" Blood tests
A general or biochemical blood test or some other test must be taken periodically. This is necessary in order to keep all blood parameters under control. Most often, the number of red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes is monitored. Plasma, which also contains a very large number of indicators important for the body’s vital functions, also comes under control.
Before taking a blood test, you need to remember some existing warnings or even prohibitions. In this article we will talk directly about examination during menstruation. At this time, the body itself experiences significant discomfort and one might even say shock. Some indicators rise and fall, and naturally the blood test will no longer show reliable information. There is no special prohibition on undergoing this procedure, it’s just that the permissible limits will be slightly different.
- 2 What is being changed?
- 3 What studies are recommended?
- 4 Norm of indicators
- 5 Menstrual pause
The effect of menstruation on blood
Throughout a woman's menstrual cycle, not only hormone levels vary, but also many blood and urine parameters. Therefore, during critical days, it is recommended to refrain from planned surgical interventions, as well as from undergoing routine tests.
A blood test involves a general analysis, a biochemical test, and a hemostasiogram (a coagulogram that determines blood clotting parameters). During menstruation, some deviations are possible, which in certain cases can be interpreted as diseases or a tendency to them.
The following features of the female body during menstrual periods can affect the test values:
- Blood is lost . Normally, the body spends from 80 to 150 ml of blood. However, values may vary. For example, with very heavy periods or if a woman is bothered by periodic acyclic discharge. Hemoglobin levels can decrease significantly, ESR and leukocyte levels in the blood increase. This is due to blood loss. Even in healthy women, values can vary somewhat, which can confuse the doctor.
- The volume of fluid in the body decreases. Blood is not only formed elements, but also a liquid. Therefore, during menstruation, a woman may experience slight dehydration if the drinking regime is not followed. And this will lead to changes in the indicators of the general blood test, and to a lesser extent, the coagulogram and biochemistry.
- Coagulability decreases . For normal rejection of the functional layer of the endometrium of the uterine cavity, the blood becomes less viscous, which is noticeable when examining in detail tests for fibrinogen, clotting time, and D-dimers.
We recommend reading about why you should get tested for TORCH infections. From the article you will learn about what tests are taken for TORCH infections, preparation for the test, examination methods, and interpretation of the results.
And here is more information about why a smear test is prescribed for women.
Norm of indicators
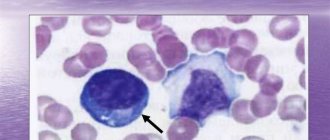
First on the list of tests are leukocytes. Normally, their number should not exceed from 3.5 to 10 thousand in 1 ml. Anything above the norm is considered a violation, and during menstruation it can give false results. If you do not take into account the time of menstruation, then with increased levels this may indicate the presence of infectious diseases. For example, various viral or fungal diseases. This also applies to the presence of bone marrow disease, colitis, gastritis, kidney failure, exhaustion or anemia.
There are many more similar situations when intervention is required when there is an increased level of leukocytes. Normal red blood cells should be no more than 3.8 - 5.8 million per ml. An increased amount indicates the presence of possible problems with the cardiovascular system, acute poisoning and fluid loss.
If the indicator is significantly underestimated, then this is an accurate sign of anemia. Hemoglobin should normally range from 120 to 160 g/l and 20 g/l more for men. Increased levels may occur with chronic leukemia, problems with blood clotting, or periodic serious bleeding.
Color index analysis typically ranges from 0.85 to 1.05. May be elevated in macrocytosis, folate deficiency anemia, or B12 deficiency anemia. If the level, on the contrary, is lowered, then this may be the reason for the presence of hemoglobin synthesis or a change in the size of red blood cells, also downward.
There is another equally important indicator in the blood - hematocrit. Its rate should be no more than 35% - 45%. The ratio may increase with an increase in erythrocyte mass. And an analysis with a decrease can only be done in case of regular bleeding or hemolysis of red blood cells. A decrease may also indicate pregnancy or high salt content in the body.
When can you take a blood test?
The most optimal time to take a blood test is the middle of the cycle and the second phase - from days 10-12 to 28. This applies to all standard types of studies: general, biochemical analysis, coagulation tests.
In some cases, blood sampling for subsequent research can be done without taking into account the day of the cycle. Namely:
- analysis for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis;
- blood for sexually transmitted infections for ELISA;
- blood for the TORCH complex must be donated when planning pregnancy;
- blood test for thyroid hormones, prolactin, testosterone, DHEA, cortisol and some others.
As for blood tests for sex hormones, they must be taken on certain days of the cycle:
- on days 5-7 - estrogens, FSH, LH;
- on days 21-23 - progesterone.
Watch this video about why and how to donate blood for sex hormones:
Recommendations for donating blood
To undergo laboratory tests, you must follow the recommendations of your doctors. They will help to obtain reliable data in one study.
- You should not eat food 12 hours before testing. During the day - drink alcohol. 2-3 hours before - smoking.
- Laboratory tests are carried out only in the morning, with the exception of hormonal studies.
- Stop taking medications 5 days before donating biological fluid. If this causes a sharp deterioration in health, the drug is not discontinued, but the doctor is warned about it.
- It is not recommended for women to take tests on menstruation days, as the data will not be reliable.
For donation, recommendations are supplemented. Biological fluid cannot be given to persons under the age of majority, pregnant women, lactating women, infectious patients, people with addiction (alcohol, drugs).
Blood readings are normal during menstruation
The following changes in tests are possible if taken during critical days:
- general blood test: decreased hemoglobin level, increased ESR, leukocytes, decreased platelet level;
- coagulogram: decreased coagulation ability;
- biochemical study: decreased level of total protein.
However, in some cases the changes will not be noticeable and the indicators will fit into the required standards.
Why do leukocytes increase before menstruation?
Laboratory research methods allow specialists to quickly identify and diagnose various diseases in women.
The number of leukocytes (white blood cells) is one of the important indicators of a woman’s health.
To determine any abnormalities, they are calculated not only in the patient’s blood, but also in her urine and vaginal discharge. What will leukocytes tell you before your period?
Leukocytes in urine analysis
The appearance of leukocytes in the urine of any person is a consequence of the presence of foci of inflammation in the body. In medicine, such a phenomenon as phagocytosis is well known. Doctors call this the ability of white blood cells to destroy foreign cells, bacteria and microbes.
In this case, the white blood cells themselves are destroyed and excreted from the patient’s body in the urine. And since there are no absolutely healthy people, leukocytes are always present in a urine test.
Experts consider the following indicators to be a normal number of white blood cells:
- in men their number ranges from 0 to 3;
- in women these figures are slightly higher and amount to 1 - 5 leukocytes per field of view.
This feature is associated with the hormonal background of a woman. During pregnancy, the number of white blood cells in the analysis may be 2-3 times higher than normal, but this is considered a physiological increase and does not require any specific correction.
Leukocytes in the urine before menstruation also increase and can reach 7 - 10 in the field of view. This process completely depends on the level of female sex hormones in the blood.
Experts note that when taking a urine test from a woman during menstrual bleeding, you should carefully follow the rules for collecting fluid secreted from the bladder. Quite often, menstrual blood gets into the urine, which makes the analysis unreliable and does not allow the woman to prescribe the necessary therapy.
We recommend reading the article about lymphocytes during menstruation. From it you will learn about normal lymphocyte counts and deviations from the norm, the reasons for high and low levels of lymphocytes in a woman’s blood.
Indicators in analyzes and menstruation
Quite often, women ask doctors at the antenatal clinic whether leukocytes increase before menstruation. The answer, naturally, will be positive. The menstrual cycle of the fair sex in terms of the level of changes in the hormonal system is not inferior to the period of pregnancy, so changes in blood tests, urine and vaginal discharge will be corresponding.
Women must understand the mechanism of many processes occurring in their body. Some fluctuations in indicators in the analyzes are possible and should not cause any particular concern.
Any young lady should undergo a preventive examination twice a year, including by a gynecologist. There, a woman will be able to receive complete and detailed advice about her health, including the behavior of the female body before menstruation.
Source: https://ProMesyachnye.ru/lejkocity-pered-mesyachnymi/
Is it possible to take a urine test?
Theoretical urine tests can be carried out without paying attention to the day of the cycle. However, if the test is taken during menstruation, the woman must ensure that the vaginal discharge does not fall into the collection jar. For this purpose, it is necessary to carefully close the entrance to the vagina with a cotton pad, or better yet, insert a tampon, and then carry out hygienic measures.
If you do not take care of this, then the elements of the discharge along with the blood will end up in the urine, which can cause false results. Namely:
- the appearance of fresh red blood cells in the urine from menstrual flow, usually a sign of injury to the urinary tract;
- there is a change in the color of urine when blood gets in, this usually happens with diseases of the liver, kidneys, and some infections;
- leukocytes from vaginal discharge usually indicate inflammation in the urinary system.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
A urine test taken during menstruation without following the basic rules turns out to be completely uninformative. This will lead to the need for repeated research, at a minimum, and in some cases, to an incorrect diagnosis.
Leukocytosis
Elena Berezovskaya, obstetrician-gynecologist: Among women, real panic often arises when leukocytes are detected in their vaginal smear and a “foggy” diagnosis of “inflammation” is made, and what exactly is almost never specified, or the woman is frightened by all sorts of hidden infections.
Leukocytosis, that is, an increased number of white blood cells, in a woman’s tissues and blood plays an important role and depends on the day and phase of the menstrual cycle. Leukocytes and a woman’s reproductive system are inseparable.
This is far from a sign of an inflammatory process, but a dynamic process that is observed in the body of women, and this process completely depends on the hormonal background. The number, as well as the type of leukocytes, changes depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
Physiological leukocytosis is observed before ovulation and in the second half of the cycle, especially before menstruation. During pregnancy, leukocytosis is an integral and necessary condition, without which pregnancy will not proceed normally.
Leukocytes are present in vaginal discharge, as they are formed from the liquid part of the blood that has leaked through the vaginal wall and adjacent vessels and migrating leukocytes . Without exception, all types of leukocytes can penetrate the capillary wall.
Cervical mucus is a depot of leukocytes , the number of which depends on hormonal levels. During pregnancy, white blood cells and mucus from the cervical canal form a dense cervical plug (which is why it is white and hard in appearance).
A large number of leukocytes appear in the tissues of the uterus, in particular in the endometrium, towards the end of the cycle. Immediately before menstruation, of all endometrial stromal cells, leukocytes make up 50%. In other words, the endometrium is “stuffed” with leukocytes before menstruation.
The endometrium contains different leukocytes: T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, neutrophils and a number of others. It also contains a unique type of white blood cell - uterine natural killer cells (uNK), which appear at the end of the luteal phase and early pregnancy.
Without a sufficient number of these leukocytes, implantation, placentation and pregnancy are impossible.
Unlike other natural killer cells, uterine NKs have a specific structure and are sensitive to hormonal fluctuations, so their number completely depends on the level of sex hormones and progesterone.
Since an increase in the number of leukocytes is observed in the endometrium at the beginning of menstruation, the amount of human leukocyte antigen class 1 (HLA or HLA 1) increases, which is normal, especially on the surface of endometrial stromal cells. This antigen plays a very important role.
MNA leukocytes are involved in the process of death and rejection of the endometrium and help in the breakdown (lysis) of exfoliated cells - without this, menstruation is impossible. But they can also lead to lysis of the basal layer of the endometrium and stroma.
However, this does not happen in nature, because human leukocyte antigen binds to this type of leukocyte and protects the stroma and basal endometrium from damage.
Prolactin (LTG), which is produced by the pituitary gland, is also produced by endometrial cells in the second half of the menstrual cycle, that is, directly in the uterus.
Uterine prolactin stimulates the production of lymphocytes .
Natural killer cells contain prolactin receptors, which allow them to respond not only to prolactin, but also to progesterone (this type of leukocyte does not have progesterone receptors).
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are present in endometrial tissue in small numbers for almost the entire menstrual cycle, but a few days before the onset of menstruation, their number increases significantly, and they dominate the entire period of menstrual bleeding.
It is believed that it is the rapid decrease in progesterone levels from the second half of the luteal phase that is the trigger for the appearance of a large number of leukocytes in the reproductive organs.
The main neutrophils of the uterus are polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs).
In all textbooks and publications you can find information that this type of leukocyte appears at the site of inflammation.
Indeed, based on the number of these types of leukocytes and their ratio to squamous epithelial cells in vaginal discharge, an inflammatory process can be suspected.
But in reality, this indicator is not determined or taken into account by most post-Soviet laboratories, and the results indicate the total number of leukocytes in the field of view and a rather rough and inaccurate count (for example, 50-100 leukocytes in the field of view).
But what do PMNs do in the uterine cavity and endometrium if there is actually no inflammation? This type of leukocyte is involved not only in the fight against the inflammatory process, absorbing (phagocytosing) both microorganisms and dead cells and tissue scraps.
During menstruation, a large number of endometrial cells die, and it also mixes with blood, creating an excellent breeding ground for microorganisms that can enter the uterine cavity from the vagina.
Neutrophils become orderlies, cleaning the surface of the area where the old endometrium has been rejected from its remains, and prevent bacteria, viruses, and fungi from entering the endometrial and uterine tissue.
Macrophages
Another type of leukocyte - macrophages - also plays an important role in the function of the endometrium. They make up up to 20% of all leukocytes appearing in the uterus by the end of the luteal phase.
Although macrophages do not have progesterone and estrogen receptors, their number in the endometrium and other tissues of the genital tract depends on the level of hormones and the day of the menstrual cycle.
Macrophages contain enzymes that break down dead endometrial cells; they also produce a number of organic substances important in tissue regeneration processes.
Thus, leukocytosis in any form is a very important stage in the physiological norm of a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Excerpt from the book “Hormonotherapy in Obstetrics and Gynecology”
Original
Source: https://soznatelno.ru/lejkoczitoz/
Conducting an ultrasound during menstruation: when it is possible and not
Whether or not an ultrasound examination can be performed depends on which organ will be examined. During critical days, if this does not cause discomfort to the woman, you can undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys, lymph nodes throughout the body, and blood vessels anywhere. For ultrasound examination there are only some restrictions on the days of the cycle if the genital organs are examined.
In case of a preventive examination, ultrasound of the uterus and appendages should be performed on the 7-10th day of the cycle. It is assumed that at this time there is still a small spotting discharge from the genital tract. However, these days are the most informative for searching for pathology of the uterine cavity and cysts on the ovaries.
If the doctor is trying to establish or refute the diagnosis of endometriosis, then it is better to do an ultrasound on the eve of menstruation, on the 25-26th day. At this time, the lesions are largest in size and have clearer outlines.
In emergency cases, an ultrasound of the genital organs is performed on any day of the cycle to help establish a diagnosis, if necessary, to carry out monitoring according to generally accepted recommendations.
Phases of the test cycle for important hormones
To obtain accurate laboratory test data, you need to know on what day of the cycle you need to take hormones. Each gland produces hormones unique to it, which are calculated at certain phases of the cycle. The list of main hormones and on what days each of them is taken can be found in the table below.
| Endocrine glands | Hormones produced | Functions of hormones | Timing of hormone delivery depending on the days of the cycle |
| Pituitary gland (anterior lobe) | Thyroid-stimulating | Activates the thyroid gland | As prescribed by the attending physician |
| Gonadotropic | Responsible for the gonads | According to the doctor's testimony | |
| Adrenocorticotropic | Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release anti-stress hormones | According to individual indications | |
| Luteinizing (LH) | Ensures the proper functioning of the reproductive system in women and men | On days 6–7 or 20–21 of the menstrual phase | |
| Follicle-stimulating (FSH) | Responsible for sexual development, maturation of sperm in men and eggs in women. The main function of FSH is procreation | From 3 to 8 and from 19 to 21 days of the beginning of the new phase | |
| Prolactin | Stimulates the development of mammary glands and milk production in women in labor. As prescribed by the attending physician | Individually as prescribed by the attending physician. But the analysis is informative only in phases 1 and 2 of the menstrual period. One day before donating blood, avoid thermal procedures (bath, sauna, bath) | |
| Pituitary gland (posterior lobe) | Vasopressin | Increased reabsorption of water in the renal tubules, constricts blood vessels | On doctor's recommendation |
| Oxytocin | Activation of the smooth muscles of the uterus at the time of birth | ||
| Hypothalamus | Neurohormones | Regulatory hormones entering the pituitary gland and through it influencing the functioning of the endocrine glands | In accordance with the prescription of the endocrinologist |
| Epiphysis (pineal gland) | Serotonin | Promotes blood clotting, affects the secretion and motility of the gastrointestinal tract, affects the paracrine regulation of uterine contractility, participates in the ovulation process, affects the hypotholamic regulation of pituitary gland functions and other purposes | Hormones of this group are donated at any time determined by the doctor as appropriate |
| Melatonin | Affects seasonal and circadian rhythms, inhibits sexual activity, and reduces mood | ||
| Pancreas | Insulin | Promotes the transformation of glucose from the bloodstream into cells to form glycogen | According to the doctor’s direction, according to the patient’s personal data |
| Thymus (thymus gland) | Thymosin | They play one of the most important roles in immunological processes, have an inhibitory effect on the thyroid gland, delay sexual development, and affect skeletal growth | Prescribed by an endocrinologist according to personal indications |
| Homeostatic thymic hormone | |||
| other hormones | |||
| Thyroid | Thyroid (iodine-containing) | Increases energy metabolism | Hormones of this group, including T3, T4, TSH, are prescribed by a doctor at a certain time according to personal indications. It is recommended for women in the 1st phase of the cycle after the end of menstruation |
| Calcitonin | Controls calcium metabolism | ||
| Parathyroid-prominent | Parathyroid hormone | Responsible for regulating calcium in the body, ensuring the full functioning of the nervous system and musculoskeletal system | According to the doctor's direction |
| Adrenal glands | Adrenalin | Strengthens the activity of the heart muscle, increases blood pressure, increases the amount of glucose in the blood | As prescribed by the doctor |
| Norepinephrine | |||
| Testes | Testosterone | Responsible for the development of male sexual characteristics, affects metabolism, strengthens nerve cells | According to individual prescription by the attending physician. Women are recommended to take it in the 1st phase of menstruation |
| Ovaries | Estradiol | Ensures the functioning and development of the female reproductive system, enhances metabolism | Days of the menstrual cycle sixth or seventh or at approximately 14 days (beginning of ovulation) |
| Progesterone | Responsible for the onset of pregnancy and its maintenance | About a week before the start of the next monthly cycle or on the 19th–23rd day from the start of menstruation |
Female hormones are given strictly according to the days of the menstrual cycle. Only a competent doctor decides whether it is possible to donate blood in certain circumstances. During menstruation, donating blood for hormonal indicators is recommended for special indications, since this period helps to identify the most eloquent picture of the content of hormones such as LH and FSH. Men need to donate blood for hormones in accordance with the recommendations of their doctor.
What other tests should not be done during menstruation?
There is no point in visiting a gynecologist during menstruation, unless, of course, there is bleeding or suspicion of some serious pathology. An inspection can be carried out, but its information content will be reduced.
Taking any smears from the vagina or cervix, even if there is only spotting and very slight discharge, is a waste of time. This is explained by the fact that in any case, signs of inflammation will be revealed in smears, and if the material was taken for oncocytology analysis, malignant cells can be missed due to the abundance of leukocytes and red blood cells in the preparation.
Cytological examination of the cervix (indicators are normal)
The same applies to PCR testing for sexually transmitted infections. Such tests can be taken only after the complete cessation of discharge from the genital tract, otherwise the results may be incorrect.
Is it possible to donate plasma during menstruation?
To donate plasma, whole blood is taken from the patient. It is filtered in a medical device, and the formed elements (platelets and red blood cells + saline) are returned back inside the vessels located on the other arm. Up to 12 procedures per year are allowed. Plasma is restored faster than formed elements. Its amount depends on the fluid consumed.
Regardless of the fact that the amount of plasma quickly returns to normal, doctors do not advise donating it during menarche due to the following risks:
- a sharp decrease in the amount of plasma, leading to blockage of blood vessels with a thrombus or atherosclerotic plaque;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- deterioration of the patient's well-being.
The timing for donating plasma is 3 days before menarche and 10 days after, when the amount of fluid returns to normal. It is recommended to drink plenty of water to help this process go faster.
What examinations can be taken?
Theoretically, any tests (except smears) can be taken during critical days; there are no specifically prescribed rules and recommendations in this case. However, if the examination is carried out as planned, according to an unspoken law, it is better to postpone them to more favorable days, when menstruation ends.
If urgent research is needed, no one ever pays attention to the day of the cycle, but when analyzing the data, some adjustments may be made taking into account critical days.
We recommend reading about which hormones are actively released during menstruation. From the article you will learn about the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle and the rules for taking hormone tests.
And here is more information about what and when to take hormone tests.
Tests can be taken during menstruation. However, many girls refuse this because of discomfort due to pain or excessive discharge. In general, the results of studies may be slightly modified, but wide values of the norm usually allow one to enter the necessary boundaries.
Consequences of donating during menstruation
In addition to the disruption to a woman's physical condition when donating during menarche, there are additional health risks. The following negative processes may occur:
- menstrual irregularities (failure, delay, premature onset);
- changes in hormone levels due to stress on the body;
- scarcity of biological fluid secretions during menstruation due to a decrease in the amount of plasma;
- reducing the body's resistance to pathogenic microorganisms.
Donation before and after the menstrual cycle
Using a menstrual calendar makes things easier
If possible, it is worth moving the expected date of blood donation to a safer period. According to doctors, 4-5 days after the end of the critical days, the body completely replenishes lost water, salts and red blood cells. However, this indicator is individual for each girl. To make sure that the body is ready for the procedure, doctors prescribe a number of special tests.
Attention! Keeping a women's calendar will make it easy to calculate the most favorable days for donation!
Doctors advise donating at least 5-6 days before your period. Donating blood is a stressful situation for the body; to compensate for losses, it is necessary to mobilize all the regenerative mechanisms of the body. You should not be exposed to it during the period when the body is busy preparing for critical days.
Features of the course of menstruation
The time of menstruation is the period when the inner lining of the uterus is shed. This is an important stage in the functioning of the body. The interval between the first day of your period and the beginning of the next period is called your cycle. At the end of the first stage of this period, the endometrium is formed, which is necessary for attaching the egg after its fertilization.
But in the absence of conception, the layer detaches from the wall of the uterus and leaves the body. This is accompanied by the opening of blood vessels, resulting in bleeding. The most abundant discharge is observed at the initial stage. And then the amount of blood begins to decrease.
Disorders and changes in women during menstruation
On the eve of menstruation, various processes occur in the female body that change its “standard” functioning. The changes affect the hypothalamic-pituitary system - because of this, the hormonal levels change, as well as the central nervous system. In this regard, many women experience irritability, drowsiness, and get tired faster. There is a decrease in endorphin content in the body, which often leads to a significant deterioration in mood and emotional swings.
After menstruation, this state is replaced by vigor and a surge of strength. Among the phenomena that are observed during menstruation, one can also highlight a decrease in the pain threshold, an increase in tendon reflexes, increased sweating and some others. When the cycle proceeds normally, the changes occurring in the female body are within acceptable limits and practically do not affect performance. Blood loss is insignificant and easily compensated by the body, however, when the process occurs with some disturbances, negative sensations may arise. For example, bleeding may be too heavy, and there may be several reasons for this: from poor blood clotting to inflammation or a tumor in the uterus. If such a symptom occurs, especially in combination with severe pain, dizziness and high fever, you should immediately contact a gynecologist rather than try to solve the problem yourself.