STIs are infections that are transmitted during unprotected sexual contact. They can rightfully be called one of the most widespread on the planet. According to medical statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), every year on Earth more than 350 million people receive one of the diagnoses caused by a sexually transmitted infection in their medical records!
Almost all STIs have a negative impact on human health, especially if they are diagnosed late or have not been adequately treated for a long time. Diseases transmitted through sexual contact have the strongest negative impact on genitourinary and reproductive functions.
All people should get tested for STIs from time to time. And those who engage in unprotected sexual contact with unverified and casual partners need to be checked regularly.
What allows you to detect
Sexually transmitted infections are a very wide range of diseases. A smear for STIs can detect most of them:
- Chlamydia.
- Syphilis.
- Gonorrhea.
- HIV.
- Human papillomavirus.
- Mycoplasmosis.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Ureaplasmosis.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Chancroid.
- Urogenital shigellosis.
- Trichomoniasis.
- Herpes.
- Gardnerellosis.
This is a list of diseases that are diagnosed in patients most often. It is important to know that a smear for STIs can detect any infections located in the secretion produced by the urethra (in men) and vagina (in women). Viruses are the most difficult to diagnose. This is because they are so small that they are very difficult to see even under a microscope.
What infections are smeared for PCR?
The most informative is a PCR smear when testing for:
- gonorrhea
- trichomoniasis
- chlamydia
- herpes
- mycoplasma
- ureaplasma
- gardnerella
- papillomavirus
Most often, they are screened for all infections at once.
Including in situations where:
- a pathogen has already been identified in a person’s urogenital tract (for example, a gonococcus was identified during a microscopic examination of a smear);
- the diagnosis of the source of infection is known.
The presence of one pathogen does not exclude the presence of another in the urogenital tract.
Many patients develop 2 or more infections at once.
Underexamination is one of the most common reasons for treatment failures, when clinical recovery does not occur after an etiological, laboratory-confirmed recovery.
Symptoms persist because the person has no other STD pathogen identified.
As a result, diagnosis and treatment must be repeated.
To prevent this from happening, it is better to immediately get tested for all STDs.
Indications
For both men and women, a smear test for STIs is a standard procedure included in the list of annual preventive examinations. The study is mandatory for employees whose professional activities are related to the food industry.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to donate biomaterial at least once a year. This is true even if the person is not bothered by any alarming symptoms.
It is imperative to visit a doctor and take a smear if the following signs of sexually transmitted infections appear:
- Increased degree of fatigue.
- Discharge from the urethra that is different from normal. As a rule, they are mucous or purulent in nature.
- Cloudy urine.
- Severe itching and burning in the genital area.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area.
- Painful sensations during the act of urination.
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels.
- Discomfortable sensations during sexual intercourse.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Abscesses and ulcers formed on the external genitalia.
These are clinical manifestations of STIs that are characteristic of both sexes. Women may additionally experience the following symptoms: menstrual irregularities, irritation in the anus, unusual discharge from the anus, rash on the labia, swelling of the vulva.
Specific signs of STIs in men: the presence of blood in the seminal fluid, frequent urge to urinate, problems with ejaculation, pain in the scrotum, rash on the penis.
In addition, in women, a smear for STIs is taken both when planning pregnancy and during the gestation period. It is also recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible after sexual contact without the use of barrier protective equipment.
PCR swab from mouth infection
Many pathogens can infect the oral cavity, pharynx, and tonsils.
It could be:
- gonococcus
- chlamydia
- pallidum spirochete (syphilis)
- herpes
To identify them, a swab is taken from the mouth.
Clinical material is obtained from the place where signs of inflammation are found.
The study of such smears using PCR has little diagnostic value if there is damage to the urogenital tract.
Because in any case, the disease is treated with systemic antibiotics, so the bacteria die everywhere.
But about 5% of infections occur in an isolated oropharyngeal form.
That is, there are bacteria in the mouth, but there are none in the urogenital tract.
These are almost all cases of primary syphilis if infection occurred through oral sex.
Isolated gonococcal or chlamydial pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and stomatitis are often encountered.
Their appearance is most often caused by the use of a condom during vaginal sex.
But during oral contact, contraception is not used, so transmission of infection occurs.
Preparation
In order for the results of the study to be as reliable as possible, it is necessary to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Rules for preparing for the collection of biomaterial:
- About 2 weeks in advance you need to stop taking any antibacterial agents. If this is impossible for health reasons, it is important to inform your doctor about this. As a rule, in such cases, the study is postponed to another day. This is due to the fact that antibiotics can erase traces of the activity of the causative agent of a sexually transmitted disease. In some cases, doctors ask you to stop taking medications for at least 24 hours. During this period, the patient’s body will not be harmed, and the results will be more reliable.
- It is recommended to carry out hygiene measures using regular soap. It is unacceptable to use antibacterial agents on the eve of collecting biomaterial.
- It is not recommended to empty your bladder approximately 3 hours before the test.
- For two days you must abstain from any sexual contact.
- Women are recommended to take a smear test immediately after menstrual bleeding has ended.
In some cases, doctors advise making adjustments to your diet the day before. This method is called provocation. The patient is recommended to eat fatty, fried, smoked, salty foods the day before. Eating such dishes somewhat weakens the body’s defenses, allowing pathogens to manifest themselves to the maximum.
Algorithm for collecting biomaterial from women
A smear test for STIs is taken during an appointment with a gynecologist. Immediately before collecting the biomaterial, the specialist interviews the patient. The doctor must be provided with all the information regarding the existing symptoms and their intensity (if any). After this, the specialist proceeds with a physical examination and directly taking a smear.
Algorithm for collecting biomaterial:
- The patient frees the lower part of the body from clothing.
- The woman is placed on a gynecological chair.
- The doctor puts on disposable sterile gloves and examines the woman’s external genitalia.
- The specialist inserts a special dilator into the patient’s vagina. Then he examines the mucous membranes using a mirror.
- The doctor takes a tool for collecting biomaterial (outwardly it resembles an ordinary cotton swab) and inserts it alternately into the cervix, vagina and urethra. After this, the medical device, along with the resulting secretion, is sealed in a test tube and sent to the laboratory for testing.
The procedure for collecting biomaterial is not associated with painful sensations. The patient may experience only some discomfort due to the difference in body temperature and the gynecological instruments used. The exception is cases when severe inflammation occurs in the genital area.
Who needs to be tested for PCR?
PCR testing for sexually transmitted infections is done primarily for those who have symptoms of inflammation in the urogenital tract.
These are discharge, soreness, redness, rash.
In addition, PCR is carried out:
- after unprotected sexual intercourse with a source of infection
- as part of secondary prevention of STDs, if over the past year a person has had 3 or more sexual partners
- in case of infertility, in the process of searching for the cause of this condition
- before pregnancy or in the first trimester if it occurs spontaneously
- before IVF or other assisted reproductive technologies
- in preparation for genital surgery
The process of collecting biomaterial from men
The algorithm for taking secretions is carried out at an appointment with a urologist. The specialist also initially interviews the patient, asking if he is bothered by any alarming symptoms.
Algorithm for taking a smear for STIs in men:
- The doctor asks to remove the genitals from clothing.
- The specialist puts on disposable gloves and examines the skin and mucous membranes to identify rashes and purulent foci.
- The doctor takes a special probe. A swab for STIs is taken from the urethra. The doctor inserts the probe 3-4 cm and rotates it slowly.
- After this, the specialist removes the medical device and makes a smear on a glass slide. The latter is then sent to the laboratory.
According to numerous reviews, the collection of biomaterial is accompanied not so much by painful sensations as by psychological discomfort. However, with regular visits to the doctor, it disappears very quickly.
Diagnostic methods
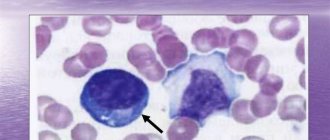
The simplest method for examining a smear is microscopy. It allows you to get results in a short time. The method involves examining biomaterial under a microscope.
Currently, PCR smear testing for STIs is increasingly being performed. The essence of the polymerase chain reaction is as follows. In the laboratory, a specialist selects from the biomaterial those areas that contain the DNA of the causative agent of a particular disease. Then the cells increase many times over, making it quite easy to recognize the provoking agent.
A smear test for STIs using the PCR method is most often carried out. This is due to the fact that this analysis is considered the most reliable to date. To confirm the diagnosis, bacterial culture may be additionally prescribed.
Interpretation of examination results
Each type of analysis has certain pros and cons. For an accurate diagnosis, doctors prescribe several tests at once, and their results help identify a specific problem.
Flora smear testing is an inexpensive and simplest method for detecting viruses. When decoding the data, the location from which the biological material was taken is indicated, the presence of pathogens and leukocytes are recorded. If the latter are detected, the infection is confirmed, and if it is not one of the 3 possible, then the patient is sent for another test to clarify. The transcript is issued the next or same day.
The cultural method of examination helps to find out the type, concentration and form of the virus in the body; susceptibility to antibiotics is immediately determined in order to prescribe the correct drugs for therapy. The diagnostic accuracy is 95%, the main disadvantage is the duration and cost of the test. The transcript indicates the infection itself and the quantitative number of colonies:
- a value of 103–104/ml indicates 1-5 colonies, the result indicates successful treatment or a dirty biomaterial sample;
- 105/ml – 5-15 colonies, signals the need for therapy or its continuation;
- 106/ml – more than 15 colonies, which means a pronounced course of sexually transmitted pathology.
In addition, you need to look at the number of leukocytes; if there are more than 15, then inflammation has begun in the body and this indicates infection with an STI.
PCR is an accurate test, even if the biomaterial contains a minimal amount of the pathogen. The results of a qualitative analysis will be positive (there is an STD) or negative (no infection). A quantitative PCR study determines the stage of pathology and the effectiveness of treatment:
- A value of 8x105IU/ml is an acute form of the disease or reactivation of the pathogen.
- The indicator 4x105IU/ml is the patient’s recovery process.
ELISA gives results for antibodies to viruses. The decoding of the results indicates positive or negative classes. Basic values indicating the presence of pathologies:
- 5 days after infection IgM antibodies appear;
- IgA development will occur 2-4 weeks after infection;
- IgG appears after 3-4 weeks.
After the ELISA, a form is issued indicating the described values; if they are not there, then there is no infection either. In the presence of all types of immunoglobulins, the problem is the exacerbation of the chronic course of the pathology. The acute form of the disease is characterized by positive IgM and any IgG, IgA. By comparing the results with the norm, patients can independently find out about the presence of the disease.
Normal indicators for women
After the study is completed, a conclusion is drawn up in the laboratory. It reflects norm indicators and actual values.
A gynecologist should decipher a smear test for STIs in women. However, the patient herself is able to compare the obtained indicators with those that should be.
Normal values:
- Leukocytes - from 0 to 10 units.
- Epithelium - 5-20 units.
- Mucus - small amount.
- Trichomonas, gonococci, chlamydia, yeast and other pathogenic microorganisms are absent.
- Another microflora is rod-shaped.
- Degree of purity - 1-2.
Thus, normally there should be no pathogenic microorganisms in biological material.
Normal indicators for men
In this case, decoding a smear for STIs is more difficult, and therefore it is recommended to entrust this to a specialist.
The following values are considered normal:
- Leukocytes - from 0 to 5 in the field of view. If they are elevated, it is recommended to retake a urethral smear for STIs using the PCR method (only if the biomaterial was initially examined under a microscope).
- Epithelium. Normally it should be flat, but a cylindrical one is allowed. The number of epithelial cells in the field of view should be from 5 to 10. When this indicator increases, it is customary to talk about an inflammatory process. The presence of transitional epithelial cells indicates prostatitis.
- Mucus - moderate amount. Sometimes you can see the value “++” or “+++” in the conclusion. In this case, it is also customary to talk about the development of the inflammatory process.
- Gonococci, Trichomonas, yeast, fungi, chlamydia, ureaplasma and other pathogenic microorganisms were not detected.
In addition, the microflora should normally be represented by single cocci.
How much to wait
The deadlines for completion directly depend on the method by which the biological material is studied. The simplest way is microscopy. As a rule, in the laboratory a smear is studied by this method quite quickly. Most often, the analysis takes no more than an hour. Patients who go to a medical institution equipped with its own laboratory receive the results of the study the fastest. Otherwise, it is necessary to take into account the time spent on delivery of the biomaterial. As a rule, you can receive the results of the study the very next day.
PCR smear analysis is not only a reliable, but also a quick method for diagnosing sexually transmitted diseases. On average, it takes 4 hours. Thus, it is possible to receive the results of the study on the day of delivery or the next day.
Bacteriological culture is a method that requires at least 1 week. Its essence is to place the biomaterial in a favorable environment and monitor the vital activity of pathogens if they are present. This is why research takes a long time.
Photo gallery
PCR for hidden infections
PCR for papillomavirus
PCR for genital infections
Sperm analysis for PCR for STDs
Deviations from the norm: what to do
If pathogens are identified, treatment should be started as soon as possible. If a microscopic examination has been carried out, the doctor may recommend taking a smear for STIs again, but in this case the biomaterial will be examined by PCR. Bacteriological culture is rarely prescribed.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor draws up the most effective treatment regimen. It may include taking medications (antibiotics), local treatment of the external genitalia, and douching. The choice of drugs is made exclusively by the doctor. The specialist must take into account not only the type of pathogen, but also the individual health characteristics of the patient.
What tests are done for STIs?
For each specific case of sexually transmitted disease, it is necessary to select an individual examination plan and a set of procedures.
What is included in the list of tests for STIs, and what tests are performed?
First of all, a general blood and urine test is done.
These methods are used to examine practically everyone who has applied for an appointment, but they cannot be called basic.
They can provide indicative information.
They will show whether there is an inflammatory process in the body, whether the urinary tract is affected, etc.
This remark also applies to biochemical blood tests.
It is included in the examination plan for viral hepatitis and can help assess the degree of liver damage.
For the choice of treatment, an important role is played by which pathogens caused the disease.
Therefore, the list of tests for STIs includes the following types:
- Smear microscopy (bacterioscopic method).
- Bacterial culture with antibiogram (bacteriological method).
- Serological methods for determining pathogen antigens or protective antibodies in the blood (mainly ELISA is used).
Molecular genetic methods (PCR and real time PCR).
In each case, the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination using several methods.
Individual clinical laboratories have developed their own examination systems.
Therefore, the attending physician needs to clarify this information and know what tests are performed.