease in body weight.
- Cases of intestinal cancer in close relatives.
- Presence of blood fragments in stool.
- Discharge of pus or mucus from the rectum.
- Entry of a foreign body into the rectum.
- Regular stool disorders, which are expressed in alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- Previously performed surgical interventions on the intestines.
In addition, the absolute indication for performing a colonoscopic examination is a suspicion of obstruction of the large intestine. Also, the study is indicated in the presence of malignant neoplasms, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Preparation for the procedure
To prepare the patient for the examination, it is necessary to spend at least 3 days before the procedure. A slag-free diet is prescribed in combination with regular use of laxatives.
Diet
The following products should be consumed:
- Flour products without a lot of sugar and a variety of low-fat cereals.
- Low-fat meat. It is most acceptable to eat broths with meatballs, boiled meat, and soufflé.
- One egg per day.
- Fish with a minimum amount of fatty components.
- Dairy products, especially the most calcium-rich elements.
Should be excluded from the menu:
- Grain-containing products.
- Vegetables, fruits and berries, especially those with small seeds.
- Cabbage and dishes with it.
- Fatty meats or fish.
- Legumes.
- Smoked, sour and fried foods.
- Spicy food additives.
- Alcohol.
Intestinal lavage
It is necessary to use a solution using Fortrans or Lavacol. You should prepare at least 4 liters of product. You will have to drink it gradually, distributing 2 liters in the evening and morning before the procedure. The advantage of this solution is the free passage of fluid through the intestines without absorption, which allows you to maintain a normal water-electrolyte balance.
Patients' opinions about the procedure
As you know, how many people, so many opinions. Some say good things, some say not so much, everyone can be understood, and they are all right in their own way. Someone ended up with an unqualified specialist, or was simply deceived, and this happens. Some, on the contrary, easily endured the procedure under the strict supervision of a doctor. However, most agree on one thing - undergo the procedure only under anesthesia. Almost everyone who has dared to do this without anesthesia speaks of unpleasant and even painful sensations. Choosing the anesthesia option is easier for both the patient and the doctor conducting the study. He will not be distracted by noise from the patient and will be able to focus on observing and determining what the colonoscopy shows. In this case, the reviews will be more positive, and the patient himself will forget about the procedure and will not worry.
For some, it is not the procedure itself that causes fear, but the preparation for it. It will be especially difficult for those who eat poorly and are used to eating a lot. You will have to limit yourself for a few days. But even this food can be balanced and tasty, the main thing is to prepare everything correctly.
To reduce irritation from frequent urges to go to the toilet, patients recommend waiting a little and not going there right away, so there will be less pain.
The consequences and sensations from the procedure also depend on the individual characteristics of the structure of your intestines, so no one can say for sure what sensations you will have. You should not be afraid of this procedure, because what a colonoscopy shows cannot be shown by any test. It’s worth going through this and moving on with a calm life.
How is it carried out?
Sometimes, to facilitate the procedure, the patient is given general anesthesia.
Its necessity is determined in each specific case. It is recommended to put the patient into temporary sleep if his general condition worsens, as well as in the presence of psychological pathologies that interfere with the correct conduct of FCS, cause careless movements of the doctor or patient, which can lead to negative consequences.
Sometimes the need for anesthesia is predetermined by the presence of severe manifestations of the disease, for example, with cracks in the anus.
The procedure is roughly divided into the following stages:
- First, the examination is carried out without the use of a special device, but using the method of digital examination of the intestines from the anus.
- A special tube is inserted into the anus and gradually deepened.
- It is gradually moved further along the organ, and when the desired size of the recess is reached, air is supplied. This is necessary so that all areas of the mucous membrane undergo swelling and straightening. Then the doctor receives the most detailed picture of the condition of the internal organs.
- At the first stage of gas supply, the patient may complain of a bursting sensation in the anus and the need to defecate. This phenomenon occurs when the intestinal muscles are not ready for stress. Gradually they get used to the effects and the negative sensations lose their intensity.
- Polyps are removed immediately as they are detected. This is one of the main advantages of this diagnostic method.
- A biopsy is taken if there are preliminary indications or in cases where the doctor independently identifies questionable areas and wants to clarify the tissue structure to exclude unpleasant diseases.
- When all the necessary manipulations have been completed, the intestinal FCS is completed. To do this, simply slowly remove the tube from the intestines.
How do they do it?
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is performed strictly in a hospital setting. In the morning before the examination, the doctor examines the patient again to determine his state of health, the likelihood of ARVI or a cold, and the type of anesthesia is finally determined.
The algorithm looks like this::
- The patient is placed on the couch on his left side with his knees pulled up to his stomach;
- The anus is treated with an anesthetic and anesthesia is administered.
- Next, a diagnostic examination of the intestinal cavities is carried out. If it is necessary to remove polyps, stop bleeding or perform surgical procedures, special surgical instruments are used. The removed fragments of tumors or polypous lesions are sent for histological analysis.
- After the procedure, the patient is taken to the recovery room. All this time, the patient’s condition is monitored by specialists.
In some cases, after general anesthesia, a 24-hour hospital stay is required. If a colonoscopy under anesthesia is required for a young child, then after the manipulation it is recommended that he and one of his parents stay in the hospital for 1-3 days.
What anesthesia is used?
In principle, there are several main types of pain relief that are effectively used during colonoscopy, regardless of the purpose of the study:
- Local anesthesia . During the manipulation, the tip is treated with anesthetic compounds to facilitate the passage of the probe and eliminate severe pain symptoms.
- Colonoscopy during sleep (sedation). The patient remains half asleep throughout the procedure, can respond to the doctor’s demands, does not feel pain, and feels movements in the intestines. The degree of immersion in sleep depends on the dosage and the chosen drug. The main task of sedation is to relax the body and muscle structures. The advantage is the lack of influence on the respiratory centers, the possibility of rapid transfer to general anesthesia. The only objective disadvantage is the high cost.
- General anesthesia . Under systemic anesthesia there is no pain, the patient's consciousness is completely depressed. Despite the absolute absence of pain, waking up from anesthesia is always unpleasant: a feeling of thirst, chills, a heavy head. There is no memory at all from the moment the drug was administered. There are several types of such anesthesia: intravenous and inhalation anesthesia. In the first case, the drug is supplied through a vein, in the second, the drug is supplied through an oxygen mask.
The choice of anesthesia depends on multiple criteria:
- testimony,
- complexity of the clinical situation,
- goals of diagnostic research,
- age and general medical history of the patient.
Note ! Any type of general anesthesia, including sedation, is performed in the office with the ability to provide emergency resuscitation in the event of unpredictable reactions during the procedure.
How long does an intestinal colonoscopy take under general anesthesia?
The duration of the procedure under anesthesia is somewhat longer and is completely determined by the purpose of the diagnosis. If it is necessary to remove pathological foci, treat certain diseases, or stop bleeding, the procedure can last about an hour. In the case of routine diagnostics, 15-20 minutes are enough for a full examination.
Thus, the difference between a conoscopic examination with and without anesthesia is due only to the absence of painful sensations. There are no significant differences in other criteria.
Can there be consequences after the procedure?
FCS is a relatively easy procedure, so if it is performed correctly, complications are very rare. In most cases, after the examination, the patient immediately has the opportunity to begin taking food and the necessary fluids.
Sedatives used before the test may have side effects. To minimize the risk of their occurrence, it is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of allergic reactions, chronic intolerances or diseases of the hematopoietic organs and excretory system.
There is a risk of bleeding. They usually appear after taking a biopsy or resection of a small polyp. Most often, this process is quickly stopped or controlled by a competent specialist. The colonoscope may tear or perforate tissue. This is an extremely rare complication, however, if the procedure is not carried out carefully, the design of the device can cause damage to the mucous membrane.
What do you do before the test?
To receive an informative video, you must undergo preparation for a colonoscopy:
- Diet for 3-5 days. All waste ingredients and dishes that stain, clog the intestines and contribute to constipation or flatulence are excluded. Products are selected from the list of approved ones.
- Taking laxative solutions. Before diagnosis, drink 2-4 liters of special liquids, which ensure maximum cleansing of the organ.
- In some cases, enemas are given immediately before the test. Although if the first 2 points are carried out correctly, they are not necessary.
Attention! If a colonoscopy is scheduled under anesthesia, then you should not drink on this day, and the evening before you stop eating.
Patient reviews
Galina, 44 years old
At first I wanted to do FCS under anesthesia, but the doctor dissuaded me, as it poses an increased risk of injury to the mucous membrane. Everything turned out to be not so bad, although before the diagnosis I heard a lot of negative comments from friends. When inserting the tube, practically nothing is sensitive at all. Pain appears only when air is pumped. The good news is that this process rarely lasts more than 10 minutes.
Vasily, 35 years old
I did it once and that was enough for me. Not only is the tube shoved into the butt, but all this is also accompanied by a maximum of unpleasant sensations. I don’t recommend it to anyone, only if you really need it.
Daria, 29 years old
Tolerable. The doctor said that I might have to go to the hospital, but due to the situation at home I can’t do that. I agreed to the FCC. Based on the results, the doctor said there was nothing to worry about, so I’m glad.
Ekaterina, 59 years old
I have a high pain threshold, so I don't tolerate FCS well. If I do it again, I will have to take anesthesia. During the entire manipulation you feel discomfort, so I advise you to do it only with clear and reasonable indications from a doctor.
Vladimir, 48 years old
I had FCS for quite a long time. This is a full examination, but it does cause pain. If I go through this procedure again, it will only be as a last resort.
Intestinal inflammation: symptoms and treatment with medications, folk remedies.
Find out from this article how to properly dilute Smecta powder.
Instructions for use for Gastritol - https://vashjeludok.com/lekarstva/kapli/gastritol-instrukciya-po-primeneniyu.html
Colonoscopy video
Naturally, colonoscopy can and should be used exclusively on an outpatient basis. Below is a video of an intestinal colonoscopy, after watching which you can roughly imagine how the colonoscopy procedure goes:
If, during an examination by a doctor, you have identified symptoms of the development of colorectal cancer or the appearance of polyps, you simply need to undergo a video examination of the intestines. Sometimes, for people who generally have discomfort during bowel movements, a colonoscopy may also be indicated.
During a colonoscopy, tissue samples may be taken from the patient if further laboratory tests are needed. If necessary, the patient can immediately remove polyps that may form on the intestinal walls.
In general, polyps are benign formations. However, if you do not pay due attention to them, then after a long time they have every chance of developing into malignant tumors.
Results: advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Advantages:
- Visualization of the complete picture of the disease.
- Conducting a detailed study with the possibility of photographing areas of interest.
- It is possible to take a biopsy and perform minor surgical interventions.
- The most common side effect is a temporary feeling of bloating, which goes away very quickly.
Flaws:
- In some cases, it is necessary to administer anesthesia to the patient.
- There is a risk of injury to the mucous membrane.
- Many patients complain of discomfort during the procedure.
FCS is a popular method for diagnosing various pathologies on the internal intestinal tracts. With its help, you can get rid of vain suspicions, confirm and clarify the diagnosis.
If necessary, small tumors are removed or cells of certain tissues are taken for analysis, which makes this method of assessing the condition of the mucosa multifunctional and very popular.
Technique and stages of the procedure
After the patient has undergone preliminary preparation, he will have to directly visually examine the walls of the large intestine using a colonoscopic probe. It is important to remember that this manipulation is accompanied by a certain discomfort and pain, so the attending physician may recommend one of the options for pain relief.
Anesthesia
If the patient has a low threshold for pain sensitivity or experiences a pronounced fear of the colonoscopy procedure itself, then, in the absence of contraindications, he is given one of the types of pain relief. The following measures help eliminate discomfort and minimize the intensity of pain when performing this study:
- Drug sedation. This technique is based on the preliminary administration of pharmaceutical drugs that have an analgesic (pain-relieving) and sedative effect. After sedation, the patient ceases to feel pain and discomfort, but remains half conscious.
- General anesthesia. For general anesthesia, another group of medications is used, after the administration of which the patient is unconscious, does not feel discomfort or pain, and also does not have any memories of the course of the study.
Each of the listed pain relief options has a number of indications and contraindications, advantages and disadvantages. The key advantage of general anesthesia is the complete absence of negative sensations, but the disadvantage of the method is the increase in the duration of rehabilitation, as well as the suppression of laryngeal reflexes.
The advantages of drug sedation include partial preservation of consciousness in the absence of negative sensations, and the disadvantages of the method include the insignificant likelihood of pain during colonoscopy.
Preparation for colonoscopy using the drug "Fortrans"
A packet of Fortrans is diluted in 1 liter of water (clear juice or weak tea can be used). The more acidic the liquid, the easier it will be to drink the solution.
You should start drinking the solution on the day before the colonoscopy, no earlier than two hours after lunch. Lunch should be light (broth, tea). The Fortrans package contains 4 sachets. It is advisable to use all four (for persons whose weight is more than 50 kg). You need to drink a glass of the solution every 15-20 minutes for 4-5 hours. The optimal time to take Fortrans is from 9 a.m. to 11 p.m. You can wash down the solution with a small amount of sour juice (without pulp) or eat it with a slice of lemon. Loose stools will appear 1-2 hours after starting to take the drug, and 2-3 hours after taking the last dose, the intestines will be completely cleansed.
After which you cannot eat anything until the colonoscopy.
Contraindications
For some patients, doctors do not recommend this diagnostic method.
In particular, examination is harmful for the following diseases and conditions:
- peritonitis (including suspicion);
- various pathologies of blood formation;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- acute psychiatric and neurological disorders (eg epilepsy);
- disruptions in the functioning of the respiratory system;
- acute infectious diseases;
- pregnancy;
- allergies to certain drugs (anesthetics);
- severe blood clotting disorders.
The list is not complete and there is no disease that is an absolute prohibition for colonoscopy.
Absolute and relative readings
Colonoscopy is the most reliable technique that can detect diseases of the lower intestine. There are diagnostic and therapeutic indications for the procedure. These include:
Bleeding of gastrointestinal origin.
- Polyps of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Recurrent intestinal obstruction.
- Difficulties in making a diagnosis with recurrent abdominal pain.
- Suspicion of ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn's disease, but the procedure is not performed in the active stage of this disease due to the risk of perforation of the colon.
- Suspicion of neoplasms.
- Simultaneous weight loss, anemia and persistent increase in body temperature.
- Persistent constipation.
- Removal of benign tumors.
- Coagulation of the source of bleeding.
- Treatment of intussusception or volvulus.
Indications for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy may be prescribed for the following complaints (symptoms):
- pain and cramps in the abdomen;
- bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation or diarrhea);
- flatulence: feeling of heaviness in the stomach, bloating;
- belching, feeling of nausea after eating;
- decreased appetite.
Contraindications for the study
The procedure is a complex and time-consuming technique. The endoscope passes through the entire intestine, so it is important to know what contraindications exist for intestinal colonoscopy in order to avoid complications.
- Purulent inflammation in the abdominal cavity and peritonitis.
- Myocardial infarction and ischemia of the heart muscle.
- Shock state with a decrease in pressure below 70 mm Hg. Art.
- Acute stages of ulcerative and ischemic colitis.
- Perforation of the intestinal wall or perforation.
- Pregnancy.
- Stages of pulmonary and heart failure, characterized by serious circulatory disorders.
These are absolute contraindications when performing a colonoscopy poses a threat to the life or health of the patient. In some cases, the study will be useless and will not show correct results. These include:
- The accumulation of blood in the intestine due to bleeding makes it impossible to see the intestinal walls.
- The study is not carried out immediately after surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity, since the introduction of an endoscope may cause sutures to diverge.
- If there is a strong protrusion of the intestine, the colonoscope cannot pass through the intestine and adequately examine it.
- An inguinal or umbilical hernia may impede the passage of the endoscope due to prolapse of the intestinal loop.
- If an artificial heart valve is installed, the procedure is postponed, since the risk of infection cannot be ruled out.
The specialist may postpone a colonoscopy due to the intestines being poorly prepared for the examination.