What is a biopsy
Essentially, this is the collection of biological material for further examination under a microscope. The main goal of the invasive technique is to timely detect the presence of cancer cells. Therefore, biopsy is often used in the complex diagnosis of cancer. In modern medicine, it is possible to actually obtain a biopsy from almost any internal organ, while at the same time removing the source of pathology.
Due to its pain, such laboratory analysis is performed exclusively under local anesthesia; preparatory and rehabilitation measures are required. A biopsy is an excellent opportunity to promptly diagnose a malignant neoplasm at an early stage in order to increase the patient’s chances of maintaining the viability of the affected organism.
Carrying out an excisional biopsy
An excisional biopsy involves complete removal of the lesion. Removal is carried out by making several small incisions using a scalpel. Therefore, unlike the incisional type, excisional biopsy is not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic surgical intervention. But before carrying out this procedure, a preliminary puncture examination is required. If the needle examination does not provide accurate information, doctors prescribe an excisional biopsy.
The completely remote education is sent to the laboratory for further research. This helps improve the effectiveness of cancer treatment and identify the causes of a specific tumor.
10.10.2017
Why do they take it?
A biopsy is prescribed for the timely and rapid detection of cancer cells and the pathological process accompanying their presence. Among the main advantages of this invasive technique performed in a hospital setting, doctors highlight:
- high accuracy in determining tissue cytology;
- reliable diagnosis at an early stage of pathology;
- determining the extent of the upcoming operation in cancer patients.
Recovery period
After the excisional biopsy, the patient is immediately discharged home and resumes her previous activities on the second day. After the procedure with cutting off a piece of tissue, she must stay in the hospital for 1 or 2 days. A certificate of incapacity for work is issued for 10 days.
Sometimes a woman may feel pain, but analgesic medications are allowed. It is recommended to place a non-hot compress on the lower back.
Gynecologists advise wearing underwear made from natural fabrics and using sanitary pads. For washing, you need to use soap without fragrances. The perineal area needs to be well dried.
The healing of the wound takes place over the course of a month - the patient is examined again. Menstruation usually arrives on time or with a slight delay.
What is the difference between histology and biopsy
This diagnostic method studies cells and their potential mutation under the influence of provoking factors. A biopsy is a mandatory component of diagnosing cancer and is necessary to take a tissue sample. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia using special medical instruments.
Histology is considered an official science that studies the structure and development of tissues of internal organs and body systems. The histologist, having received a sufficient fragment of tissue for examination, places it in an aqueous solution of formaldehyde or ethyl alcohol, and then stains the sections using special markers. There are several types of biopsy, histology is carried out in a standard sequence.
Methods for studying biopsy material
The obtained biopsy specimen is studied using several methods - histological or cytological. The first is considered more accurate, since tissues are studied, not cells. Both methods involve the use of microscopic technologies.
Histological examination
Tissue sections are studied, placed in a specialized solution, paraffin, and then stained. The latter procedure is necessary so that cells and their areas are better distinguished under a microscope.
The results of the study are known after 4–14 days.
If urgent research is necessary, the biopsy is frozen, sectioned and stained. The procedure lasts 40 minutes.
Cytological
If histology studies tissue sections, then cytology examines cellular structures in detail. The technique is performed if it is not possible to obtain a piece of tissue. Diagnosis is carried out to determine the nature of the formation - benign or malignant, reactive, inflammatory, precancerous. A smear is made on glass using the biopsy specimen and examined under a microscope. The procedure is faster and simpler than histology.
Kinds
In case of prolonged inflammation or suspected oncology, it is necessary to perform a biopsy to exclude or confirm the presence of an oncological process. It is first necessary to perform a general analysis of urine and blood to identify the inflammatory process, and implement instrumental diagnostic methods (ultrasound, CT, MRI). The collection of biological material can be carried out in several informative ways, the most common and popular among them are presented below:
- Trephine biopsy. It is carried out using a thick needle, which in modern medicine is officially called a “trephine”.
- Needle biopsy. The collection of biological material is carried out by puncturing the pathogenic neoplasm using a thin needle.
- Incisional biopsy. The procedure is carried out during a full-fledged operation under local anesthesia or general anesthesia and involves the productive removal of only part of the tumor or affected organ.
- Excisional biopsy. This is a large-scale procedure, during which a complete excision of an organ or malignant tumor is performed, followed by a rehabilitation period.
- Stereotactic. This is a diagnosis carried out by preliminary scanning for the further construction of an individual scheme for the purpose of surgical intervention.
- Brush biopsy. This is the so-called “brush method”, which involves the use of a catheter with a special brush for collecting biopsy material (located at the end of the catheter, as if cutting off the biopsy material).
- Loop. Pathogenic tissues are excised using a special loop (electric or radio wave), in this way a biopsy sample is taken for further research.
- Liquid. This is an innovative technology for identifying tumor markers in liquid biopsy, blood from a vein, and lymph. The method is progressive, but very expensive, and is not carried out in all clinics.
- Transthoracic. The method is implemented with the participation of a tomograph (for more careful control) and is necessary for collecting biological fluid mainly from the lungs.
- Fine needle aspiration. With such a biopsy, the biopsy material is forcibly pumped out using a special needle to conduct exclusively cytological examination (less informative than histology).
- Radio wave. A gentle and absolutely safe technique, which is carried out using special equipment - Surgitron in a hospital setting. Does not require long-term rehabilitation.
- Preskalennaya. This biopsy is used to diagnose the lungs and consists of taking a biopsy sample from the supraclavicular lymph nodes and lipid tissues. The session is carried out with the participation of a local anesthetic.
- Open. Officially, it is a surgical procedure, and tissue collection for examination can be done from an open area. It also has a closed diagnostic form, which is more common in practice.
- Core. Soft tissue sampling is performed using a special trephine with a harpoon system.
Types of cervical biopsy
- Dot sighting
- Circular (conical)
- Excision
- Curettage of the cervical canal
Biopsy methods
- Pincer (plucked)
- puncture
- Loop (radiosurgery)
- Knife
Biopsy quality requirements
- The size of the sample (pinch) of cervical tissue taken during biopsy must be at least 3-5 mm
- The sample should include: - superficial epithelium - and underlying connective subepithelial tissue (3-5 mm of stroma)
- It is advisable to cut the sample so that it includes the border between healthy and pathological tissue
- The edge section of the biopsy specimen must be without traces of thermal damage (burn, charring)
- The collected tissue sample should be immediately placed in a container with formaldehyde to prevent drying out.
- Each biopsy is placed in a separate labeled container
Preserving the structure of the cervical tissue and obtaining high-quality material for histological examination is possible only with a “clean cut” using a sharp surgical instrument (biopsy forceps with a cutting edge, puncture needle, scalpel) or a “radio knife”.
A laser beam or a hot electric loop is of little use for “cutting out” a full-fledged biopsy.
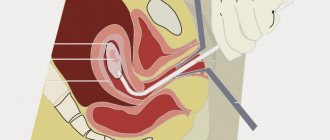
Colposcopy and cervical biopsy
Any type of cervical biopsy is carried out under mandatory visual control during colposcopy.
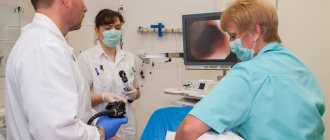
Colposcopy is a method of examining with the “armed eye” the surface of the vagina and the outer part of the cervix at 15-40 times magnification using an optical colposcope and lighting equipment.
Modern expert-class colposcopic complexes are equipped with advanced magnifying optics that provide three-dimensional images. They allow you to detect the smallest anomalies, damage on the vaginal surface of the cervix and conduct the most accurate targeted biopsy.
Binocular operating colposcopes with “top feed” are convenient, mobile, and leave sufficient space for the doctor to carry out the necessary therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations.
Operating binocular colposcope
Targeted cervical biopsy
A targeted point biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue from an abnormal area of the cervix using various instruments.
For better diagnostic reliability, it is recommended to take tissue samples not from one, but from several of the most affected areas of the cervix.
What tool can be used
- Biopsy forceps (forceps or pincer biopsy, punch-biopsy)
- Thick needle (puncture biopsy)
- Small loop electrode ≤5 mm in diameter (spot radio wave biopsy)
Pinch and targeted loop biopsy of the cervix Advantages of the method
- Can be carried out on an outpatient basis in a equipped treatment room or a small operating antenatal clinic
- Short-term
- Low-traumatic
- Easy to perform
- Does not deform the cervix
- Does not have negative consequences for further pregnancy and childbirth
- Can be used by nulliparous women
Disadvantages of the method:
Insufficient sensitivity. By locally sampling a piece of tissue from only one or the “wrong” area, you can miss a nearby more severe degree of dysplasia, microinvasive cancer.
Sensitivity of targeted biopsy (according to A. Jordan, 2006)
| Nature of biomaterial collection | Probability of an accurate diagnosis |
| 1 biopsy from a visible abnormal area | 70% |
| 2 biopsies from visible abnormal areas | 80% |
| 3 or more biopsies from visible abnormal areas | 90-100% |
| Random biopsies - taken from different parts of the cervix without visible signs of pathology | 25,3 — 42,9 % |
Despite known shortcomings, colposcopy with targeted biopsy remains the “gold standard” for diagnosing precancer and cervical cancer.
Read more about the precancerous condition of the cervix: Cervical dysplasia of the 2nd (second) degree, is surgery necessary?
Circular biopsy of the cervix
Circular or conical biopsy of the cervix is a circular “cutting out” of the central region of the cervix, capturing the cervical canal to a depth of 1-1.5 cm.
Circular or cone biopsy of the cervix
The procedure is similar to therapeutic and diagnostic conization, but cone biopsy is less radical and is initially diagnostic in nature.
Read more: Conization of the cervix: how the operation is performed, why and when it is done
What tool is used
Scalpel
Advantage of the method
During a knife biopsy, a biopsy sample of ideal quality is obtained
Disadvantages of the method
- Performed in a hospital
- Requires general anesthesia (short-term intravenous anesthesia)
- Highly traumatic
- High risk of postoperative bleeding
- Can lead to subsequent deformation of the cervix and negatively affect further pregnancy and childbirth
- Not recommended for young and nulliparous women
Circular knife biopsy is rarely used in today's clinical practice.
Extended excisional biopsy of the cervix
Wide or extended radio wave excisional biopsy (LEEP, LLETZ, CONE) is an improved version of the circular cervical biopsy.
Compared to a targeted biopsy, an extended biopsy allows one to obtain more informative and objective material for histological examination.
Indications for extended biopsy
- Suspicion of severe dysplasia CIN2-3
- Abnormal colposcopy, with transformation zone 2-3
- Local lesion on the outer part of the cervix extending into the cervical canal
- The need for partial (or complete) removal of the transformation zone for subsequent histological examination
- Suspicion of a pathological process in the cervical canal
Extended loop biopsy of the cervix
If during an extended excisional biopsy it is possible to remove the entire affected area of the cervix within healthy tissue, then the diagnostic procedure becomes a full-fledged therapeutic and diagnostic operation.
What tool is used
- LEEP biopsy: standard loop electrode of appropriate size
- CONE biopsy: “sail” electrode (conizer) of the appropriate size
Necessary equipment
Safe to use for the doctor and the patient, an electric high-frequency device for radio wave surgery:
- "Surgitron" (USA) or
- "Fotek" (Russia)
Advantages of the method
- Non-contact surgical “cold” radio wave incision without mechanical (compression, crushing), without deep thermal damage to tissue
- Coagulation (soldering) of dissected vessels and nerve endings with “cold” steam ensures a relatively “dry” bloodless incision and minimal pain during the procedure
- Jewelry precision cut
- Preservation of adjacent tissues without trauma and necrosis ensures rapid healing without the formation of a rough scar
- The sterilizing effect of radio waves minimizes postoperative complications (swelling, pain, infection)
- Can be used in young and nulliparous women
Radio wave biopsy allows you to obtain a high-quality tissue sample for a full histological examination. There is no strong evidence to support the effectiveness of knife biopsy compared with radio-loop biopsy.
Disadvantages of the method
- Requires special equipment
- Requires additional training and highly qualified medical personnel
Cervical biopsy by curettage - endocervical curettage
When performing a cervical biopsy, all patients are recommended to undergo endocervical curettage - diagnostic curettage of the walls of the cervical canal to exclude precancerous processes or adenocarcinoma inside the canal.
All biomaterial obtained during curettage is sent for histological examination in a separate labeled container bottle.
Indications for mandatory curettage of the cervical canal
- An abnormal change on the outer surface of the cervix extends into the cervical canal
- “Bad” cytology from the cervix canal (atypia of columnar epithelium, AGC)
- The transformation zone is located inside the canal (ZT2-3), invisible and poorly accessible for other biopsy techniques
Return to contents
How they do it
The features and duration of the procedure itself completely depend on the nature of the pathology and the location of the suspected focus of the pathology. Diagnostics must be monitored by a tomograph or ultrasound machine, and must be carried out by a competent specialist in a given direction. Below are described options for such a microscopic examination depending on the organ that was rapidly affected in the body.
In gynecology
This procedure is appropriate for extensive pathologies not only of the external genitalia, but also of the uterine cavity, its cervix, endometrium and vagina, and ovaries. Such laboratory research is especially relevant for precancerous conditions and suspected progressive oncology. The gynecologist recommends undergoing the following types of biopsy strictly for medical reasons:
- Sighting. All actions of the specialist are strictly controlled by extended hysteroscopy or colposcopy.
- Laparoscopic. More often, the technique is used to take biological material from the affected ovaries.
- Incisional. Involves careful excision of affected tissue using a classic scalpel.
- Aspiration. In this case, the biopsy can be obtained using the vacuum method using a special syringe.
- Endometrial. Carrying out a pipel biopsy is possible with the assistance of a special curette.
This procedure in gynecology is an informative diagnostic method that helps to identify a malignant neoplasm at an early stage, initiate effective treatment in a timely manner, and improve the prognosis. With progressive pregnancy, it is advisable to abandon such diagnostic methods, especially in the first and third trimesters; it is first important to study other medical contraindications.
Blood biopsy
Such laboratory testing is considered mandatory if leukemia is suspected. In addition, bone marrow tissue is collected for splenomegaly, iron deficiency anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia, performed by aspiration or trepanobiopsy. It is important to avoid medical errors, otherwise the patient may suffer significantly.
- Wen on the face
- Pills to reduce appetite - reviews of effectiveness. The best pills to reduce appetite
- Horseradish leaves from salt deposits
Intestines
This is the most common method of laboratory research of the intestines, esophagus, stomach, duodenum and other elements of the digestive system, which is carried out with the participation of puncture, loop, trephination, pinching, incisional, scarification technology, necessarily in a hospital setting. Preliminary pain relief and a subsequent rehabilitation period are necessary.
In this way, it is possible to determine changes in the tissues of the gastrointestinal mucosa and promptly recognize the presence of cancer cells. In the stage of relapse of a chronic disease of the digestive system, it is better not to conduct the study in order to avoid gastric bleeding or other potential complications. Laboratory testing is prescribed only on the recommendation of the attending physician; there are contraindications.
Hearts
This is a complex procedure that, if there is a medical error, can cost the patient his life. A biopsy is used if serious diseases such as myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, or ventricular arrhythmia of unknown etiology are suspected. Due to rejection of a transplanted heart, such diagnostics are also necessary to monitor sustainable positive dynamics.
More often, modern cardiologists recommend conducting a right ventricular examination, accessing the source of pathology through the jugular vein on the right, the subclavian or femoral vein. To increase the chances of success of such manipulation, during the collection of biological material, fluoroscopy and ECG are used, and the process is monitored on the monitor. The essence of the technique is that a special catheter is advanced to the myocardium, which has special tweezers for “biting off” biological material. To exclude thrombosis, medicine is administered into the body through a catheter.
Skin
Invasive examination of the epidermis is necessary if skin cancer or tuberculosis, lupus erythematosus, or psoriasis are suspected. An excisional biopsy is performed by shaving off the affected tissue in a column for further microscopic examination. If a minor area of skin is deliberately damaged, after completion of the session it must be treated with ethyl or formic alcohol. With large amounts of damage to the dermis, it may even be necessary to apply sutures in compliance with all aseptic rules.
If the focus of the pathology is concentrated on the head, it is necessary to examine a 2-4 mm area of skin, after which a suture will be applied. It can be removed a week after the operation, but for skin diseases this biopsy method is the most informative and reliable. It is not recommended to collect biological material in case of visible inflammation, open wounds and suppuration. There are other contraindications, so an individual consultation with a specialist is first required.
Bone tissue
This session is necessary to detect cancer and is an additional diagnostic method. In such a clinical picture, it is recommended to perform a percutaneous puncture with a thick or thin needle, depending on medical indications, or by a radical surgical method. After receiving the first results, there may be an urgent need to re-examine a similar biopsy.
Eye
If the development of retinoblastoma is suspected, an urgent biopsy is necessary. Action is required immediately, since such a malignant neoplasm very often progresses in childhood and can cause blindness and death for the clinical patient. Histology helps to give a real assessment of the pathological process and reliably determine its extent and predict the clinical outcome. In such a clinical picture, the oncologist recommends performing an aspiration biopsy using vacuum extraction.
FGDS with biopsy
To understand what we are talking about, you need to decipher the abbreviation FGDS. This is fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which is an instrumental examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a fiber-optic endoscope. When carrying out such a procedure, the doctor gets a real idea of the source of the pathology, and moreover, he can visually examine the condition of the affected digestive system - tissues and mucous membranes.
A biopsy is performed under local anesthesia, so it is an absolutely painless diagnostic method. This is especially important for patients at risk of gag reflex. A distinctive feature of this diagnosis is the ability to detect Helecobacter pylori infection and the degree of damage to the digestive system and mucous membranes.
- Ombre manicure at home step by step. Photos and videos of ombre manicure at home
- How to find a phone using GPS via a computer and the Internet. Phone tracking via satellite
- How many claws does a cat have on its hind and front paws? How much does it cost to declaw a cat?
Is it necessary to do a biopsy?
Importance of a biopsy
- It's stupid to even ask such a question. Of course it is necessary. If you value your health and peace of mind, then you shouldn’t even think about whether you need to do a biopsy.
- Conducting this study will either confirm the presence of dangerous conditions or refute it. If, in fact, the tissue contains cancer cells, and a biopsy is not performed and appropriate treatment is not prescribed, there is a possibility of serious complications and death.
- If a biopsy is performed in time and the disease is detected, you can still have time to apply the necessary therapy, as well as gain additional time and chances of recovery.
- In this case, a biopsy can show the presence of benign rather than malignant tissues, which will significantly ease both the patient’s mental state and the drug impact on his body.
Material research methods
After the biological material is obtained, it can be examined in detail under a microscope to promptly identify the nature of the pathological process. The most common and popular research methods and their brief descriptions are presented below:
- Histological examination. In this case, sections of tissue taken from the body (exclusively from the surface or contents of the pathology site) come under observation. Using a special tool, biological material must be cut into strips of 3 micrometers, after which sections of such “strips” must be stained to detect cancer cells. Then the prepared material is examined under a microscope to determine the presence of cancer cells dangerous to health in the structure.
- Cytological examination. This technique has a fundamental difference, which lies in the study of cells, not affected tissues. The method is less informative, but is used if an insufficient amount of biological material was taken for histological examination. More often, cytology is performed after a fine-needle (aspiration) biopsy, taking swabs and smears, which also causes discomfort when collecting biological material.
Needle biopsy
A minimally invasive method is a puncture biopsy. Its principle is that a hollow needle is inserted into the pathological formation or organ that needs to be examined. Pieces of tissue through which the needle passed get into it. After the needle is removed, these areas are sent for examination. If you need to examine an organ that is located deeply (that is, it cannot be seen and “palpated”), then the puncture is done under ultrasound or X-ray control.
For greater accuracy and to reduce trauma, a biopsy can be done under the control of ultrasound, endoscope, or x-ray.
In practice, two types of puncture biopsy are used:
- fine-needle (aspiration, classic);
- thick needle (cutting, trephine biopsy).
The advantage of a puncture biopsy is that this procedure is minimally painful. It is done without general or local anesthesia .
How long to wait for the result
If we talk about histological examination, the reliability of laboratory research is 90%. There may be errors and inaccuracies, but this depends on the morphologist who did not perform the sampling correctly, or use obviously healthy tissue for diagnosis. Therefore, it is advisable not to save on this procedure, but to seek help only from a competent specialist.
It is important to clarify that the histological examination is final, i.e., based on its results, the doctor prescribes the final treatment. If the answer is positive, an intensive therapy regimen is selected individually; if negative, repeat biopsies are performed to clarify the diagnosis. Cytological examination, due to its less informative content, is an intermediate “link” of diagnosis. Also considered mandatory. If the result is positive, this is the basis for an invasive histological examination.
What is the accuracy of a biopsy?
What is the accuracy of a biopsy?
- The accuracy of the biopsy largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor performing the procedure. If the doctor has extensive experience in performing this kind of manipulation, then you can rely on the results of his work. If the biopsy sample is taken incorrectly or in insufficient quantity, this will radically affect the results of the biopsy.
- The research method is also very important. If an urgent biopsy is performed, then due to the omission of some important steps used in a planned biopsy, its results can hardly be called one hundred percent
- Cytological studies can also be considered incomplete or insufficiently complete. They help identify malignant cells, but do not provide a complete picture of the disease.
results
When performing a histological examination, the result will be obtained after 4–14 days. When a quick response is needed, the biological material is immediately frozen after collection and sections are made and then stained. In such a clinical picture, the result will be obtained after 40–60 minutes, but the procedure itself requires high professionalism on the part of a competent specialist. If the disease is confirmed, the doctor prescribes treatment, and whether it will be medicinal or surgical depends entirely on the medical indications and the specifics of the body.
As for cytological examination, this is a faster, but less informative diagnostic method. The result can be obtained 1–3 days after the collection of biological material. If it is positive, it is necessary to start oncology treatment in a timely manner. If negative, it would be a good idea to perform a repeat biopsy. This is explained by the fact that doctors do not exclude errors and inaccuracies. The consequences for the body become fatal. Additionally, histology, gastroscopy (especially if the gastrointestinal tract is affected) and colonoscopy may be required.
Timing of biopsy results
Timing of biopsy results
Biopsies can be divided into urgent and planned. An urgent biopsy is usually performed during surgery, so its results must be obtained urgently. Urgent biopsy analysis takes up to half an hour.
If the biopsy is performed routinely, then its results should be ready within five to ten days.
Care after collection
After the biopsy, the patient needs complete rest, which includes bed rest for at least the first day after the procedure, proper nutrition and emotional balance. At the site where the biopsy is taken, the patient feels some pain, which becomes less and less pronounced every day. This is a normal phenomenon, since some tissues and cells were deliberately injured by a medical instrument. Further postoperative measures depend on the type of procedure and the characteristics of the affected organism. So:
- If a puncture was performed, there is no need for additional sutures and bandages. If the pain increases, the doctor recommends taking an analgesic or using an ointment with an analgesic effect externally.
- When making incisions to collect biological material, a suture may be required, which can be removed after 4 to 8 days without serious consequences for the patient’s health. Additionally, you will have to apply bandages and be sure to follow the rules of personal hygiene.
The recovery period should proceed under strict medical supervision. If the pain intensifies, purulent discharge or pronounced signs of inflammation appear, a secondary infection cannot be ruled out. Such anomalies can equally occur during biopsy of the bladder, breast, pancreas or thyroid gland, and other internal organs. In any case, action must be taken immediately, otherwise the health consequences could be fatal.
How to prepare for a biopsy
In order for the results of the study to be reliable, you need to properly prepare. Helpful Tips:
- A cervical biopsy is performed 5–7 days after the first day of menstruation. During the day, douching, tampons, medicated suppositories or creams, and intimate hygiene products are canceled.
- Before the study, blood and urine tests are taken, the levels of bilirubin, creatinine, urea, and sugar are determined. A coagulogram is taken and, if necessary, a smear.
- If an infectious process is detected, a biopsy is done after it has been eliminated.
- For 2 weeks, you should stop taking Aspirin, Warfarin, Ibuprofen.
- One day before, you need to stop smoking and eliminate alcohol.
- During anesthesia, food and liquid intake is canceled 12 hours before.
Complications
Since such a surgical procedure is associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin, doctors do not rule out the addition of a secondary infection with subsequent inflammation and suppuration. This is the most dangerous consequence for health, which can even result in blood poisoning, exacerbation of other unpleasant diseases with periodic recurrence. So a temporary scar of different sizes at the site of direct biopsy sampling is not the only problem of an aesthetic nature; potential complications that are no longer dangerous to health may be as follows:
- excessive bleeding at the sampling site;
- acute pain syndrome in the diagnostic area;
- internal discomfort after completion of the session;
- inflammatory process with high body temperature;
- injury to the organ being examined (especially if a biopsy forceps is used);
- infection of the organ being examined;
- septic shock;
- blood poisoning;
- suppuration at the puncture site;
- spread of bacterial infection with fatal outcome.
Are there complications after a biopsy?
Possible complications after a biopsy
In very rare cases, any complications are observed after a biopsy. As a rule, the only side effects after a biopsy may be short-lived and mild pain. Moreover, after hours, in rare cases, days, they disappear. In addition, pain can be controlled with painkillers.
However, it is worth noting that one in ten thousand cases of biopsy results in the death of the patient. We must also owe such statistics to the unqualified specialists who undertake this complex procedure.
Contraindications
Biopsy is not permitted for all patients according to indications; there are absolute and relative medical restrictions that are important not to violate. Medical contraindications affect the following clinical pictures:
- blood clotting disorder;
- periods of pregnancy and lactation;
- diseases of the reproductive system;
- inflammatory and infectious processes of the acute stage;
- systemic, somatic diseases;
- high threshold of pain sensitivity;
- after extensive blood loss.
Features of biopsy examination
A biopsy is considered a reliable diagnostic method; the procedure is often prescribed to make an accurate diagnosis in cases where alternative types of research have proven to be insufficiently informative.
In addition, biopsy is almost always used to determine the nature of tumors, the specifics of the processes associated with their development, and to monitor the results of oncology treatment.
There are few contraindications for biopsy:
- pathological processes in the hematopoietic system, blood clotting disorders;
- individual intolerance to certain medications;
- any form of heart failure.
After the biopsy, the resulting tissue samples are treated with agents that prevent cell decomposition and sent for research.
Histological diagnosis is the examination of a tissue sample under a microscope. To improve the quality of informative data, sections of biomaterial can be stained.
Video:
This type of study can take a long time, so biopsy results arrive within 4 to 14 days.
If a histological analysis needs to be carried out urgently, then its results will be ready the next day. Urgent histology is practiced when cancer is suspected, so as not to miss time.
Cystological examination consists of studying cells - this method is especially effective in cases where it is not possible to take a biopsy of a tissue section. To do this, a smear is made on the glass, after which its cellular structure is studied using a microscope.
READ Performing a prostate biopsy procedure
The use of cystology allows us to determine the nature of tumors and the degree of their development. However, histological examination is considered more informative.
Preparing for a biopsy involves undergoing some tests and changes in your usual lifestyle:
- stop taking medications at least one day before the procedure;
- if the treatment will take place under general anesthesia, you must refrain from eating for several hours before the examination;
- a cervical biopsy involves abstaining from sexual intercourse and stopping the use of vaginal suppositories one day before the scheduled date;
- necessary tests - general analysis, determination of the Rh factor and blood group, coagulogram, detection of hidden infections (herpes, chlamydia, toxiplasmosis), blood test for hepatitis and sexually transmitted diseases.
Additional tests may be ordered according to the specifics of the planned biopsy. On average, the procedure takes a short amount of time. After completion of the treatment, the patient receives release from work for 2 days.
Price
On the territory of the Russian Federation, such an invasive technique has a wide range of prices, the fluctuations of which depend on the specific region (more expensive in the capital, cheaper in the provinces), the reputation of the private clinic and the rating of the specialist who will perform the biopsy in the hospital. Before giving consent to perform a biopsy, you need to select a rated medical center and study reviews of certain diagnostic doctors.
In the capital, diagnostics are somewhat more expensive, but the quality of the services provided meets the needs of all interested patients. The main thing is to choose the right medical center that treats a specific disease. Below are the prices for Moscow, which will help the patient quickly make the final choice of place for diagnostics:
| Procedure name | Price, rubles |
| tissue research | 2 000 |
| breast examination | 2 500 |
| thyroid puncture | 3 000 |
| prostate puncture | 9 000 |
| vacuum aspiration | 4 000 |
| biopsy pistol "Cobra" | from 5 000 |
Where can I get a biopsy?
Where is the best place to do a biopsy?
- It is best to apply for a biopsy procedure to trusted large medical institutions with high-quality equipment and qualified medical workers
- Before choosing a particular institution, ask its staff if they have all the relevant permits and certificates. Also, do not hesitate to ask the doctor who will perform the biopsy about his specialty and experience in performing this type of procedure.
- And as always, no one canceled word of mouth and forums on the Internet. Thanks to such an information base, you can learn a lot about biopsy specifically in your city or nearby cities
Chorionic villus biopsy
A biopsy is a test that can detect the presence of any diseases even in a fetus in the womb. To do this, chorion tissue is taken - the fetal membrane that connects the fetus with the mother's body. Later, the chorion turns into the placenta.
When and why
A chorionic villus biopsy is prescribed to identify chromosomal mutations and diseases, as well as genetic abnormalities.
The study is especially indicated in the following cases:
| Poor prenatal screening results | If the results of prenatal screening were poor or questionable, then a chorionic villus biopsy is necessary to confirm or refute the diagnosis. |
| The presence of children with identified genetic diseases or the presence of past pregnancies with a fetus with genetic abnormalities | In this case, the risk of having subsequent children with chromosomal abnormalities or genetic diseases is very high. Even if a woman already has a child with a genetic disease, and the other child (with whom she is pregnant) has a different father, a chorionic villus sampling is still necessary. |
| One of the parents or blood relatives has genetic abnormalities or hereditary diseases. | In this case, a chorionic villus biopsy is necessary for the early detection of diseases in the fetus, since if there are genetic abnormalities in the family, the risk of their manifestation in the offspring can reach 100%. |
| Unfavorable course of pregnancy in the first trimester | If a pregnant woman in the first trimester of pregnancy or shortly before the start of pregnancy was exposed to radiation or took drugs with embryotoxic or teratogenic effects, then a chorionic villus biopsy is necessary to identify genetic abnormalities. The listed factors have a strong influence on the development of chromosomal abnormalities. |
| The pregnant woman is over 35 years old | In this case, the procedure is necessary to exclude pathologies of fetal development, since after 35 years the risk of having a child with genetic diseases (especially Down Syndrome) increases. |
| The father and mother of the child are blood relatives | When germ cells from parents who are blood relatives merge, mutations occur. |
Also, during the study of chorion tissue, the sex of the child can be determined if any genetic disease is sex-linked (transmitted only on the X or Y chromosome). A referral for a biopsy is given to a pregnant woman by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
If conception occurred with the help of a reproductive specialist, then he can prescribe the procedure. If one or both parents have previously undergone genetic diagnostics, a geneticist can give a referral for a chorionic villus biopsy.
Preparation
Before taking a chorionic villus biopsy, urine, blood, and smear tests for genital infections are required. It is also necessary to establish the blood type and Rh factor of the pregnant woman in order to prevent Rh conflicts when collecting biomaterial.
The procedure for taking biomaterial can be carried out transabdominally (by puncturing the anterior abdominal wall) or transcervically (through the cervical canal of the cervix).
In the first case, before the procedure, you need to gradually drink about 1 liter of water to fill the bladder - in its full form, it “pushes out” the uterus and allows you to better visualize it (since the procedure for collecting chorionic tissue is carried out under ultrasound supervision). In the second case, the bladder must be emptied.
Carrying out analysis
The most suitable time for the procedure is from 9 to 12 weeks of pregnancy. However, for some indications, the study can be carried out from 12 to 16 weeks.
The chorionic villus biopsy procedure begins with a standard ultrasound - this is necessary to determine the condition of the fetus and placenta and identify uterine hypertonicity. If there are no contraindications, then the needle insertion site is treated with an antiseptic and anesthetic.
Next, if the procedure is performed transabdominally, the doctor inserts a thin needle into the abdominal wall and pierces it, moving it towards the uterus. Using this needle, the specialist takes samples of chorionic tissue into a special syringe, then removes the instrument.
If the procedure is performed transcervically, the woman lies down in a gynecological chair, then the doctor inserts a dilator and a speculum into the vagina. Next, he inserts a special thin catheter into the cervix, through which samples of chorionic tissue enter the collection container.
The procedure does not require hospitalization for the pregnant woman. After it is completed, the woman can go home if she does not experience any discomfort. On the first day after taking the biopsy, bed rest is indicated.
Decoding the results
At the conclusion of the analysis, either a negative result is written (no genetic diseases or anomalies were identified) or the specific identified pathology is indicated with a description and precise characteristics.
Biopsy and pregnancy
The removal of a fragment of uterine tissue causes the formation of a connective tissue scar on the organ. Its size does not change, which is why the risk of cervical damage increases during childbirth. Giant scars change it, so the threat of involuntary termination of gestation increases.
A biopsy for women who have never had children is performed as sparingly as possible. It would be better if they use the radio wave method.
After the study, pregnancy proceeds mostly without complications. But if complex analysis methods were used on the patient, the risk of miscarriage increases.
The removal of a sample of cellular material from the uterus during the fetal development of a baby is done in the rarest cases - to detect a cancerous tumor. It is safer to carry out this examination in the 2nd trimester.
Types of manipulation
Types of cervical biopsy:
- Excision (puncture). A small piece of tissue is taken using a special instrument - biopsy forceps. To determine the site of analysis, the doctor may pre-treat the cervix with acetic acid or iodine.
- Wedge-shaped, or conization, involves the removal of a cone-shaped section of the cervix using a scalpel, laser beam or other physical factors. General anesthesia is used for this procedure.
- Cervical curettage is the removal of cells from the cervical canal using a curette.
The choice of intervention method depends on the expected disease, its severity and the general condition of the patient.
Preparation
Before the biopsy, the patient must undergo laboratory testing of blood and urine for the presence of various types of infections and inflammatory processes. In addition, magnetic resonance, ultrasound, and x-ray diagnostics are performed.
The doctor studies the picture of the disease and finds out whether the patient is taking medications.
It is very important to tell your doctor about the presence of pathologies of the blood clotting system and allergies to medications. If the procedure is planned to be carried out under anesthesia, then you should not eat or drink liquid 8 hours before taking the biopsy sample.
Biopsy histology results
After examination, the following pathological signs may be detected:
- the presence of white areas of epithelial tissue that appear after treatment with a weak vinegar solution;
- the presence of areas that do not change color with iodine solution during the Schiller diagnostic test (such changes occur with leukoplakia);
- the appearance of reddish objects on the mucous membrane (punctuation) as a result of the proliferation of small blood vessels;
- mosaic - the presence of branched papillae in some parts of the uterus;
- tuberosity (a sign of a carcinoid neoplasm);
- condylomas on the cervix;
- mucosal pathologies;
- reduction in endometrial thickness;
- polyp growth;
- inflammation of the endometrium.
How does this happen?
It will be useful to learn not only what a biopsy is, but also how a biopsy is taken. The term “biopsy”: what it is in oncology, deciphering the meaning is known to many. Literally, this is the excision of a living organism (in this case, tissue).
A biopsy can be removed from almost any part of the body. This is done under anesthesia - general or local. The second option is preferable because it is less traumatic to the body, but sometimes the collection of material requires only general anesthesia.
When asked how long it takes to perform a biopsy, experts answer that the procedure itself does not last long. How long does a biopsy take specifically – from 10 to 20 minutes.
If you know where to take the biopsy test and it is a difficult place to reach, the procedure can last up to 40 minutes. But how long does it take to analyze a biopsy - that is, study the obtained material - this depends on the nature of the study.
Biopsy is the general name for one of the types of diagnostics of body cells. This procedure has several subtypes, depending on the size of the extracted biopsy, the location of the problem area, and the medical instruments used.
Why is a biopsy done?
A biopsy is indicated in cases where, after other diagnostic procedures, the results obtained are not sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis.
Typically, a biopsy is prescribed when tumor processes are detected to determine the nature and type of tissue formation.
This diagnostic procedure is today successfully used to diagnose many pathological conditions, even non-oncological ones, since in addition to malignancy, the method allows one to determine the degree of spread and severity, stage of development, etc.
The main indication is to study the nature of the tumor, however, a biopsy is often prescribed to monitor the ongoing oncology treatment.